AP Bio unit 7 : Natural Selection.
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
Natural Selection
developed by charles darwin
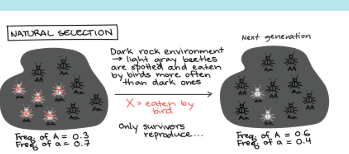
organisms with favorible trait will survive and produce offspring and pass the good traits
ex: peperred moths, antibiotic resistance (adaptive melanism)
mutations will create new variants
Artificial Selection
organisms with certrain traids are bred
like dog breeds, or corn
known as selective breeding
Types of Selection
stabalizing
diversifying or distruptonal
directional selection

Hardy-Weinburg
states
means no change in allele frequency in the gene pool
large population - can hide mutations and genetic drift and maintains
no genetic drift -
random mating
no natural selection
no gene flow - no new alleles
Hardy Weinburg Equations
p = freuqnecy of dominant allele
q = frequency of ressesive allele
p2= freqency of homozgous dominant
q2= freqneucyt of the homozygous resseive
2pq = freqnecy of honmozygous resseisve
p+q=1
p2+2pq +q2= 1
Equation to determine equillibrum
if whave a population and we want to know if its evolving.
Find allele frequency by adding and stuff
input the data into the hardy weinburg
multiply the genotype freqenices and the total popultion
if it matches, its in equillbrium, if not, then not in equillibrum
Equation to find others
if we know the frequency or population of some
we can use that info to determine the others if the population is in equillibrum
what does it mean when a population evolved
it means that the genotype and allele frequncies change in a gene pool
this may be due to mutations, natural selection, a genetic drift,
Founders Effect
Small population is isolated from orignal population → different allele frequencies
genetic drift
Bottleneck Effect
population is reduced by a natural disaster like a fire flood, hurricane
selection is not based on traits (Lucky)
can reduce gnetic diversity and make harmful alleles more pelavent
phylogentic/ cladogram tree
the one of with most differneces (outgroup) first
nodes can switch (keep that in mind)
the closest ones are together
Speciation
creation of speicies
serperated by reporuductive barriers
2 different speices cannot interbreed and cannot produce fertile, viable offsrping
Prezygotiac Barriers
prevent formation of the zygote in the first place
Behavioral - different mating rituals (dance, song)
Temporal - mating at different times of year, day, etc
Geographic- separation by geopgraic barrier
Habitat/ Ecoligocal - organisms use different things of the same geographic area (bees on different plants)
Mechincal - the morphology wont let the pipe go in, or sperm cant reach
Gametic - molecular mismach
Post Zygotic Barriers
Species can mate and form a zygote but their offspring is not viable
Reduced Hybrid Viability - the hybrid is not viable, and sick and not fit
Reduced Hybrid Fertillity - the hybrid is not fertile (mules cannot repdocue bc odd)
Hybrid Breakdown - the first hybrid generation is ok but as the generations pass, the viability and fertility goes down
Sympatric Speciation
New speicies froma surivving speices and both still inhabit the same geogrpahic reigion
habitat and behavioral isolation
sexual selection
polyplody (error in meosis)
allopatric Speciation
geographic changes cause isolation
can cause genetive drift
spliting off gene pools
Species spread, barrier is made, the differences cause differentiation and then leads to no possible interbreeding
sources of genetic variation
Molecular
Point Mutations - Frameshift, Nonsense, Missense, → change in nueclotide sequences which changes the amino acids → protein structure → phenotype or gene expression
Duplication - genes, chromosomes, genomes, sypatric speciations → causes an extended genome or in ploidy. → altered gene number
rearrangements- sometimes gene order, inversions, chromosomes fusion, transposons → alerted chromosome structure
Other: fast reproduction (especialy in virusus)
lack of repair of DNA in virus
Genetic Variatiopn - Cellular or Repdouction
Crossing Over
Indepdent Assortment
nondisjucntion
Random Mating
Created many dfiffent gamete combinations and diversity
Genetic Variation - Population
Genetic Drift -
Bottleneck → change in allele frequencies
Founders Effect - New population
Gene flow - migration, leads to new types of genes, could be individuals or gametes
Geographic Isollatioj or Allopatric Seperation - seperated populations
Nonrandom mating
Sympatric Speciation - same enviroment but diffrent niche or habitat overtime
mutations
Ways to determine phylogeny of organisms or evidence of evolution
Fossils - morphology- shape, can show the common ancestors and the “in between”
Embryonic- some features and similarities are only seen before full development
Reproduction
Molecular Biology or Biochemical comparisons - DNA sequence Protein sequencing, , DNA is best because it can show specific sequences and been silent mutaitons
Morphological - homologous structures (not the most accurate because if analogous)
Biogeography - uses the distribution of species. Unrelated species can look alike due to similar pressures
Homologous vs Analogous structures/ etc
Homologous structures - from same ancestors, can be structures or proteins like insulin
can be useful or vestigial (non useful)
Analogous structures- not from same ansestors but similar function due to similar pressures (convergent evolution)
Convergent evolutiona
Evolution which causes species to be similar and have similar traits due to similar pressures
→ analogous structures
on a cladogram, the animals will not be close
Divergent evolution
Bacially
Speciation
Polyploid
a condition in hwich an organism has extra sets of chromosomes
this leads to more
This can lead to sympatric evolution
It can occur due to abnormal cell division (non disjunction), such as when chromosomes don't separate during meiosis, or when an egg is fertilized by more than one sperm.
Autopolyploid - same species
Allopolyploid - species interbreed and produce a hybrid → sterile but can reproduce asexually (plants) → leads to fertile new species
sexual selection
male compeition (intrasexual selection)
or female choice (intersexual selection)
what is measure of fitness
the ability to reproduce
gene flow
is the trading of genes between different populations
adaptive radiation
one parent speices produces many decandant species with unique adaptations and niches
example is the galapagos birds
pseudogenes as evidecne for evolution
non functional gene that is a variant of a gene from related species
all living thingsd have
DNA
ATP - chemiosmosis
Genetic Code
Ribosomes
Metabolic Pathways like glycolysis, krebs ETC
evidence that all of Earth’s organisms are descended from a common ancestor
-all organisms even bacteria use ATP
-DNA is used as genetic code
micro vs macro evolution
-micro: small changes or adaptation, for example, bacteria evolving to be resistant to antibacterial
-macro: is the big changes in evolution that results in vastly differnt and new spceies