biol 191 lab 8 - chordates
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
notochord, dorsal hollow nerve cord, pharyngeal gill slits, postanal tail
4 characteristics in Phylum Chordata
Eukarya, Animalia, Chordata, Urochordata, Tunicates, sessile adults, free-swiming larvae, bilateral symmetry
Domain, Kingdom, Phylum, Subphylum, common name, structural information of this species
Eukarya, Animalia, Chordata, Cephalochordata, Lancelets, many pharyngreal slits, notochord runs the entire length of dorsal nerve cord
Domain, Kingdom, Phylum, Subphylum, common name, structural information of this species
notochord replaced by vertebral column
cranium (except for fishes)
endoskeleton made of cartilage or bone
neural crest - development of vertebrate structures
internal organs (endocrine, circulatory, excretory)
joint appendages
evolved features of Subpylum Vertebrata
wings, fins, legs, forelimbs, hindlimbs
examples of jointed appendages
Clade Cyclostomata - jawless fish
Clade Chondrichthyes - cartilaginos fishes (sharks, skates, rays)
Clade Osteichthyes - bony fishes and lobe-finned fishes
Classes of fish that live in water
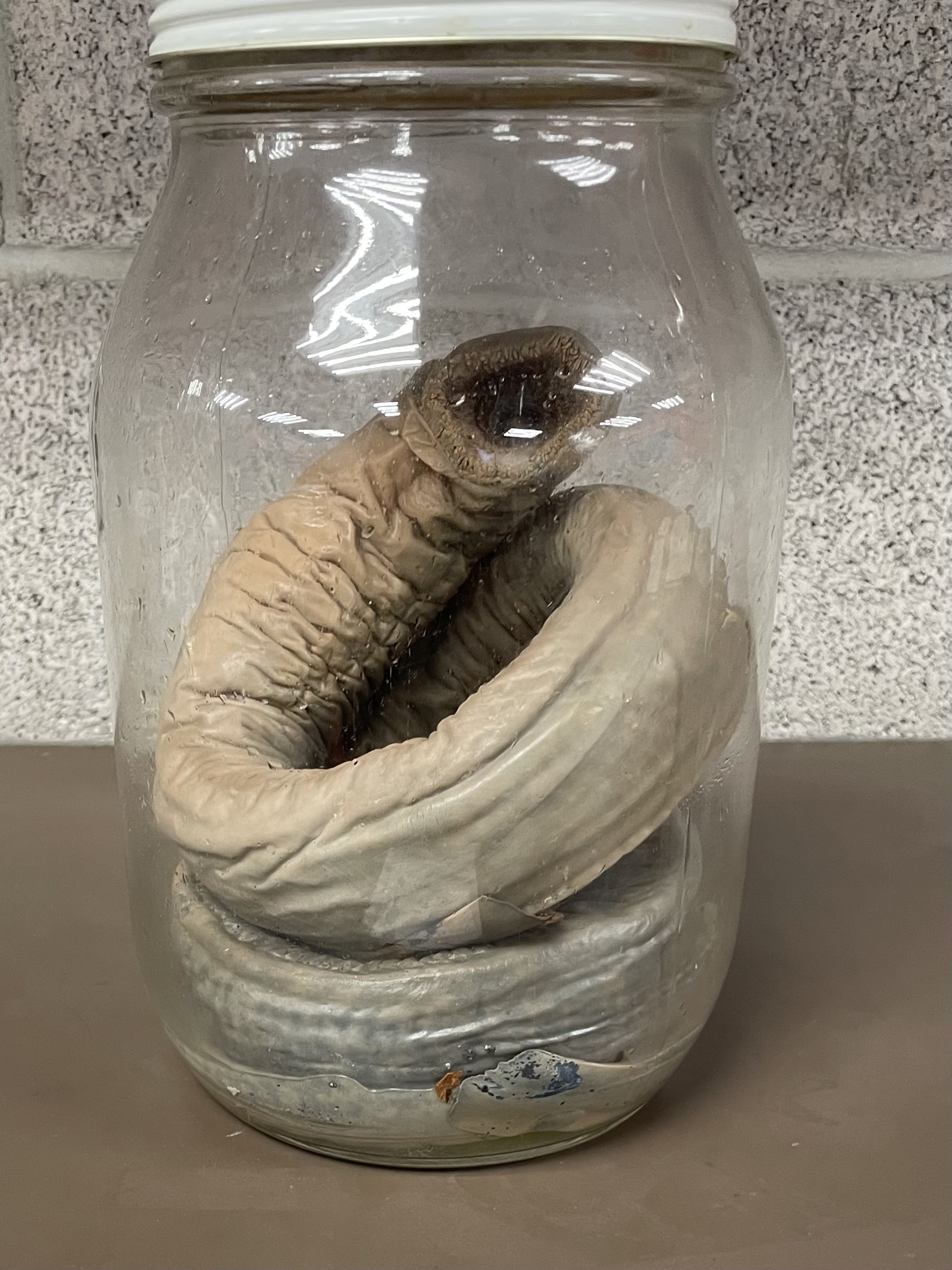
Eukarya, Animalia, Chordata, Vertebrata, Cyclostomata, Jawless fishes; 2 chambered heart, cartilaginous skeletons, no paired fins, single nostril, no scales
Domain, Kingdom, Phylum, Subphylum, Class/Clade, common name, structural information of this species

gnathosomes
vertebrates with true jaws
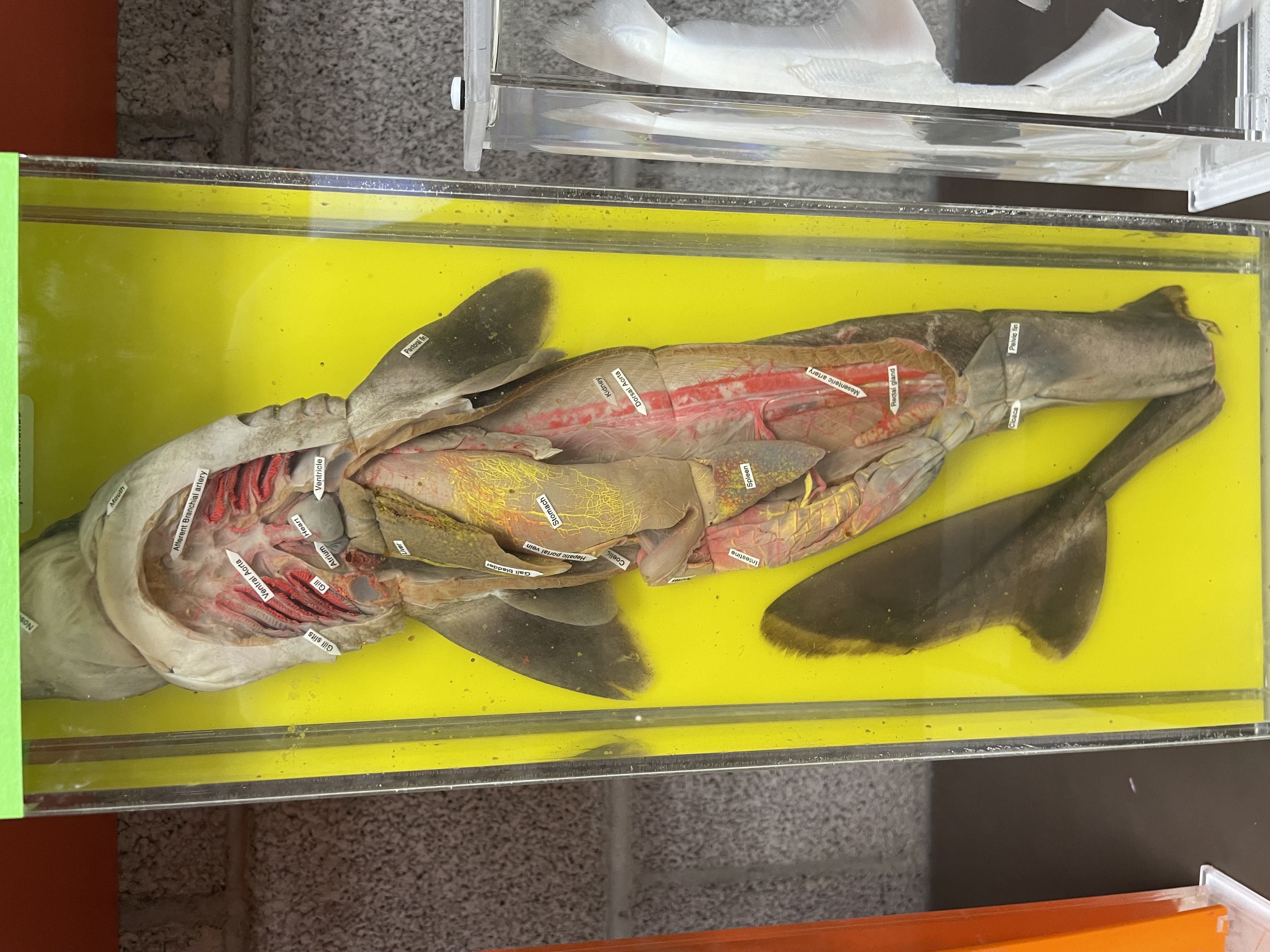
Eukarya, Animalia, Chordata, Vertebrata, Chondrichthyes, Cartilaginous fishes; gnathosome, cartilaginous skeleton, placoid scales, paired fins, nares (paired nostrils), males have claspers to transfer sperm, birth are viviparous, oviparous, or ovoviparous, caudal fin longer than ventral side, 2 chambered heart
Domain, Kingdom, Phylum, Subphylum, Class/Clade, common name, structural information of this species

viviparous
live birth
ovoviviparous
egg is hatched internally, followed by live birth
oviparous
hatched from egg
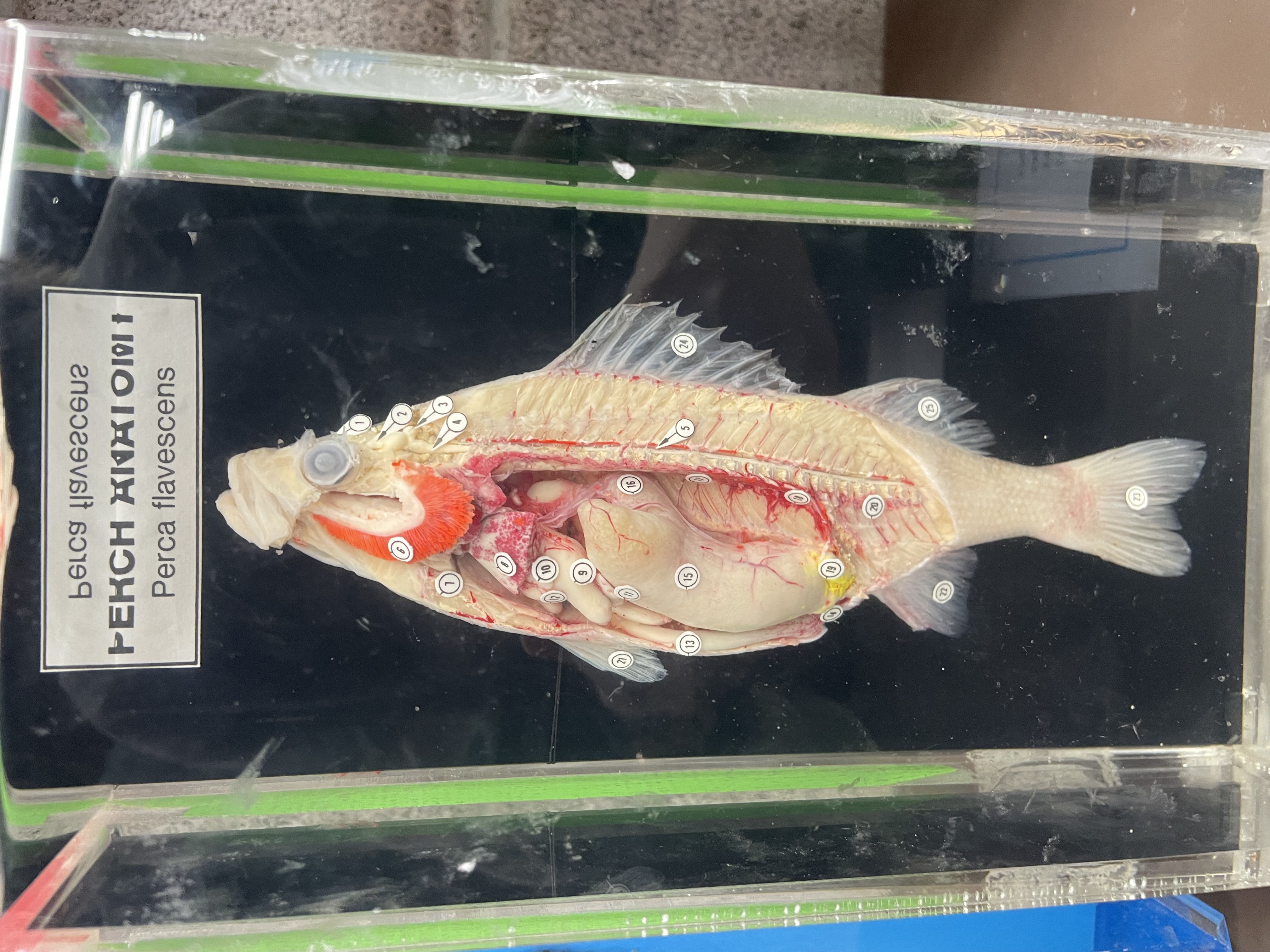
Eukarya, Animalia, Chordata, Vertebrata, Osteichthyes, bony fishes; fusiformed for locomotion, dermal scales, lateral line is a sensory organ to detect vibrations, swim bladder keeps them buoyant,
Domain, Kingdom, Phylum, Subphylum, Class/Clade, common name, structural information of this species

Clade Actinopterygii - bony rayed fish
Clade Sarcopterygii - lung fish and coelacanths (fleshy fins)
name the two clades from Clade Osteichtyes
Eukarya, Animalia, Chordata, Vertebrata, Amphibia; 3 possible types of respiration: lungs (adults), through the skin, gills (larval), three chambered heart, ectothermic, tympanic membrane (hearing by sensing vibrations)
Domain, Kingdom, Phylum, Subphylum, Class/Clade, structural information of this species
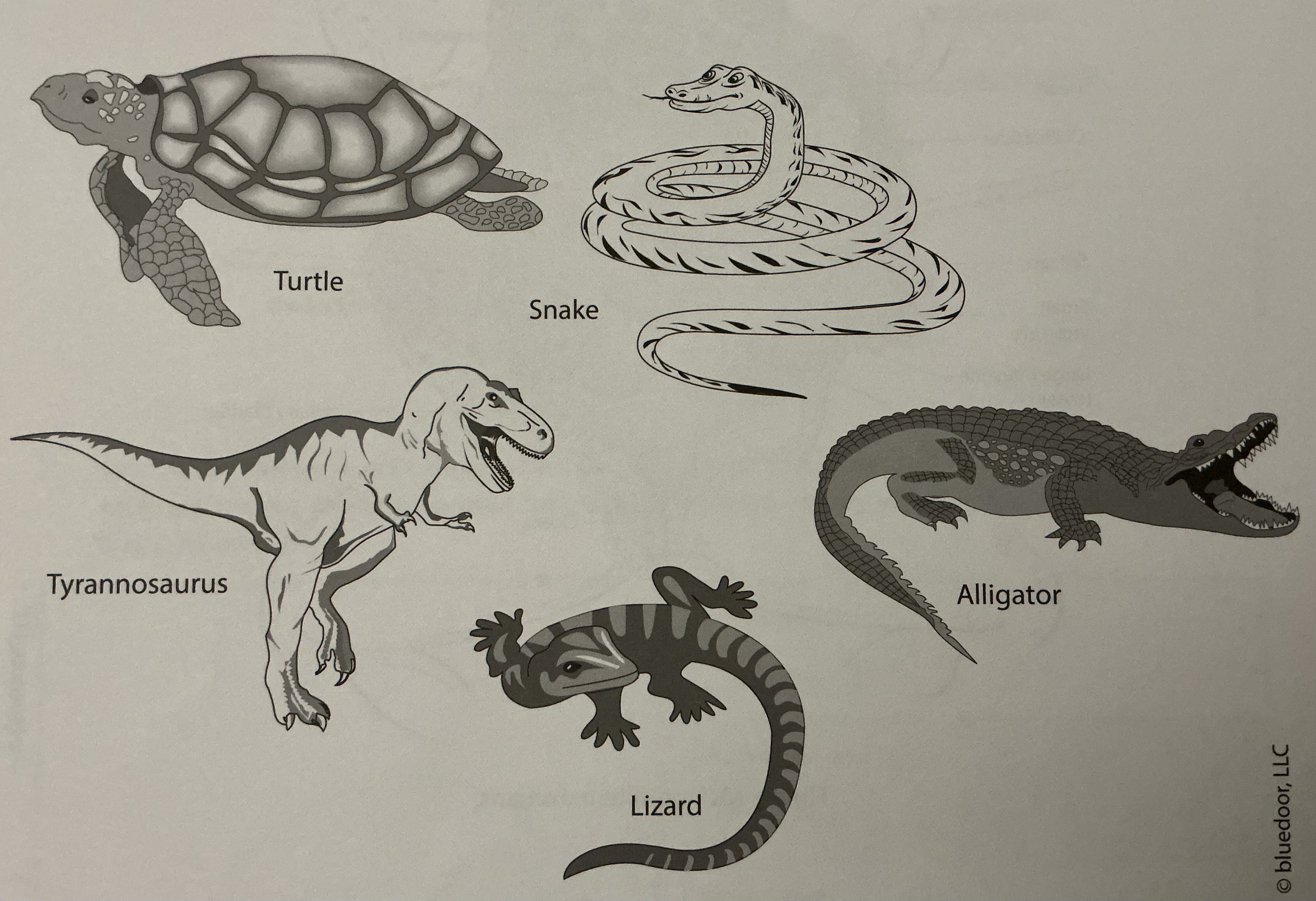
Eukarya, Animalia, Chordata, Vertebrata, Reptilia, Reptiles; amniotic eggs (bypass larval stage), ectothermic, 3-4 chambered hearts, lay eggs
Domain, Kingdom, Phylum, Subphylum, Class/Clade, common name, structural information of this species

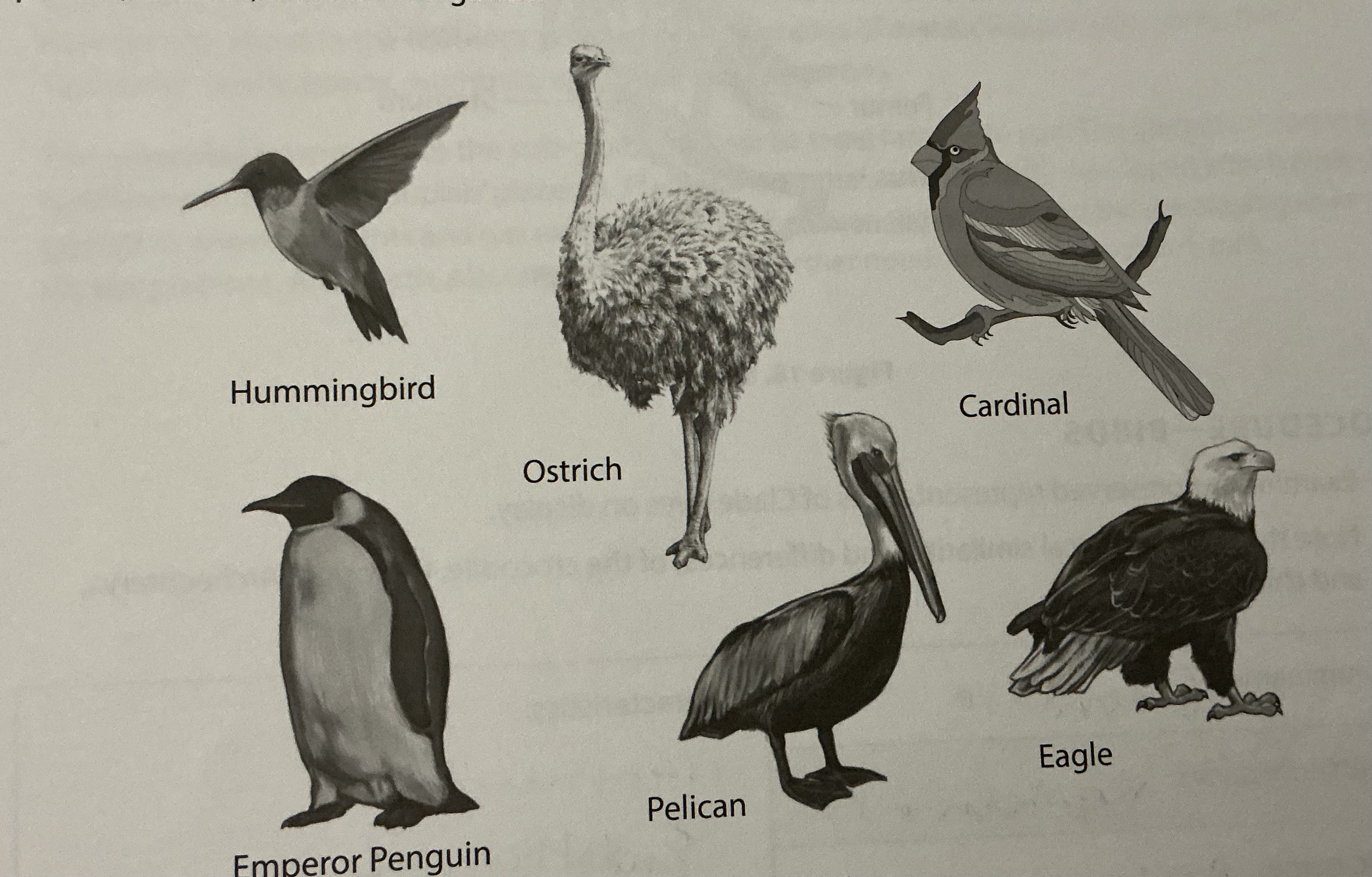
Eukarya, Animalia, Chordata, Vertebrata, Aves, Birds; endothermic, 4 chambered heart, 3 kinds of feathers: contour (flight), down (insulation), filoplumes feathers (sensory)
Domain, Kingdom, Phylum, Subphylum, Class/Clade, common name, structural information of this species

hair
mammary glands
endothermic
4 chambered heart
traits of modern mammals
quadrapedal (4 footed)
5 digits on each limb
early mammal traits
Eukarya, Animalia, Chordata, Vertebrata, Mammalia; Monotremata (monotremes), Metatheria (marsupials), Eutheria (placental mammals)
Domain, Kingdom, Phylum, Subphylum, Class/Clade; 3 subgroups
cloaca
only in monotremes:
single opening where digestive, excretory, and reproductive systems all discharge
bilateral
tripoblastic
coelomate
deuterostome
name the following for vertebrata:
symmetry
tissue organization
body cavity
embryonic development