PP 14: Invasive Species
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
49 Terms
Invasive species
-what are they?
-why should we care?
ecological concerns
Human, plant, and animal health
economic concerns
What prevents species from dispersing globally?
-Geographic barriers:
Oceans
Mountains
Deserts
large lakes
-barriers are in the eye of the beholder: what is a barrier for one species is not a barrier to another
e.g. mountains may restrict plant distributions, but not birds
Limits to dispersal
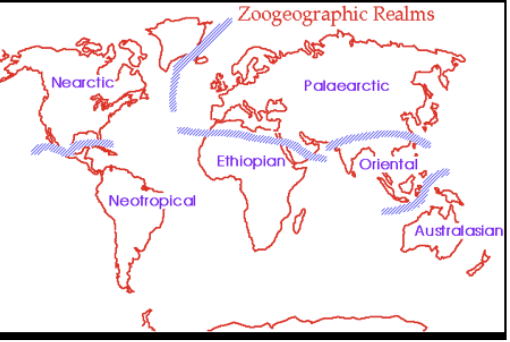
Wallace identified 6 global biodiversity realms, each different from the other
! know his name
Neotropical, Nearctic, Palearctic, Ethiopian, Oriental, Australasian
What are invasive species?
-Invasive species
to be invasine you have to be damaging to the ecosystem
likely to cause harm to the envrionment or human health
-Exotic species
just means from another part of the world
-introduced species
physically, intentionally, introduced
not necessarily capable of reproduction
-alien species
implies introduction to a particulat ecosystem
capable of reproduction in the new envrionment
not often used
Classical model of invasion
what prevents species from dispersing globally?
Establishment requires dispersal across barriers, colonization in acceptable number, and successful reproduction
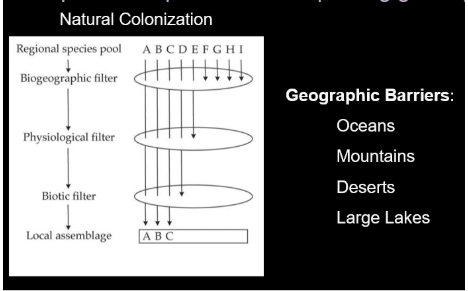
Natural colonization and human-mediated invasion
-humans allow them to get through the biogeographic filter

What allows invaders to invade
Only some novel species will survive and establish self-sustaining population in the novel habitat
a subset of these species may not only survive, but become invasive, dominating the new community and even causing the extinction of natives
but, what allows a species to become invasive?
no checks and balances, they can just take off
What allows invaders to invade, establish, and thrive
-Broad environmental tolerance
posses life history traits that confer superior colonizing ability or ability to acclimated to a wide range of habitats
-Local adaptation
Readily adapt to local selective pressures
-Life history traits
lack of predators in invaded habitat, high reproductive capacity, non-pocky eaters, wide ecological niche
Drivers of species change
aquatic systems are impacted more by invasive species
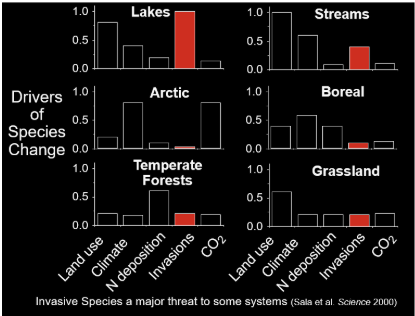
Negative impacts of invasive species
-Ecosystem level impacts
disturbance regimes
hydrology: alternations of water regimes
phragmites is doing this
geomorphological processes (erosion, sedimentation)
-Community or population level impacts
habitat structure
community composition
resource competition
population reductions, eliminations
genetic impacts
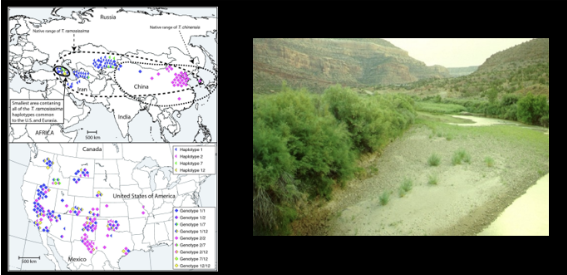
Hydrology: alteration of water regimes
Salt cedar (Tamarisk): absorbs large quantities of water along riverbanks in arid regions, and excretes salt into soils; forms monocultures
Homogenization of flora and fauna
more species change due to introduction of nonindigenous fishes than to loss of native fishes
this pattern may not be general- may vary from system to system
Predation
-Lake Victoria, Africa
introduced nile perch drove hundreds of cichlid fishes extinct
current problem with introduced water hyacinth (plant) from S. America

Economic impacts
-along with irreplicable losses to biodiversity- billions per year from
lost agriculture productivity
lost forest productivity
lost recreational opportunity
The invasion curve
-prevention is key, how do we prevent organisms from coming in
boat wash station
-Eradication: do whatever you can do to stop it immediately. if its a small lake, just kill the entire lake
-containment: gets very hard in the great lakes
-assest based prodction and long-term management: figure out hot to handle it longterm
graph
pic
Public and wildlife health impacts
-vector borne diseases
-dreissenid mussel beds are hot spots for bacteria
avian botulism
-poisonous and venomous plant and animal introduction
-alter food webs which may cause population boom of detrimental organisms
dreissenid mussels and cyanobacteria blooms
suck up algae. they will keep in the algae and spit out the cyanobacteria, giving it a competitive advantage
white nose syndrome in bats and mosquitoes
Aquatic invasive species (AIS) in the great lakes
pic

Invasion history in great lakes
pic

Our lakes are vulnerable
-Asian carp are poised to enter the great lakes
1. bigheaded carp
3 found in Lake Erie in 2000
sold live in Asian food markets in Toronto
2. Silver carp
-Asian carp reproduce in great lakes watershed (grass carp)
Opening of the St. Lawrence seaway
pic

Welland Canal
pic

Nonindigenous animals in the great lakes
pic

Zebra mussels
pic

Mussel species change
pic

Invaders use corridors to the great lakes
pic
How can we determine where invasive species originated?
1. Track the vector: look at import- export records
2. look at pathways that airlines and ships utilize
3. assess at genetic composition of the population in introduced areas and source areas

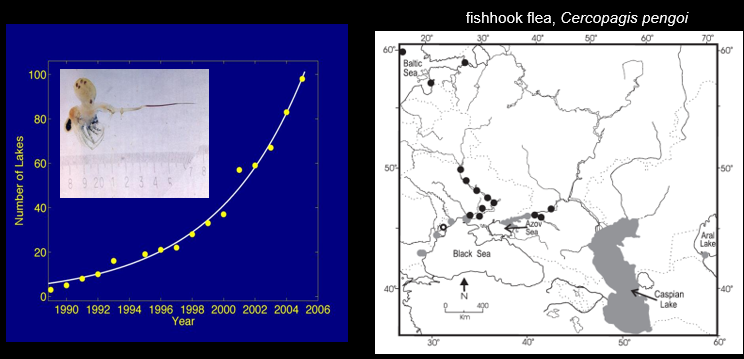
Eurasian distribution of the fishhook flea
native to Aral and Caspian Lakes, Azoz and Black Seas
introduced to several rivers and baltic sea
discovered in lake ontario in 1998
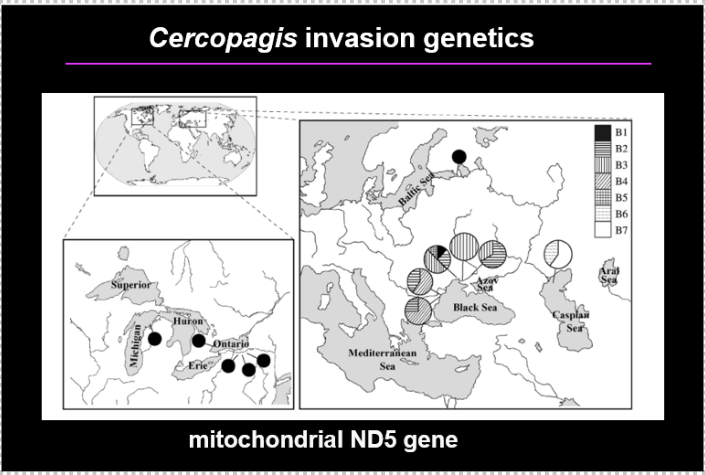
Cercopagis invasion genetics
pic
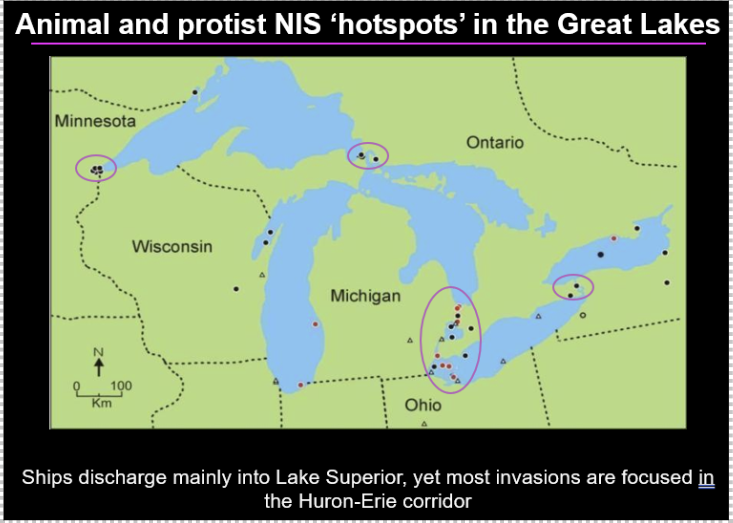
animal and protist NIS hotspots in the great lakes
-a lot of these are salt water ports
-a lot of ships will discharge in lake superior because its colder there and the species wont survive
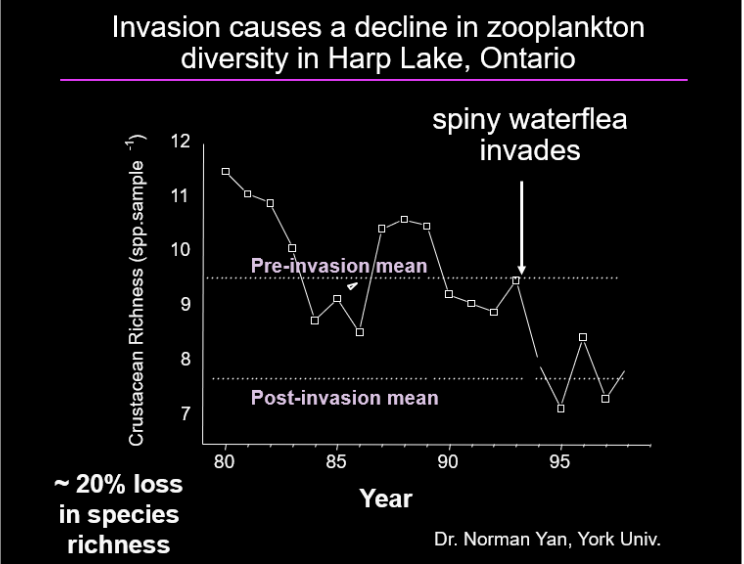
Invasion causes a decline in zooplankton diversity in Harp Lake, Ontario
pic
Pathways of introduction pt. 1
-attached to ships’ hulls
Underwater view of a highly fouled ship hull showing attached fouling organisms
-dumping of live bait containers and packing materials (overland transport)
Attached to fishing gear, anchors, lines
Pathways of introduction: Overland transport mechanisms
-Bythotrephes:
fishing/downrigger lines
bait buckets
live well water
bilge water
Macrophytes attached to boat
Pathways of introduction: Overland transport mechanisms pt. 2
-Boats and trailers
recreational boats and trailers are frequently and rapidly transported over significant distances
litter regulation regarding cleaning boats, trailers, other exposed equipment
Pathways of introduction: Overland transport mechanisms pt. 3
-Live bait
non-native species of fishes and many species of invertebrates are sold live as bait
bait boxes (worms) also contain up to two dozen species
poorly regulated, little inspection capacity
Pathways of introduction: Overland transport mechanisms pt. 4
-Ballast water
the most well-known pathway
More than 2 million gallons of ballast water are dumped in U.S. harbors every hour
up to three hundred species have been identified in ballast of single ship
Uncertainty about viability of organisms
high quantity but low quality
Pathways of introduction: Overland transport mechanisms pt. 5
-Aquarium introductions
many non-native species of fish, invertebrates and algae sold in U.S.
in CA, there are 900 non0native species of fish for sale in aquarium stores
pets commonly ”released" when get too big
many species could potentially become establish
transfers of aquaculture products or fish stocks
intentional introductions to establish new fisheries
escape from backyard ornamental ponds
Pathways of introduction: Overland transport mechanisms pt. 5
-Backyard ponds
fastest growing segment of horticulture industry
16 million backyard ponds
little regulation regarding placement near waterways or strom security
ex. Hydrilla, water hyacinth, Eurasian watermilfoil
Pathways of introduction: Overland transport mechanisms pt. 6
-live seafood
many species of non-native fish and invertebrates (oysters, mussels, clams, crayfish) are sold on live seafood market
Potential for release during storage or after sale
Failed biological control
-asian carp were introduced in Arkansas in the 1960s and 70s by and for fish farmers to control vegetation, plankton, and most recently snails in catfish rearing ponds
escape or released and some intentional stocking occurred after that
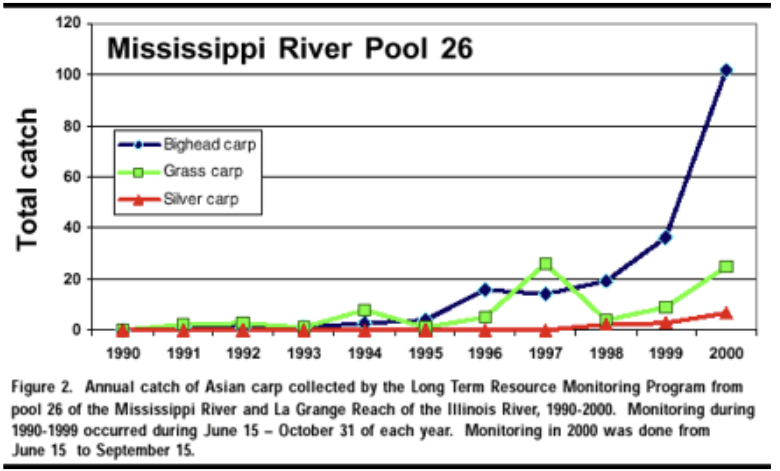
Early detection rapid response (EDRR)
Most cost-effective investment is to fund a regular survey of high priority sites of introduction
early detection of an invasion can allow eradication just after the species has become established
Prevention, prevention, prevention
-Keep them out!
tighten important and interstate transport regulations
maintain clean species list
educate the public on the risk of releasing new species
increase fines and penalties for intentional illegal releases
if still in captivity, destroy all existing stocks
close all avenues of escape
install organisms barriers
improve water and waste treatment
modify the navigation system
Prevention, prevention, prevention pt 2.
-Barriers
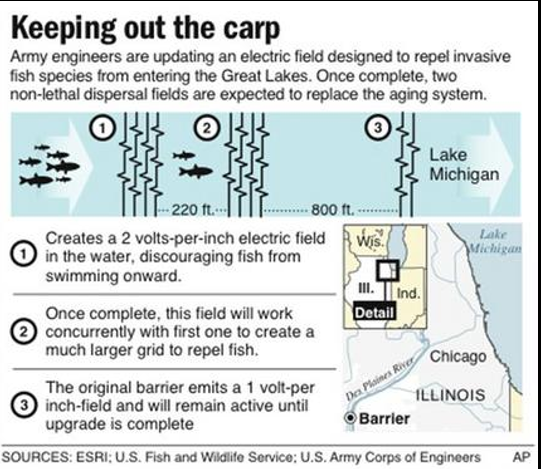
Prevention, prevention, prevention, pt 3
-Hydraulic separation
“replumb” or hydraulically separate the Great Lakes and Mississippi River basin watersheds, essentially reversing or amending the engineering feats of the past (ex. Like the re-engineering project of the Kissimmee River in Florida)

Control methods
Kill them
sterilize
10 nasty invasive species in the US exported to Europe
Red-eared slider turtle
American lobster
Bullfrogs
Gray squirrels
Raccoons
American mink
Crayfish
Largemouth bass
rosy wolf snail
Colorado potato beetle
Impact on environmental justice
How do invasive species impact tribal fishing and hunting right? Traditional food (ex. Wilf rice) growth and acquirement?
How do invasive species impact sustenance fishing?
As vectors of disease and who is impacted?
Solutions? What can I do?
Individual level
Community level
State government level
federal government level
Global level
Invasive species management and prevention resources:
RIPPLE (reduce invasive pet and plant escape)
USGS non-indigenous aquatic species list
Ontario’s invading species awareness program
Invasive species centre- Canada
Great Lakes non-indigenous aquatic species information system
UK guidance on control and management of ballast water
National exotic marine and estuarine species information system
University of Florida center for aquatic and invasive plants
Michigan.gov/invasives
Minnesota Aquatic invasive species research center
Midwest invasive plant network
! not on test