PS395 - Analysis of Variance Midterm
1/6
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Content: Paired t-test, RM one-way ANOVA
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
7 Terms
Paired t-test
A parametric statistical test that uses the t-distribution to explore differences in mean dependent variable scores across two within-group conditions across a single group.
other names: related, dependent
continuous IV with 2 categorical levels — “type of IV/condition/level”
continuous DV — “amount of DV reported”
benefits: reduces unsystematic variance compared to an independent t-test
participants are their own control — there is no unsystematic variance across conditions, therefore reduced error (i.e., we need fewer people to detect an effect)
H0: no difference; average pairwise difference = 0
HA: difference; average pairwise difference ≠ 0
assumptions:
DV is continuous
paired observations (2 measurements per subject)
differences between pairs are normally distributed
parameters:
t= statistic
Dbar= average pairwise difference/mean difference
sd= standard deviation
N=number of participants
SPSS: analyze — compare means — paired sample t-test
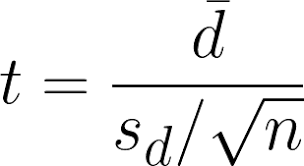
Within-subjects Design
The same participants are exposed to all levels of the IV — measurements of the DV are being measured twice, but within each subject
other names: repeated measures design
conceptual formula: (observed pairwise difference)/(estimate of SE of the pairwise difference)
requires less participants, may introduce order effects (e.g., practice, fatigue)
reduces individual differences
Between-groups Design
Compares different groups of participants, where each group experiences only one level of the independent variable (IV)
other names: independent measures design
requires more participants
eliminates carryover effects — influences from previous conditions
Power
The probability of detecting a real effect, if there is a real effect
Repeated Measures One-way ANOVA
A parametric statistical test that examines variance in a single dependent variable, in respect of one within-group independent variable.
tests whether three or more related groups have significantly different means
used when we have the sam subjects being measured under 3+ conditions (e.g., drug dosage levels)
used when we want to repeat measurements over time (e.g., pre-test, mid-test, post-test)
assumptions:
DV is continuous
repeated measurements on the same subjects
sphericity
each group’s differences should be normally distributed
Sphericity
A term usually applied to within-group studies to measure equality of variance across pairs of conditions.
tested using Mauchly’s test
Mauchly’s Test
A statistical measure that examines sphericity of within-group variance across pairs of conditions in repeated-measures ANOVA — the assumption of equal variances is violated if the outcome (Mauchly’s W) is significant; if it is violated, an adjustment is needed (use Greenhouse-Geisser)
F = (variance between conditions, effect)/(variance within subjects, error)
SPSS: analyze — general linear model — repeated measures