mcat missed questions
1/151
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
152 Terms
protelysis
aggreagation
adaptive immunity
new immunity
innate immuinty
immunity we are born with
t and b
t cells primarily target infected or cancerous cells through cell-mediated responses, while B (humoral response) cells target pathogens in body fluids through antibody-mediated responses.
g-c base pairing
higher metling points stronger strutures
disulfide bridges
held by cycstiene
polydester bonds
held by nucltdtodes
glycosidic linkages
sugar polymers are linked by a-1,4-bonds (like one long chain), and the branching points of that are made of 1,6-linkages (which would ultimately form multiple chains of a-1,4-linked sugars)
GI gut bacteria
PS into short chain fatty acids
endrocien signalling
ndocrine signaling is a form of long-distance cell communication in which hormones are secreted by endocrine glands into the bloodstream to target distant tissues or organs
paracrine signaling
Paracrine signaling involves local effects on nearby cells, while endocrine signaling involves hormones released into the bloodstream to affect distant target cells.
autocrine signaling
Autocrine signaling differs from paracrine signaling in that autocrine effects occur within the same cell that produces the signal, while paracrine effects occur in nearby cells.
Erythrocytes
he primary function of erythrocytes is to carry oxygen to tissues and organs and to transport carbon dioxide back to the lungs for removal from the body.
Fibroblast
The primary function of fibroblasts is to produce and maintain the extracellular matrix and collagen, providing structural support to tissues and aiding in wound healing.
Monocytes
Monocytes are a type of white blood cell that plays a key role in the immune system by differentiating into macrophages and dendritic cells, which help to engulf and destroy pathogens and debris
glycoprotein
can’t cross membranes so stays in plasma membrain
pronated
low ph
deprotonated
high ph
Malate dehydrogenase
malate dehydrogenase is an enzyme that catalyzes the conversion of malate to oxaloacetate in the citric acid cycle, using NAD+ as a cofactor to produce NADH.
Succinate dehydrogenase
In the citric acid cycle, succinate dehydrogenase catalyzes the conversion of succinate to fumarate, which is the only enzyme that is part of both the citric acid cycle and the electron transport chain.
Isocitrate dehydrogenase
n the citric acid cycle, isocitrate undergoes oxidative decarboxylation to form alpha-ketoglutarate, a reaction catalyzed by isocitrate dehydrogenase, which produces NADH and releases carbon dioxide
Α-Ketoglutarate dehydrogenase
Alpha-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase is an enzyme that catalyzes the conversion of alpha-ketoglutarate to succinyl-CoA in the citric acid cycle, utilizing NAD+ to produce NADH and releasing carbon dioxide.
Keq > 1
Exergonic with low activation energy level
high blood glucose
Pancreatic beta cells secrete insulin
low blood glucose
pancreatic alpha cells secrete glucagon
unit membrane model
The unit membrane model is a biological hypothesis that describes the structure of cell membranes as consisting of a phospholipid bilayer with proteins embedded within it, creating a semi-permeable membrane.
fluid membrane model
Definition: The fluid mosaic model describes the structure of cell membranes as a flexible and dynamic arrangement of various components, including lipids, proteins, and carbohydrates, that allows for movement and functionality.
Contraction of the diaphragm results in:
decreased intrathoracic pressure and inhalation
enhancer seqeunce
n enhancer sequence is a regulatory DNA element that can increase the transcription of a gene by providing binding sites for transcription factors, which can enhance the assembly of the transcriptional machinery at the promoter.
coding sequnce
A coding sequence refers to a portion of a gene's DNA that is transcribed into messenger RNA (mRNA) and translated into a protein. It contains the necessary information to generate a specific polypeptide chain.
glysoic linkages
hydrolases
diggestih discchrihes (lactase)
Enterocytes of the duodenal villi
prmidines
c-t
purines
a-g
um > m
1um> 10^-6
1mm>1m
1mm>10^-3
molarity
m=n/v
moles
n=MV
Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle
The Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle states that it is impossible to simultaneously know both the position and momentum of a particle with absolute precision.
Pauli Equation
The Pauli equation describes the behavior of a spin-1221 particle, such as an electron, in a magnetic field.
Bose-Einstein equation
Bose-Einstein equation describes the average number of bosons in a given quantum state as a function of temperature and the energy of the state
polarity
increases with electronegativity so N,O…
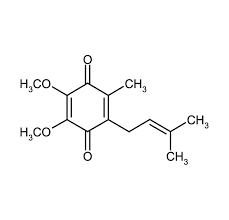
ubiquinone
biquinone, also known as coenzyme Q10, is a lipid-soluble antioxidant that plays a crucial role in the electron transport chain and energy production in cells.
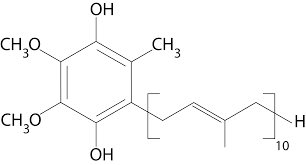
ubiqunol
Ubiquinol is the reduced form of ubiquinone, serving as a more potent antioxidant and is critical for cellular energy production.
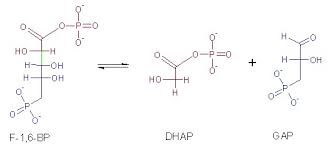
Lyase
cleavage of a bond w/o water
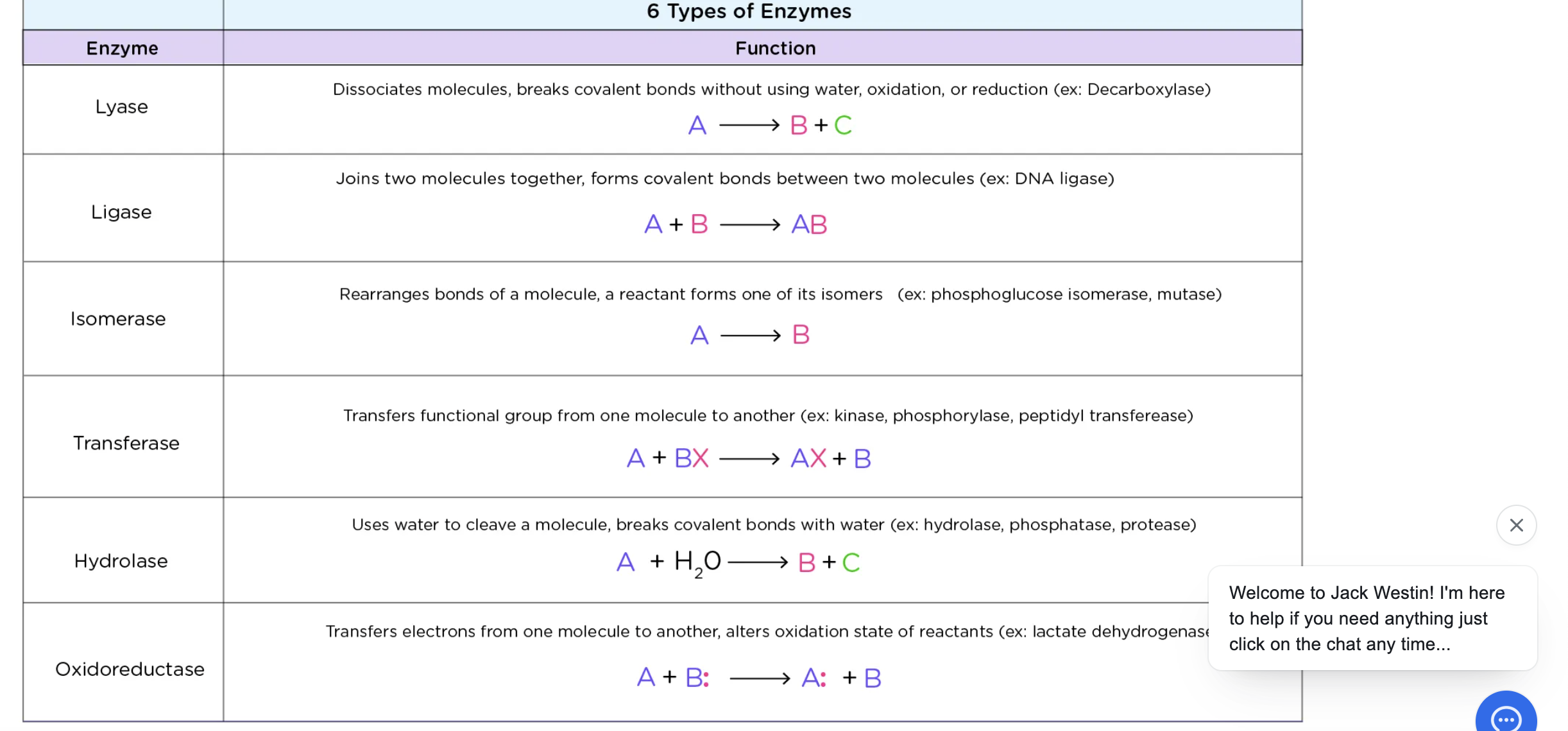
ligase
joining of 2 molecules (synthetase)
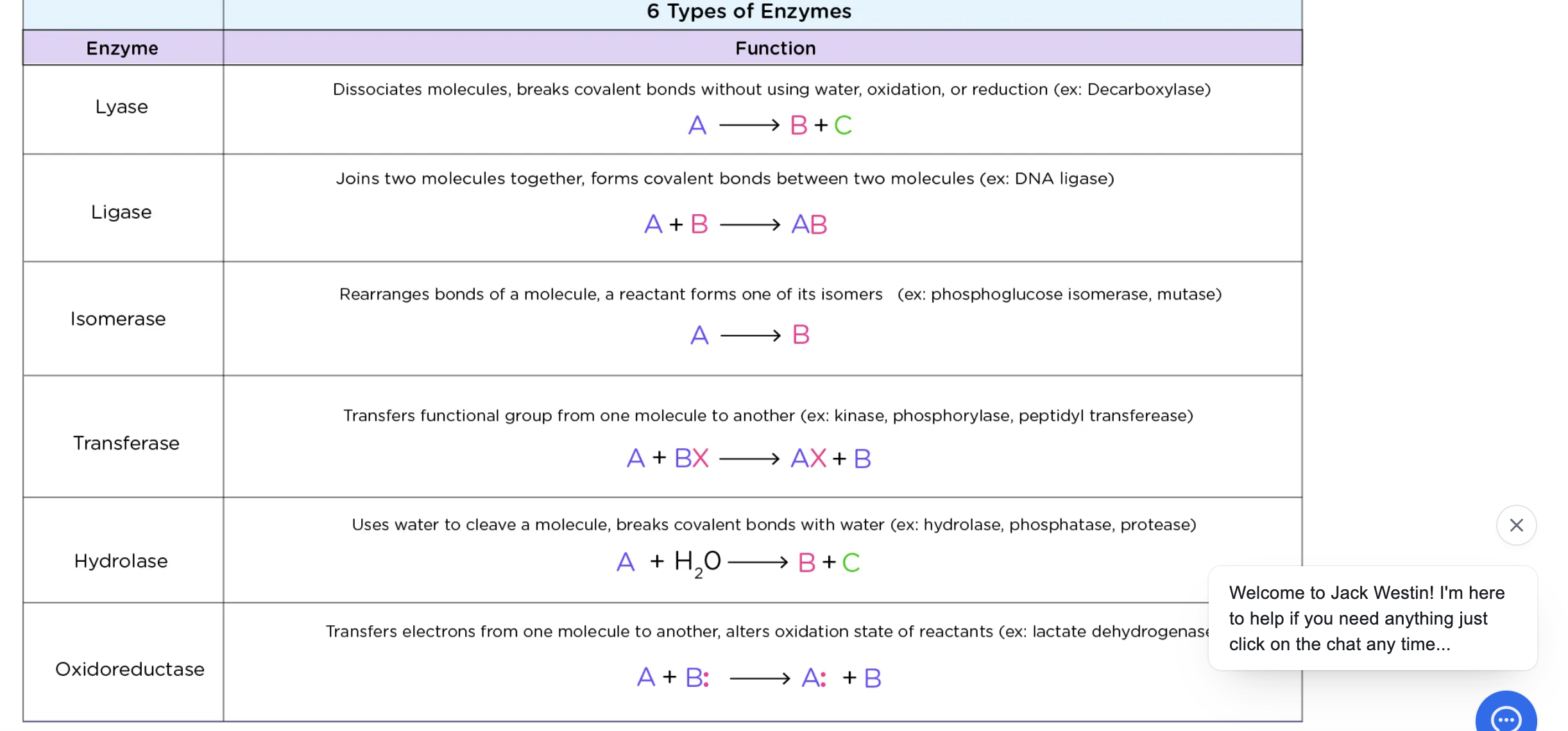
Isomerase
-rearrangement of functional groups w/in a molecule (mutase)
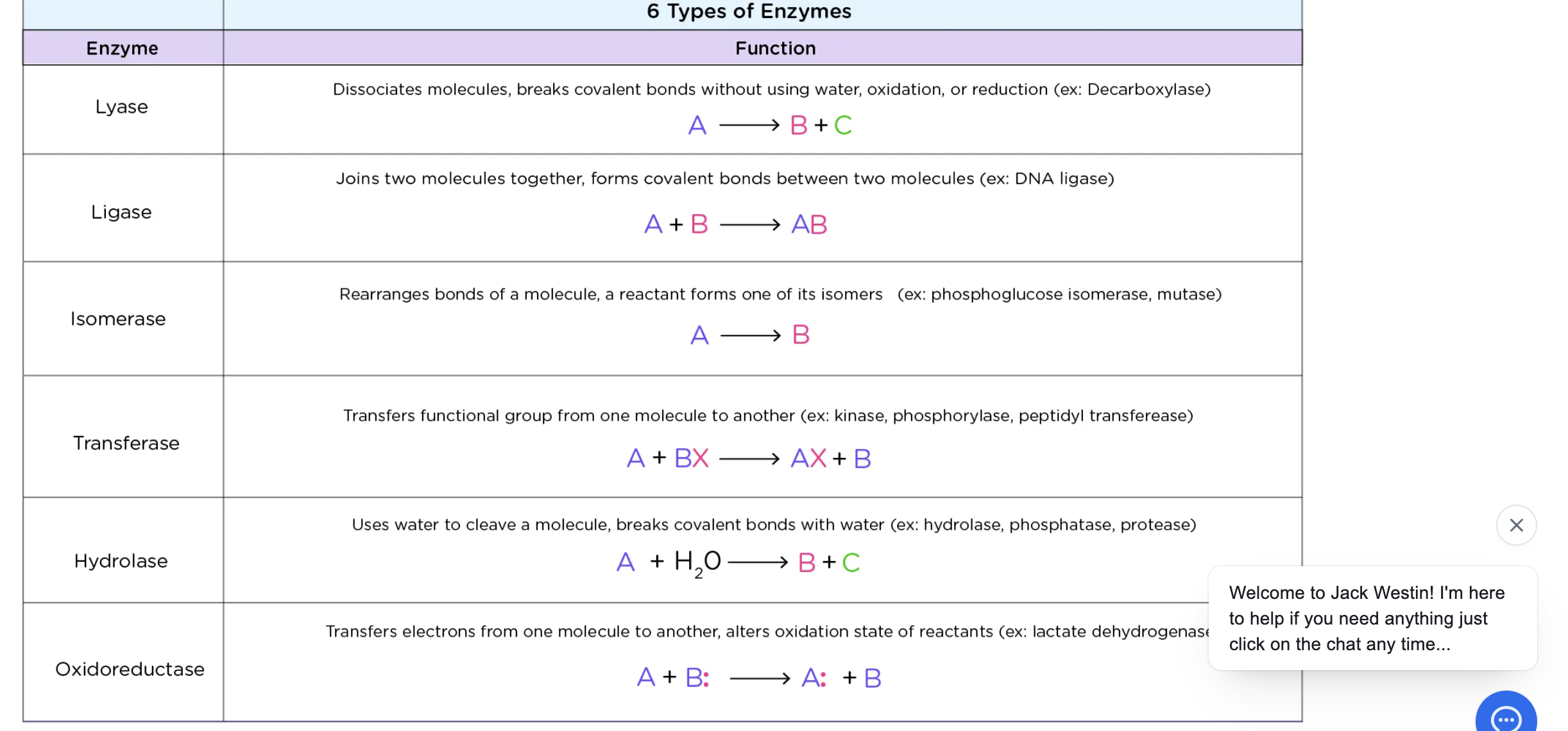
Transferase
transfer of functional group
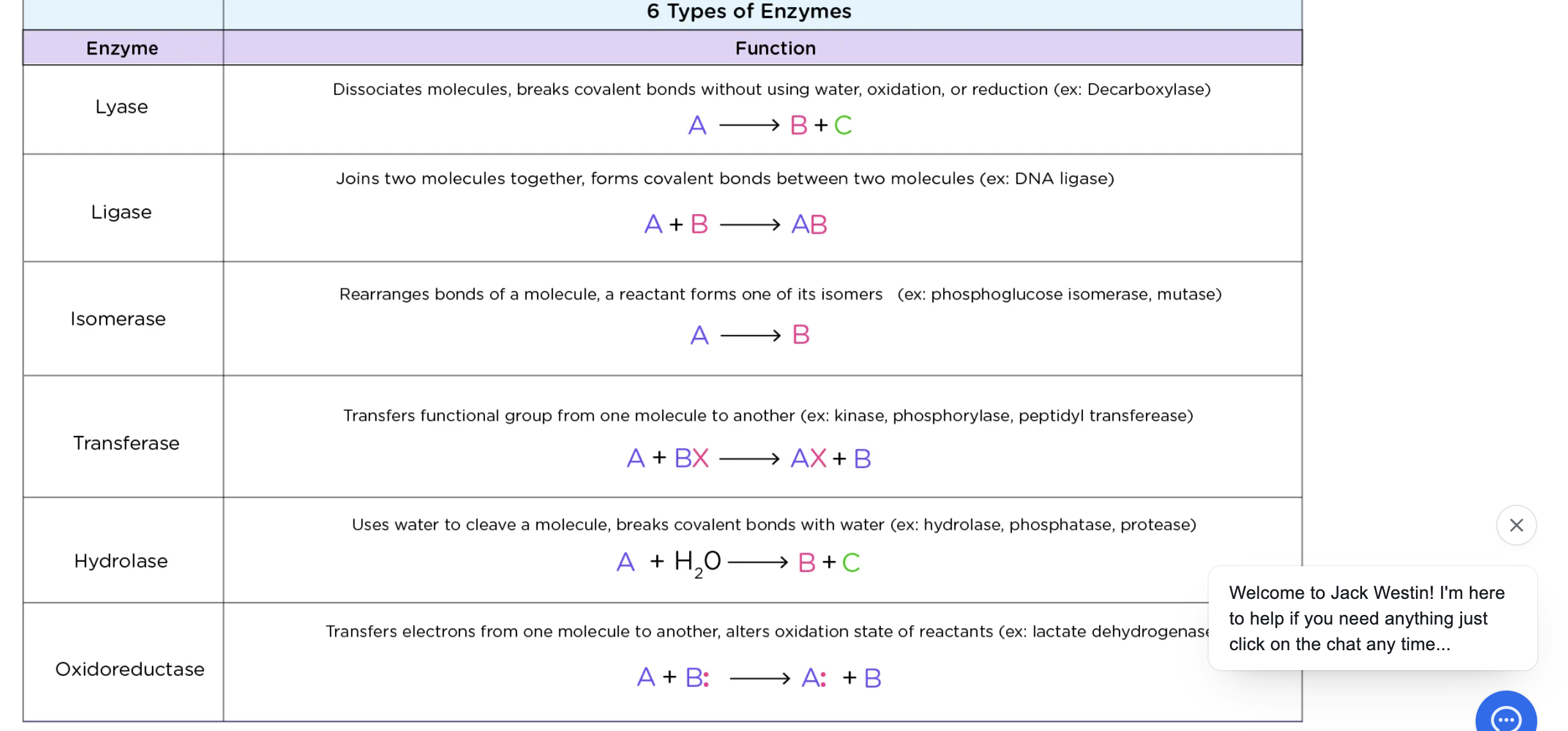
hydrolase
cleavage of bond w/ water
Oxidoreductase
transfer electrons through H atoms or hydride ions (dehydrogenase)
boyles law
p1v1=p2v2
charles law
v1/t1=v2/t2
the number of neutrons
atomic mass-# of protons
ml>cm
1ml>1cm^-3
Fluorescent energy
absorbs radiation
secondary structures
alpha and beta sheets
alpha sheets
are chiral
beta sheets
achiral
triery structures
held by polypeptides
polypeptide structure
n terminus has amion group other terminus has carboxyl group
disulfide bonds
held by cysteine groups
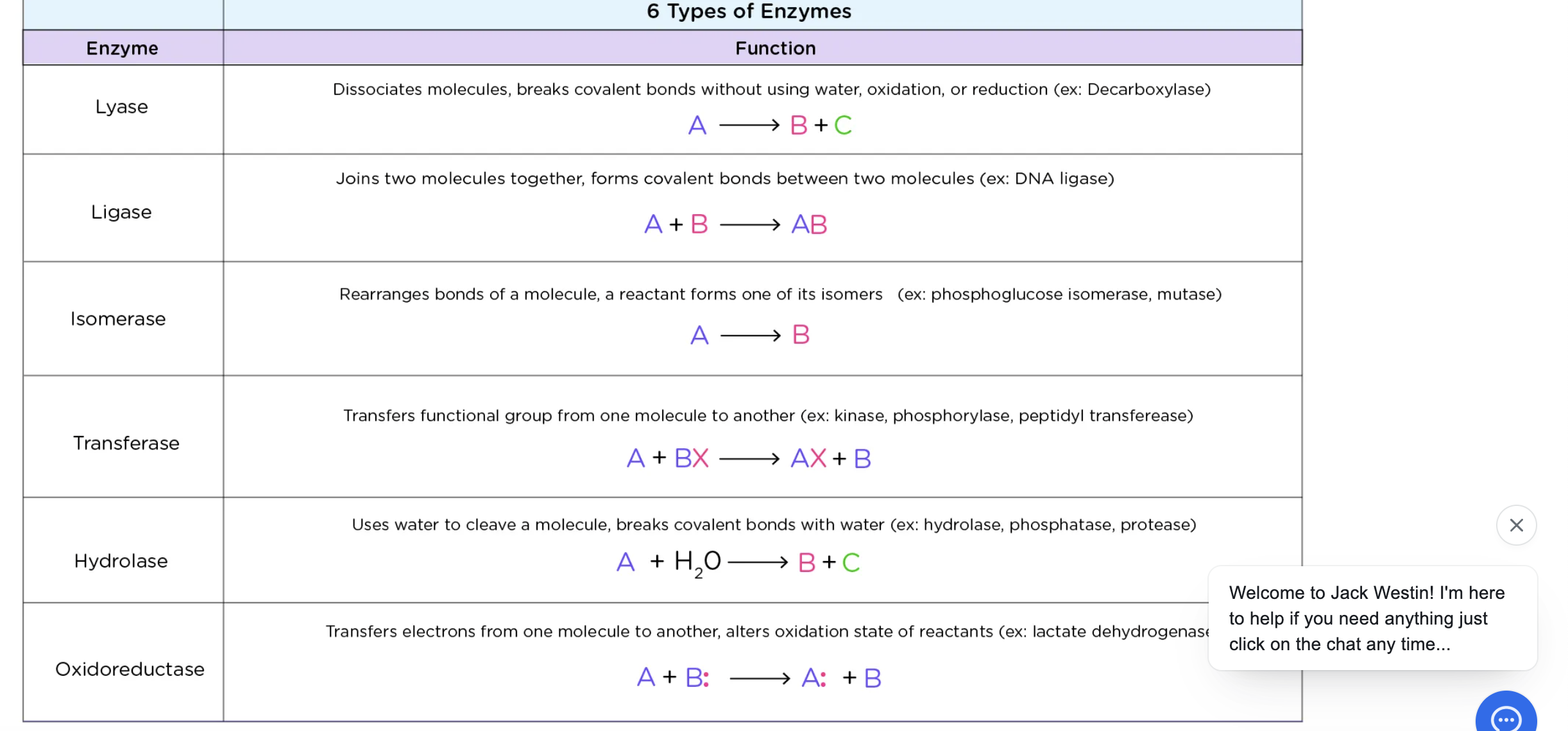
salt bridges
held by lysine groups
steroids
a form of lipid molecule
column binding
affinity
size exclusion
weight
cation/anion exchange
by different ions
entromieres vs distromiers
share similar properties but smell
indole
his
enzyme inhibitor equation
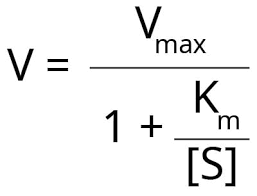
decrease km affinity increases
no substrate needed
increases km decreases affinity
more substrate needed
competitive inhibition
bind to the same site as the substrate (so they compete for binding). This means that it decreases the affinity of the enzyme for the substrate (raising Km)
mixed inhibition
they can either increase or decrease the enzymes affinity for the substrate (depending on if they bind the enzyme-substrate complex or just the enzyme
noncompetitive inhibition
don’t bind to the same site as the substrate (as in, they don’t compete for binding), meaning that the affinity of the enzyme for the substrate doesn’t change (Km stays the same). But, these inhibitors bind to allosteric sites and do something to stop the activity of the enzyme, which lowers the maximal reaction velocity (Vmax).
uncompetitive inhibition
bind to the enzyme-substrate complex and keep it together. By preventing the enzyme and substrate from dissociating from one another, the enzyme’s affinity goes up, and Km and goes down
spontaneous reaction
delta g <0 and low ea
nonspontaneous
delta g>0 and high ea
E3-E1
endothermic
e3-e2
exothermic
electron acceptor
those with higher electronegativity so S,O,N..
To improve boiling points in distillations
Slowing the heating of the distillation flask allows you to more precisely control the temp
enantiomers “how to tell the difference”
chiral centers( c connected to four different atoms excluding double bonds)
vacuum distillation
helps with decreasing boiling point
carbonic acid
Carbonic acid is highly unstable and rapidly decomposes to H2O and CO2.
Color participates
are formed by metals (nominally transition metals with unfilled d orbitals)
orientation with chair conformation
help with forming bonds/or not
Rf values and polarity
higher Rf values indicating less polar compounds that travel further on the plate, while lower Rf values indicate more polar compounds that travel shorter distance
strong bases
are seen as OH byproducts
strong acids
are seen in CIO-s
kcal to cal
1kca to 1000cal
OH bonds
the more oh bonding the incrsed in boiling point
what makes a good nucelphile
something that is basic, wealky charged anything opposite of polar: being electron-rich, having a negative charge, being weakly electronegative, and having low steric hindrance, allowing it to readily donate an electron pair to form a bond.
aromaitcs steric hindrance
can either be nucleophile or electrophile
the number of peptides can be calculated as
n! (n factorial). Ex so if there were 4 amino acids then we would do 4x3x2x1 If there were 5 we would do 5x4x3x2x1
Electric condutivity : covalent and noncovalent bonds
non covalent bonds=nonmetals thuse can’t conduct electricity
covalent bonds= can have metals thus conduct electricity
entropy delta s
disorder decreases with phase changes so from gas to solid
deviations from gas law
high pressure low temp
higher KI
menas incresed in temprature
wave speed
waves travel faster when going from gas to solid (longer wavelength)