AP Bio - Unit 2
1/63
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
64 Terms
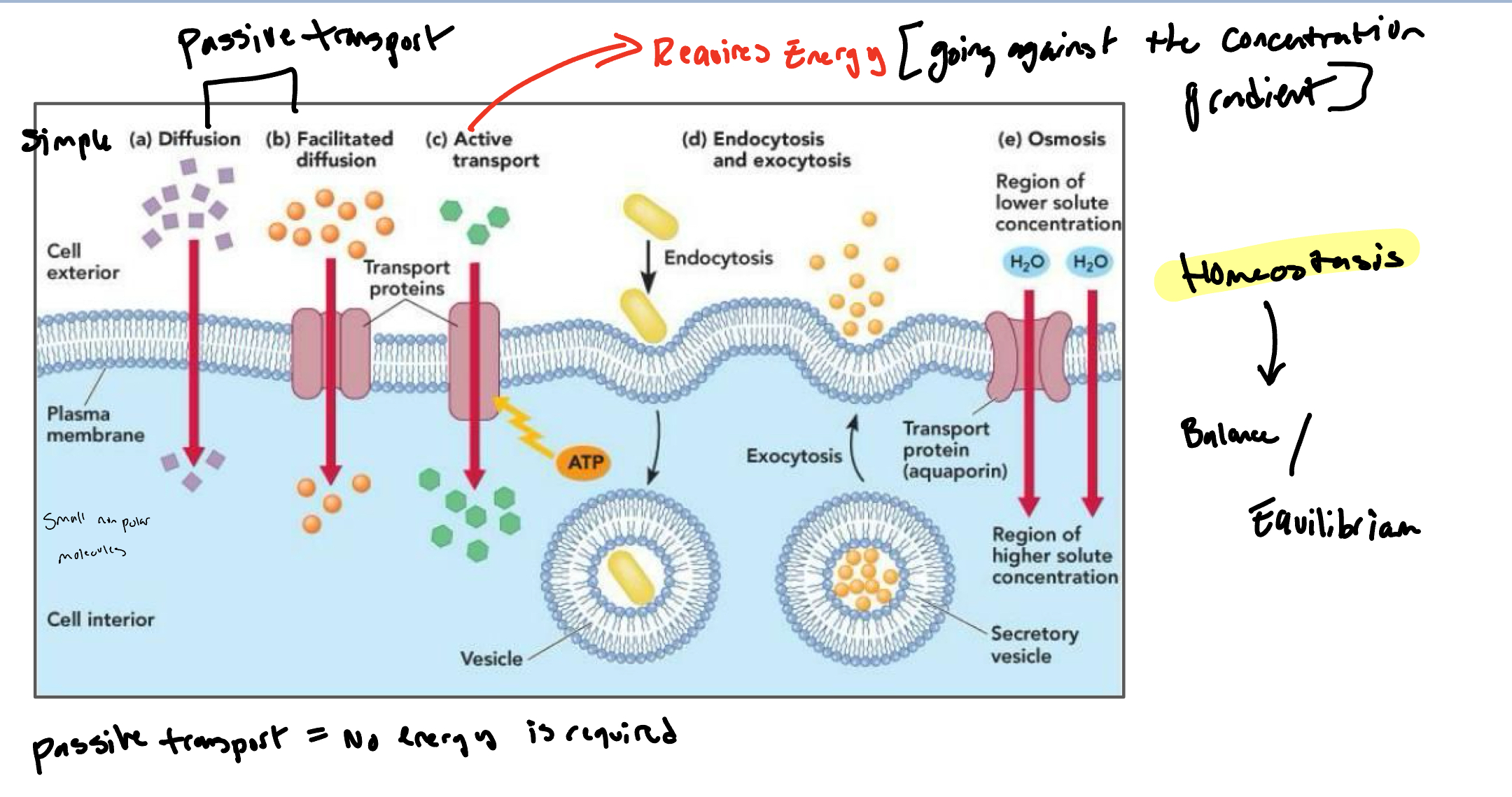
osmosis
The process by which water molecules move across a selectively permeable membrane from an area of lower solute concentration to an area of higher solute concentration, aiming to equalize concentrations on both sides.
Hypertonic
solution with a higher solute concentration than another solution, leading to water moving out of cells placed in it.
Hyoptonic
A solution that has a lower solute concentration compared to another solution, resulting in water moving into the cells placed in it, causing them to swell.
Isotonic
A solution with equal solute concentration compared to another solution, resulting in no net movement of water across the membrane.
simple diffusion
The process where molecules move from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration without the use of energy or transport proteins.
facilitated diffusion
the process by which molecules pass through the plasma membrane via special channels or transport proteins, allowing substances to move down their concentration gradient without energy.
Tonicity
The ability of a surrounding solution to cause a cell to gain or lose water
Prokaryotic Cells
bacteria
Eukaryotic Cells
Animals, Humans, Plants
What do all cells have?
plasma membrane, cytosol (semifluid substance), chromosomes (DNA), and Ribosomes (proteins)
What do Prokaryotic Cells have?
No nucleus, DNA in the Nuceloid, no membrane bound organelles, cytoplasm, bound by the plasma membrane
What do Eukaryotic Cells have?
DNA in the nucleus, membrane bound organelles. cytoplasm in the region between plasma membrane and nucleus.
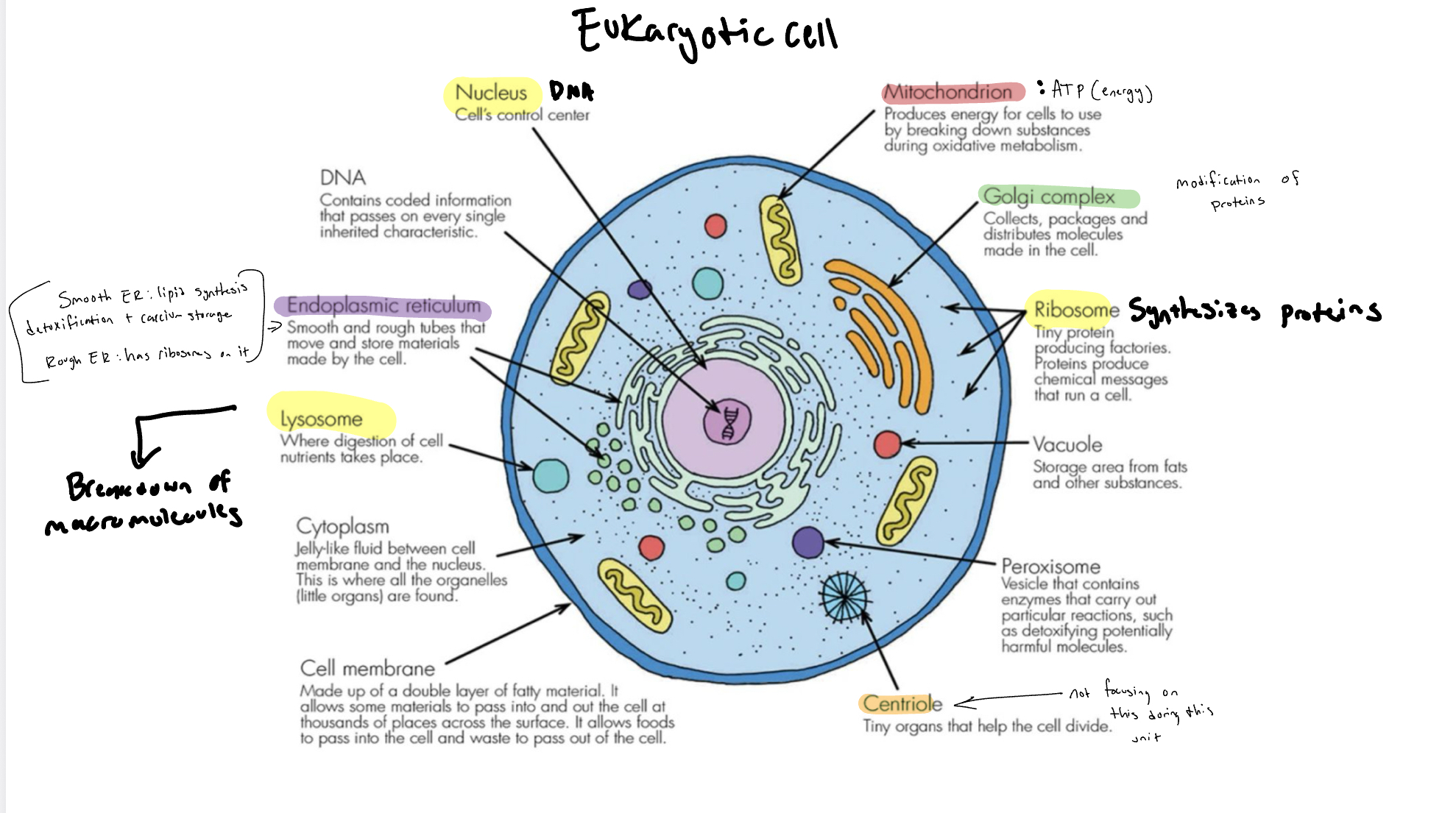
Are Prokaryotic or Eukaryotic Cells larger?
Eukaryotic Cells are larger.
Where are Bound Ribosomes found?
Rough ER
Where are Free Ribosomes found?
Cytosol
What is the purpose of the nuclear envelope?
To enclose around the nucleus and protect our genetic information
What does the Endosome do?
it is known as the sorting center
What does the Lysosome do?
It breaks down and recycles
What is Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER)?
contains more than half of the total membrane in many eukaryotic cells. The ER membrane is continuous with the nuclear envelope
What is Smooth ER
lacks ribosomes + synthesizes lipids, detoxifies drugs and poisons by adding OH, and stores calcium ions which helps neuron function
What is Rough ER
studded with ribosomes + creates glycoproteins which are bonded to carbohydrates, distributes transport vesicles, and is a membrane factory for the cell
What is the Golgi Apparatus?
modifies products of the ER, manufactures certain macromolecules, sorts and packages materials into transport vesicles + goes from the cis fact to the tran face
What do Lysosomes contain and what do it’s contents do?
They contain hydrolytic enzymes which digest macromolecules through hydrolysis + these enzymes work best in acidic environments so there are proton pumps which pump H+ ions inside.
lysosomal enzymes can also hydrolyze proteins, fats, polysaccharides, and nucleic acids.
What is photosynthesis?
CO2 + light + H2O = glucose
Where are chloroplats found?
found in plants and algae and are sites of photosynthesis.
What is the purpose of mitochondria?
They are sites of cellular respiration, which is a metabolic process that uses oxygen to generate ATP.
Explain the charactersistcs of mitochondria?
They are found in nearly every eukaryotic cell + they have a smooth outer membrane and an inner membrane folded into cristae
What is the purpose of Cristae?
Cristae presents a large surface area for enzymes that synthesize ATP
What two compartments are present in the inner membranes?
Inter-membrane space and mitochondrial matrix
What is the cytoskeleton?
The cytoskeleton is a network of fibers extending throughout the cytoplasm and organizes the cell’s structures and activities anchoring many organelles
What is the cytoskeleton composed of?
Microtubules, microfilaments, and intermediate filaments
What does the cytoskeleton do?
it helps support the cell and maintain its shape, interacting with motor proteins to produce motility.
vesicles can travel along the “monorails” provided by the cytoskeleton
What is the most abundant lipid in the plasma membrane?
phospholipids
If phospholipids are amphiphatic, what does that mean?
Amphiphatic contains hydrophobic and hydrophilic regions
What are aquaphorins?
proteins that allow for water to move across cell membranes
What does cholesterol do?
helps maintain proper fluidity of the membrane, not too rigid and not too loose
What does Glycoproteins do?
Cell recognition and cell to cell binding
Glycolipids
stabilizing the membrane and are involved in communication (receptors and regulators)
What are peripheral proteins?
Found at the surface of the membrane
What are integral proteins?
Found at the hydrophobic core
What are integral proteins that span the membrane called?
transmembrane proteins
What are alpha helices?
hydrophobic regions of an integral protein that consist of one or more stretches of non-polar amino acids + usually found coiled
What do you call membranes carbohydrates that bind covalently to lipids?
glycolipids (and if formed to proteins they are called glycoproteins)
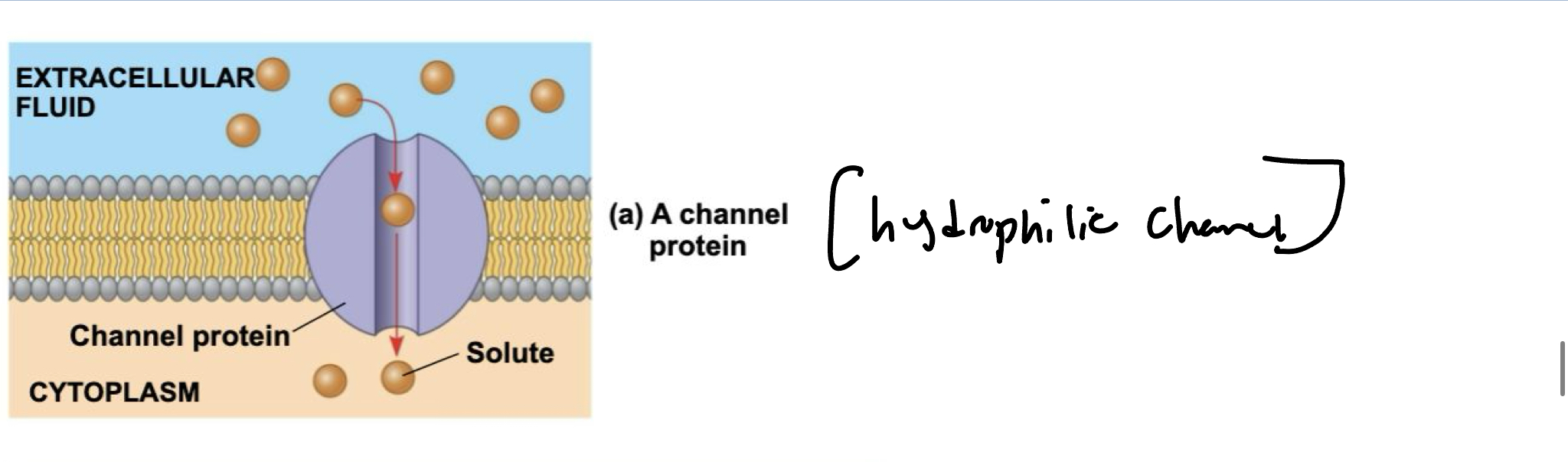
What are transport proteins?
Also called channel proteins, have a hydrophilic channel that certain molecules or ions can use as a tunnel.
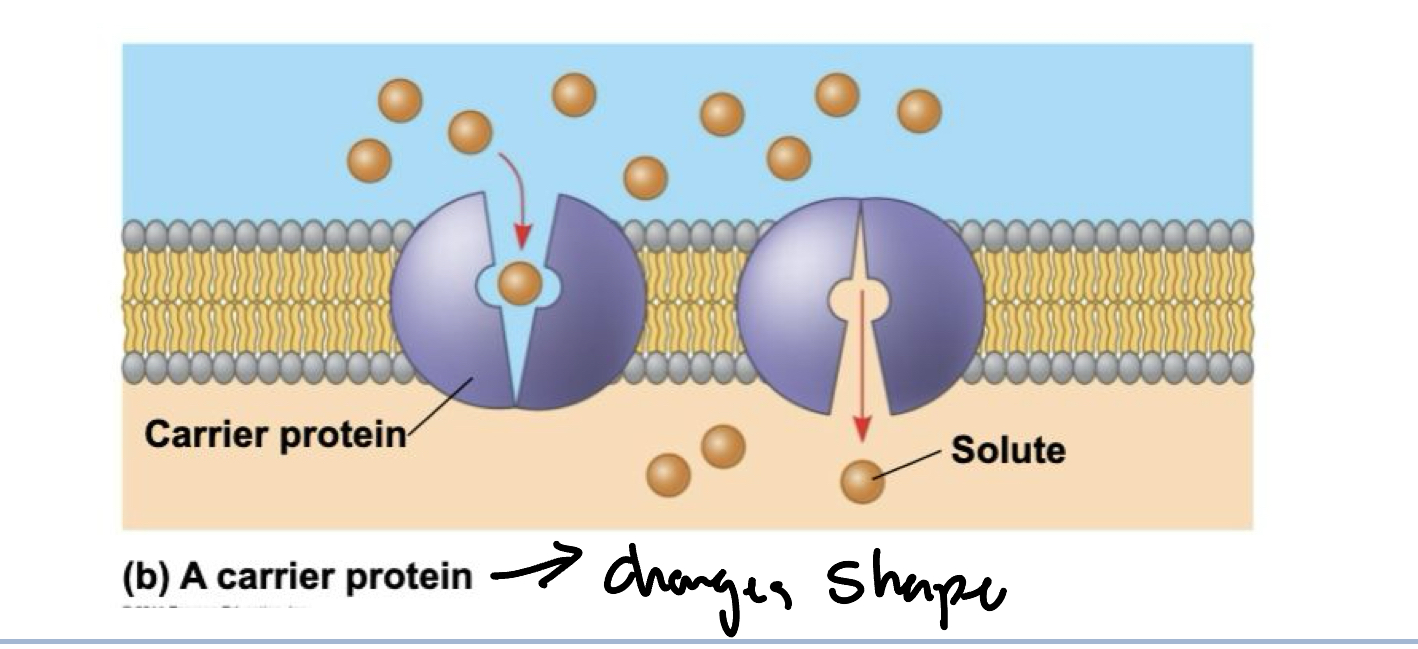
What are carrier proteins?
Another type of transport proteins that bind to molecules and change shape to shuttle them across to membrane
Example of transport proteins
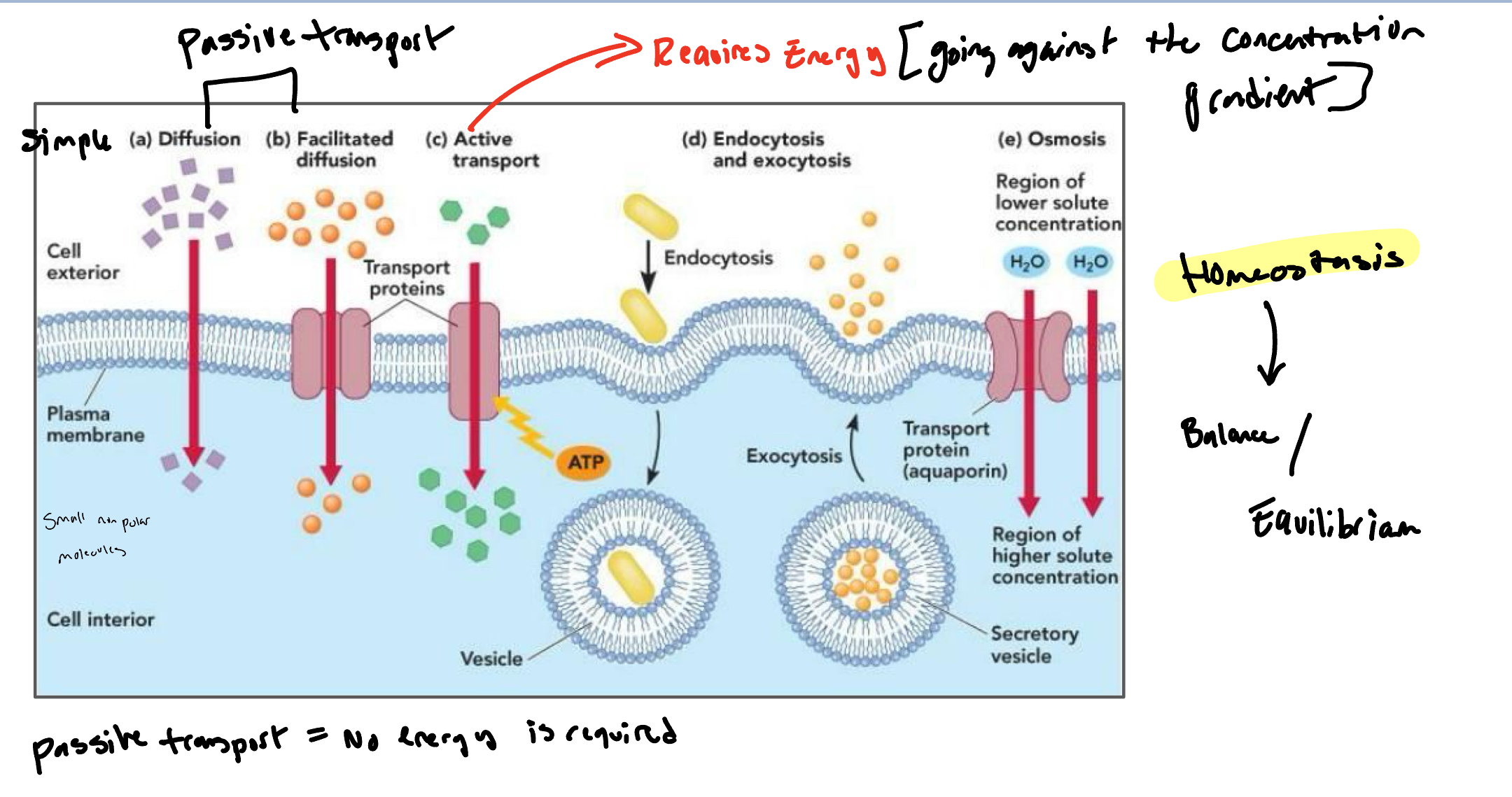
What is active transport?
move substances against their concentration gradients + requires energy usually in the form of ATP
What is phosphorylation?
changing the protein structure
What is reception?
A signaling molecule that binds to a receptor protein, causing it to change shape + a bond between a ligand and a receptor is highly specific
What do most signal receptors come in the form of?
plasma membranes
What is a G-protein-coupled-receptor?
They are the largest family of cell-surface receptors and they work with the help of G-proteins.
If the GDP is bound to the G protein, the G protein is inactive
What are receptor tyrosine kinases and what can they do?
They are membrane receptors that attach phosphates to tyrosines + can trigger multiple signal transduction pathways at once
*abnormal functioning of RTKs is associated with many types of caners
What are intracellular receptors?
They are proteins that are found within the cytosol or nucleus of target cells.
Small or hydrophobic chemical messengers can readily cross the membrane and activate receptors.
*example would be thyroid hormones of animals
What is transduction?
Cascades of molecular interactions which relay signals from receptors to target molecules in the cell + usually involves multiple steps
What do multistep pathways do?
They can amplify signals, which molecules do to produce a large cellular response + allow for more opportunities for coordination and regulation of the cellular response
What are the processes of signal transduction pathways like?
like falling dominoes, the receptor activates another protein, which activates another, and that continues until the protein producing the response is activated
What are protein kinases?
They add a phosphate group and transfer phosphates from ATP to protein, which is called phosphorylation
What are protein phosphates?
They remove the phosphates from proteins, which is called dephosphorylation
What is apoptosis?
It is programmed or controlled cell suicide leading to components of the cell to be chopped up and packaged into vesicles that are digested by scavenger cells
Where do two hormones meet in a cell?
The ligand
What are vacuoles?
They are the storage of materials
How are vacuoles found in plant cells?
There is one large central vacuole
How are vacuoles found in animal cells?
There are several smaller vacuoles
What is the process for movement throughout the cell?
Nucleus > Ribosome > Rough ER > vesicle to golgi apparatus > secreted outside of golgi apparatus > vesicle to the membrane layer