Radioactivity, Chemistry
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
32 Terms
Half life
Length of time required for half of the radioactive atoms in a sample to decay
Isotope
Atoms with the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons
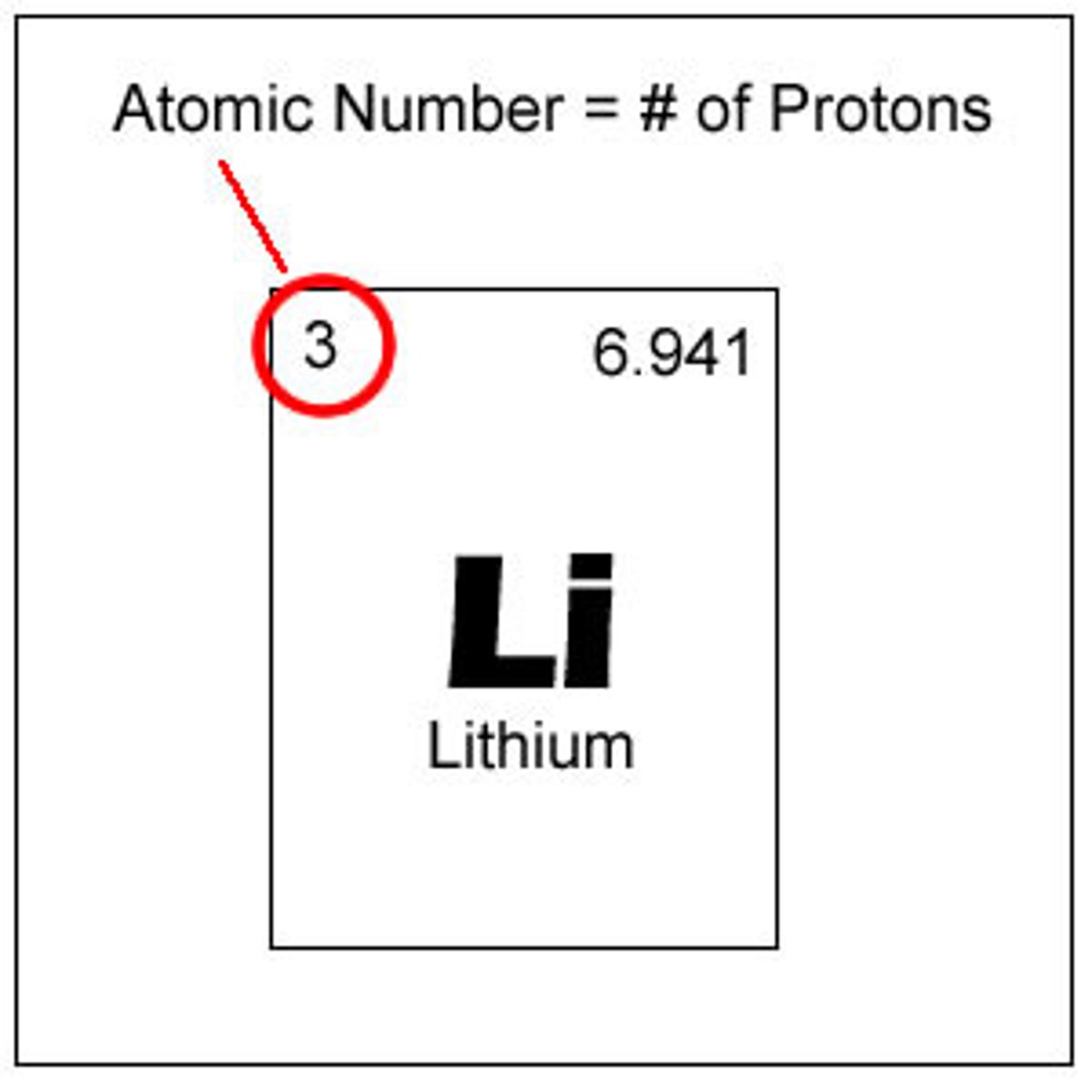
Atomic number
The number of protons in the nucleus of an atom
Mass number
the total number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus of an atom
Fission
Process in which heavy atomic nuclei split into smaller, lighter nuclei
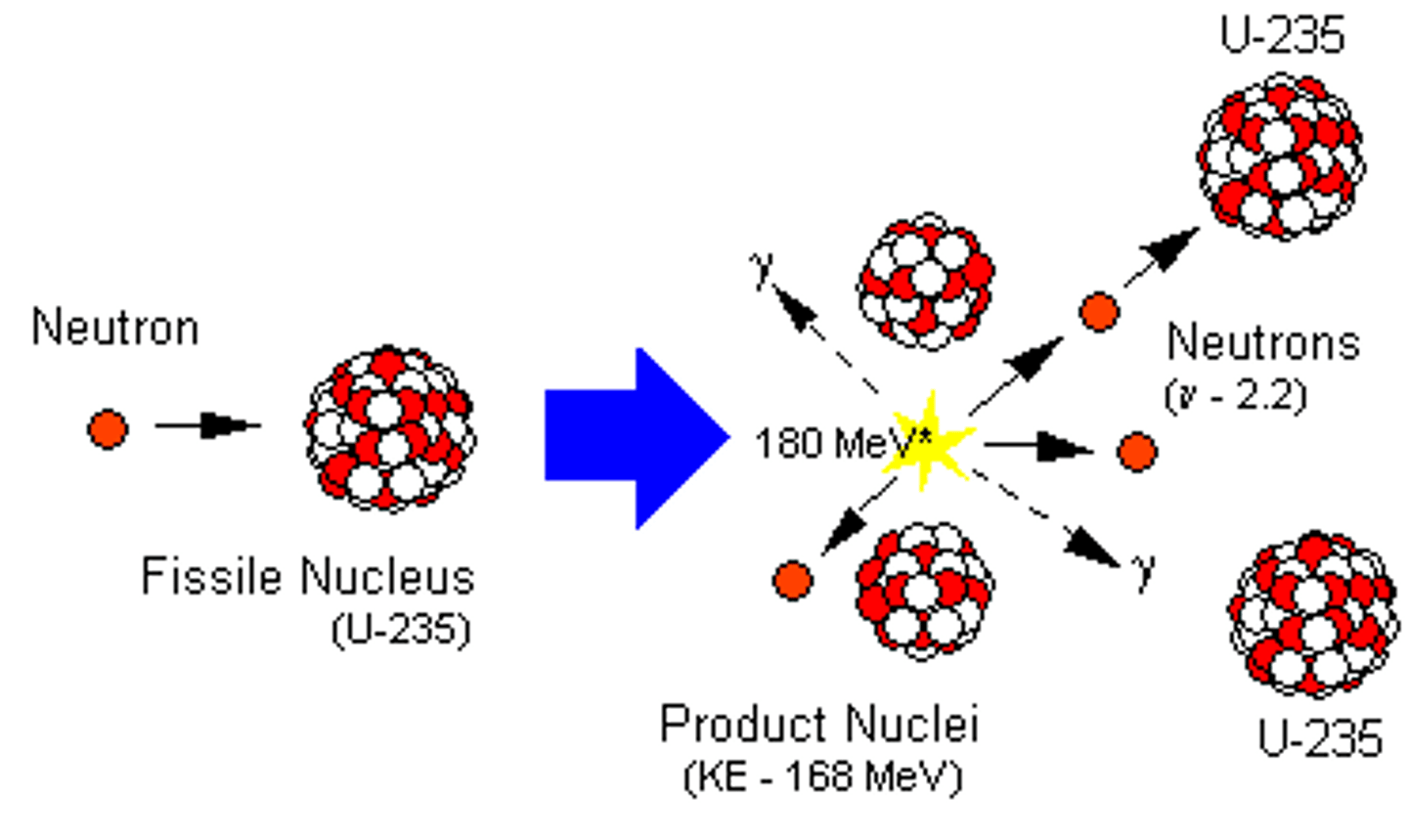
Fusion
Lighter nuclei combine to form heavier nucleus with release of energy
Alpha particle
particle emitted by a radioactive source that contains two protons and two neutrons, and has a double positive charge
Beta particle
a high-speed electron or positron emitted in the decay of a radioactive isotope
Gamma wave
High energy Electromagnetic radiation
Radioactivity
The emission of elementary particles by some atoms when their unstable nuclei disintegrate.
Strong force
Holds particles together in the atomic nucleus. This is the strongest force known in nature.
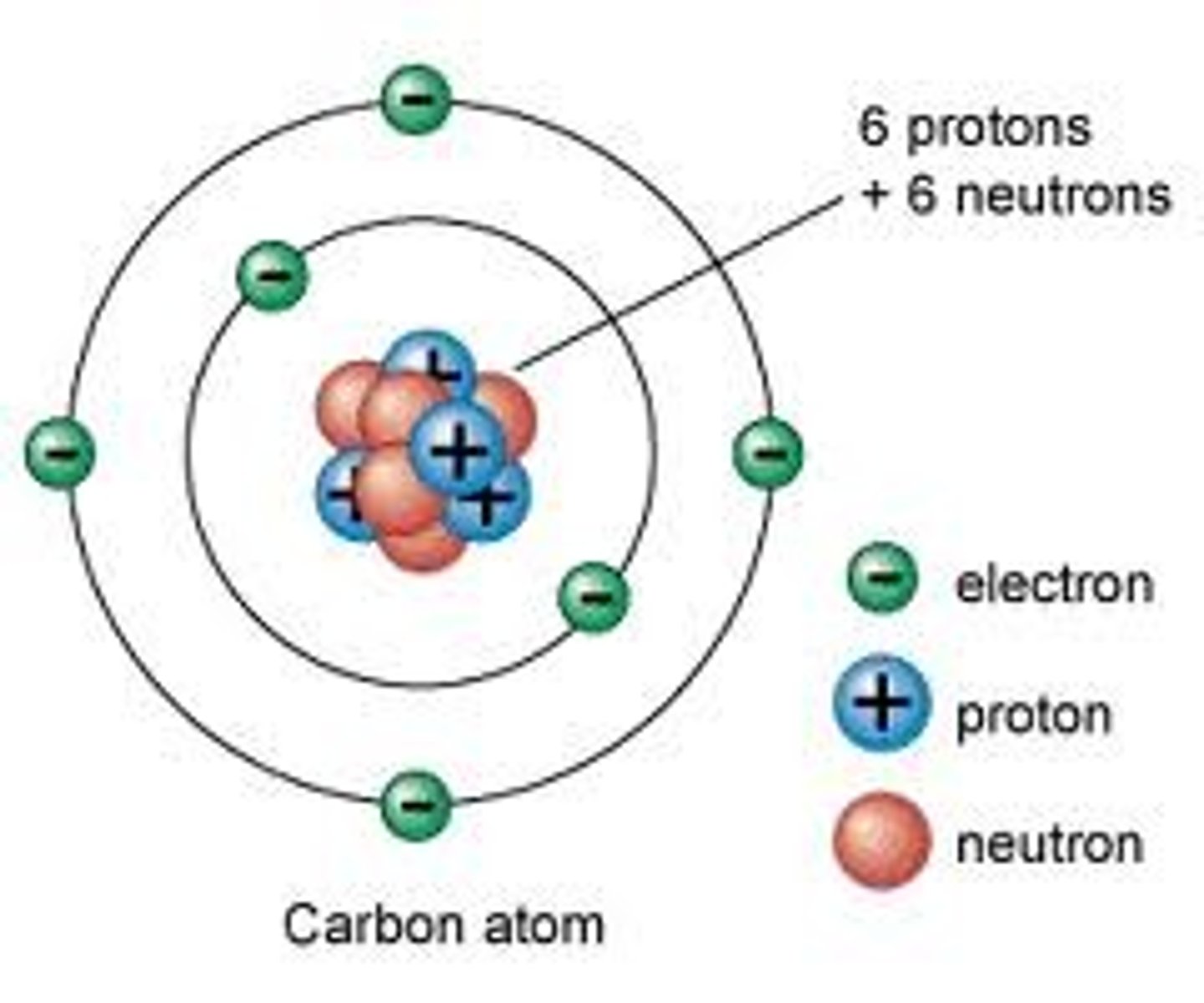
atom
the smallest object that retains properties of an element. Composed of electrons and a nucleus (containing protons and neutrons)
atomic number
number of protons in an element
chemical equation
an expression of a fundamental change in the chemical substance
compound
two or more atoms joined together chemically, with covalent or ionic bonds
covalent bonds
when two atoms share at least one pair of electrons
Radioactive decay
change of an element into a different element, usually with some other particle(s) of energy emitted
density
mass per unit volume of a substance
endothermic
process that absorbs heat from its surroundings as the reaction proceeds
half life
the amount of time it takes for half an initial amount to disintegrate
ion
removing or adding electrons to an atom creates an ... (a charged object very similar to an attom)
ionic bond
when two oppositely charged atoms share at least one pair of electrons but the electrons spend more time near one of the atoms than the other
Le Chatlier's Principle
states that a system at equilibrium will oppose any change in the equilibrium conditions
mass number
the number of protons and neutrons in an atom
molar
a term expressing molarity, the number of moles of solute per liters of solution
moles
a collection of 6.022 * 10 to the 23 power number of objects. Usually used to mean molecules
molecular mass
the combined mass (as given on the periodic table) of all the elements in a compound
percent composition
expresses the mass ratio between different elements in a compound
valence electrons
The electrons in the outermost shell of an atom
volume
Measures the size of an object using length measurements in three dimensions
wave
A signal which propagates through space
wavelength
On a periodic curve, the length between two consecutive troughs (low points) or peaks (high points)