Electron Configuration
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
45 Terms
Light as a wave
Has crest and trough = frequency;
Electromagnetic Spectrum
organized list of all forms of electromagnetic radiation
Electromagnetic radiation
wavelike energy; traveling through space
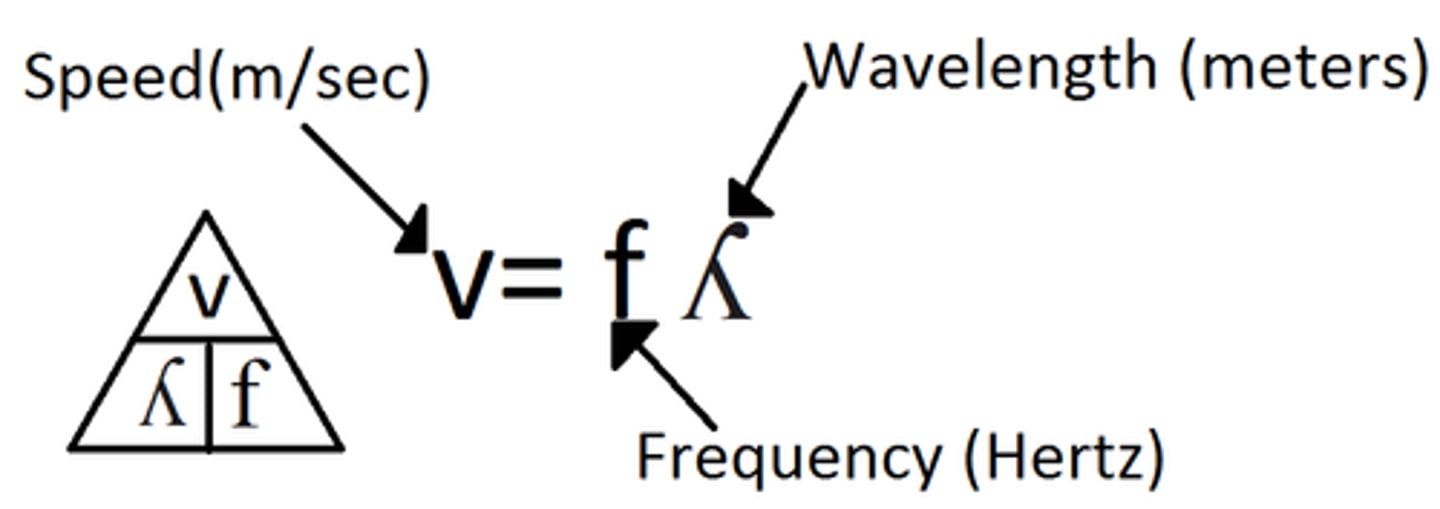
The Wave Equation
Wave speed = frequency x wavelength (v=fλ) (v can also be c)
Quanta
minimum amount of energy that can be lost or gained by an atom
Photon
Particle of electromagnetic radiation having zero mass and carrying a quantum energy
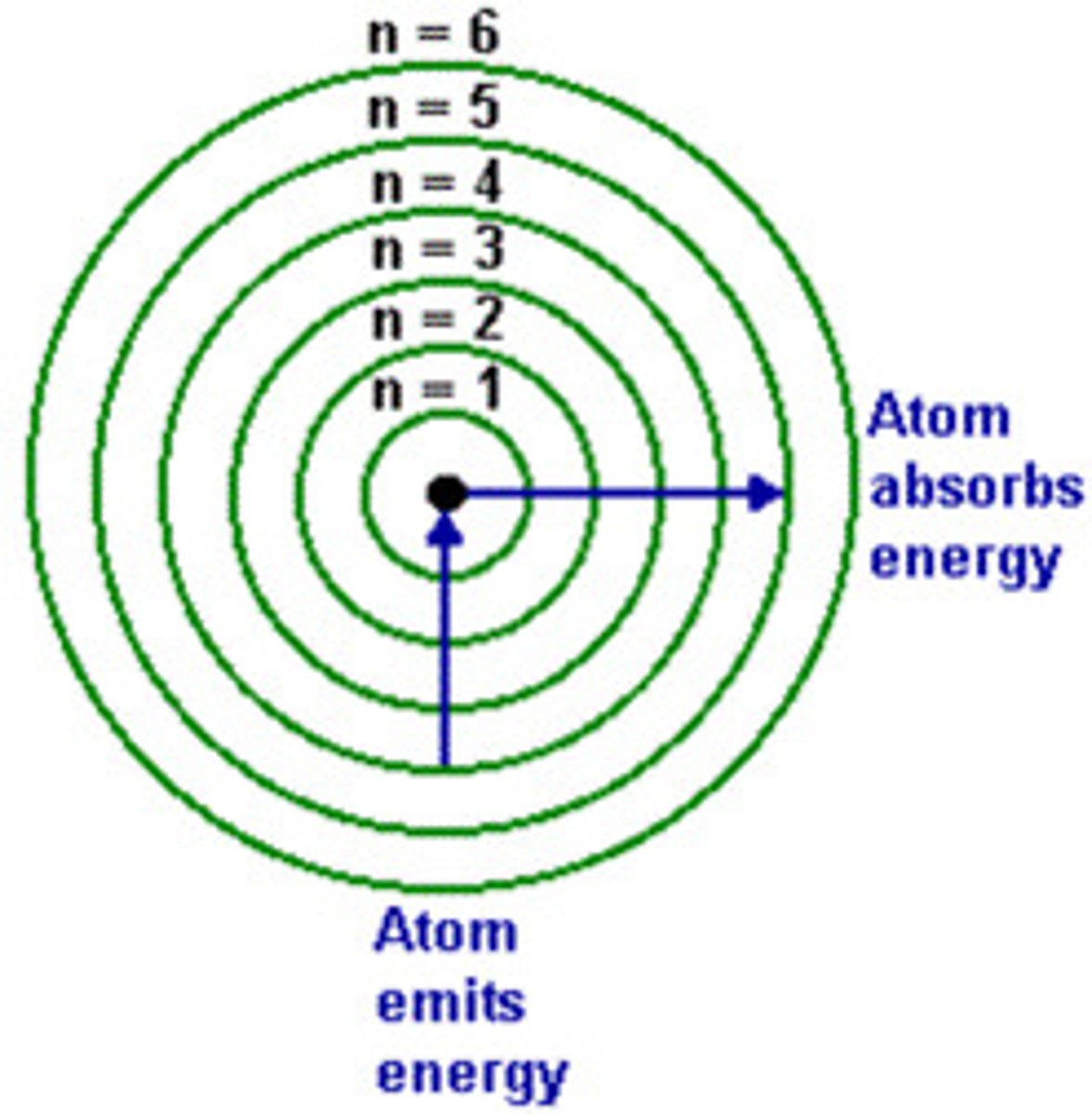
Ground State (Atomic State)
Lowest energy state of an atom; Neutral
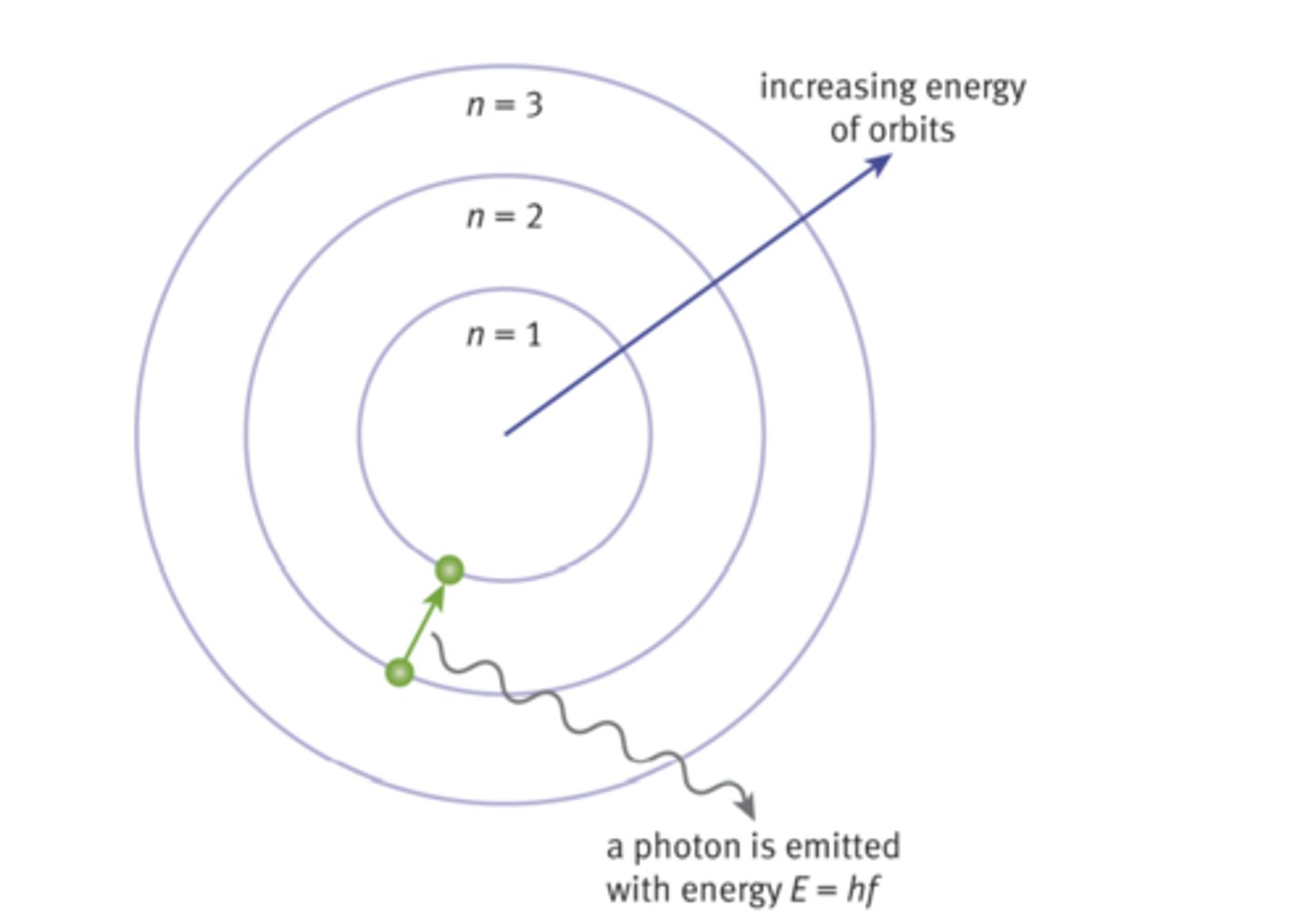
Excited State (Atomic State)
Atom has a higher potential energy than it does in ground state
Gives off light (Atomic State)
Moving from excited back to ground state
Line-Emission
Narrow beam of light, when passing through a prism
Continuous
Emission of a continuous range of frequencies of electromagnetic radiation
Absorption
Electron jumps from lower to higher energy level; Energy must be added
Emission
Electron falls to a lower energy level; Photon is emitted
Heisenberg Principle
It is impossible to determine simultaneously both the position and the velocity of an electron or any other particle
Quantum Theory
Describes mathematically the wave properties of electrons and other very small particles
Gives the probability of finding an electron in a given orbital
3 dimensional region around the nucleus that indicates the probable location of an electron
What is Electron Configuration?
Arrangement of electrons in an atom; Unique for each element; Coding system for the periodic table
Aufbau Principle
Electrons occupy the lowest energy orbital that
can receive it first; Start with s before moving to p
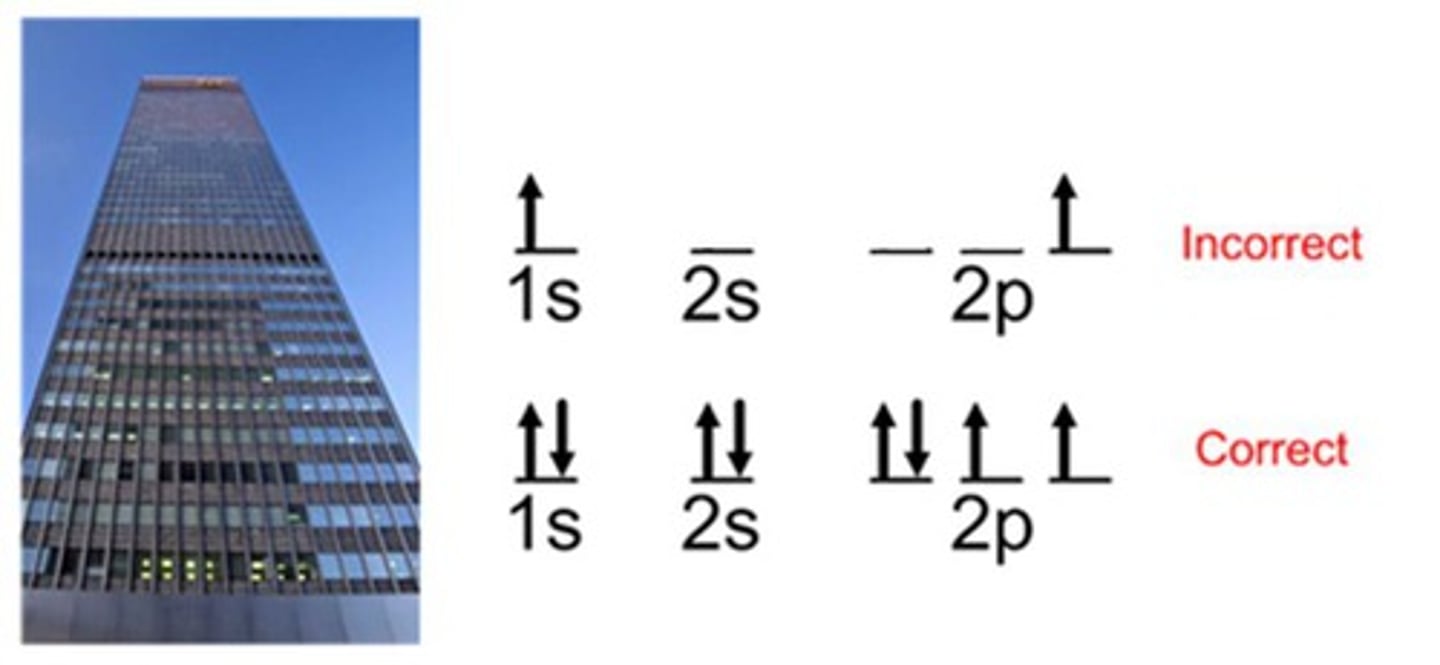
Pauli Exclusion Principle
No two electrons in the same atom can have the; same set of four quantum numbers; Arrows represent different spin states
Shorthand Notation
Uses the previous noble gas as a starting place in [ ]
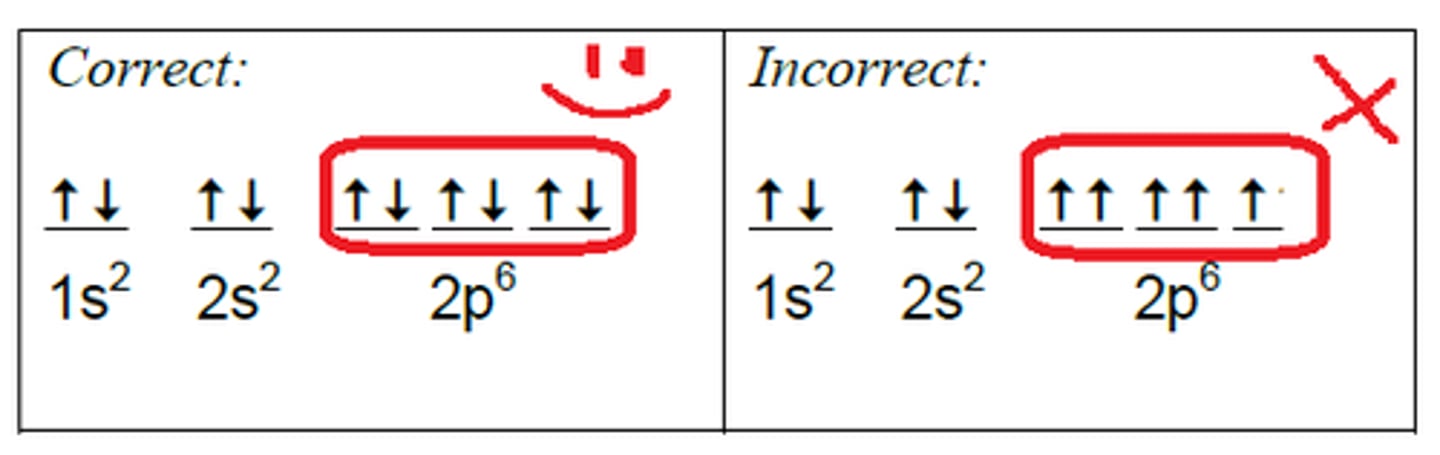
Hund's Rule
Orbital's of equal energy are each occupied by one; electron before any orbital is occupied by a second; electron; All electrons in singly occupied orbital's must have the same spin state
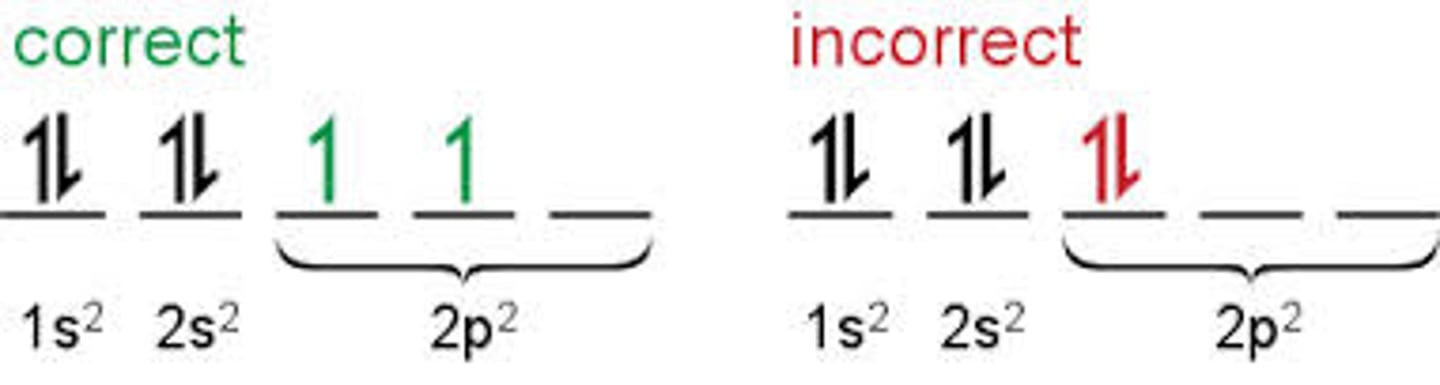
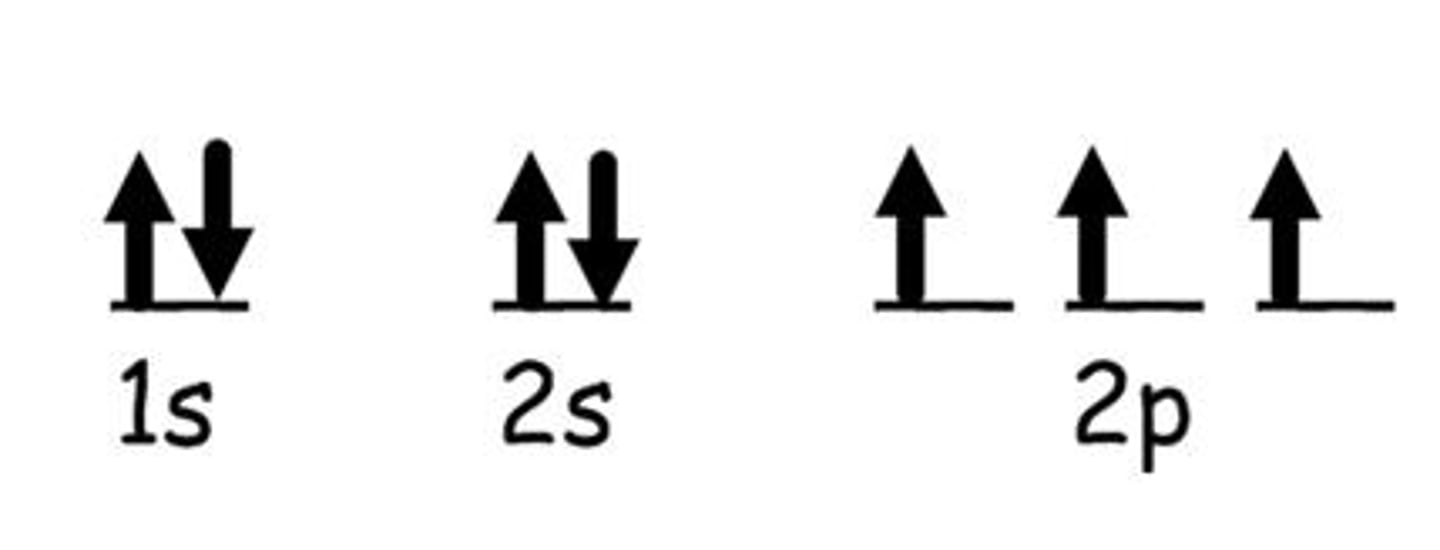
Orbital Notation
Uses lines to represent orbitals and places arrows
as electrons; Quantum # and Sublevel underneath
(Ex: S- 1 line (up to 2 e-)
P- 3 lines (up to 6 e-)
D- 5 lines (up to 10 e-)
F- 7 lines (up to 14 e-))
Electron Configuration
Eliminates lines and arrows; Uses superscripts
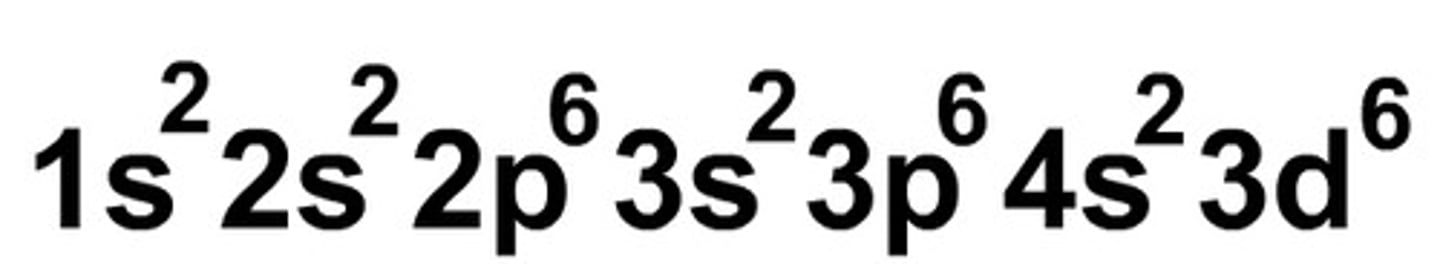
Inner e-
Electrons not in the highest occupied energy level; Every electron minus valence electrons
Valence e-
electrons on the outermost s and p orbitals (what you write in shorthand); Electron available to react; Up to 8 (octet)
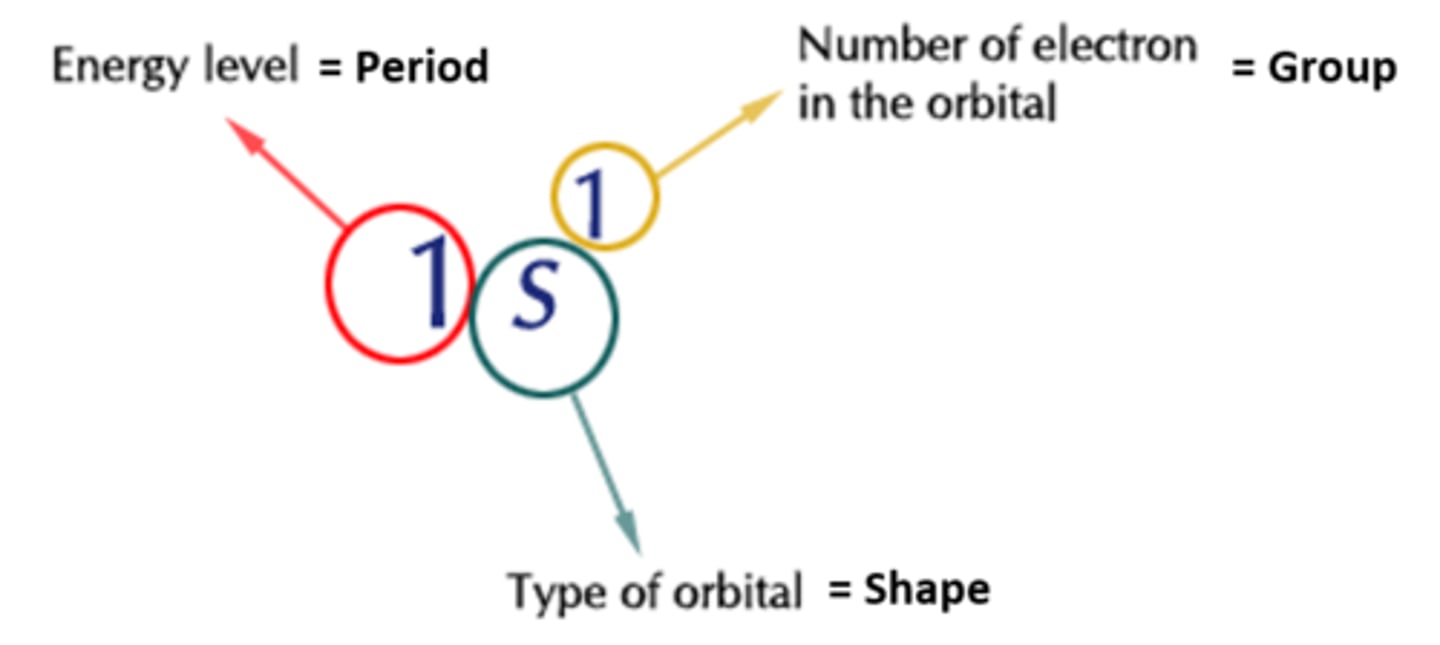
Quantum Numbers
Set of numbers used to completely describe an electron
principal quantum # (n)
indicates the main energy level occupied by the electron (Value: -l to +l (make a number line with 0 in the
middle)
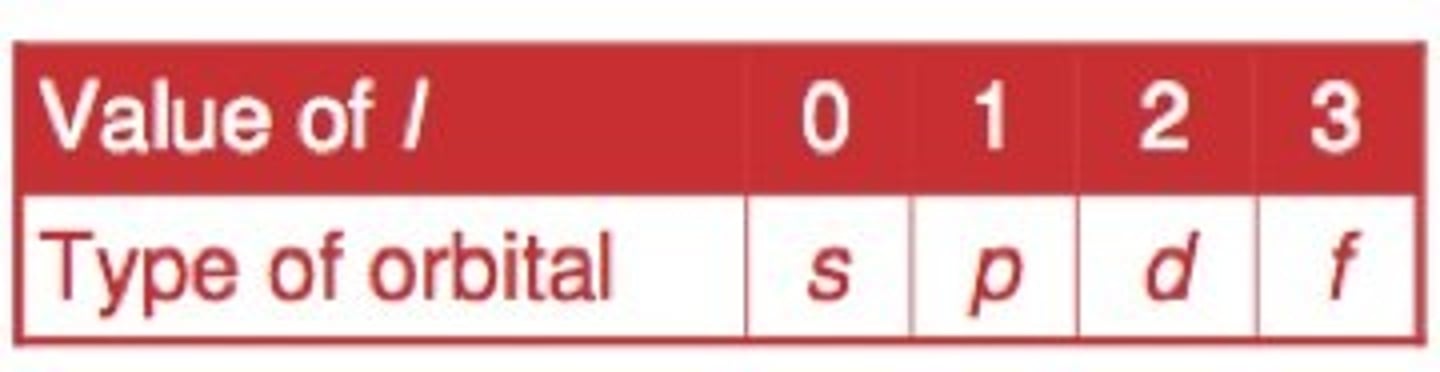
angular momentum quantum number (l)
indicates the shape of the orbital (s,p,d,f)
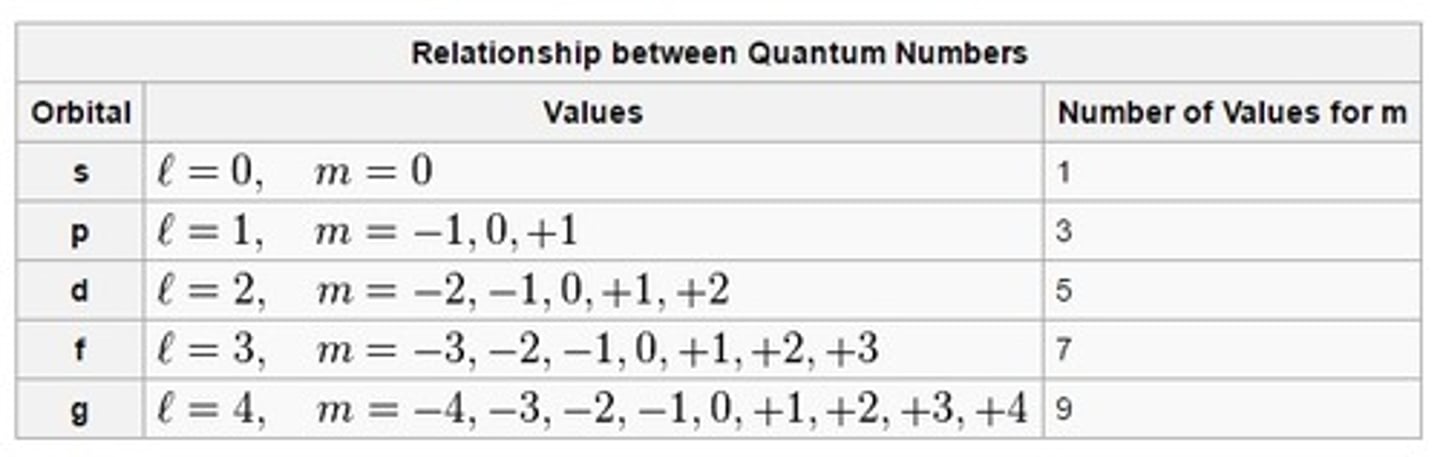
magnetic quantum number (m)
indicates the orientation of an orbital around the nucleus
spin quantum number (s)
The quantum number that has only two possible values, +1/2 and -1/2, which indicate the two fundamental spin states of an electron in an orbital
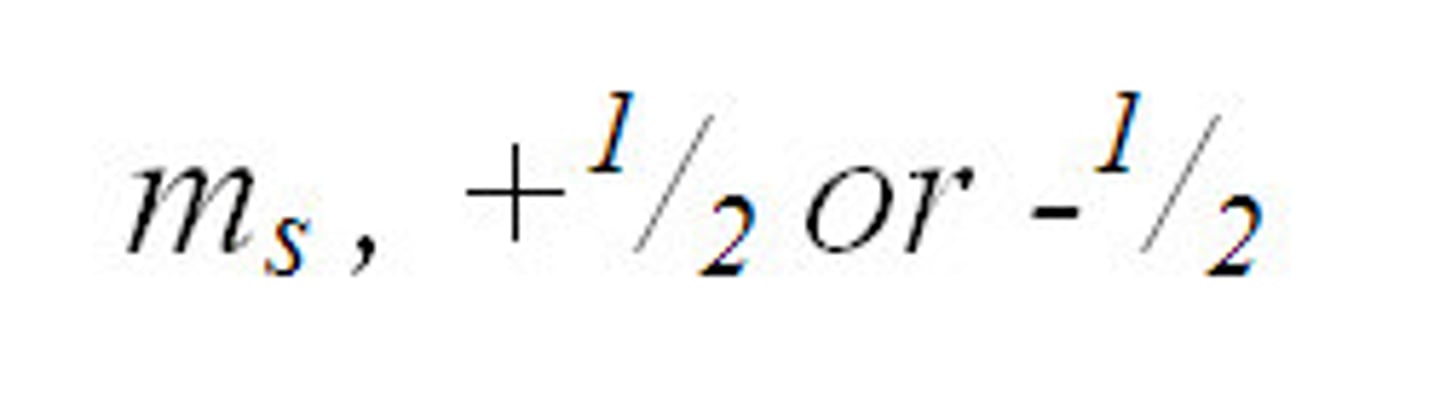
Mendeleev's Periodic Table
1869; Placed elements in order by increasing atomic
mass & similar properties; Then arranged by trends & patterns; Left spaces for elements he predicted would be discovered
Mosely's Periodic Table
Arranged by increasing order based on nuclear charge(# of protons)
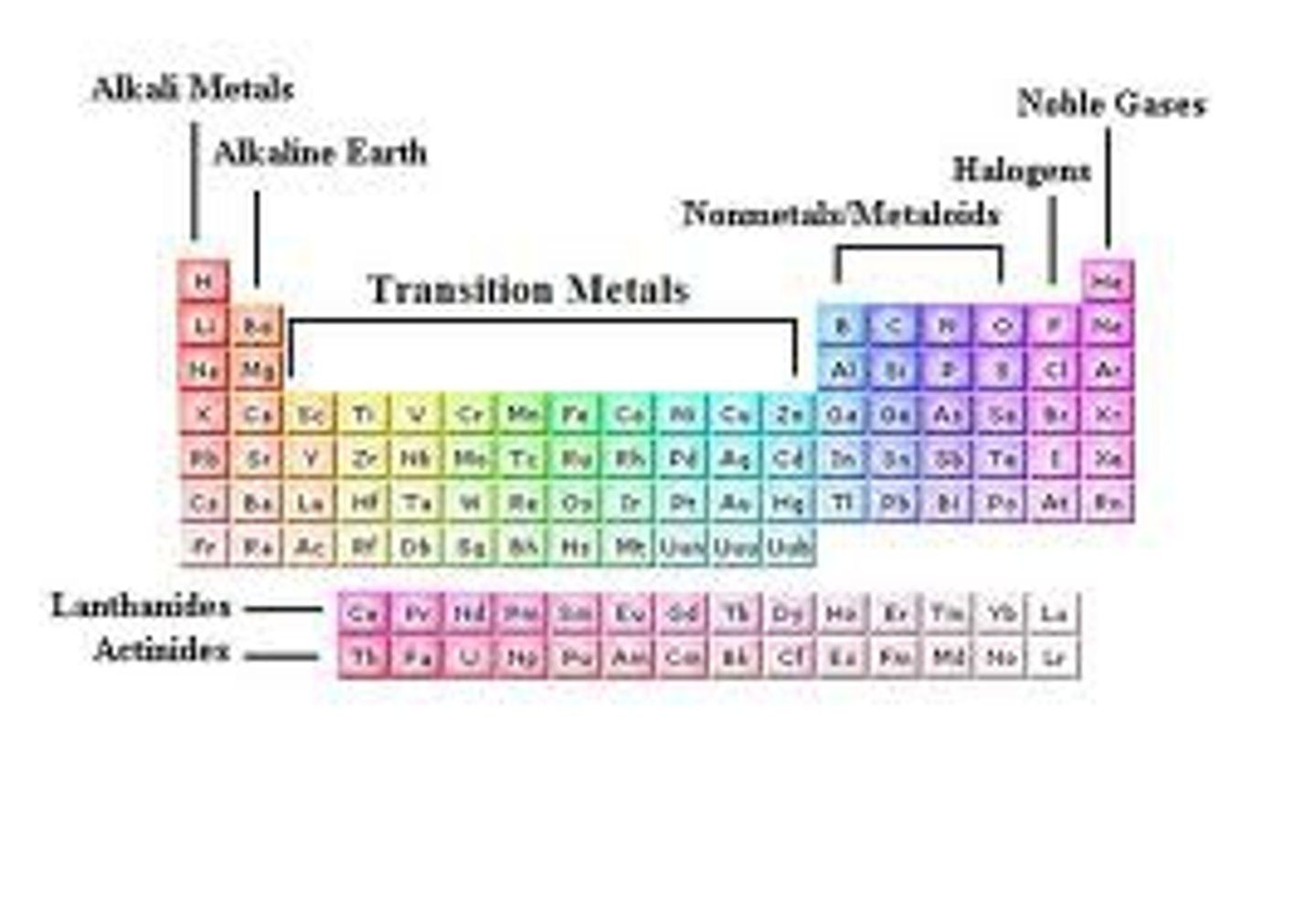
Modern Periodic Table
Elements arranged in order of atomic #; Similar properties fall in the same group
Periodic Law
the physical and chemical properties of the elements are periodic functions of their atomic numbers
Atomic Radii
one-half the distance between the nuclei of identical atoms that are bonded together
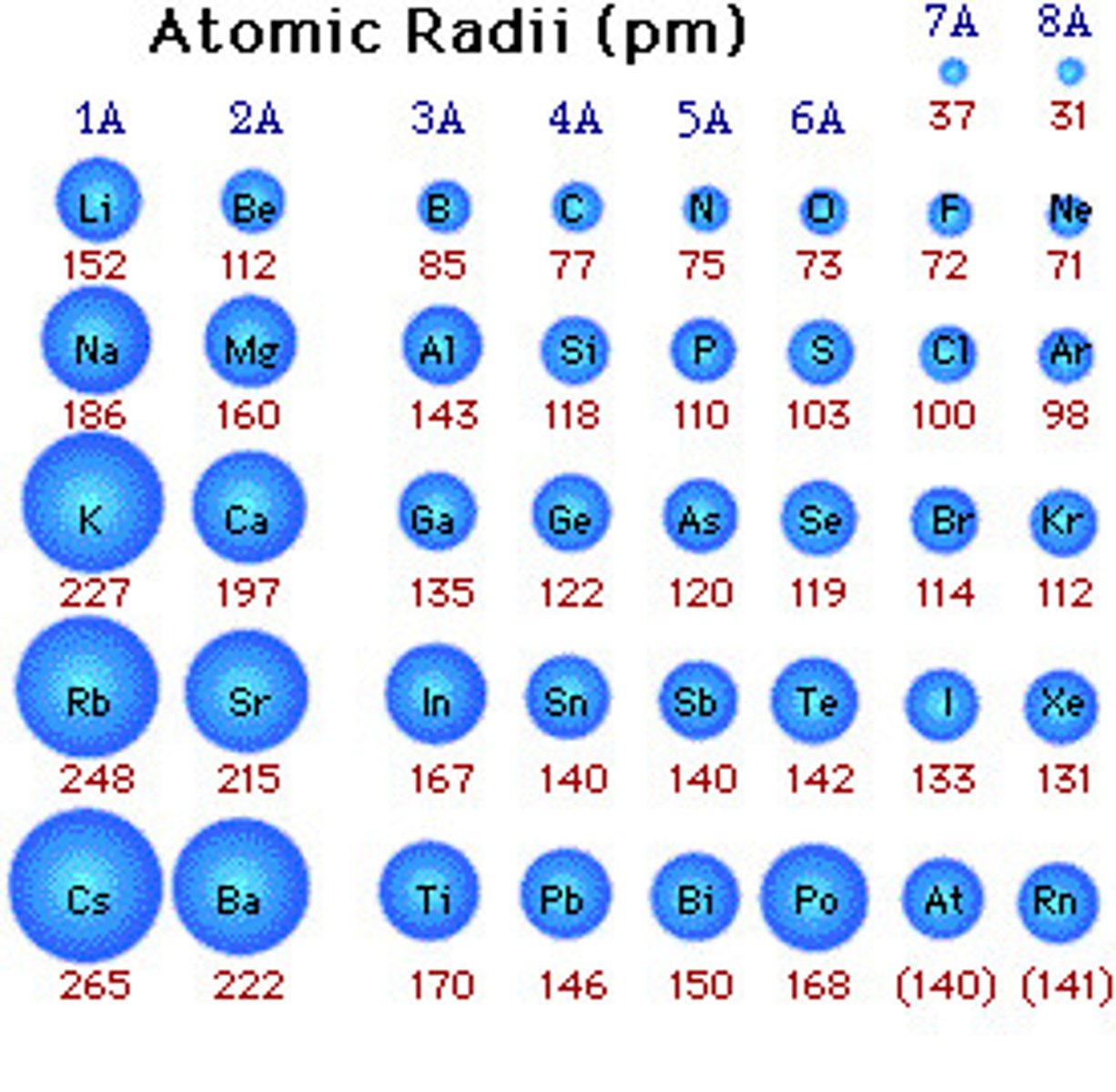
Down a Family (Atomic Radii)
Size increases due to more filled orbitals = less attraction from
the nucleus
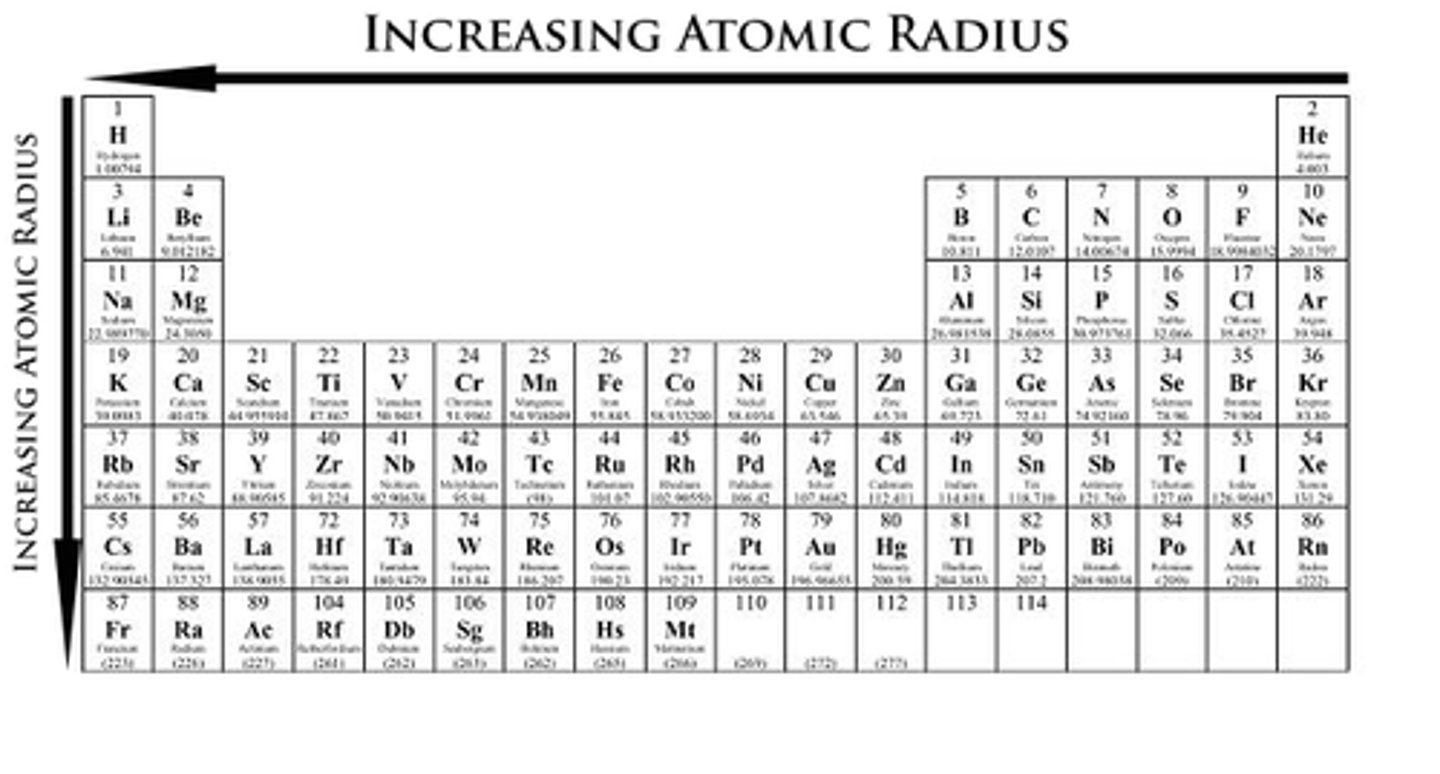
Across A Period (Atomic Radii)
Size decreases due to more p+ and e- attraction. Called Effective Nuclear Charge (Zeff)

Ionization Energy
The amount of energy required to remove an electron from an atom
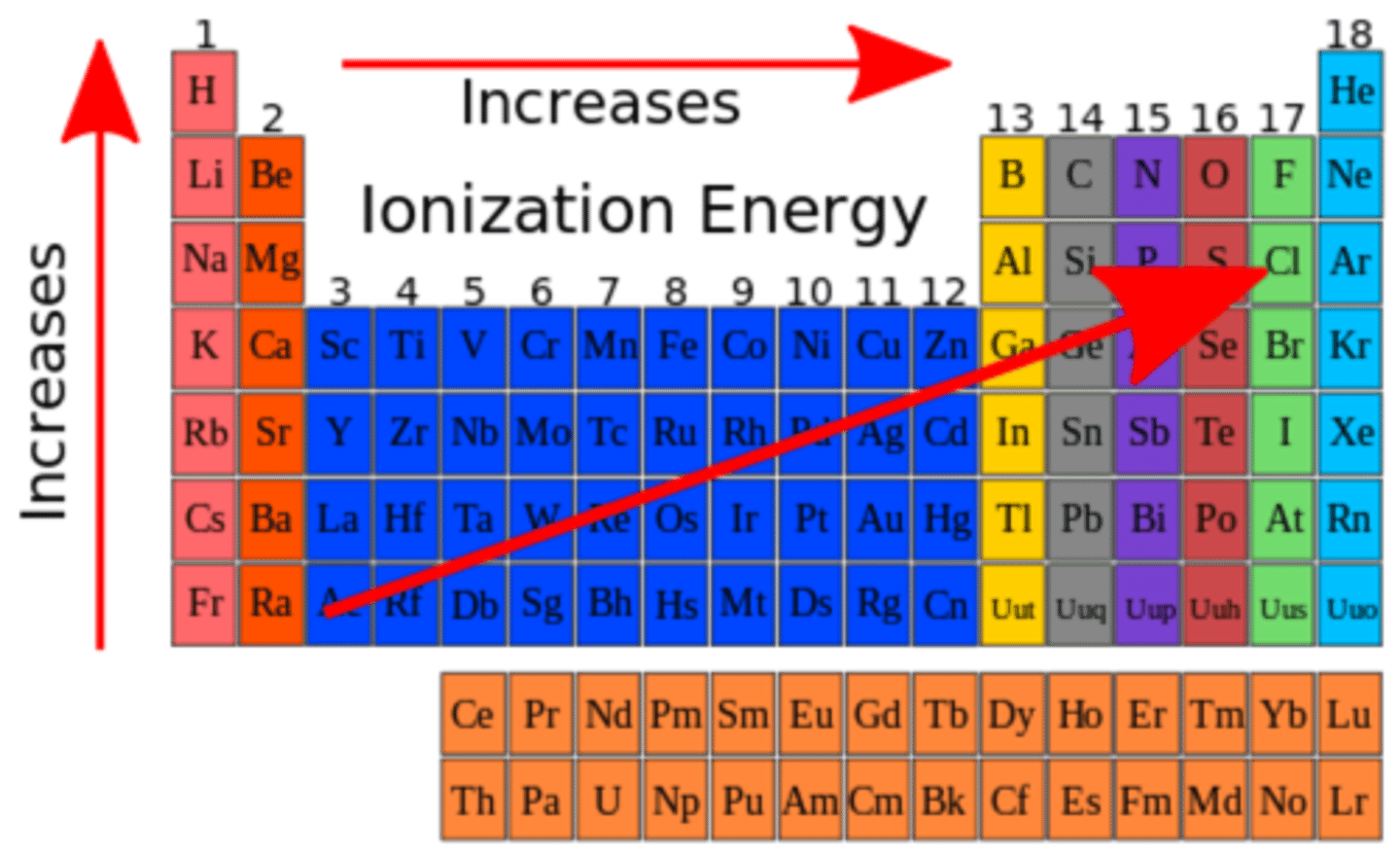
Down A Family (Ionization energy)
Energy required decreases due to valence electrons being farther from nucleus
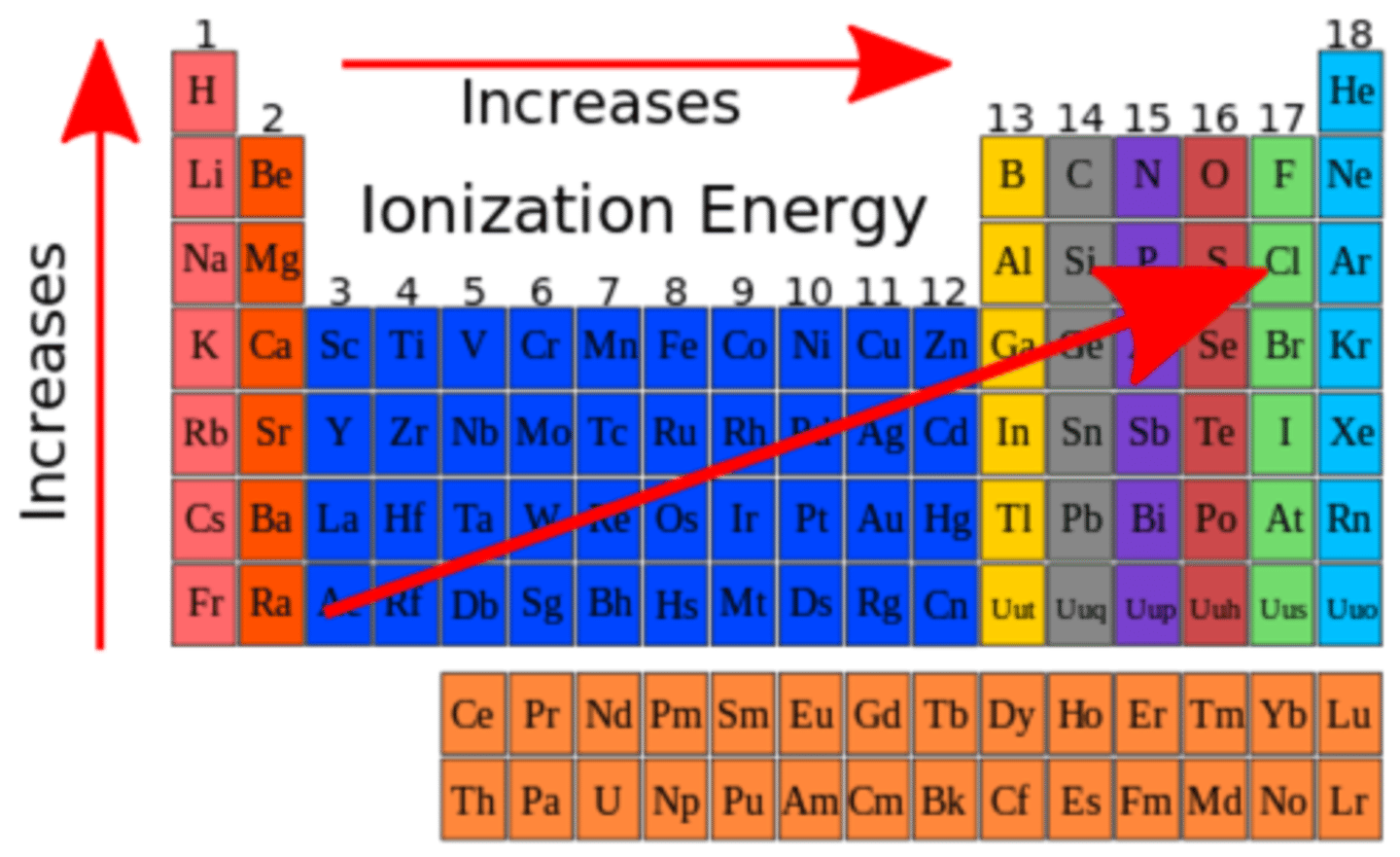
Across a Period (Ionization Energy)
Energy required increases due to valence electrons being closer to the nucleus
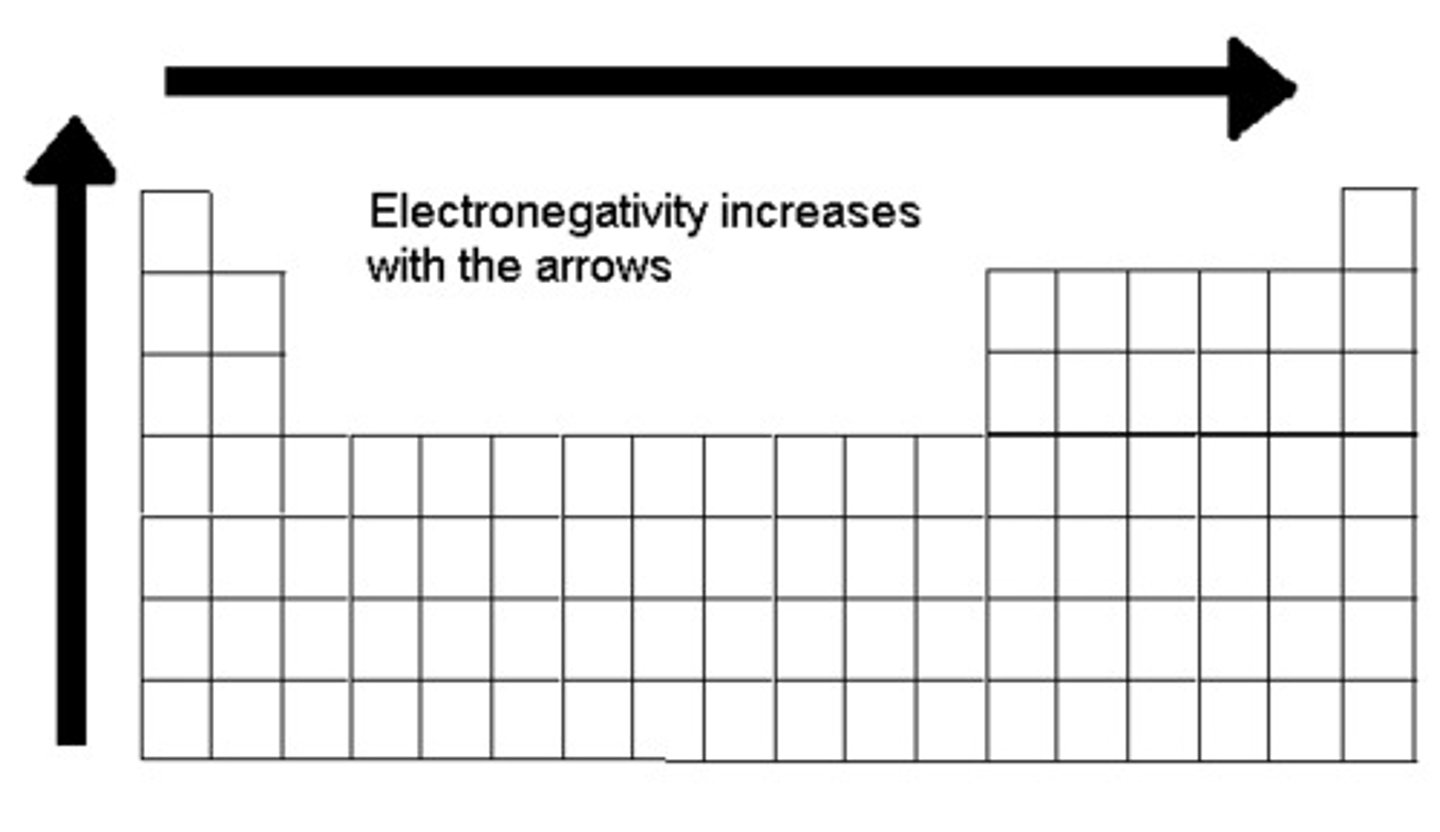
Electronegativity
A measure of the ability of an atom in a chemical compound to attract electrons from another atom in the compound
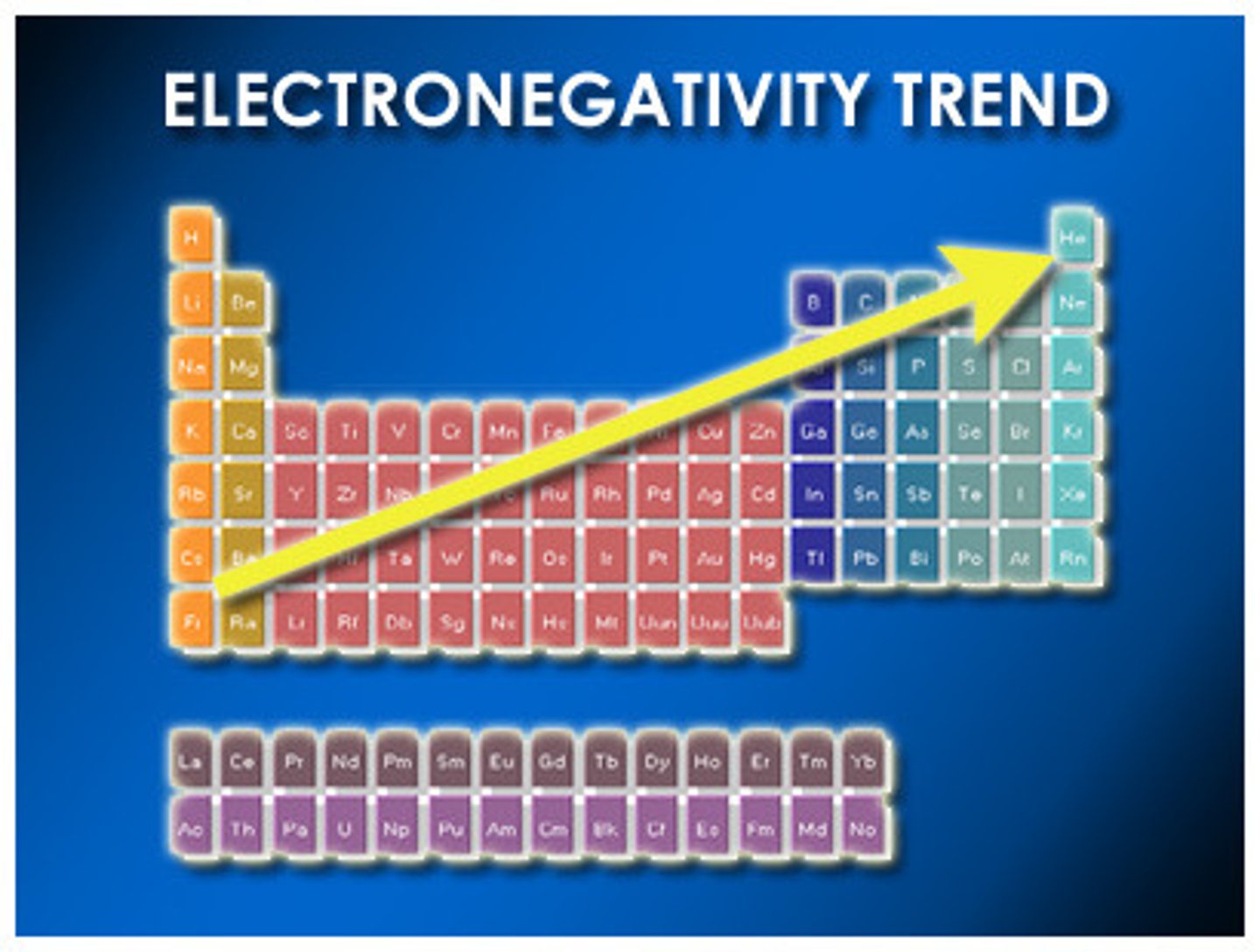
Down a Family : Electronegativity
decreases or remains the same
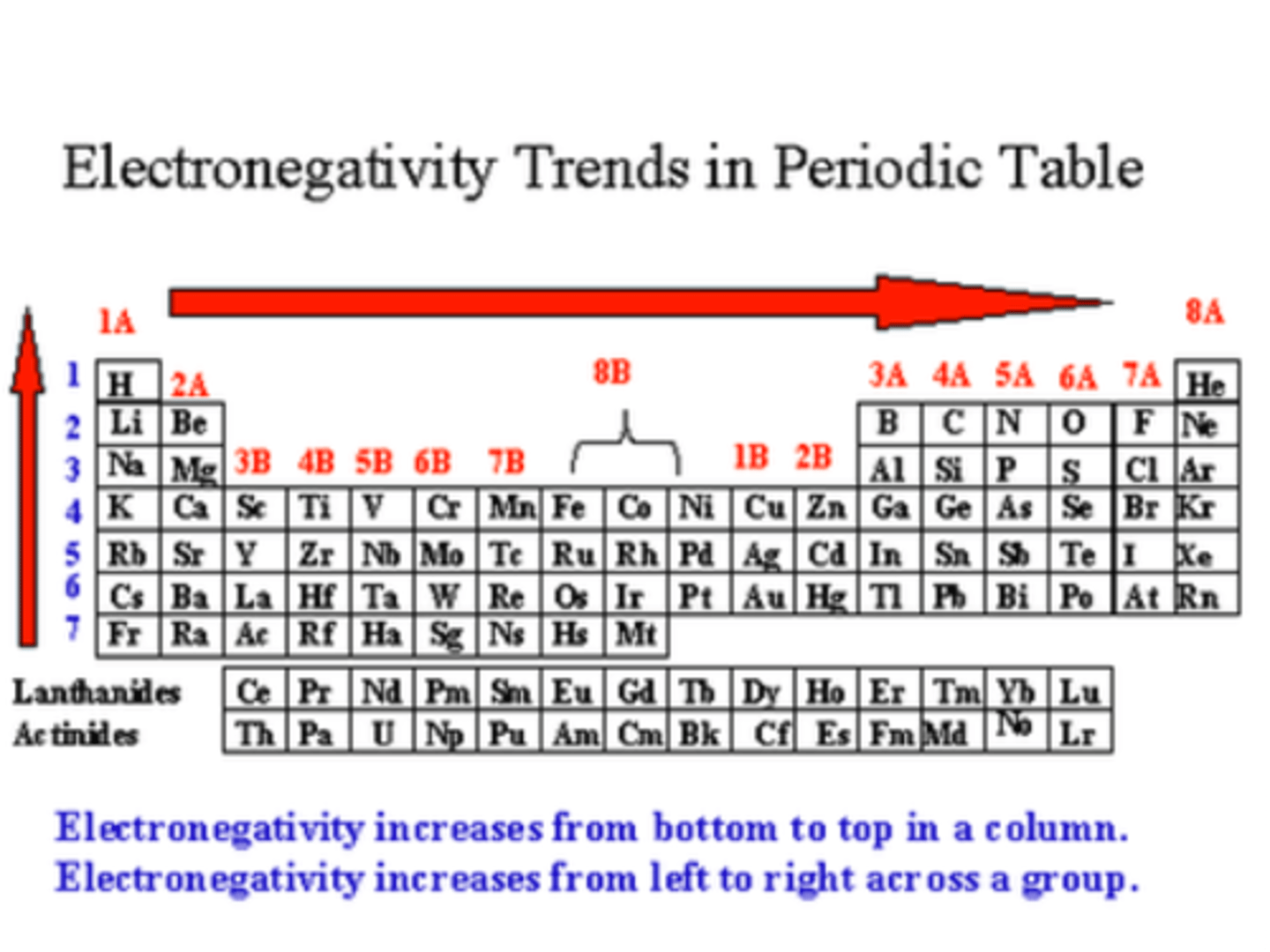
Across a Period: Electronegativity
increases
Cations
positive ions; Forms with loss of 1 or more electrons yields a
decrease in atomic radii; Electron cloud comes together

Anions
negative ions; Forms with addition of 1 or more electrons yields
and increase in atomic radii; Electron cloud spreads out