Bio cells and microscopes
1/91
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
92 Terms
Microscope
An instrument that makes small objects look larger
1665, Robert Hooke
Observed a thin slice of cork (plant material) and called them cells
Leeuwenhoek
Observed living organisms in pound water
Schleidan, 1838
Concluded plants to have cells
Schwann, 1839
Concluded animals are made of cells
1855, Virchow
Concluded that new cells can only from pre-existing cells
cell theory
Cells are basic units of life, all organisms are made of one or more cells, all cells come from other cells by reproduction
Prokaryotes
Have no nucleus
Prokaryotes are
smaller and simpler than eukaryotes
Prokaryotes, eukaryotes
Cells that gave genetic material (DNA)
Example of Prokaryotes
Bacteria, virus (not living)
Eukaryotes
Cells that do contain nucleus
Eukaryotes examples
Fungi, plants, animals, protist
Cells are surrounded by cell membrane and contain DNA
All
Function of nucleus
make ribosomes
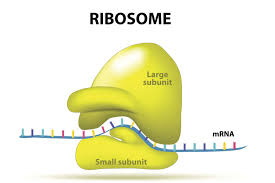
Where are ribosomes
On rough endoplasmic reticulum, free in cell
Function of ribosomes
make proteins
What does cell wall do
provides structural support
The endoplasmic reticulum
Makes lipids, highway
Cell membrane
Controls what goes in and out
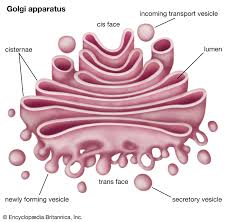
Golgi body
Packages lipids and proteins
Chloroplast
Performs photosynthesis
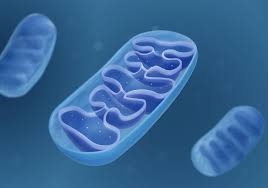
Mitochondrion
provides energy ATP
Nuclear membrane
enevlope
Nucleus
Stores DNA, Brain of cell
Lysosomes (animals have many plants dont)
Breaks down food
Final-initial
Formula to determine change in mass
(final-initial/initial) 100
formula to determine % change
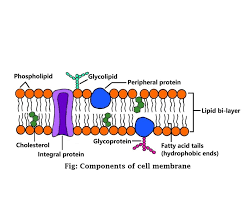
Cell membrane
regulates what enters and leaves and also provides protection and support
2 lipid bilayer
Cell membrane consists of ___ layers called _______
Hydrophilic, Hydrophobic
Head of lipid is _____, tail is _____
Called mosaic because
Many different kids of ,molecules that make it up
Cell wall
Present in plants, algae, fungi, and many prokaryotes
Cell wall is
Located outside the cell membrane; Main function is to provide support and protection of the cell
Phospholipids
Double layer
Hydrophilic
Head
Hydrophobic
Tail (moves> fluid)
cholesterol
Helps keep the membrane fluid, located in between
Carbohydrate
cell recognition, cell signaling, cell adhesion
Glycolipid
Carbohydrate attached to a lipid
Glycoprotein
Carbohydrate attached to a protein
Integral proteins
Transport proteins, enzymes, call recognition
Peripheral proteins
anchored cytoskeleton filaments
Plant cell
Which cell has plant cells
one large, several small
Plant cells have __ ___ vacuole, animal cells have__ ___ ones
animals cells
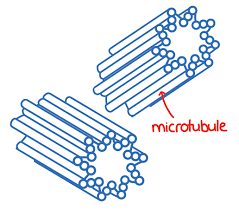
which cells have centrioles
plant cells
Which cells have outer cell wall?
Many few
Animal cells have___ lysosomes: plants have ___
Rectangular
Plants cells are ______ (shape)
Circular or irregular
animals cells are ____ __ _____ (Shape)
Water and grass
can move freely (Small)
Proteins and carbohydrates
cannot move freely (large)
Food, wastes, cell membrane
Cells must exchange ___ and ___ with its environment, most cross ___ ____
Semi permeable
Cell membrane is___-____ (only allows certain molecules to pass through easily)
Diffusion
The movement of molecules from an area of high concentration to low concentration
Faster, smaller, larger
Diffusion occurs ___ at high temps, ___ molecules move faster than ___ones
Passive
Diffusion is ____ transport
Concentration Gradient
The distribution of particles across space from high to low concentration
Osmosis, even
_____ is the diffsion of water through a semi-permeable membrane (large); everything wants to be ____
Hypertonic solution, above
_____ ____ is the solution with the greater concentration of solutes, means “_____ strength”
Cell
Hypertonic solution has higher solute concentration than the ____
Out shrivel (get smaller)
When SOLUTUON hypertonic, the water will be pulled ___ of cell ad cell will _____
Hypotonic solution, below
_____ ____ is the solution with the lower concentration of solutes; means “______ strength”
Lower, cell
Hypotonic solution has a ____ solute concentration than the ____
Into, swell (get larger)
when SOLUTUION is hypotonic, water will go ___cell, cell will___
Isotonic Solution
Concentration of solutes is the same inside and outside the _____
Same rate
During isotonic solution water moves in and out of cell ___ ___
Facilitated diffusion, passive
_____ ______ is the movement of specific molecules across cell membranes through protein channel;_____ transport
Active transport, ATP
_____ ___ is using energy to move across cell membrane against a concentration difference
Low, high
Active transport is ___ to ___ concentration
Big, Ions
Active transport is needed for___ particles or ___ (charged particles)
Protein pump
In active transport, smaller molecules move with a ___ ___
Bulk transport
The movement of macromolecules such as proteins or polysaccharides into or ____
Endocytosis, exocytosis, active
Two types of bulk transport are ____ and ___ (bulk transport is ___ Transport)
Small, proteins, pumps
____ molecules are carried across membrane by ____ the act as ___
endocytosis
cell membrane fold into a pouch (vesicle) and encloses the particle
Pinocytosis, phagocytosis
Two types of endocytosis
Pinocytosis
______ cytosis-ingesting liquids
Phagocytosis
_____cytosis-ingesting solids
Exocytosis
Wastes and cell products leave cell (opposite of endo)
osmosis
hypertonic, hypotonic and isotonic are form sof what passive transport
Phospholipids are molecules that hvae
One polar phosphate head and two nonpolar fatty acid
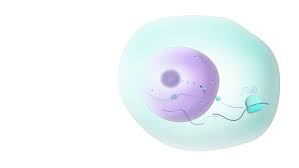
Nucleus
Mitochondria
Ribosomes
Cell membrane
smooth endoplasmic reticulum
Rough endoplasmic reticulum
nucleolus
Golgi appartus
Cytoplasm
centrioles