Geology Exam 2
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
48 Terms
Slow moving water only carries
small sediment
Fast moving water carries
both small and large sediment
As water velocity increases
nearby sediment will be eroded (picked up)
As water velocity decreases
nearby sediments will be deposited (set down)
Delta
River deposits all its sediment when water slows down at the coast
order of making sedimentary rocks
1.Weathering
2.Erosion
3.Transport
4.Deposition
5.Lithification/Diagenesis
Recurrence Interval
the average time between successive geologic events
Categories of sedimentary rocks
clastic, organic, chemical, bioclastic
Viscosity
resistance to flow
Mafic
low viscosity
lavas flow long distances
gasses escape easily
effusive eruptions
Felsic
high viscosity
lava stays to vent
gasses build high pressure, escapes all at once
explosive eruptions, eject via debris
Low Viscosity
flows easily
High Viscosity
much more difficult to flow
Magma Viscosity
how resistant a fluid is to flowing
Lava
forms extrusive igneous rocks
Volatiles
gasses, water, like H2O, CO2, SO2, and other hazardous gasses
Ash
very tiny particles of solidified lava, carried far away by atmosphere
Volcaniclastic debris
broken chunks of rocks and lava
Effusive Eruption
lava flows gently down the side
Explosive Eruption
large section of mountain erupts/explodes all at once
Shield Volcano
Mafic magma chamber where there is a gently sloping side and gasses can easily escape
Volcaniclastic debris(describe)
Felsic magma chamber where gasses get trapped and lava doesn't flow far.
Caldera
a large crater caused by the violent explosion of a volcano that collapses into a depression
Pyroclastic flow
avalanche of volcaniclastic debris
Lahar
mix of volcaniclastic debris of water
Transgression(sea level rise)
sea level goes up and depositional environment shifts landward, new deposits are deeper water ,further offshore
Regression(sea level fall)
sea level goes down and depositional environment shifts seaward, new deposits are from shallower water, further onshore
Stratovolcano magma chemical composition
felsic
Stratovolcano igneous rock formed from erupted lavas
rhyolite
Stratovolcano magma viscosity
high viscosity
How far do lavas flow in stratovolcanoes?
Lavas stay close to vent
Shield Volcano magma chemical composition
mafic
Shield Volcano igneous rock formed from erupted lavas
basalt
Shield Volcano magma viscosity
low viscosity
How far does shield volcano lavas flow?
Lavas flow long distance from vent
Stratovolcano dissolved gasses
gasses not easily able to escape
Stratovolcano gas pressure
gas pressure builds up very high
Stratovolcano eruption style
explosive
Shield Volcano dissolved gasses
gasses able to easily escape
Shield Volcano gas pressure
gas pressure never builds up very high
Shield Volcano eruption style
effusive
Stratovolcano erupted material
both lavas and volcaniclastic debris
Stratovolcano resulting volcano shape
volcano has steep slopes
Stratovolcano example plate tectonic context
subduction zone under continental lithosphere
Shield Volcano erupted materials
mostly just gentle lava flows
Shield Volcano resulting volcano shape
volcano has broad gentle slopes
Shield Volcano example plate tectonic context
hot spot under oceanic lithosphere
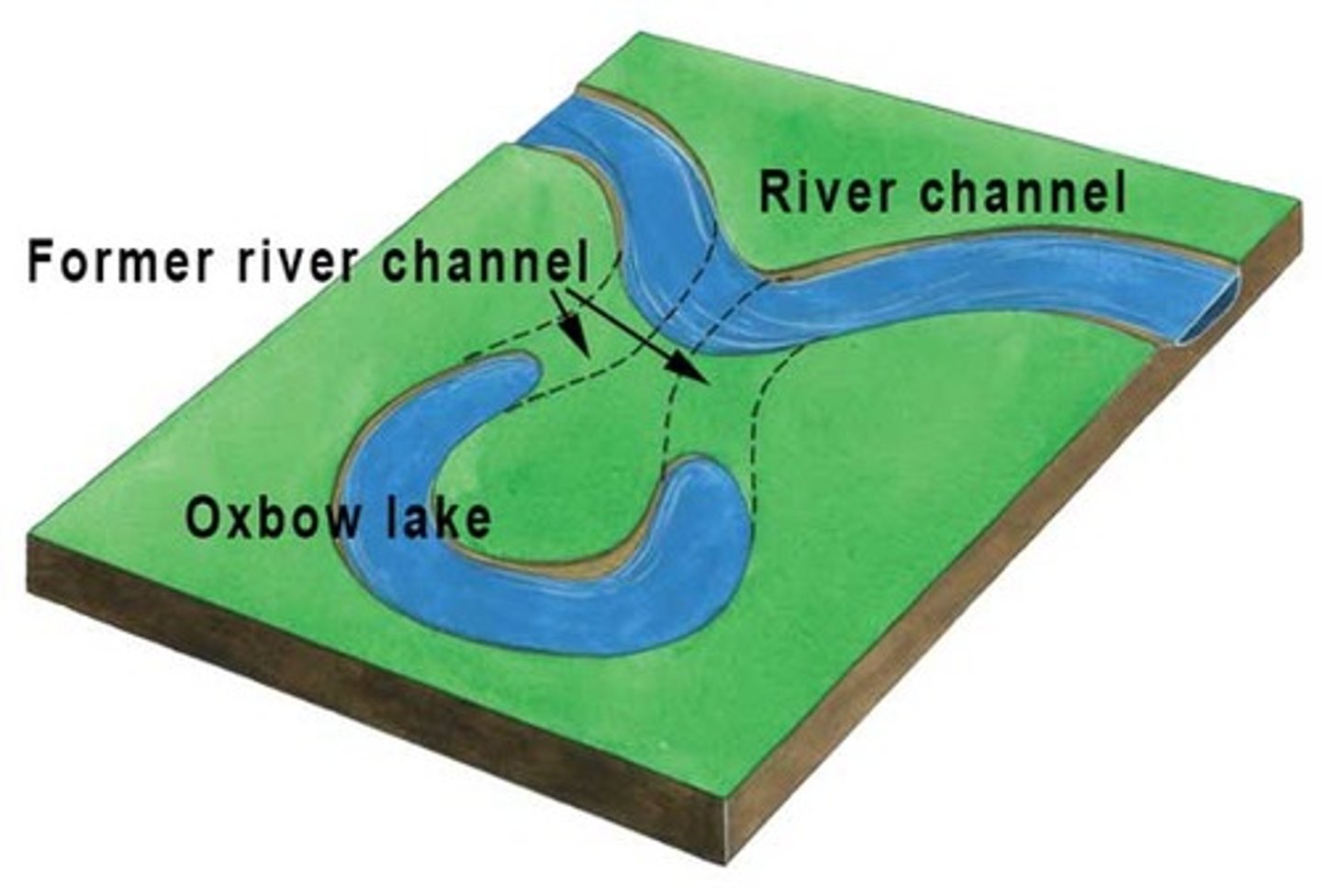
When the meander is cut off and abandoned by the river, what do you call the remaining body of water?
Oxbow Lake