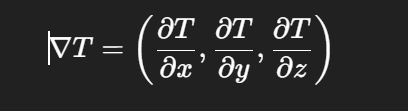3.5 Heat: Conduction, Convection, and Radiation
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
What are the 3 mechanisms for heat transfer ?
conduction, convection, and radiation
What is Conduction ?
Conduction is the transfer of heat through direct contact between particles in a solid. Faster-vibrating atoms transfer their energy to neighboring atoms without any movement of the material itself.
This happens through interatomic bonds, which act like tiny springs: when one atom vibrates more, it pulls and pushes on its neighbors, spreading the energy across the solid.
What is the Power of a conduction ?
rate of conducted heat through a body
-k is the coefficient of thermal conductivity, depending on the type of material only and expressed in W/(m*k)
-A is the contact area with the body
-L length of the body through which heat is conducted
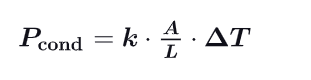
What is Convection ?
transfer of heat through the movement of a fluid (liquid or gas)
Hotter, less dense regions rise while cooler, denser regions sink, creating a circulation that transports heat
What is the formula for the power of a convection ?
h = convection heat coefficient h
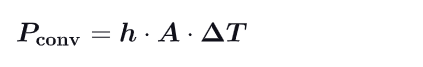
What is Radiation ?
Radiation occurs through to the exchange of electromagnetic waves between sources of heat.
A thermal radiation process is different from magnetic or nuclear radiation.
does not necessitate direct contact between the source and the body.
What is the power of a radiation ? (towards a cold or emoty environment)
ε : emissivity of the surface, number between 0&1
σ : Stefan Boltzman constant
why cold ? Because there’s no radiation from the environment when it’s cold
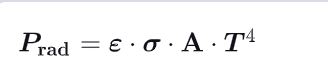
What is the power of radiation when both the BODY and the ENVIRONMENY radiate ?
T = temperature body
T0 = temperature nevironment
According to Kirchoff’s law of thermal radiation, we consider the emmissivity equal to the absorptivity (so you can use the same coefficient ε)
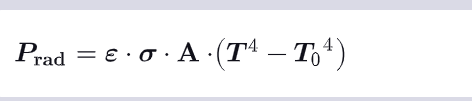
How does the incident amount of light interact with a body ?
A part is ;
absorbed α
reflected ρ
transmitted to another τ

What is a perfect absorber ?
A body with an absorptivity equal to 1.
Absorbs all radiation without reflecting any.
What other names can we use for a perfect absorber ?
“black body” & “perfect emitter”
What is the heat flux density ?
tells us how much heat moves per unit area and in which direction.
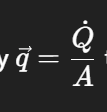
What is the heat flux density using the gradient operator ?
λ is the thermal conductivity,
∇T is the gradient of the temperature.
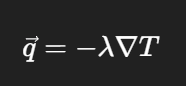
What is the gradient operator ?
The gradient ∇T is a vector of partial derivatives