SKELETAL SYSTEM
1/65
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
66 Terms
Parts of the skeletal system
Bones (skeleton)
Joints
Cartilages
Ligaments
Two subdivisions of the skeleton
Axial skeleton
Appendicular skeleton
Functions of the Bones
Protect soft organs
Support the body
Attach skeletal muscles
Store minerals and fats
Blood cell formation (hematopoiesis)
Blood cell formation
(hematopoiesis)
The adult skeleton has
206 bones
Two basic types of osseous (bone) tissue
Compact bone Dense, smooth, and homogeneous
Spongy bone, Small needlelike pieces of bone Many open spaces
Bones are classified on the basis of shape into four groups
Long, Short, Flat, Irregular
Makes up most of bone’s length?
Diaphysis (shaft)
Outside covering of the diaphysis
Perosteum
Secures the periosteum to underlying bone
Perforating Fibers
Composed mostly of spongy bone enclosed by thin layer of compact bone (bone ends)
Epiphysis
Articular Cartilage
Covers the external surface of the epiphyses
Made of hyaline cartilage
Flat plate of hyaline cartilage seen in young, growing bone
Epiphyseal plate
Calcified epiphyseal plate, remnant of the EP
Epiphyseal line
Lines the inner surface of the shaft
Endosteum
Cavity inside the shaft
Medullary Cavity
BONE ANATOMY SUPERFICIAL TO DEEP
Perosteum → Perforating Fibers → Compact bone → Spongy bone →
Endosteum → Medullary Cavity → Bone marrow
Sites of attachments for muscles, tendons, and ligaments
BONE MARKINGS
Categories of bone markings
Depressions and Projections
Mature bone cells situated in bone matrix
OSTEOCYTES
Cavities in bone matrix that house osteocytes
LACUNAE
Concentric circles of lacunae situated around the central (Haversian) canal
LAMELLAE
Opening in the center of an osteon
Central Canals
Structural and functional unit of compact bone
OSTEON
A break in a bone?
Fracture
Types of bone fractures
Closed (simple) fracture is a break that does not penetrate the skin
Open (compound) fracture is a broken bone that penetrates through the skin
Bones are manually coaxed into position by physician’s hands
CLOSED REDUCTION
Bones are secured with pins or wires during surgery
OPEN REDUCTION
Repair of bone fractures involves four major events
Hematoma
FIBROCARTILAGE CALLOUS FORMS
Bony callus replaces fibrocartilage callus
Bone remodeling
TYPES OF FRACTURES
Comminuted (bone breaks to 3 or more pieces)
Depressed (indentation)
Spiral (twisted)
Greenstick (half broken)
Forms the longitudinal axis of the body
AXIAL SKELETON
(AXIAL SKELETON) Divided into three parts
Skull, Vertebral Column, Bony Thorax
Two sets of bones form the skull
Cranial bones
Facial bones
This bone is attached by a freely movable joint
MANDIBLE
Cranial bones are joined by?
Sutures
CRANIAL BONES THAT PROTECTS THE BRAIN
Frontal, Parietal, Occipital, Temporal, Ethmoid, Sphenoid
FACIAL BONES
MAXILLA, PALATINE, LACRIMAL, ZYGOMATIC, NASAL, VOMER,
INFERIOR NASAL CONCHAE, MANDIBLE
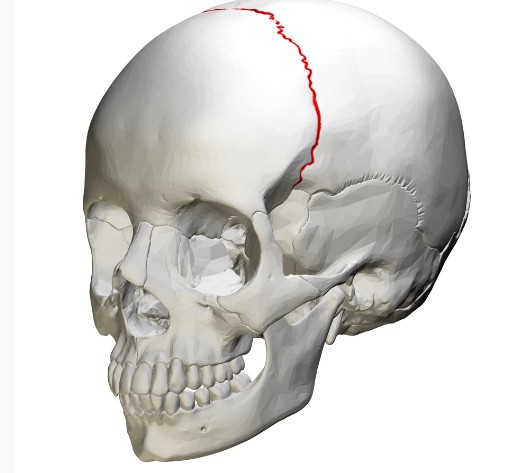
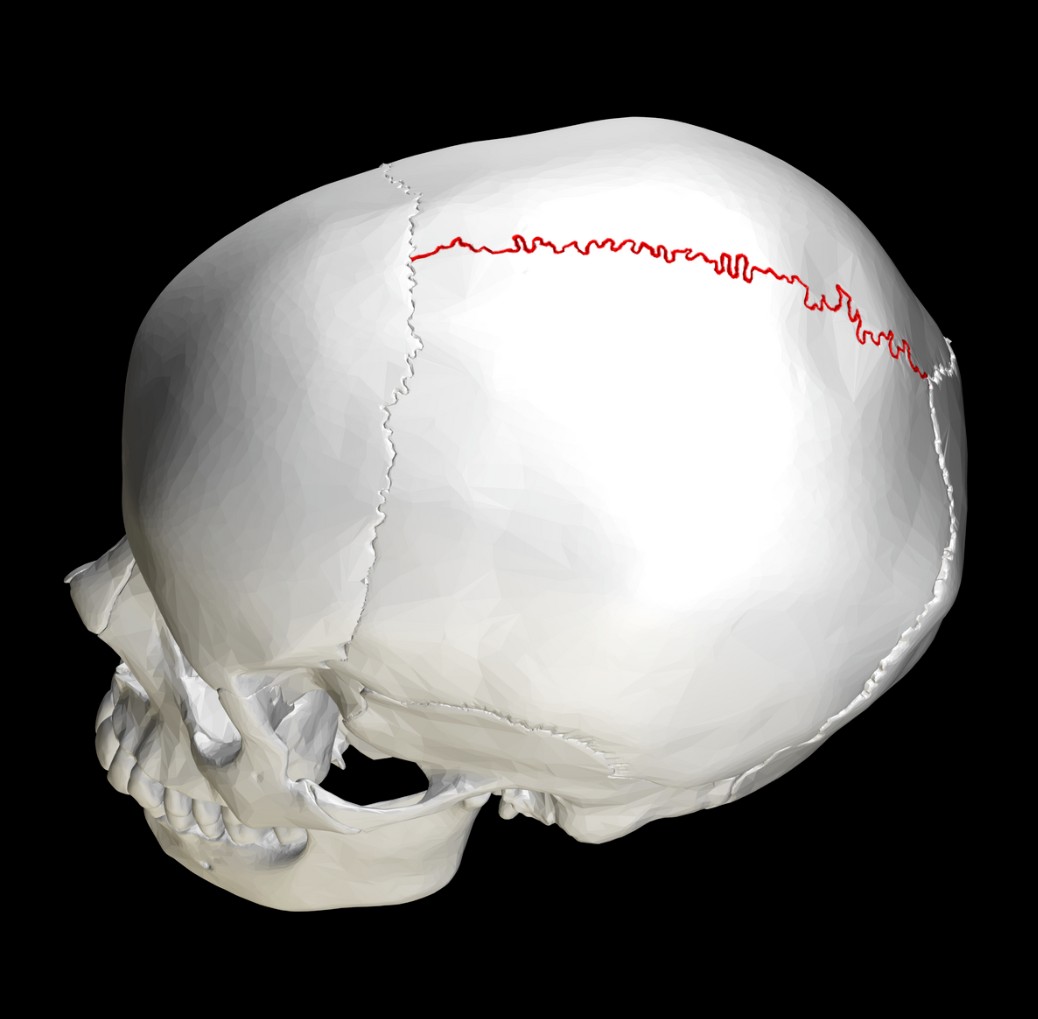
What type of suture is this?
CORONAL SUTURE
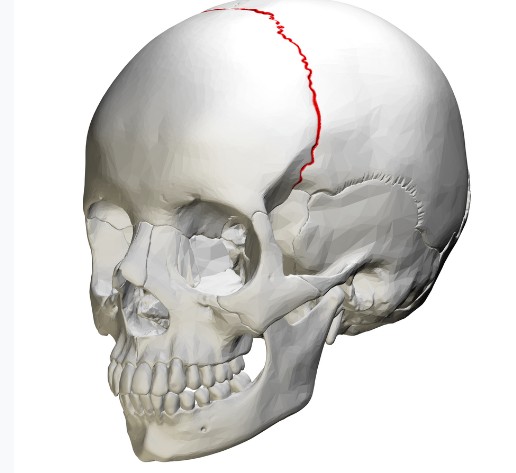
SUTURE
SQUAMOUS SUTURE
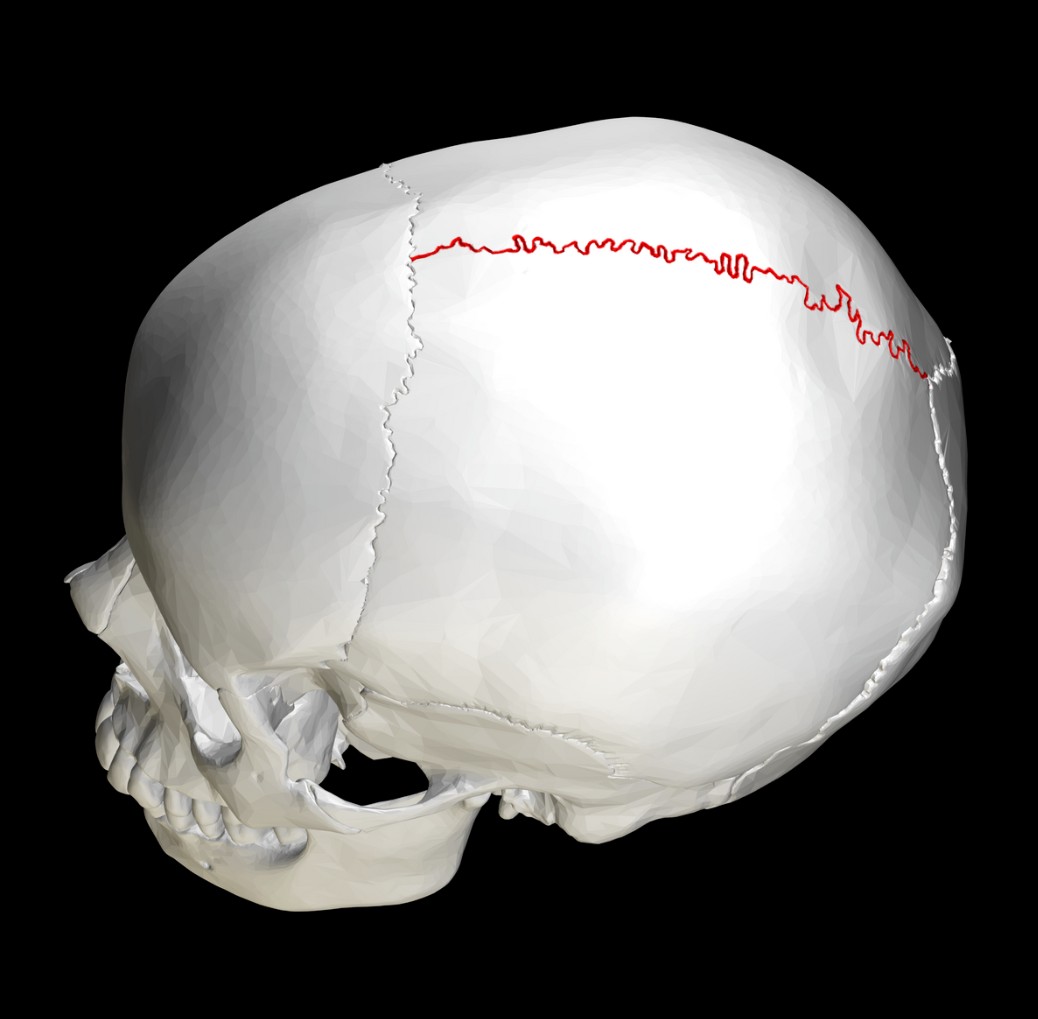
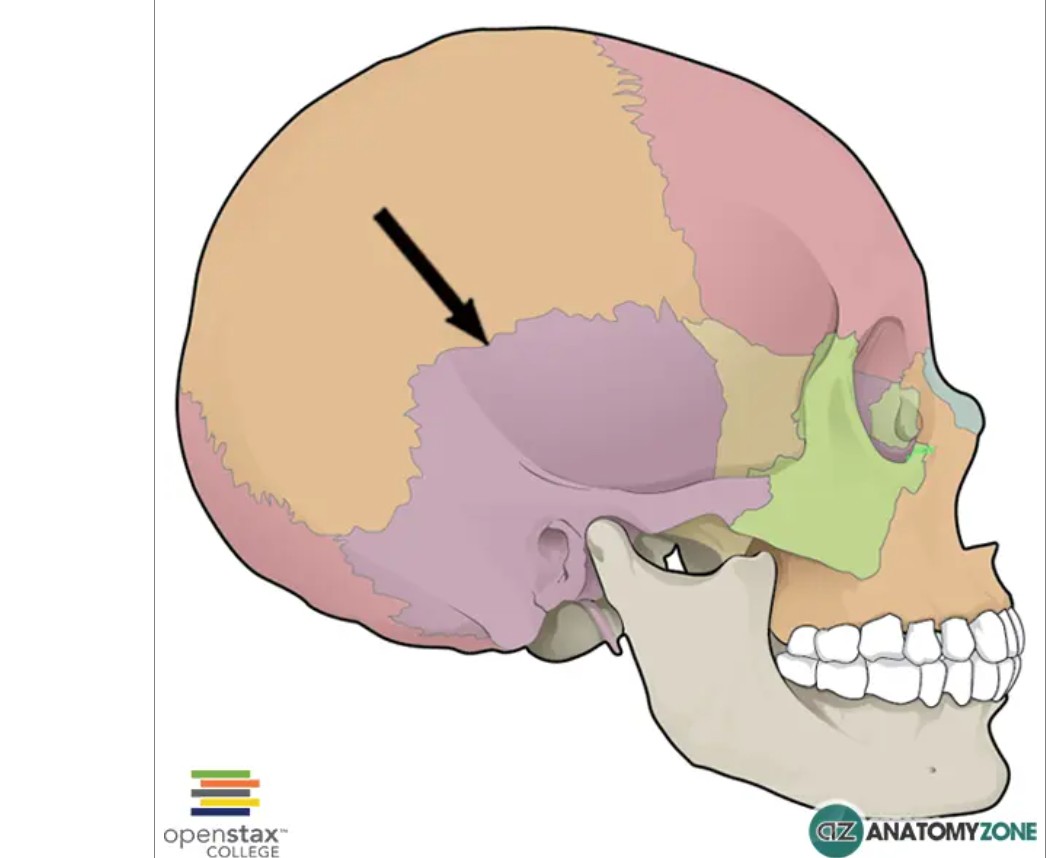
SUTURE
SAGITTAL SUTURE
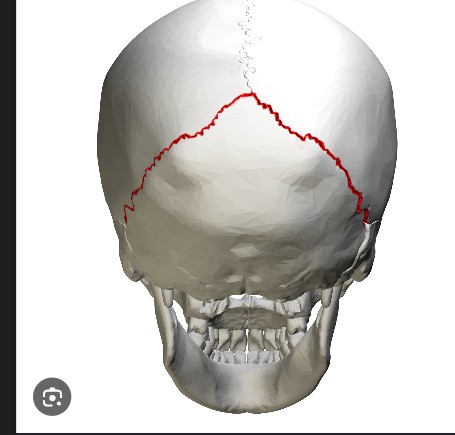
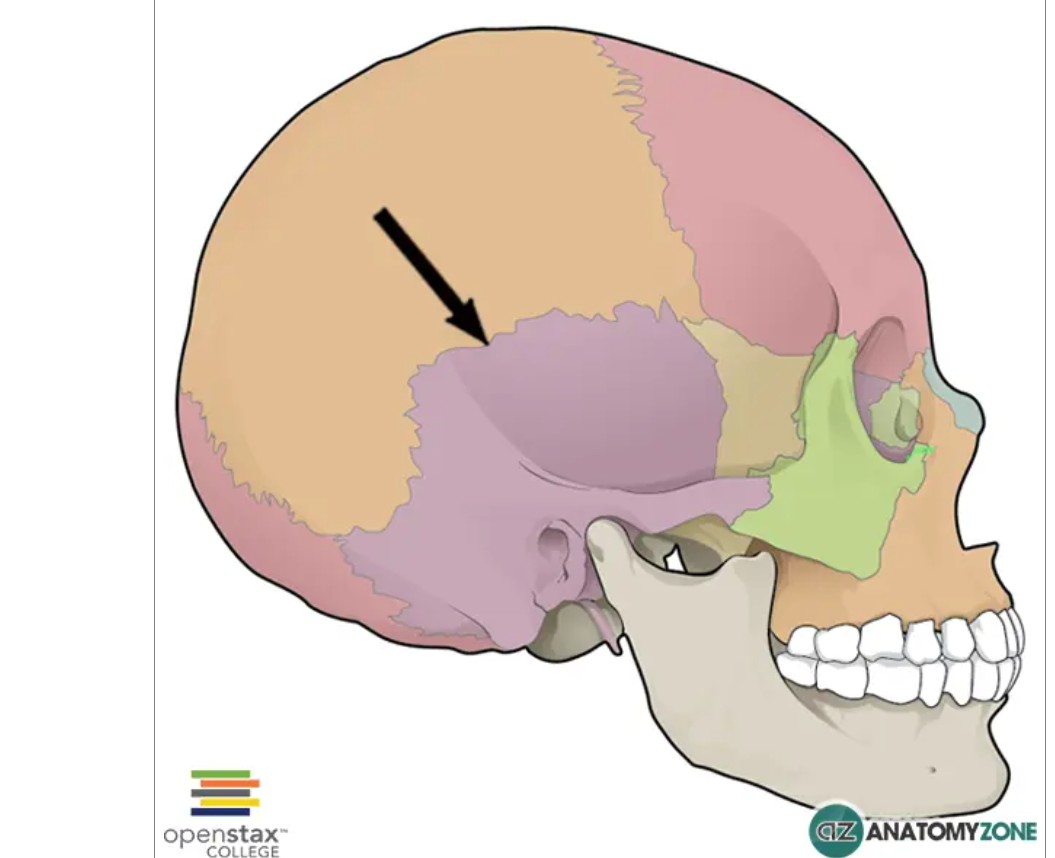
SUTURE
LAMBDOID SUTURES
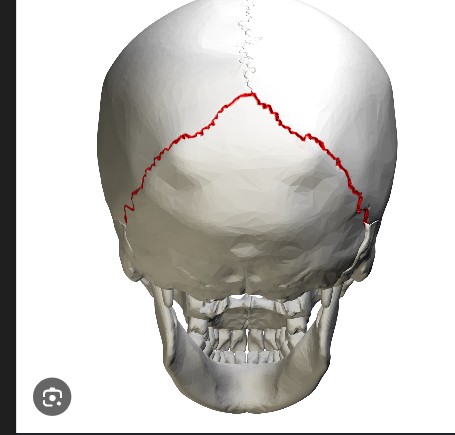
The only bone that does not articulate with another bone, Serves as a movable base for the tongue
Hyoid bone
Vertebral column (parts)
7 CERVICAL
12 Thoracic
5 Lumbar
Sacrum
Coccyx
26 vertebral bones are separated by?
Intervertebral discs
2 TYPES OF CURVATURES
C SHAPED (PRIMARY CURVATURES)
S SHAPED (SECONDARY CURVATURES)
VERTEBRAE PARTS
BODY, VERTEBRAL ARCH, VERTEBRAL FORAMEN, TRANSVERSE PROCESSES, SPINOUS PROCESS, FACET.
YES AND NO BONE OF VERTEBRAE
Atlas and Axis
BONT THORAX PARTS
Ribs, Sternum, Thoracic Vertebrae
PARTS OF THE RIBS
TRUE RIBS (7)
FALSE RIBS (5)
FLOATING (2)
PARTS OF THE APPENDICULAR BONES
Limbs, Pectoral girdle, Pelvic girdle
2 BONES OF THE PECTORAL GIRDLE
Scapula, Clavicle
FORMS THE UPPER ARM
Humerous
FOREARM BONES
Ulna, Radius
HAND BONES
Carpals, Metacarpals, Phalanges
How many bones in phalanges?
14
8 CARPAL BONES
TRAPEZIUM, TRAPEZOID, SCAPHOID, CAPITATE, HAMATE, LUMATE, PISIFORM, TRIQUETRUM
PELVIC GIRDLE’S 3 PAIR OF BONES
Ilium, Ischium, pubis
PELVIS GIRDLE PROTECTS?
Part of the large intestine, Urinary bladder, Reproductive organs ko
THIGH BONE
Femur
LOWER LEG BONES
TIBIA, FUBULA
BONES OF FEET
Tarsals, Metatarsals, Phalanges
TARSAL BONES
(MEDIAL, LATERAL, INTERMEDIATE) Cuneiform, Cuboid, Navicular, Calus, Calcaneus
JOINT CLASSIFICATIONS
Fibrous (immovable)
Cartilaginous (slightly movable)
Synovial (freely movable)
SOFT SPOTS IN A FETAL SKULL
FONTANELS
PHALANGES LOCATIONS
Distal, Medial, Proximal
LONG BONE PARTS
(LATERAL, MEDIAL,) Epicondyle, Head, Trochanter