Refractive Errors: Myopia, Hyperopia and Astigmatism
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
22 Terms
What is refraction
Change in direction of light as it passes obliquely from one optical medium to another of a different refractive index
ALSO
Process of measuring and correcting the refractive error of the ey
Refraction of eye
Human eye refracts at 2 ocular structures:
Cornea
Fixed focusing
Power approx. +40D
2/3 of total refraction
Lens
Variable focusing power - accommodation
Min power approx. +20D
(Max power approx. +33D – when accommodating)
1/3 of total refraction
Total power of eye approx. +60D
3 factors determine the eyes ability to focus light
Shape of the cornea Power of the cornea
Power of the lens
Length of the eye
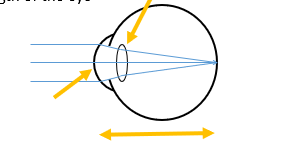
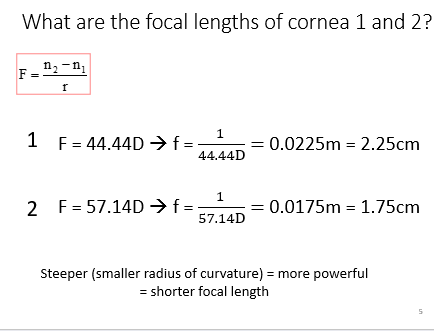
Why does corneal shape dictate power
smaller radius of curvature = steeper = more powerful = shorter focusing distance


corneal shape dictate power
flat cornea = bigger ROC
cornea - allows light pass through - hits it obliquely inside cornea = refractive index = 1.4
air = 1
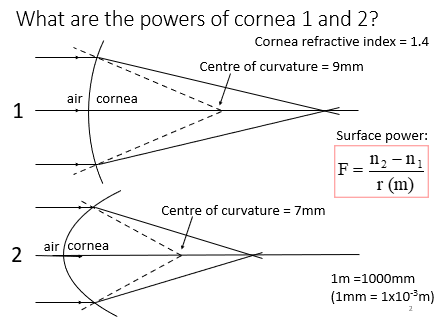
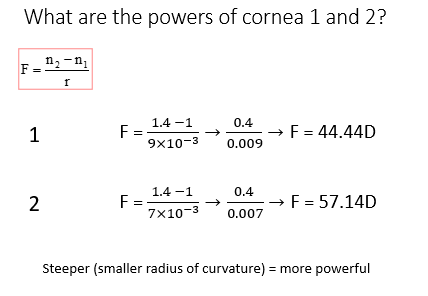
Cornea surface power
N2 = RI of cornea
N1 = RI of air
Steeper - smaller ROC = more powerful
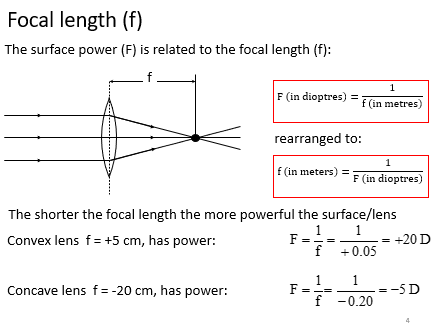
Focal length
The shorter the focal length the more powerful the surface/lens
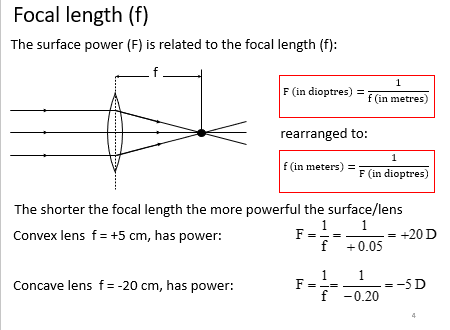
Steeper (smaller radius of curvature) = more powerful = shorter focal length
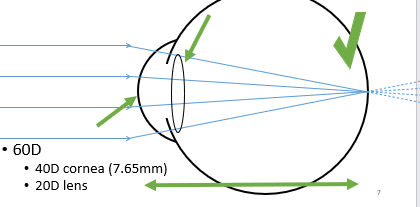
Emmetropia
Occurs when there is “matching” between the power of the eyes optical system (i.e. lens and cornea) and the length of the eye
Light focused on the retina – the eye is emmetropic
Results in clear vision
Objects at infinity
Focus at the retina
No accommodative effort
60D
40D cornea (7.65mm)
20D lens

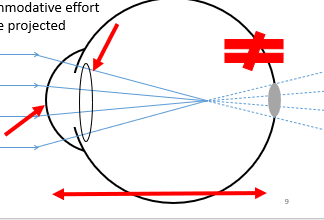
Refractive error
Occurs when there is a “mismatch” between the power of the eyes optical system (i.e. dioptric power of lens and cornea) and the length of the eye
Light is not focused on the retina – the eye is ametropic
Often results in blurry vision
Object at infinity
Light not focusing at the retina
No accommodative effort
Blur circle projected
3 types of refractive error (ametropia)
Myopia
Hyperopia (Hypermetropia)
Astigmatism
No refractive error = emmetropia
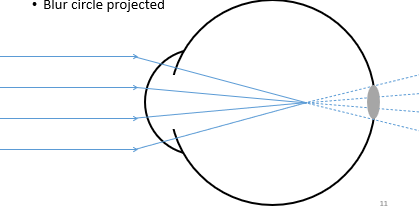
Myopia
Object at infinity (parallel light)
Focused in front of the retina
Blur circle projected
D blurry
N - clear
Object nearby (divergent light)
Focus on retina
No accommodative effort
Occurs when:
refractive myopia
Cornea is too curved
binatiLens is too powerful
Eye is too long - axial myopia
Or a combination
Correction
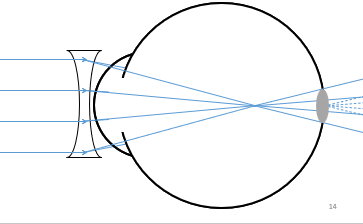
Parallel light focus before the retina
A blur circle is imaged on the retina
Use a negative spherical lens to bring the light into focus on the retina

Hyperopia
Object at infinity
No accommodative effort
Light focussed behind retina
Blur circle
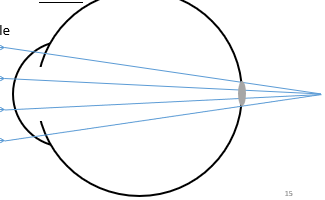
N - blurry
D - clear
Occurs when:
refractive hyperopia
Cornea is too flat
Lens is too weak
Eye is too short - axial hyperopia
Or a combination of these things
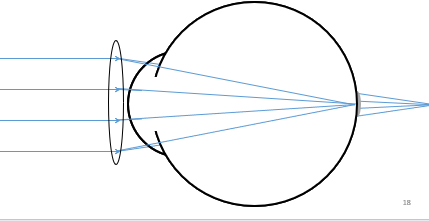
Correction
Light focuses behind the retina - blur circle
Use a positive lens to bring image into focus on retina

Accommodation
Change in the refractive power of the eye by a change in shape of the crystalline lens
Associated with convergence
Young hyperope (pre-presbyopic)
Effort of accommodation - can use accommodation to bring behind of retina to in front of retina
Brings the image to focus on the retina
Astigmatism
Light is incident on toric cornea and/or lens, this produces two foci meaning an elliptical blur is imaged on the retina
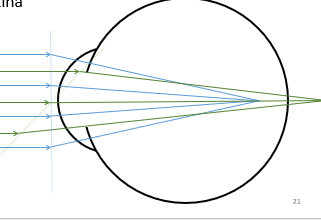
Occurs when:
Cornea and/or the lens have different curvatures in different meridians.
Types:
Regular astigmatism
Axis with greatest curvature and axis with least curvature are at 90o angle to one another
Irregular astigmatism
Irregularities in the curvature conform to NO particular geometry e.g keratoconus

Toric/Astigmatic Surface
The two principal meridians (which are located 90 degrees apart) have different curvatures
The radius of curvature of a surface determines the power, so a toric surface will have different power/ focal strength in the two meridians
The astigmatism is expressed as the difference between the 2 powers in dioptres.
With the rule astigmatism: steeper vertically.
Against the rule astigmatism: steeper horizontally.
Correction of Astigmatism
Refractive error of the eye produces two foci
An elliptical blur is imaged on the retina
A combination of spherical and cylindrical lenses used to focus the light on the retina
A combination of spherical and cylindrical lenses used to focus the light on the retina
spherical lens
A lens where all meridians have the same refractive power
Spherical lenses have power in all meridians therefore all light rays will be refracted by a spherical lens
Cylinder
curved = refractive power
A lens where one of the principal meridians has zero refractive power
Below examples:
Curved in the horizontal plane - producing refractive power
No curve in the vertical plane - giving no refractive power
correction of Astigmatism
A combination of spherical and cylindrical lenses used to focus the light on the retina
Spherical lenses have power in all meridians therefore all light rays will be moved by a spherical lens
Cylindrical lens has power in one principal meridian and no power in the other principal meridian.
This means light passing through the meridian with power is refracted, whilst light passing through the zero-power meridian is not refracted.
The position of zero power is called the cylinder axis and this has to be orientated correctly when correcting astigmatic prescriptions.
Summary of correction of ametropia/ refractive error
Measured in dioptres
A dioptre (D) is a measurement of the ability of a lens to CONVERGE OR DIVERGE light.
The amount of power, in dioptres, required to bring the light into focus on the retina
Correcting myopia - negative lens
Correcting hyperopia - positive lens
Correcting astigmatism - correct one meridian with a sphere and the other with a cylinder. The cylinder must be orientated correctly.
Recording spectacle prescription:
The spectacle prescription is recorded in terms of:
Sphere
Cylinder
Axis
E.g +3.00/-2.00 x 125
It can be recorded in negative-cylinder form and positive-cylinder form. To switch between the two forms transposition takes place.
When you wish to transpose a spectacle prescription:
Add the sphere and cylinder powers together - ensure you take sign into account
Change the sign of power of the cylinder.
Change the axis by adding 90 (if less than 90) or subtracting 90 (if greater than 90).
Rx +3.00/ -2.00 x 125 +1.00 / +2.00 x 35
Cross Line Chart
A cross line chart is sometimes used to record spectacle prescription in terms of dioptric power alone.
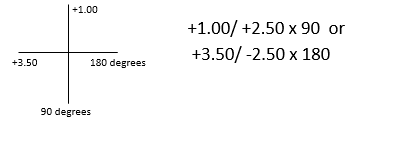
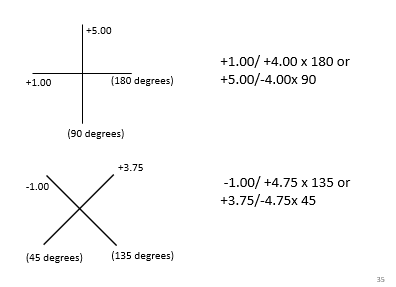

Methods for correcting refractive error…
Spectacles
Contact lenses
Rigid gas permeable
Excellent optics
Keratoconus /high cyls.
Tolerance needs to be built up
Soft
Daily disposables, Monthly
Spherical/Toric/Presbyopic correction
Infections
ADV CL
Wider Field of View.
Minimum difference in retinal image size in refractive anisometropia.
Minimises aberrations.
Appearance
Correction of complex prescription
DIS - CL
Wider Field of View.
Minimum difference in retinal image size in refractive anisometropia.
Minimises aberrations.
Appearance
Correction of complex prescriptions