Control of Heart Rate
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
12 Terms
Which part of the brain controls heart rate?
The cardiovascular centre in the medulla oblongata.
Which branch of the autonomic nervous system increases heart rate?
The sympathetic nervous system.
What initiates the heartbeat?
The sinoatrial node (SAN), located in the wall of the right atrium.
It acts as the heart's natural pacemaker, generating electrical impulses.
This is intrinsic control – the heart muscle itself (myogenic muscle) initiates the contraction
Which part of the brain controls heart rate via the nervous system?
The medulla oblongata.
It contains the cardiovascular control centre.
How does the sympathetic nervous system affect heart rate?
Increases heart rate.
Accelerator nerves release noradrenaline at the SAN.
Prepares the body for activity ('fight or flight').
What are baroreceptors and how do they influence heart rate?
Pressure receptors located in the walls of the aorta and carotid arteries.
Detect changes in blood pressure.
If blood pressure is high, they send signals to the medulla oblongata to decrease heart rate (via parasympathetic nerves).
If blood pressure is low, they send signals to increase heart rate (via sympathetic nerves).
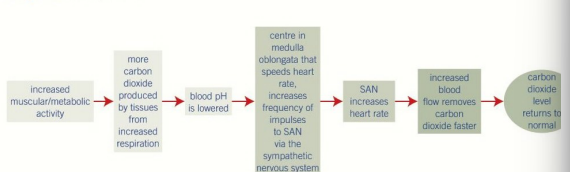
What are chemoreceptors and how do they influence heart rate?
Chemical receptors located in the aorta, carotid arteries, and the medulla oblongata itself.
Detect changes in blood pH, carbon dioxide levels, and oxygen levels.
High CO₂ / low pH (acidic blood, e.g., during exercise) signals the medulla oblongata to increase heart rate (via sympathetic nerves) to speed up CO₂ removal and O₂ delivery.
Low O₂ also signals an increase in heart rate.
Which hormone primarily controls heart rate?
Adrenaline
Where is adrenaline released from?
The adrenal medulla (part of the adrenal glands located above the kidneys).
How does adrenaline affect heart rate?
Increases heart rate and stroke volume.
Binds to receptors on the SAN, increasing the frequency of electrical impulses.
Part of the 'fight or flight' response, preparing the body for intense physical activity.
Summarise the main factors increasing and decreasing heart rate.
Increase Heart Rate:
Sympathetic nervous system (noradrenaline)
Adrenaline (hormone)
Detected low blood pressure (baroreceptors)
Detected high CO₂ / low pH / low O₂ (chemoreceptors)
Decrease Heart Rate:
Parasympathetic nervous system (acetylcholine)
Detected high blood pressure (baroreceptors)
Explain the roles of the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems in regulating heart rate during and after exercise. (4 marks)
During exercise, chemoreceptors detect increased CO₂/low pH, signalling the medulla oblongata (1 mark).
The medulla increases signals via the sympathetic nervous system.
Sympathetic nerves release noradrenaline at the SAN, increasing heart rate to meet increased O₂ demand (1 mark).
After exercise, CO₂/pH levels normalise. The medulla increases signals via the parasympathetic nervous system (vagus nerve).
Parasympathetic nerves release acetylcholine at the SAN, decreasing heart rate back to resting levels (1 mark).