Overview of the Respiratory System and Its Functions
1/108
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
109 Terms
Respiration
Gas exchange of O2 and CO2.
Oxygen (O2)
Essential for aerobic ATP production in cells.
Carbon Dioxide (CO2)
Waste product of aerobic respiration.
Respiratory System
Facilitates gas exchange between atmosphere and body.
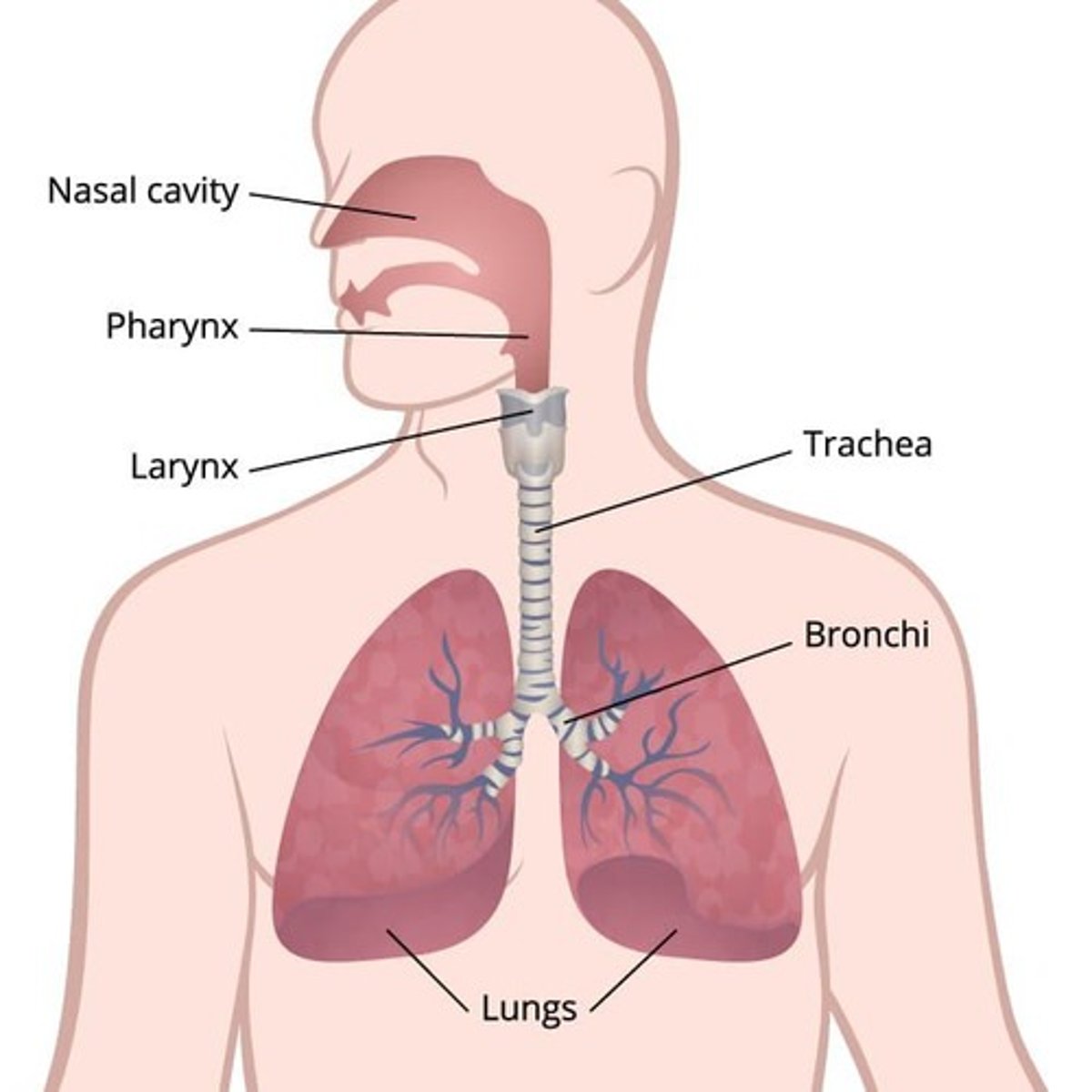
Upper Respiratory Tract
Includes nose, nasal cavity, pharynx, larynx.
Lower Respiratory Tract
Includes trachea, bronchi, bronchioles, alveoli.
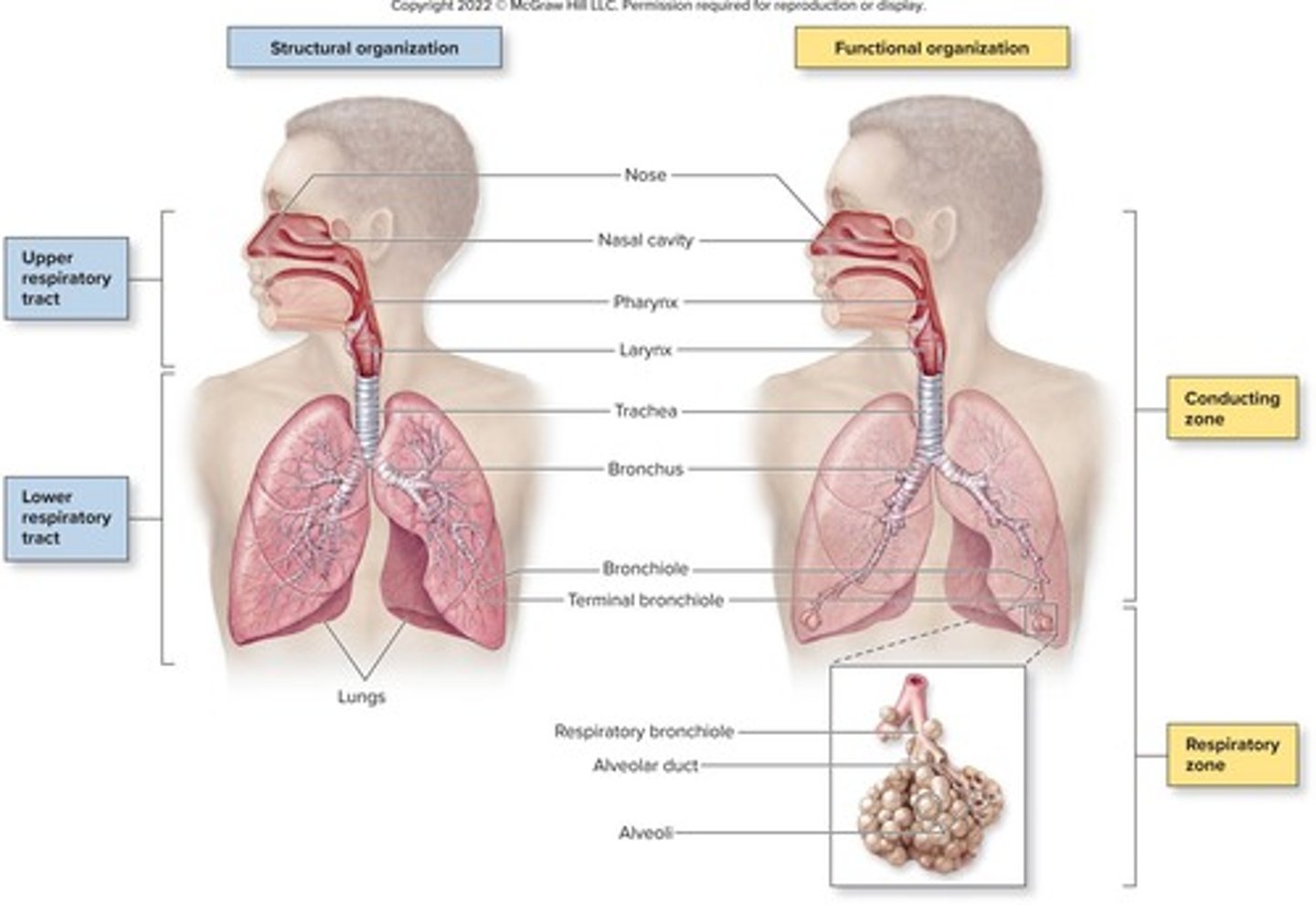
Conducting Zone
Transports air from nose to terminal bronchioles.
Respiratory Zone
Involved in gas exchange in lungs.
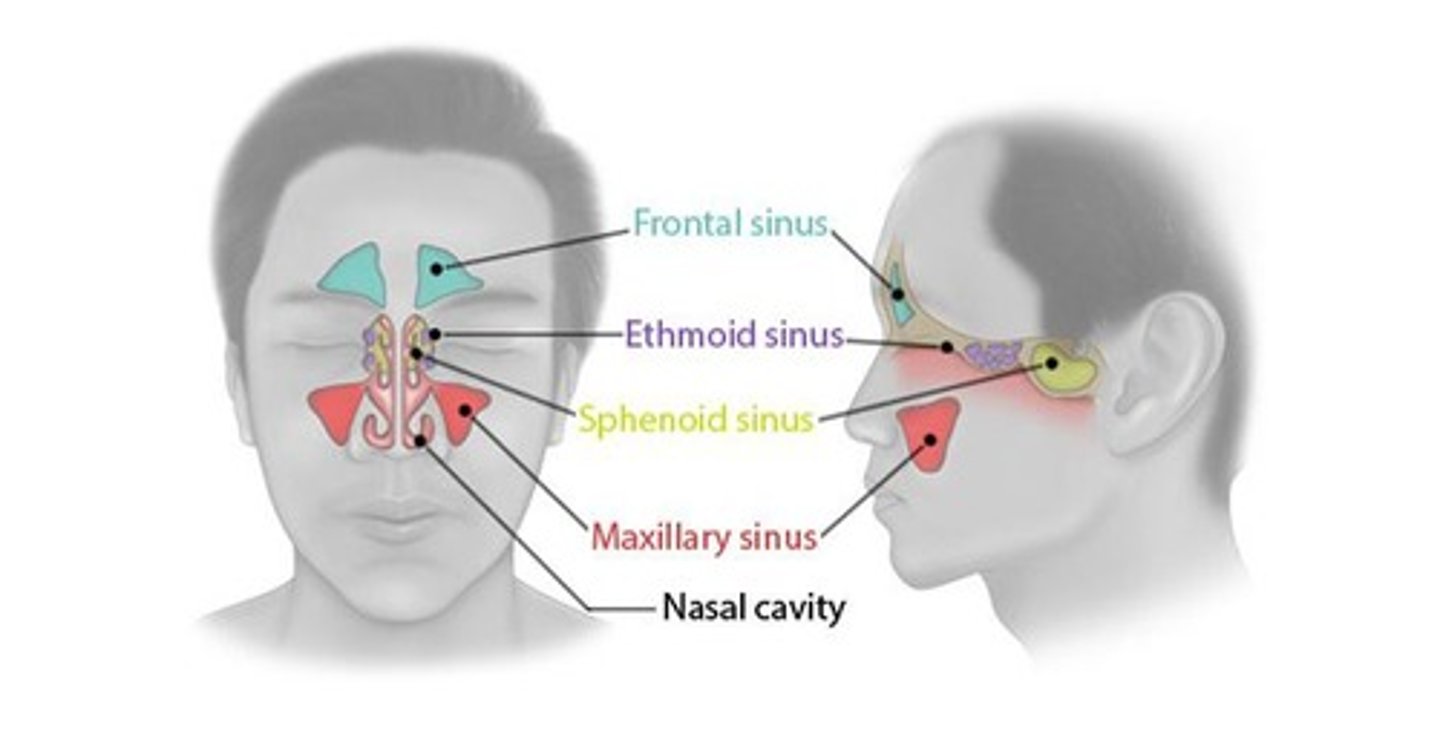
Sinuses
Air-filled spaces that warm and humidify air.
Pharynx
Conduit for air and food; three regions.
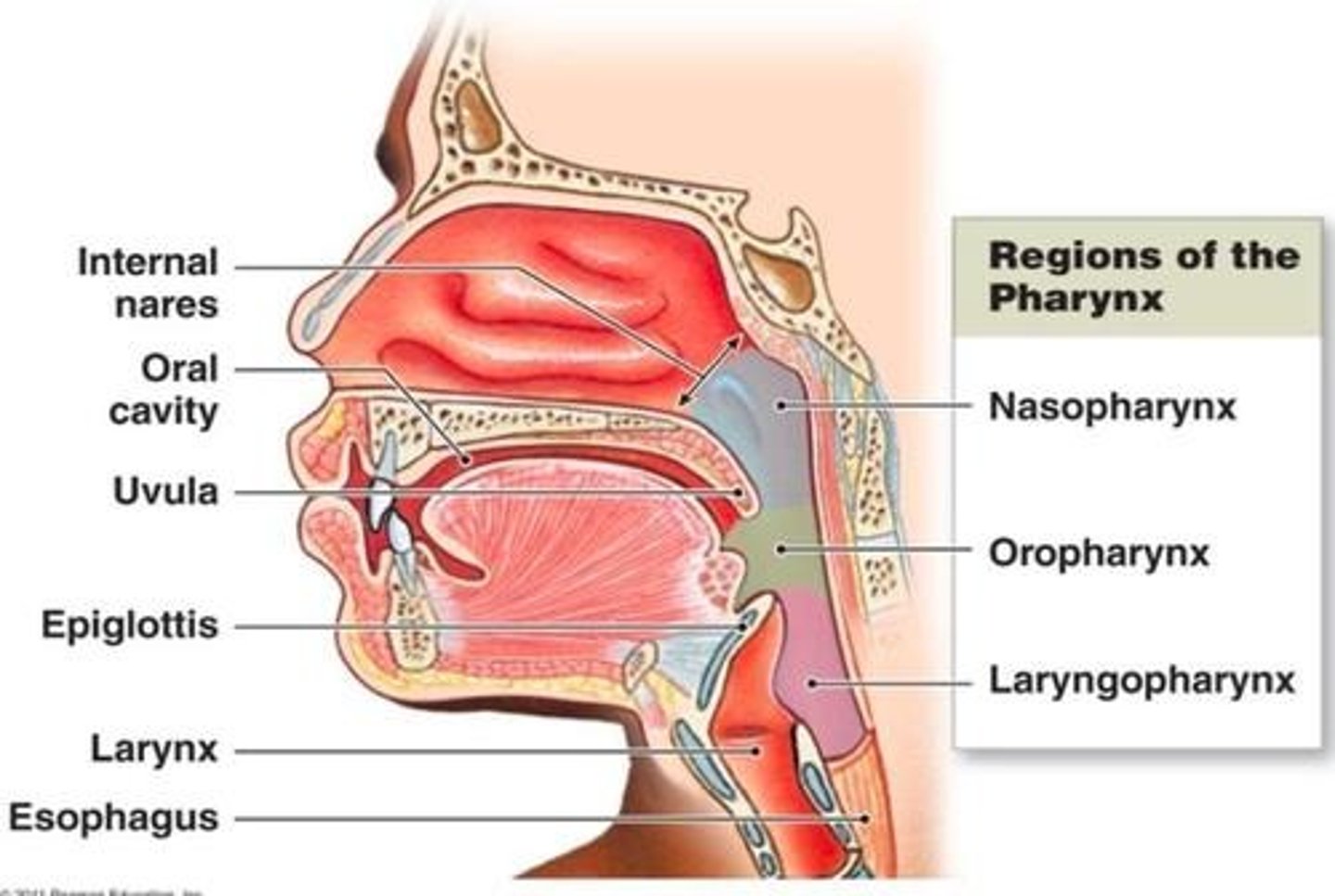
Larynx
Contains vocal cords; directs air into trachea.
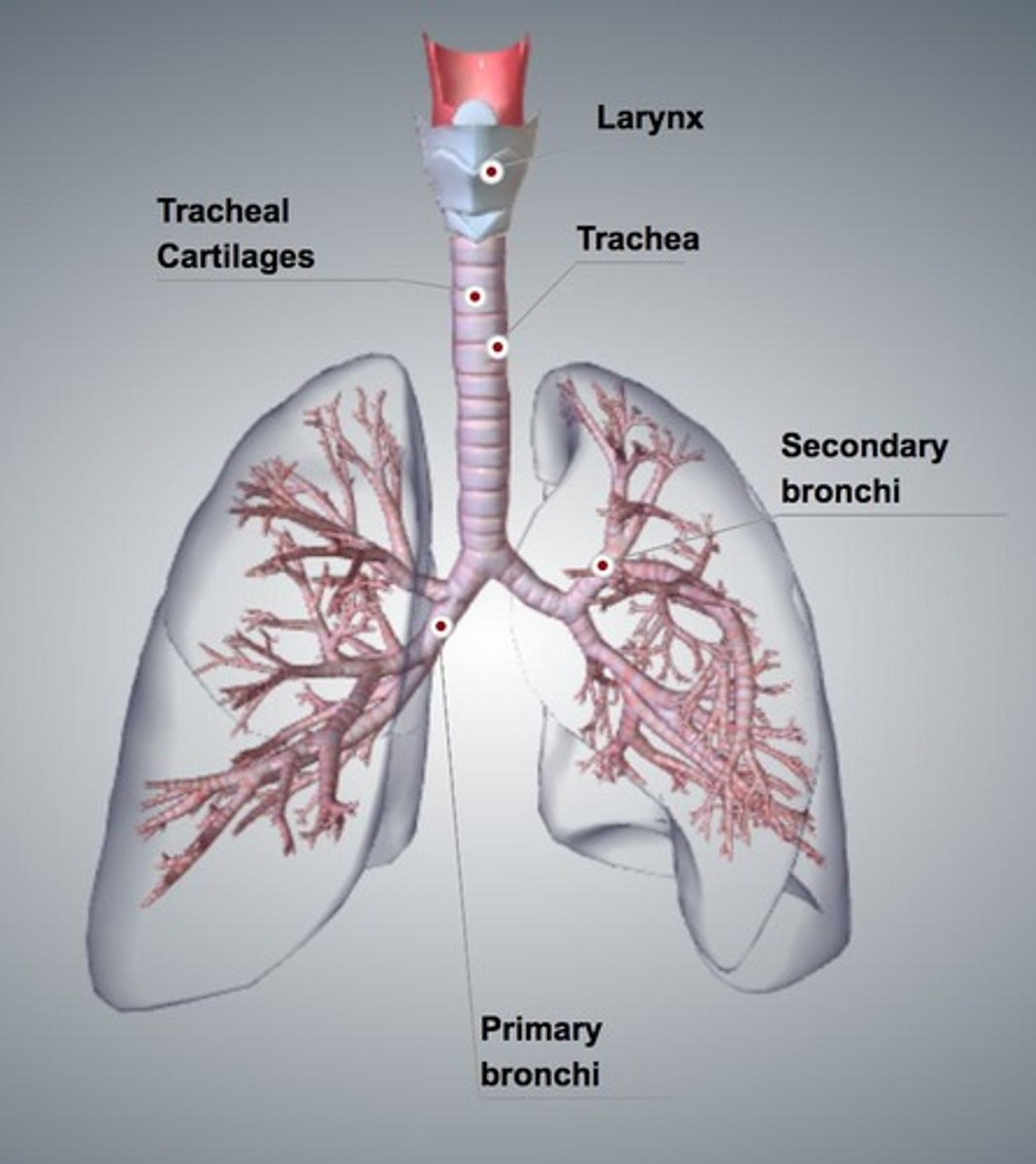
Trachea
Connects larynx to bronchi; contains ciliated cells.
Bronchi
Supported by cartilage; contain ciliated mucous cells.
Bronchioles
Lack cartilage; contain smooth muscle and ciliated cells.
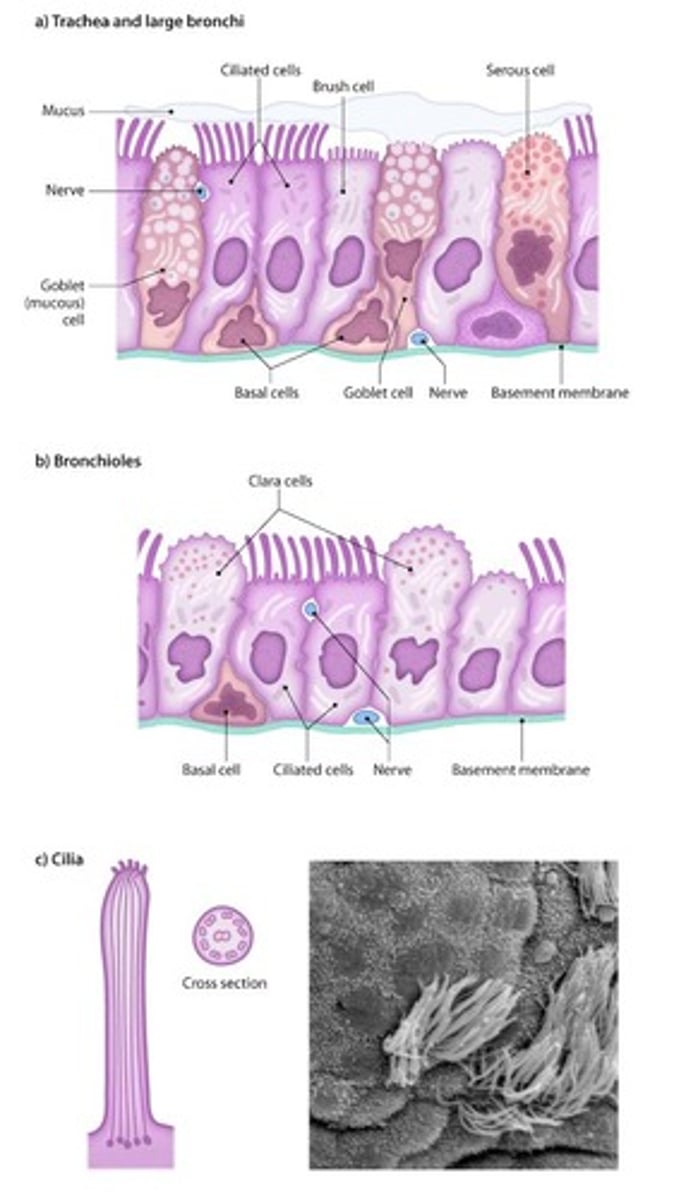
Mucociliary Escalator
Mechanism to expel trapped debris from airways.
Respiratory Mucosa
Mucous membrane lining respiratory tract.
Goblet Cells
Produce mucus in respiratory epithelium.
Mucin Protein
Increases mucus viscosity; traps particles.
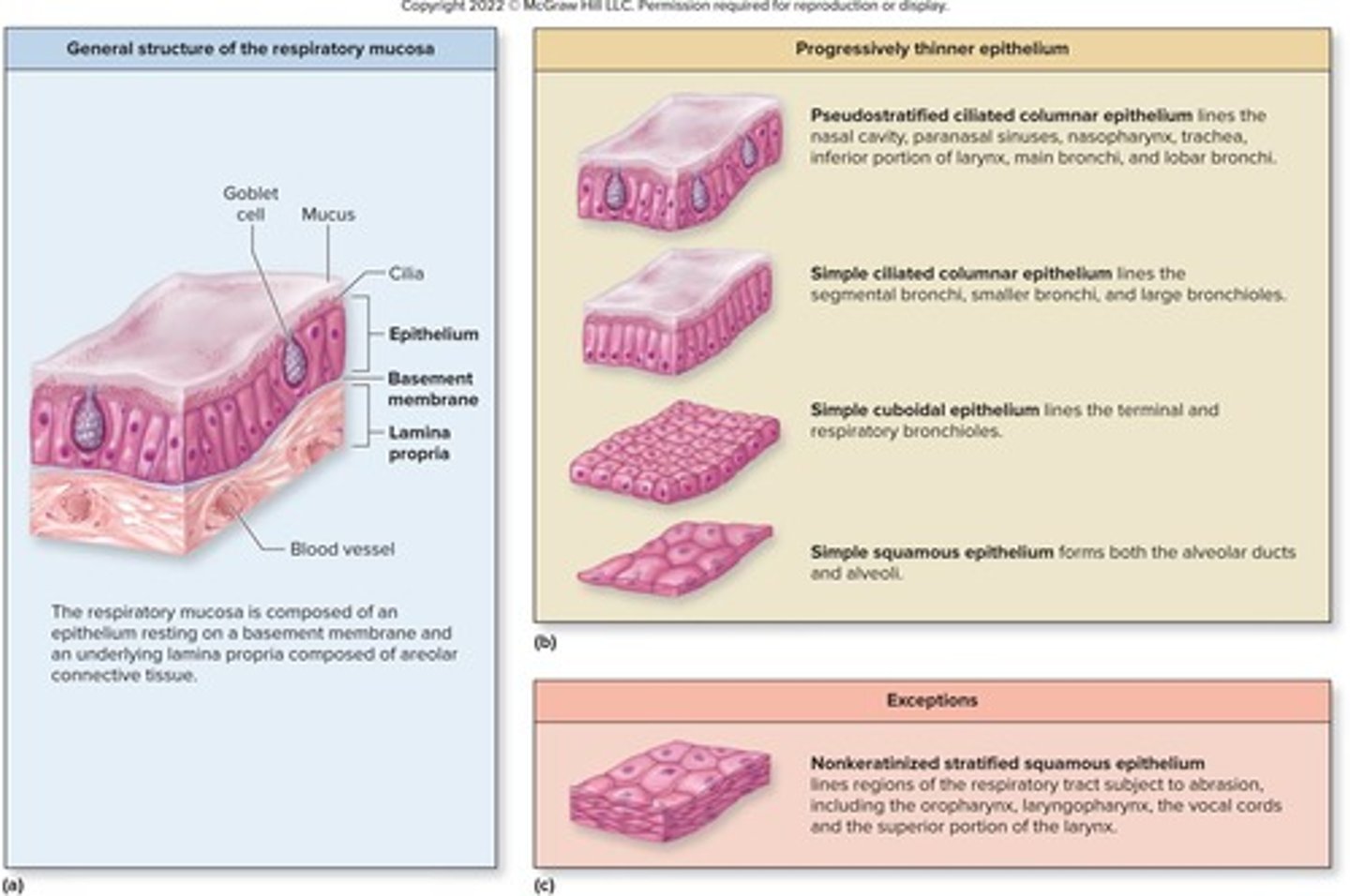
Histological Changes
Epithelium changes from nasal cavity to alveoli.
Simple Squamous Epithelium
Found in alveoli; facilitates gas exchange.
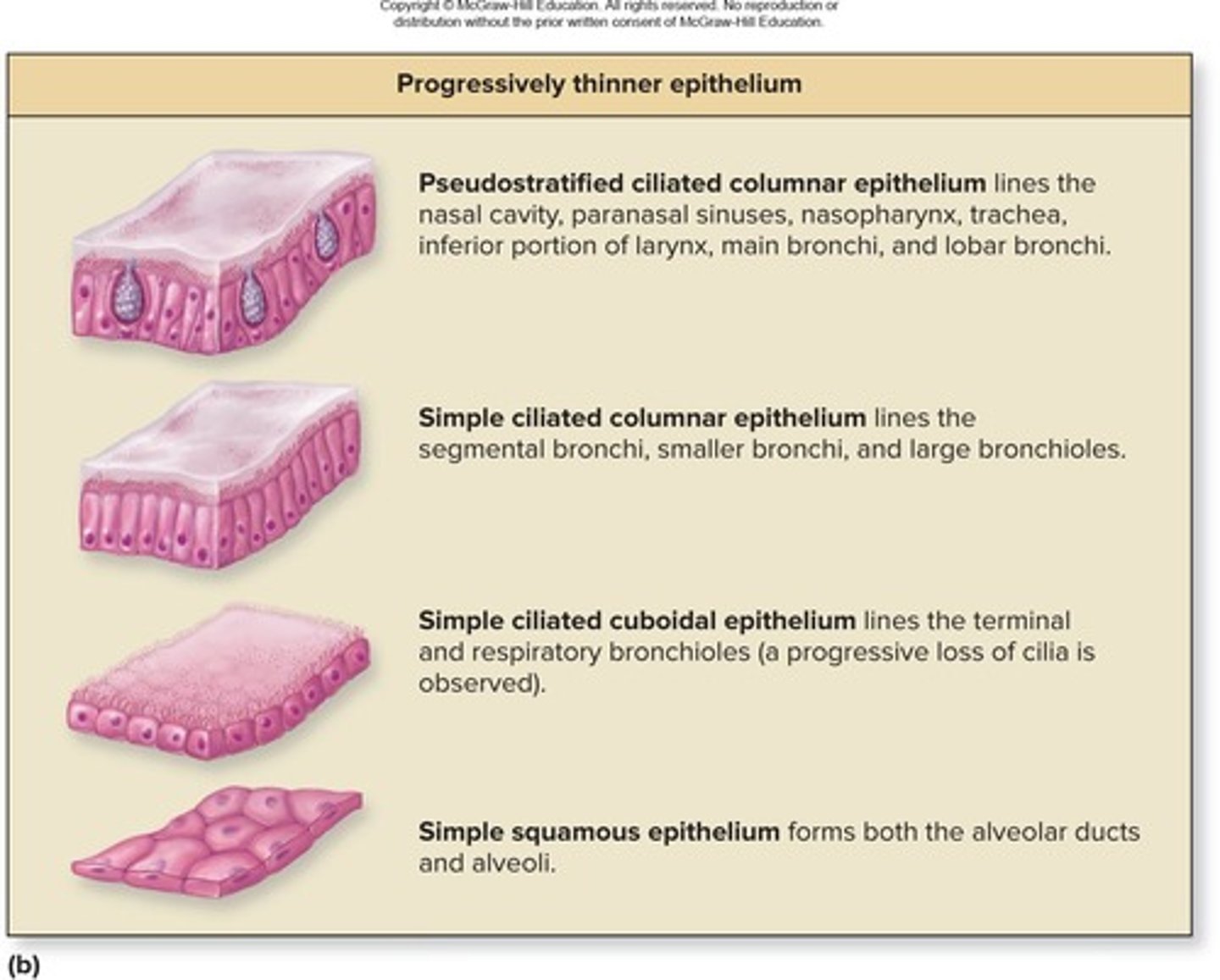
Stratified Squamous Epithelium
Found in high abrasion areas like vocal cords.
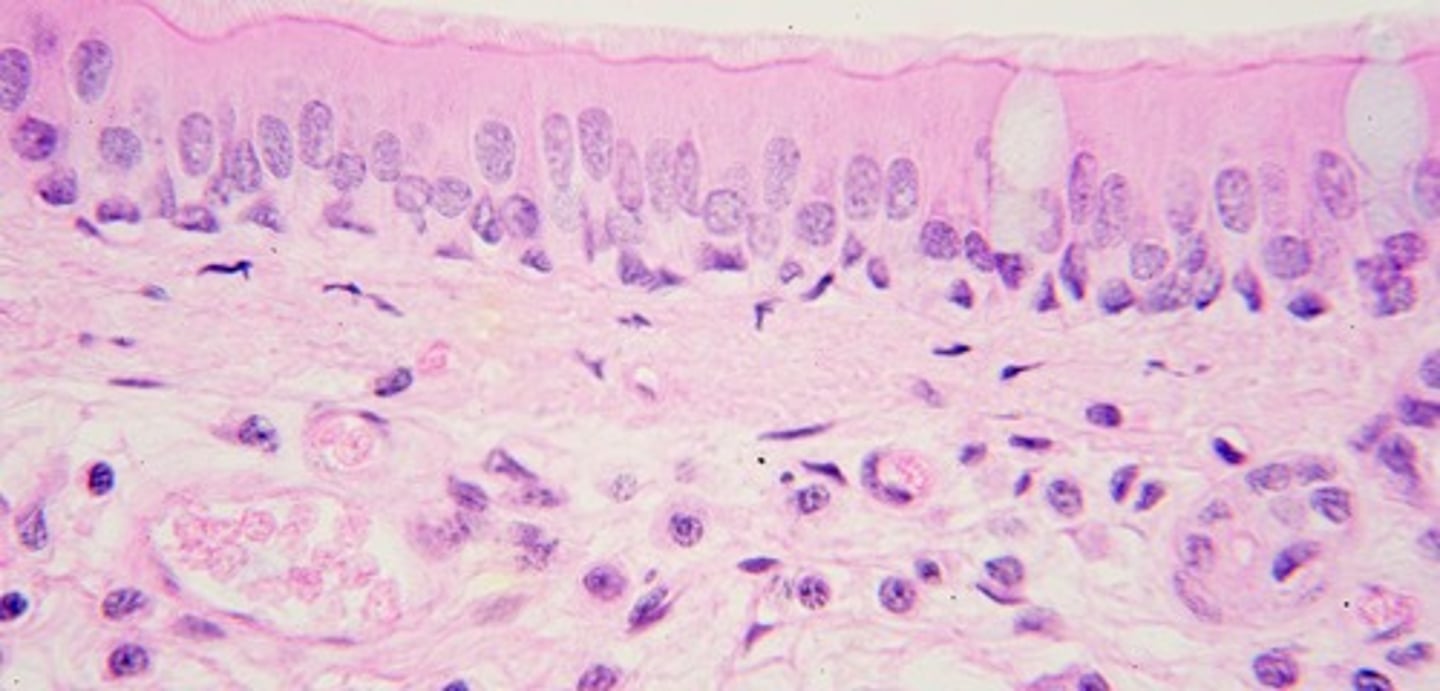
Carina
Cartilage ridge triggering cough reflex for expulsion.
Sputum
Mucus coughed up with saliva and substances.
Pleural Membrane
Two-layered membrane surrounding each lung.
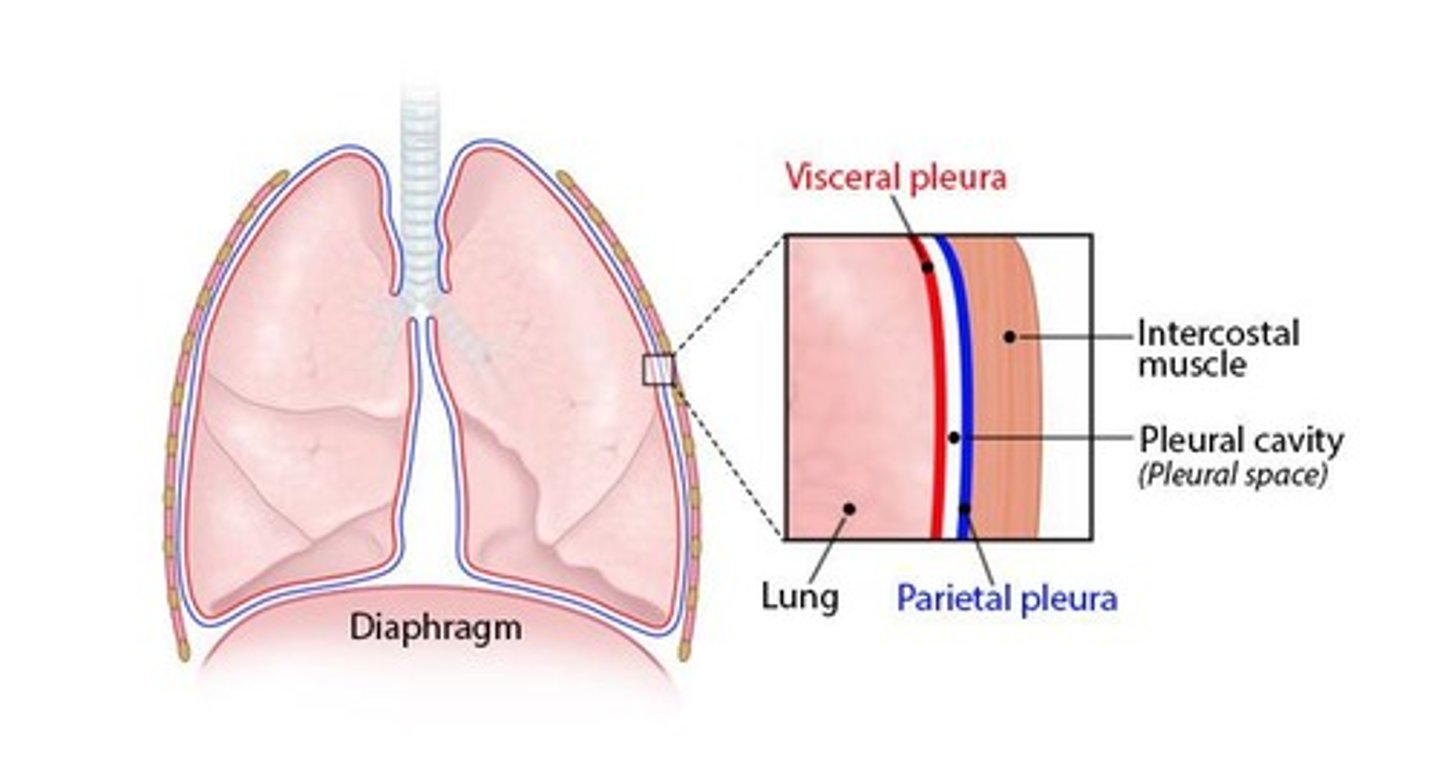
Visceral Pleura
Layer tightly covering each lung.
Parietal Pleura
Lines inner thoracic cavity wall.
Pleural Cavity
Space between pleurae containing pleural fluid.
Pleural Fluid
Lubricates pleurae and provides a barrier.
Respiratory Bronchioles
Minimal smooth muscle structures in respiratory division.
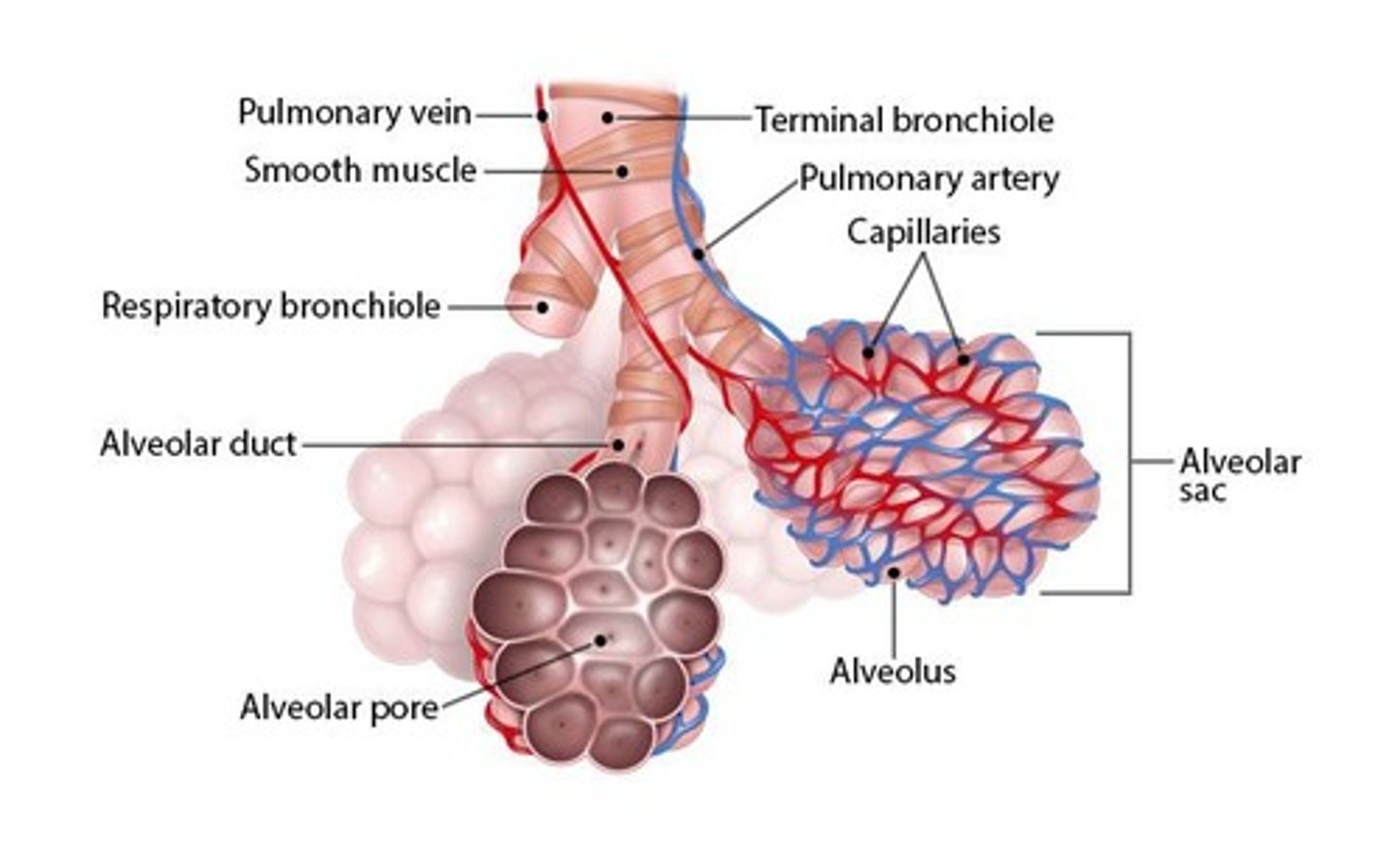
Alveolar Ducts
Short conduits primarily made of connective tissue.
Alveolar Sacs
Grape-like clusters of individual alveoli.
Alveoli
Thin-walled structures for gas exchange.
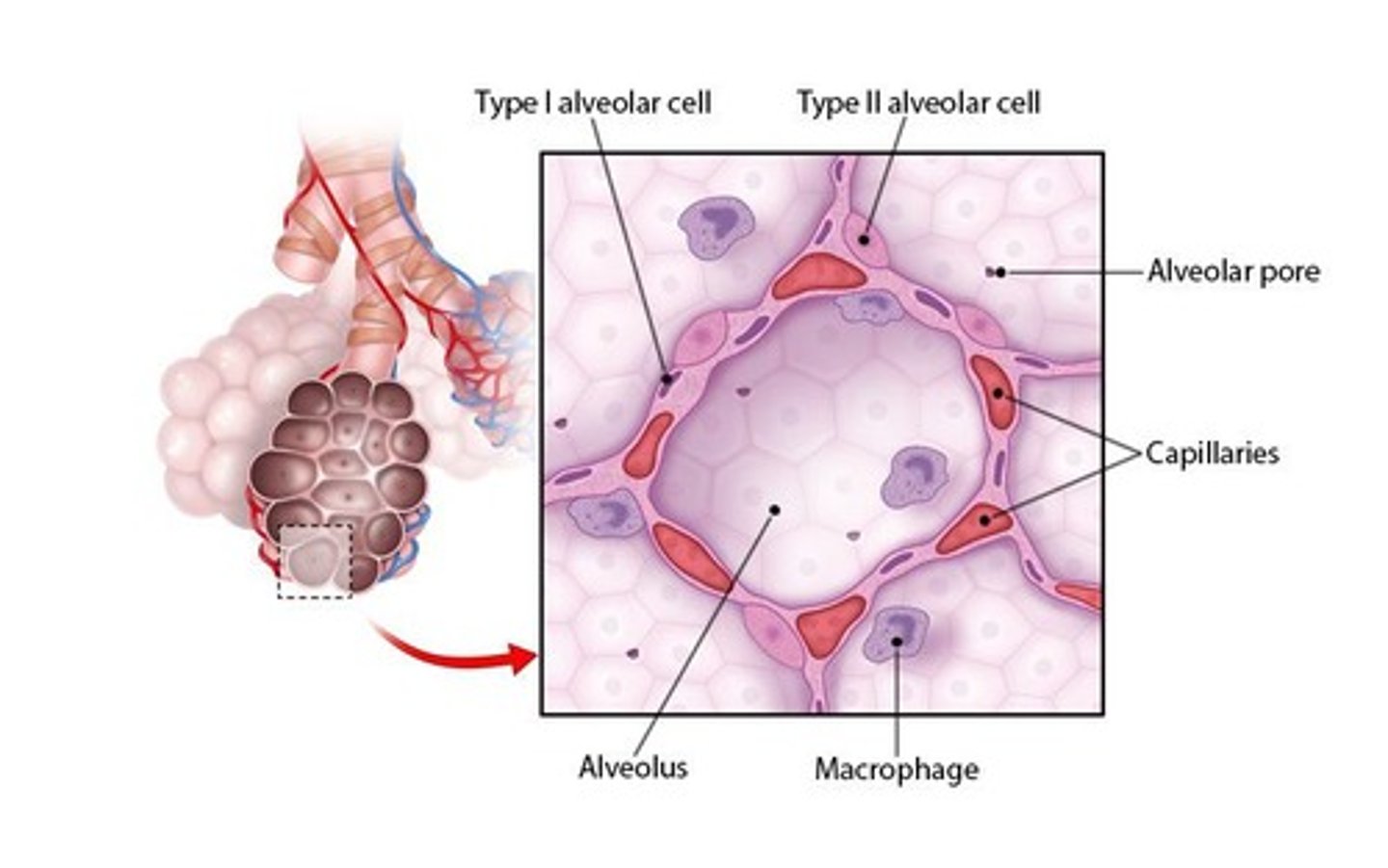
Surface Area of Alveoli
Collectively 70 m², size of a tennis court.
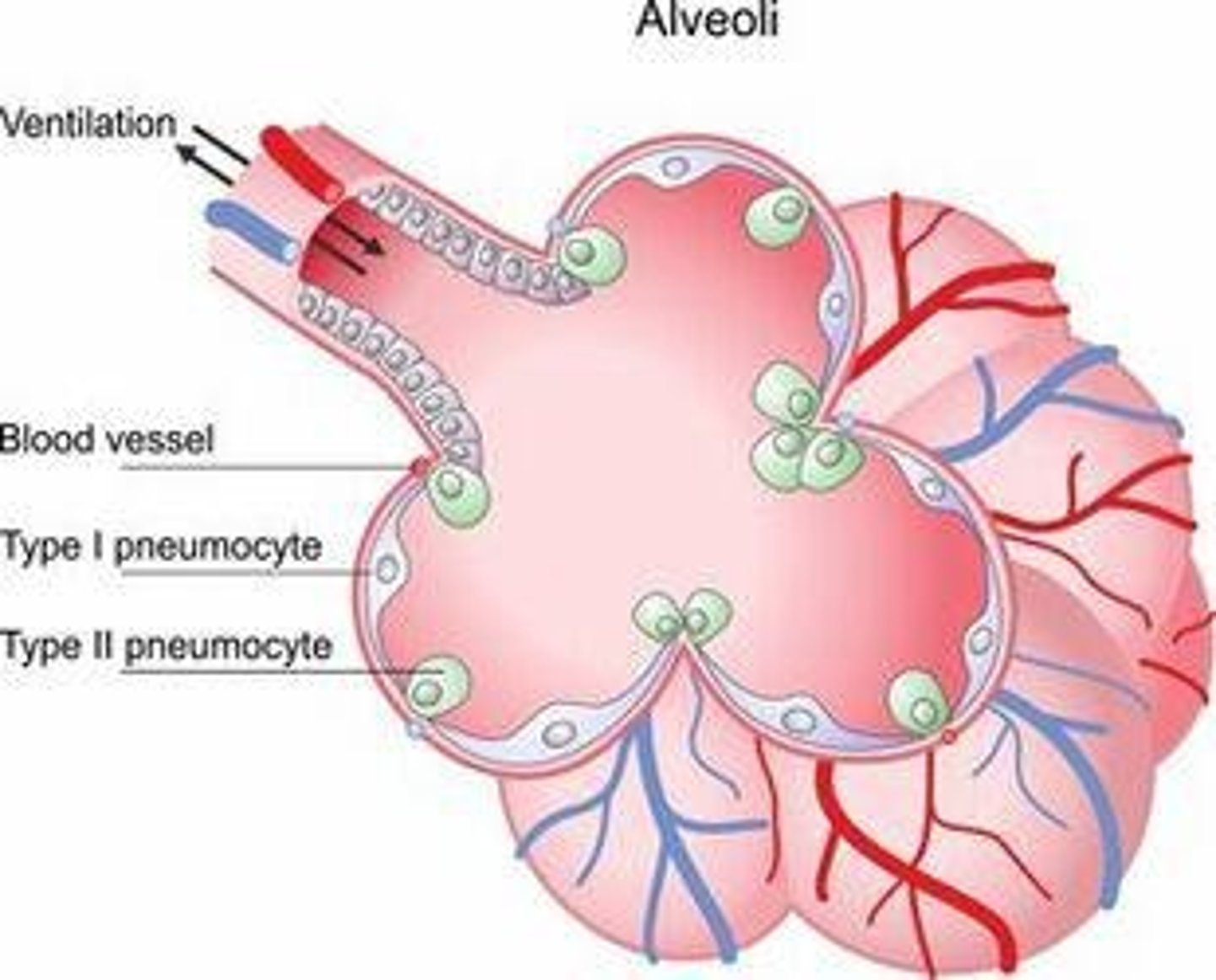
Type I Pneumocytes
Simple squamous cells forming alveolar walls.
Type II Pneumocytes
Cuboidal cells that secrete surfactant.
Surfactant
Reduces surface tension in alveoli.
Dust Cells
Alveolar macrophages that scavenge particles.
Lysozyme
Antibacterial enzyme found in respiratory secretions.
Defensins
Antibacterial proteins in respiratory defense.
Immunoglobulin A
Antibody present in respiratory secretions.
Conducting Zone
Includes nasal cavity, larynx, trachea, excluding alveoli.
Macrophage
Immune cell type found in alveoli.
Dust Cells
Macrophages in alveoli that clear debris.
Alveolar type I
Thin cells facilitating gas exchange in alveoli.
Alveolar type II
Cells producing surfactant to reduce surface tension.
Fibroblasts
Cells providing structural support in lung tissue.
Pulmonary trunk
Major vessel carrying deoxygenated blood to lungs.
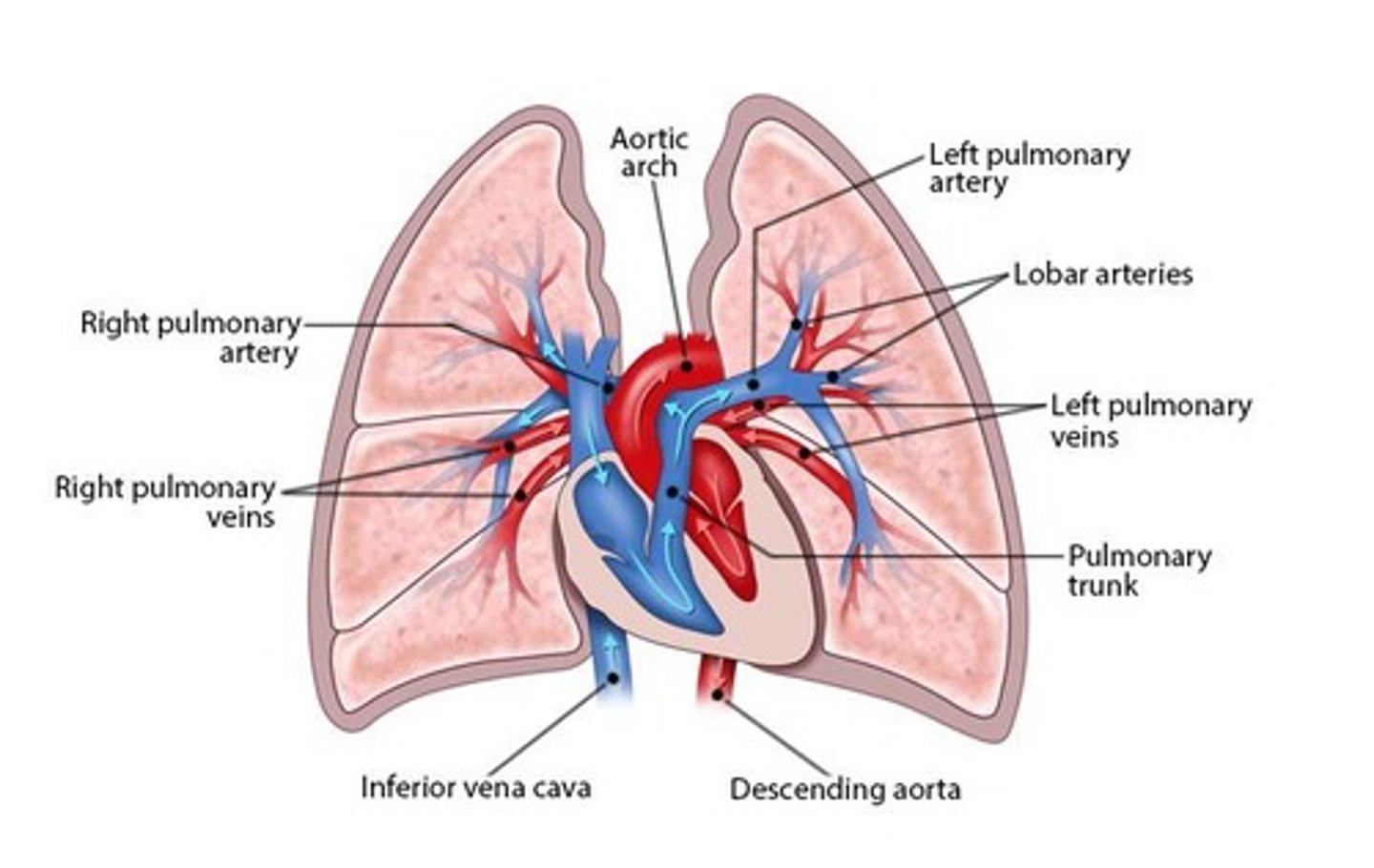
Pulmonary arteries
Transport deoxygenated blood from heart to lungs.
Lobar arteries
Branch from pulmonary arteries to supply lung lobes.
Capillary beds
Network of capillaries surrounding alveoli for gas exchange.
Venules
Small veins collecting oxygenated blood from capillaries.
Pulmonary veins
Carry oxygenated blood from lungs to heart.
Zone 1 pressure
Alveolar pressure exceeds arterial and venous pressure.
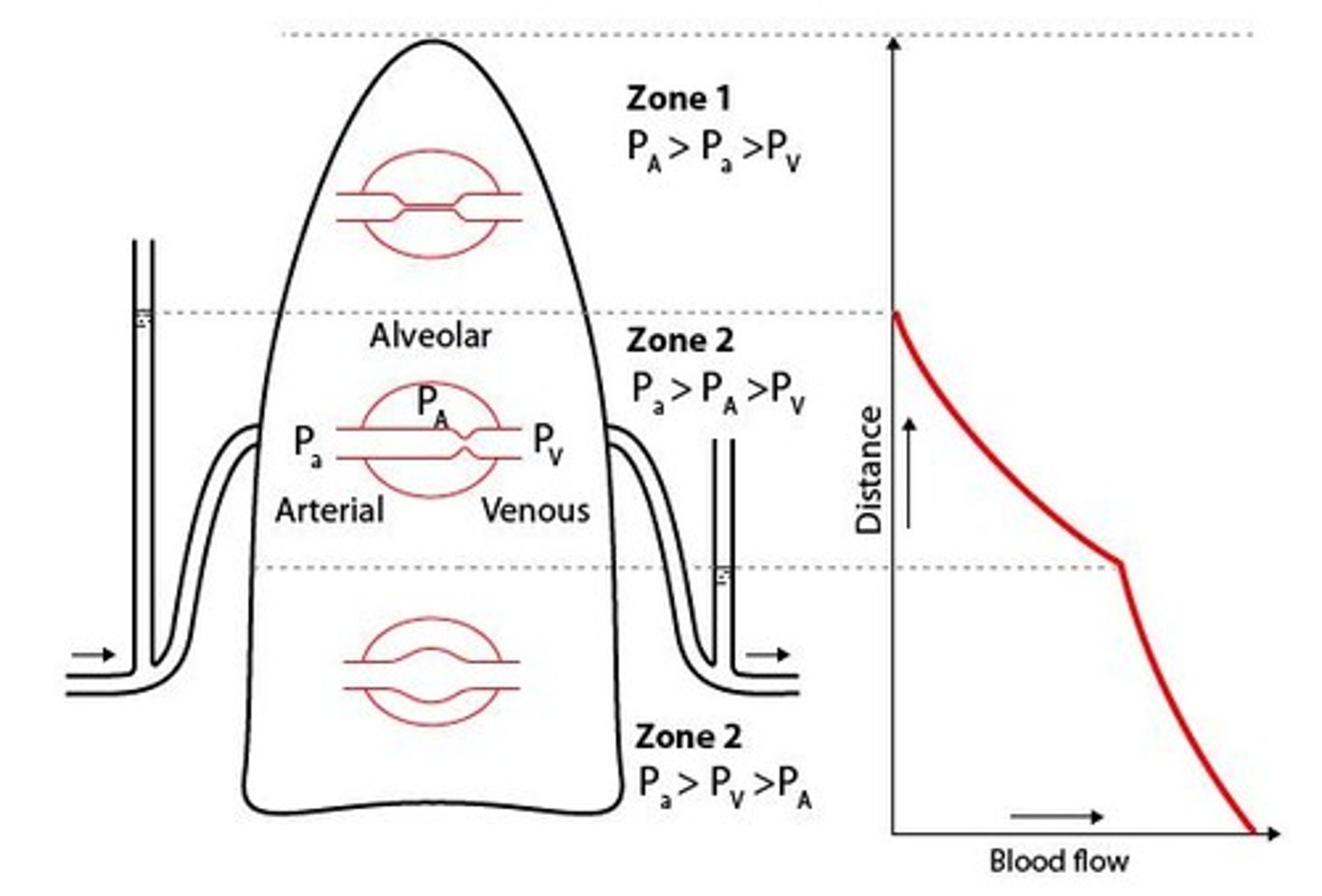
Zone 2 pressure
Arterial pressure exceeds alveolar and venous pressure.
Zone 3 pressure
Arterial and venous pressures exceed alveolar pressure.
V/Q ratio
Ventilation to perfusion ratio for gas exchange efficiency.

Alveolar dead space
Volume of air in non-exchanging alveoli.
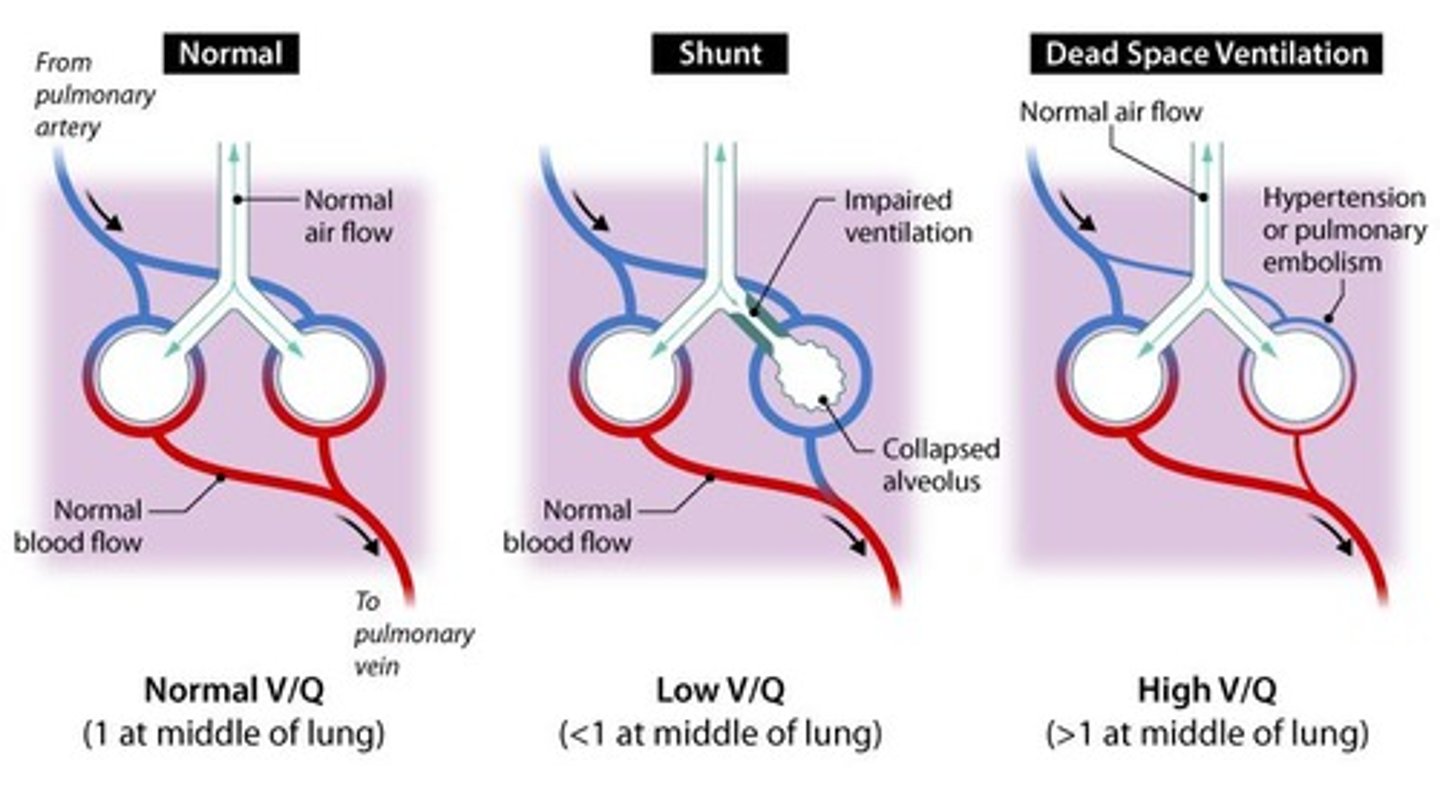
Pulmonary ventilation
Air movement between atmosphere and alveoli.
Inspiration
Phase of breathing that brings air into lungs.
Expiration
Phase of breathing that forces air out of lungs.
Eupnea
Quiet, rhythmic breathing at rest.
Forced breathing
Vigorous breathing during exercise.
Airflow
Amount of air moving in and out per breath.
Pressure gradient
Difference in pressure causing air movement.
Boyle's Law
Pressure increases as gas particle amount increases.
P1V1 = P2V2
Relationship between pressure and volume of gas.
Boyle's Law
P1V1 = P2V2; gas pressure-volume relationship.
Airflow Equation
F = ∆P/R; flow calculation formula.
Flow (F)
Volume of air moving per unit time.
Pressure Gradient (∆P)
Difference between atmospheric and intrapulmonary pressure.
Resistance (R)
Opposition to airflow in the respiratory system.
Intrapulmonary Pressure
Pressure within the lungs during breathing.
Atmospheric Pressure
Pressure exerted by the weight of air.
Intrapleural Pressure
Pressure in the pleural cavity surrounding lungs.
Alveolar Pressure
Pressure within the alveoli during respiration.
Ventilation
Process of moving air into and out of lungs.
Inspiration
Bringing air into the lungs.
Expiration
Moving air out of the lungs.
Coughing
Forceful expulsion of air to clear airways.
Sneezing
Reflex action to expel irritants from nasal passages.
Yawn
Deep inhalation to increase oxygen intake.
Hiccup
Spasm of diaphragm causing rapid air bursts.
Valsalva Maneuver
Exhaling against a closed airway.
Partial Pressure
Contribution of a gas to total pressure.
Gas Exchange
Process of oxygen and carbon dioxide transfer.
Surfactant
Substance that reduces surface tension in alveoli.
Compliance
Lung's ability to stretch and expand.
Partial Pressure
Pressure exerted by a single gas in a mixture.
External Respiration
Gas exchange in lungs between air and blood.
Internal Respiration
Gas exchange in tissues between blood and cells.
Hemoglobin
Protein in red blood cells transporting oxygen.
Oxygen Saturation
Percentage of hemoglobin binding with oxygen.
Oxygen Reserve
Oxygen remaining bound to hemoglobin post-circulation.
Haldane Effect
CO2 binds more readily to deoxygenated hemoglobin.
Apnea
Temporary cessation of breathing.
Laryngitis
Inflammation of the larynx causing hoarseness.
Bronchitis
Inflammation of bronchi due to infection or irritants.
Acute Bronchitis
Short-term bronchitis following an infection.
Chronic Bronchitis
Long-term bronchitis with persistent cough and mucus.
Pneumonia
Lung infection causing fluid accumulation in alveoli.