Chemistry Term 1 - Section A ( Principles of Chemistry)
1/58
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
59 Terms
What is the four main ideas for the particulate theory of matter
Particles move in constant, random motion
There are forces of attraction between the particles
There are spaces between the particles
All matter is made of particles
What is Osmosis
Osmosis is the movement of water molecules from a high concentration of water to a low concentration of water through a semipermeable membrane.
Explain how osmosis can be used in real world situations. For example pest control.
Salt can be used to exterminate a pest problem for example snails. Putting salt on a snail creates an isotonic condition. The water from the snail leaves its body to try and balance the water concentration.

What is diffusion
Movement of particles from an area of high concentration to low concentration.
What affects the rate of diffusion
Temperature. The higher the temperature the faster the rate.
What are the three states of matter
Liquids, Solids, Gases.
What are three differences between the states of matter?
Attraction
-Solids have a strong force of attraction
-Gases have little to no force of attraction
-Liquids particles are attracted just not as much as solids. Medium attraction
Energy
Solids have low energy
Liquids have intermediate
Gases have high energy
Shape
Gases don’t have a fixed shape
Liquids don’t have a fixed shape
Solids have a fixed shape
What is sublimation
A change of state from a solid directly to a gas. Some examples are iodine, ammonium chloride
What is Brownian motion
The random motion by small particles suspended in the fluid.
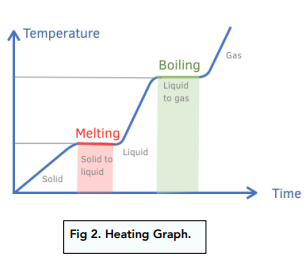
Heating curve
At melting point all the energy is being used to separate the particles.
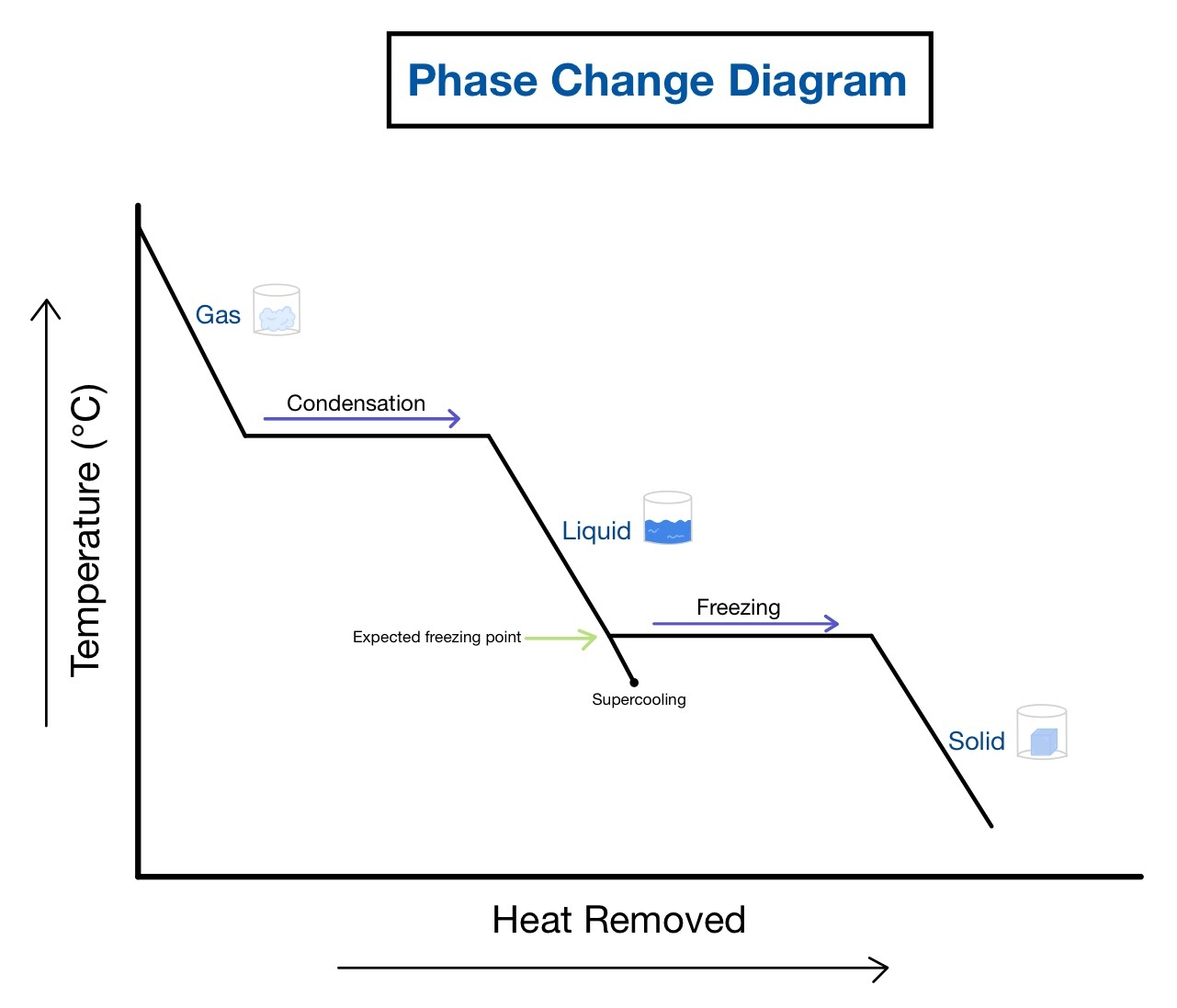
Cooling Curve
What is solubility
Solubility is the maximum amount of solute that dissolves in a specific amount of solvent.
What is an unsaturated solution
Contains less than maximum amount of solute. Can dissolve more solute.
Where would it be located in a solubility curve
It would be below the line.
Saturated Solutions
Contain the maximum amount of solute that can dissolve. It will have undissolved solute at the bottom of the container.
Where would it be found on a solubility curve
On the line
Supersaturated Solutions
An unstable solution that contains an amount of solute greater than the solute solubility.
What is a homogenous mixture
A homogeneous mixture is a type of mixture where the components are uniformly distributed throughout the mixture.
What is a heterogenous mixture
Not uniform throughout
Solutions
It is a homogenous mixture. Has very small particles. Not visible. Light passes through
Colloids
A heterogenous mixture. Small particles. Not visible.Light scatters- tyndall effect
Suspensions
A heterogenous mixture. Large particles ( Larger than solution and colloids), easily visible. No light passes through. will sediment
Filtration
Used to separate an insoluble solid from a mixture.
Evaporation
Used to remove a solvent from a mixture by being heated or boiled.
Crystallisation
Used to separate a dissolved solid from a solution, when the solid is much more soluble in hot solvent than in cold. Used to purify substances by forming solid crystals
Simple distillation
Simple distillation separates liquids in a mixture by heating and collecting the vapor produced, which is then condensed and collected separately. It works best when the liquids have DIFFERENT boiling points.
When do you use simple distillation
When you want to separate the solvent.
Fractional Distillation
Used to separate two miscible liquids that have close boiling points.
What is the difference between simple and fractional distillation?
simple distillation is suitable for separating liquids with large differences in boiling points, while fractional distillation is more effective for separating liquids with similar boiling points.
What are some separation techniques based on difference in density?
Separation Funnel, Centrifugation, Sedimentation
Separation Funnel
Used to separate two immiscible liquids of different densities. Like oil and water
Sedimentation
If a solid particle is insoluble and is more dense than the surrounding mixture. Then it will fall to the ground.
Centrifugation
Rapidly spinning a mixture of substances at an axis that have different densities
Paper Chromatography
Used to separate substances of different solubilities
What is a mixture
A mixture is two or more substances not chemically combined that can be separated by physical means
What is an element
Simplest form of pure substances. They cannot be broken down into anything else.
What is a compound
Mixture of two or more elements chemically combined. They can be broken down into simple substance by chemical means
When do you use evaporation and crystallisation
Evaporation is used to remove a solvent from a mixture or concentrate a solution. While crystallization is used to purify substances by forming solid crystals from a solution
What does the choice depend on
The choice depends on the specific separation requirements and the properties of the components in the mixture.
What is atomic number
The number of protons found in the nucleus of an atom
what is mass number
The relative mass of atoms
What is an isotope
An atom that has the same amount of protons and electron but different neutrons
What is an radio-isotope
A radioactive isotope
What makes chemical properties
The numbers of valence electrons
What are some uses of Radio- isotopes
Carbon dating, radiotherapy, pacemakers, and nuclear power .
Who introduced the law of triads
Johaan Doebereiner from 1817-1829
Who introduced the law of octaves
John Newlands in 1865
Who arranged elements in increasing atomic mass
Dmitri Mendeleev in 1869
Who arranged elements in increasing atomic number.
Henry Mosely in 1914
What is formed when alkali metals react with water?
A metal hydroxide and Hydrogen
Trend in group 2 - the alkaline earth metals
They react by losing electrons to form positively charged cations.
Trends in group 7- the halogen
They react by gaining an electron to form negatively charges ions called anions. The ease of ionization increases moving up because its closer to the nucleus.
Calculating the relative atomic mass of isotopes
Multiply percentage by the mass of each of them.
Example
75% Cl -35
25% Cl -37
75 x 35 + 25 x 37
100
Anions
- negative charge
When non metals gain electron
Cations
+positively charged
Metals lose electrons
How much electrons do metals usually have on their outer shell
1, 2, or 3
How much electrons do metals usually have on their outer shell
5, 6 or 7
Filtration
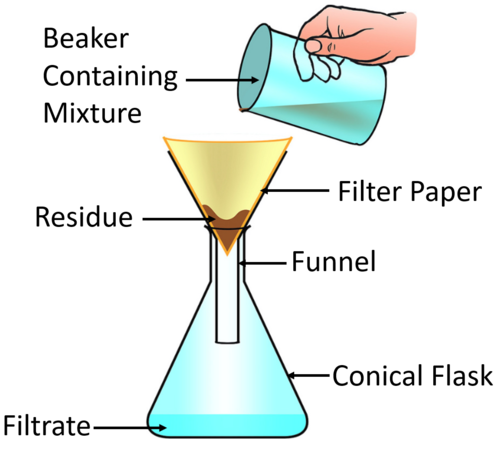
Evaporation
Separating a soluble solid from a mixture . Example being sugar and water