Amino Acids Biochemistry
1/718
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
719 Terms
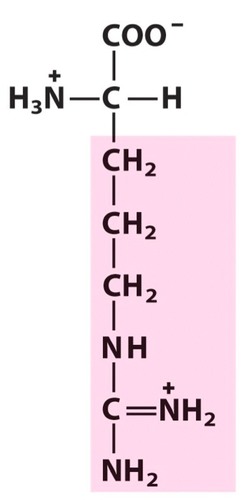

Arginine
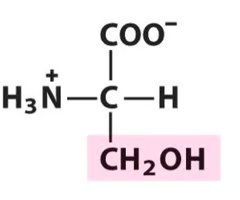

Serine
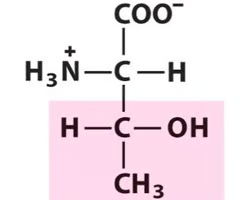

Threonine
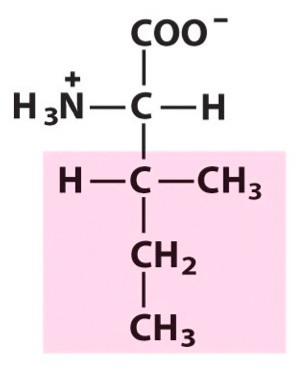
isoleucine
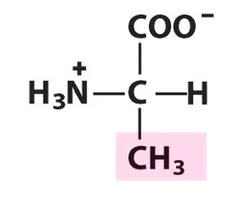

Alanine
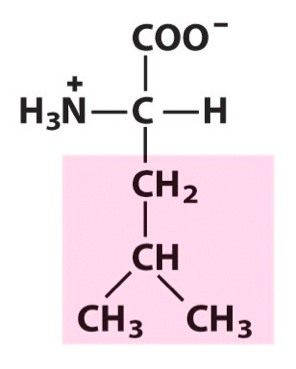

Leucine
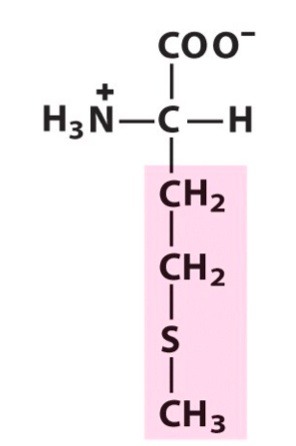

Methionine
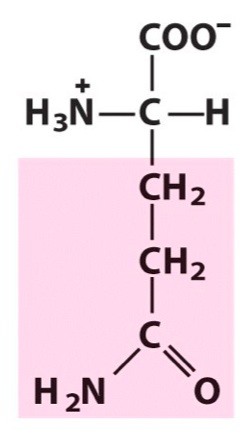

Glutamine
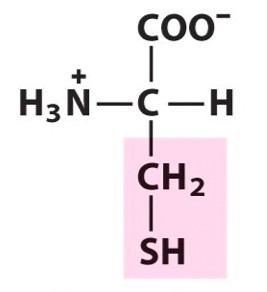

Cysteine
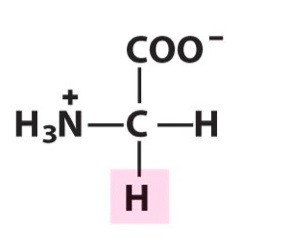

glycine
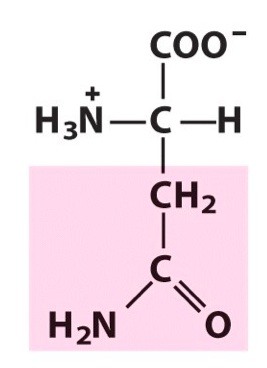

Asparagine
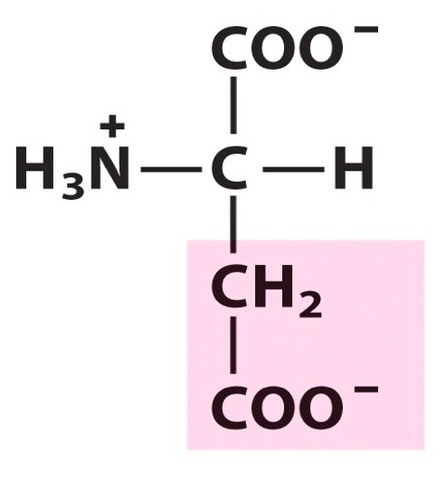

Aspartic Acid
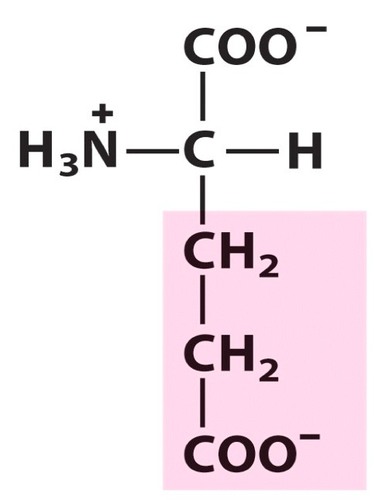

Glutamic Acid
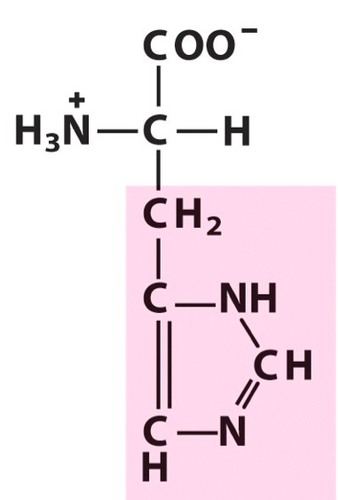

Histidine
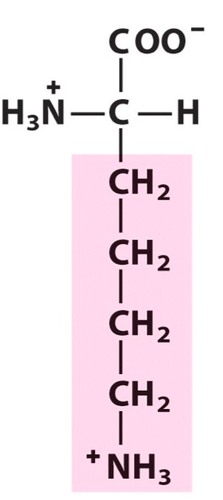

Lysine
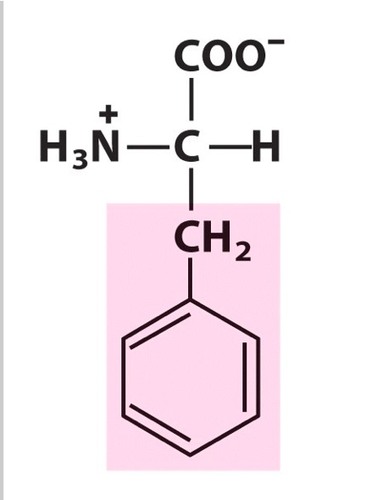

phenylalanine
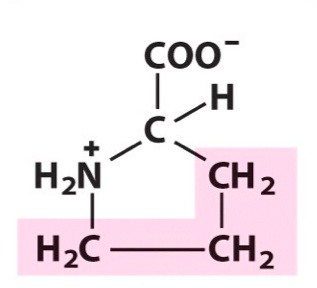

Proline
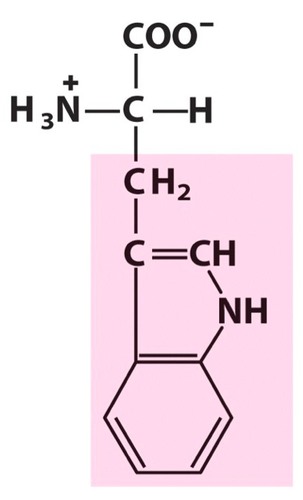

Tryptophan
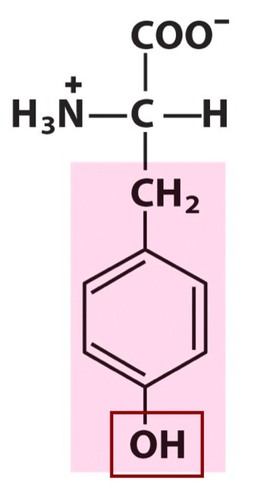

Tyrosine
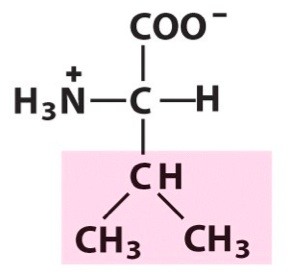

Valine
Arginine 1 letter code
R
Arginine 3 letter code
Arg
Serine 1 letter code
S
Serine 3 letter code
Ser
Alanine 3 letter code
Ala
Alanine 1 letter code
A
Asparagine 3 letter code
Asn
Asparagine 1 letter code
N
Aspartic Acid 3 letter code
Asp
Aspartic Acid 1 letter code
D
Cysteine 3 letter code
Cys
Cysteine 1 letter code
C
glutamic acid 3 letter code
Glu
Glutamic acid 1 letter code
E
Glutamine 3 letter code
Gln
Glutamine 1 letter code
Q
Glycine 3 letter code
Gly
Glycine 1 letter code
G
Histidine 3 letter code
His
Histidine 1 letter code
H
Isoleucine 3 letter code
Ile
isoleucine 1 letter code
I
Leucine 3 letter code
Leu
Leucine 1 letter code
L
Lysine 3 letter code
Lys
Lysine 1 letter code
K
Methionine 3 letter code
Met
Methionine 1 letter code
M
Phenylalanine 3 letter code
Phe
Phenylalanine 1 letter code
F
Proline 3 letter code
Pro
Proline 1 letter code
P
Threonine 3 letter code
Thr
Threonine 1 letter code
T
Tryptophan 3 letter code
Trp
Tryptophan 1 letter code
W
Tyrosine 3 letter code
Tyr
Tyrosine 1 letter code
Y
Valine 3 letter code
Val
Valine 1 letter code
V
aspartic acid sidechain pKa
3.9
glutamic acid sidechain pka
4.3
Histidine sidechain pka
6
Arginine sidechain pka
12
Lysine sidechain pka
10.7
What is the one amino acid that is achiral
Glycine because its R-group is just a H
What is the one amino acid that is a R-stereoisomer
Cysteine because it has a high priority sulfur atom
Are most amino acids L or D stereoisomers
L, NH3+ is on the left.
Are most amino acids R or S stereoisomers
S. If H is in the back it would go COO-, R-group, NH3+ (CO-R-N Rule)
What three amino acids have aromatic R-groups
Phenylalanine(F), Tryptophan(Y), Tyrosine(W)
Remember: WYF (“wife)
Which amino acids have nonpolar aliphatic R-groups
Glycine, Alanine, Proline, Valine, Leucine, Isoleucine, Methionine
Which amino acids have polar uncharged R-groups
Serine, Threonine, Cysteine, Asparagine, Glutamine
Which amino acids have positively charge R-groups
Histidine, Arginine, Lysine
Which amino acids have negatively charged R-groups
Aspartate(aspartic acid) and Glutamate (glutamic acid)
What is the ΔG(hydration) of the nonpolar aliphatic sidechains(Valine, Alanine, Isoleucine, Leucine (VAIL))
+10kJ/mol
What is the ΔG(hydration) of the S-containing and aromatic sidechains( Methionine, Cysteine, Phenylalanine)
-5kJ/mol
What is the ΔG(hydration) of the Hydrogen-bonding sidechains(Tryptophan, Tyrosine, Serine, Threonine, Asparagine, Glutamine)
-20 to -40kJ/mol
What is the ΔG(hydration) of the charged sidechains(Histidine, Lysine, Arginine, Aspartate and Glutamate)
-300kJ/mol
In what order do the aromatic sidechain amino acids absorb light from strongest to weakest
Tryptophan, Tyrosine, Phenylalanine (WYF)
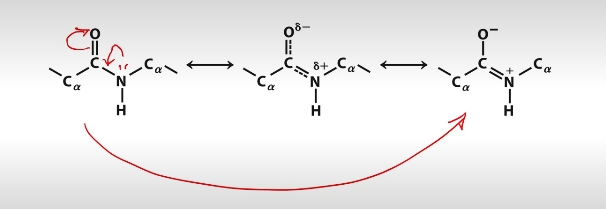
What kind of bonds do peptide bonds behave like?
Double Bonds.
What is the barrier of rotation for peptide bonds?
70kJ/mol
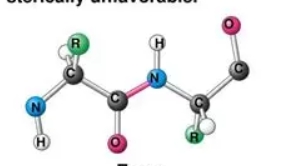
What configuration are almost all peptide bonds in?
Trans. It is the best way to get rid of any steric hinderance.
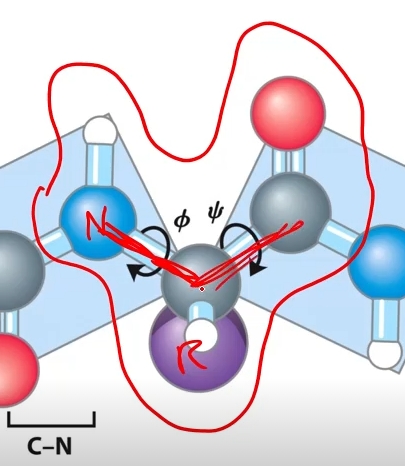
How many rotatable backbones are there in a residue?
Two
Phi bond (Nitrogen connected to alpha carbon)
Psi bond (Alpha carbon to carbonyl carbon)
What does a Ramachandran Map represent?
It represents the number of possible conformations that an amino acid can take on. Dark blue means more common, light blue, less common, white is not possible
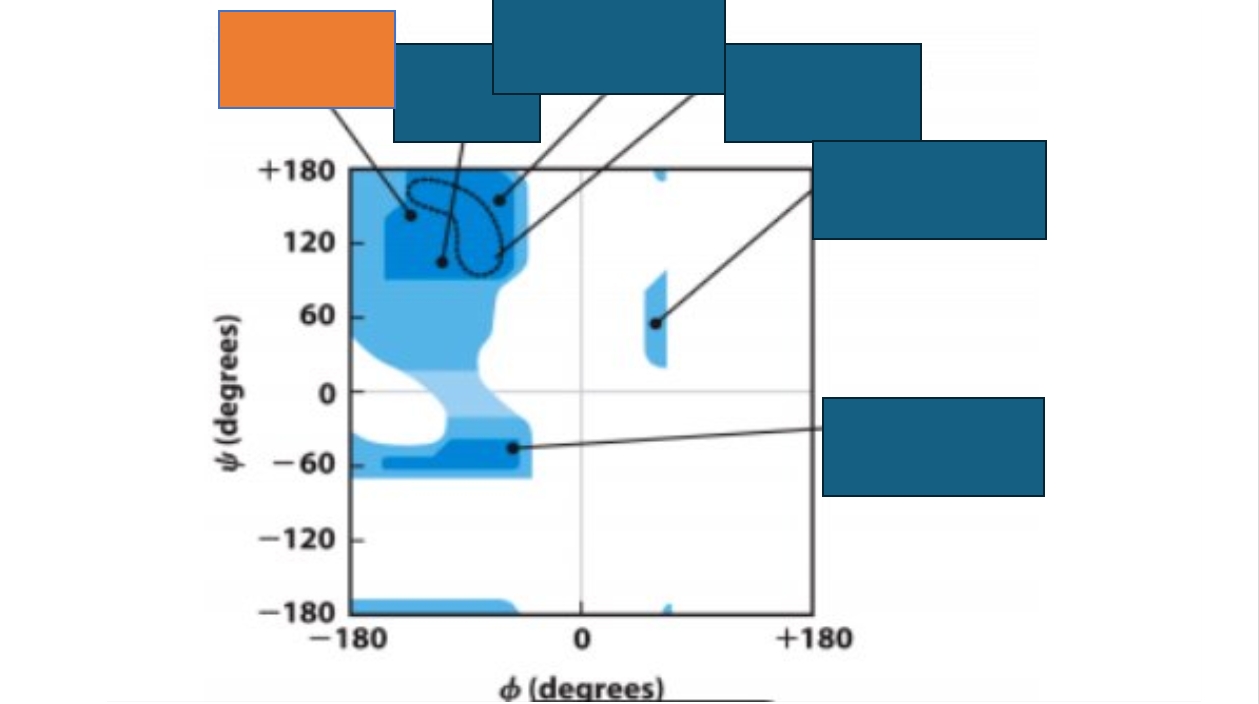
Which conformation does the orange box represent on the Ramachandran map?
Antiparallel β-sheet
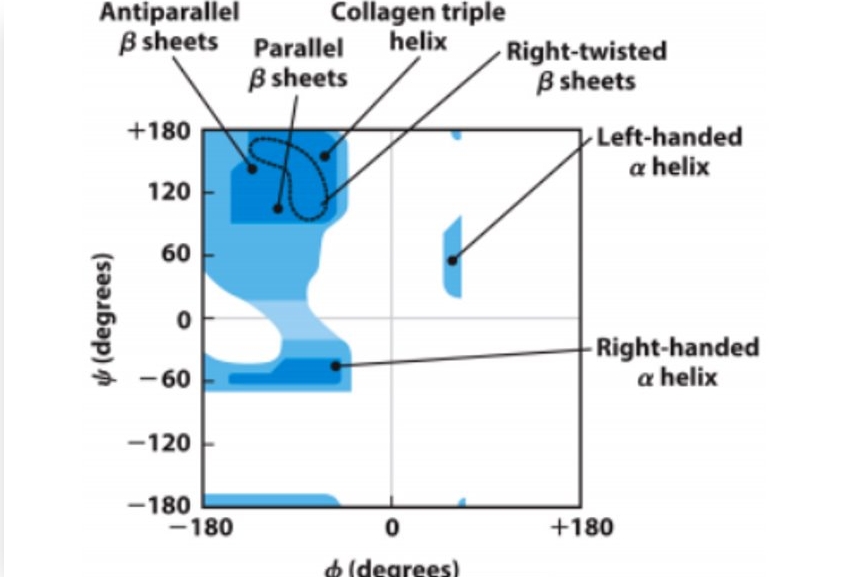
For how many of the amino acids is this Ramachandran map standard? Which ones are not included in that group?
The ones that are no included are Proline and Glycine
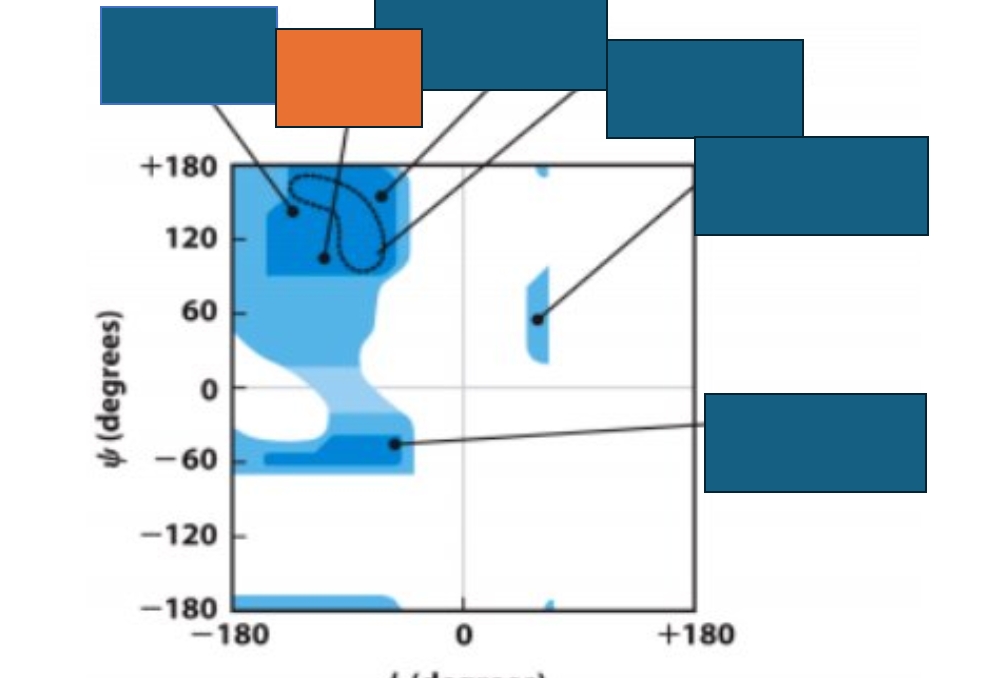
Which conformation does the orange box represent on the Ramachandran map?
Parallel β-sheet
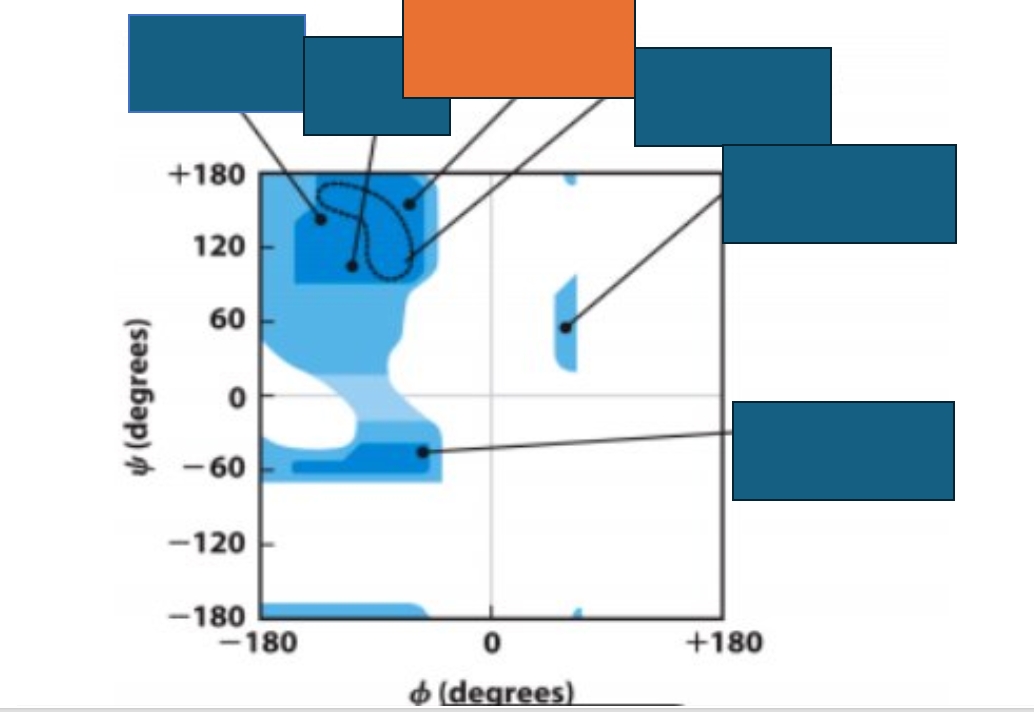
Which conformation does the orange box represent on the Ramachandran map?
Collagen triple-helix
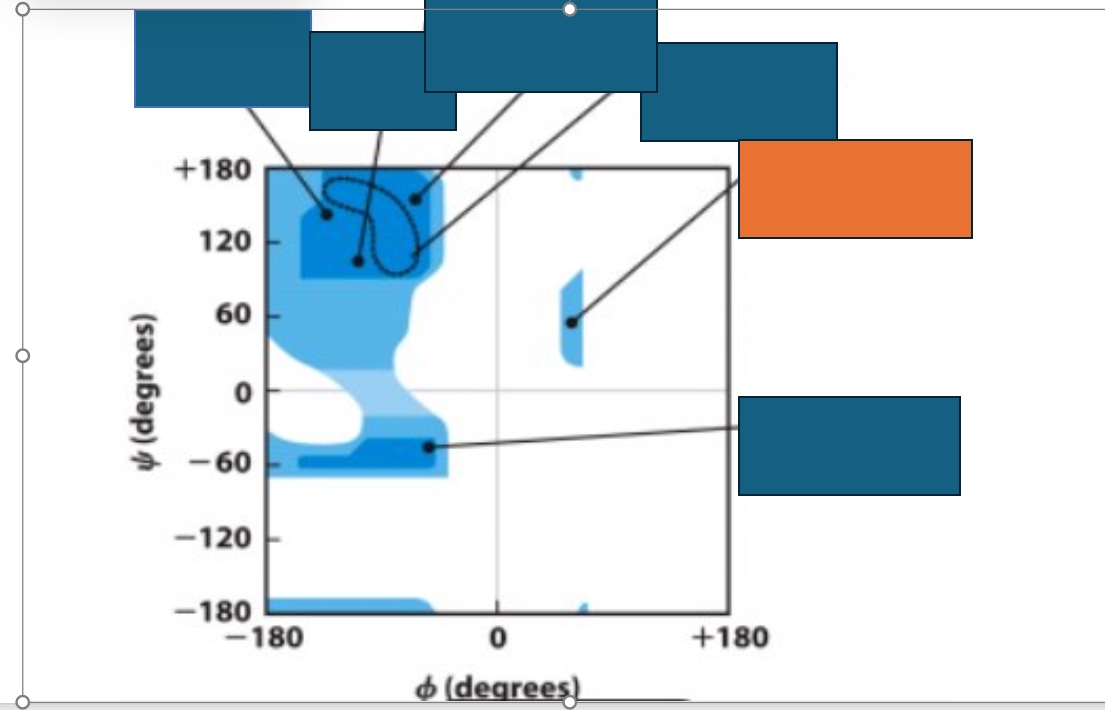
Which conformation does the orange box represent on the Ramachandran map?
Left-handed α-helix
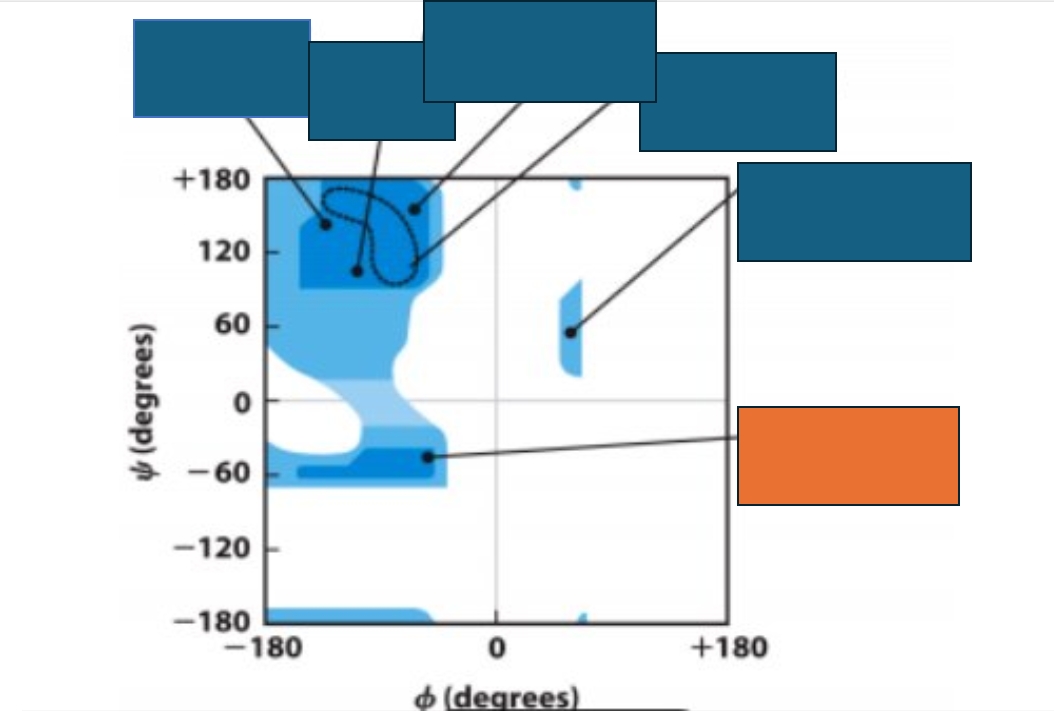
Which conformation does the orange box represent on the Ramachandran map?
Right-handed α-helix
How might a glycine Ramachandran map differ? Why
It will have a larger blue area since its side chain is only hydrogen, allowing for more conformations without any hindrance.
How might a proline Ramachandran map differ? Why?
It will have less blue area because its side chain is so bulky that it would have less possible conformations
What is primary structure of protein?
The primary structure of a protein is the unique linear sequence of amino acids in a polypeptide chain
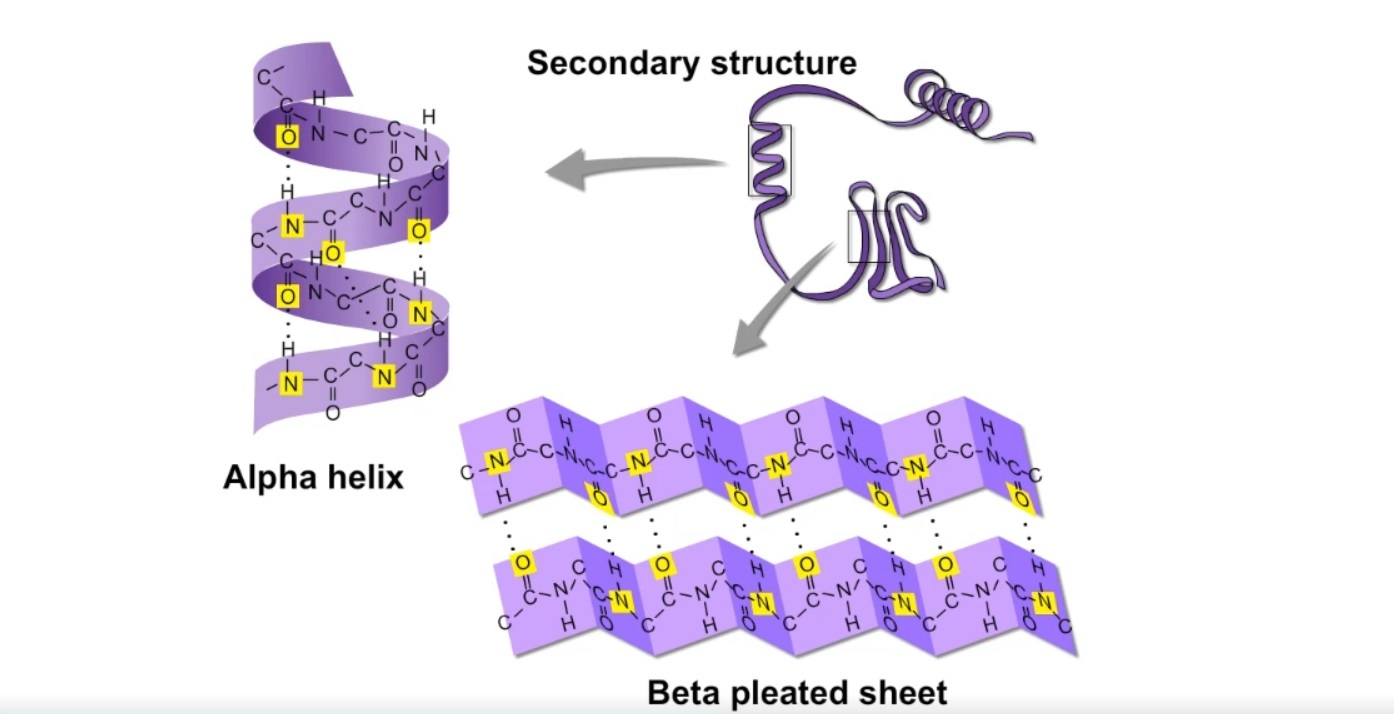
What is secondary structure of protein?
The secondary structure of a protein is the local folding of the polypeptide backbone into regular patterns, such as α-helices and β-sheets, stabilized by hydrogen bonds between backbone atoms.
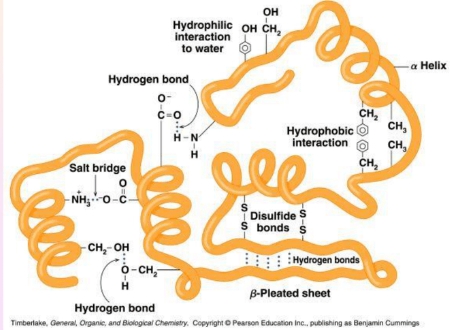
What is tertiary structure of a protein?
The tertiary structure of a protein is its overall three-dimensional shape, formed by the folding of secondary structures and stabilized by interactions among side chains, including hydrophobic interactions, hydrogen bonds, ionic bonds, and disulfide bonds.
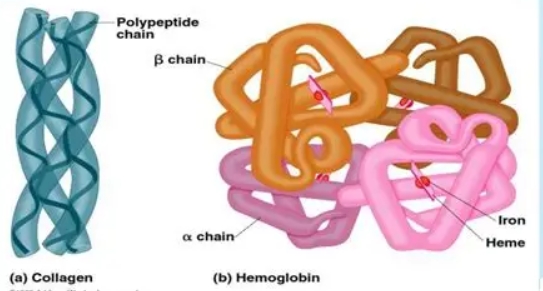
What is quaternary structure?
The quaternary structure of a protein is the arrangement and interaction of multiple polypeptide subunits in a multi-subunit protein complex, stabilized by the same forces as tertiary structure
What is the most common form of secondary structure?
α-helix
Where do the hydrogen bonds occur between in an α-helix?
Between residues i and i+4 (ie: residue 2 and 6)
Do the R-groups face outward or inward in a α-helix
Outward
How many amino acids are there per turn in an α-helix
3.6