factorial designs
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
origins of factorial designs
Agricultural research
Looking for interactions between such factors as fertilizer type and wheat stain
Invented ANOVA
factorial design
more than one independent variable; IVs referred to as factors
notation system
Digits represent IVs
Numerical values of digits represent the # of levels of each IV
2x3 factorial (say: “two by three”)
2 IVs, one with 2 levels, one with 3 = 6 total conditions
2x4x4 factorial
3 IVs, with 2, 4, and 4 levels = 32 total conditions
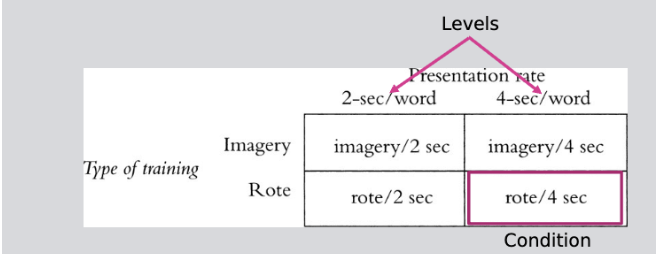
factorial matrix
2x2 (two levels each of type of training and presentation rate)
Factor 1 (two levels) and Factor 2 (two levels)
calculate row and column means
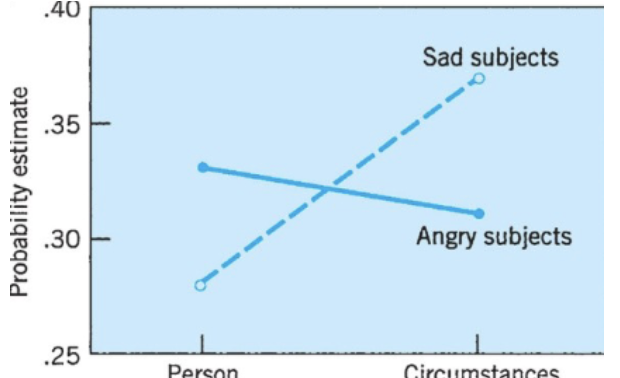
Interactions
effect of one factor depends on the levels of the other factor
Look at the means across the different combinations of factors, Compare the patterns of the means across different combinations, Statistical Analysis
main effects
refers to the impact of one factor on the dependent variable ignoring the influence of other factors
line graphs occasionally used to highlight interactions
calculate means for each level, compare means, conduct stat analysis, a sig difference means main effect exists
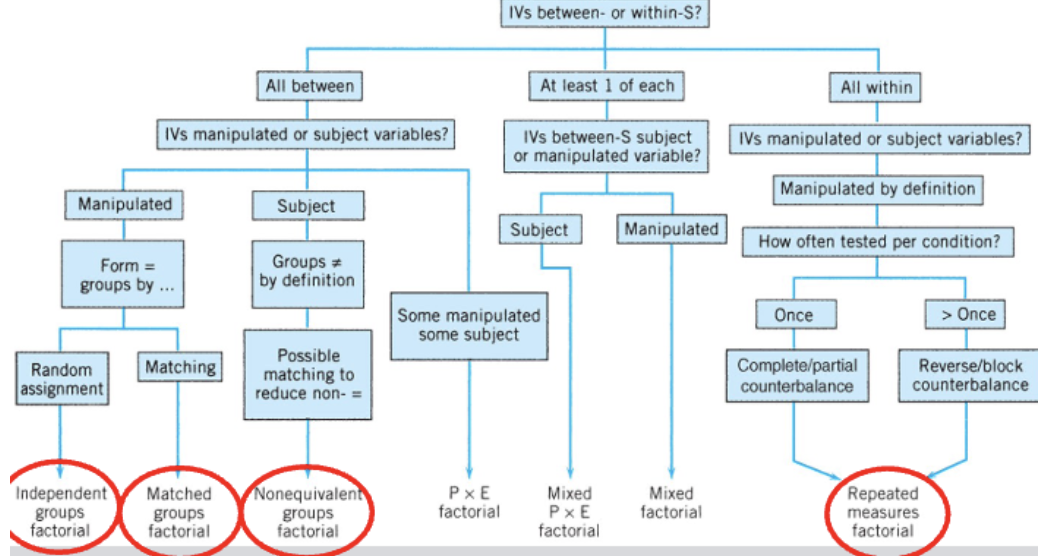
varieties of factorial designs
decision tree
mixed factorial designs
At least one IV is a between-subjects factor
At least one IV is a within-subjects design
Between-Subjects Factor: Since each participant only experiences one level of the between-subjects factor, there is no need for counterbalancing for that factor.
Within-Subjects Factor: Counterbalancing is typically used for within-subjects factors to control for order effects, but it’s not always necessary, especially if the within-subjects conditions are minimal or if order effects are unlikely to affect the results.
recruiting participants for factorial designs
Number needed depends on whether are tested between or within-subjects
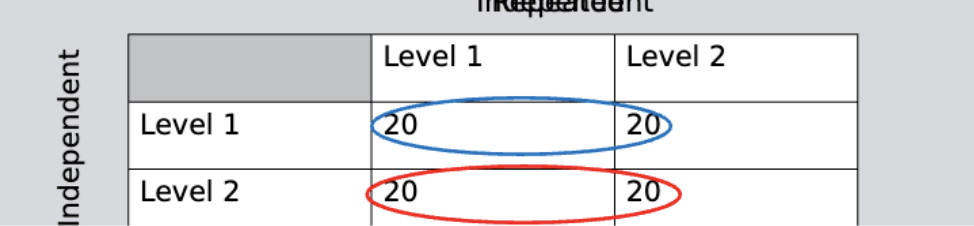
For a 2x2 design with 20 subjects in each cell
2x2 independent groups factorial
20/cell x 4 cells = 80 subjects needed
2x2 mixed factorial
20/cell, same 20 in two cells, different 20 in two other cells = 40 subjects needed
analyzing factorial design
Factorial ANOVA - F score for each main effect and interaction
Independent, dependent, and mixed ANOVA
Post-hoc testing for interactions: simple effects analysis
Factorial ANOVAs and simple effects analyses
Identify a PxE factorial and understand what is meant when such a design produces main effects and interactions
P factor represents a characteristic of the participants (e.g., age, gender, experience) and the E factor represents an environmental variable (e.g., a treatment, condition, or setting).
P (Person factor): Age Group (two levels: Young Adults, Older Adults)
E (Environment factor): Teaching Method (two levels: Lecture-based, Interactive Learning)
Main effects describe the independent impact of the Person or Environment factors.
Interaction effects indicate that the effect of one factor depends on the level of the other factor, showing how the combined influence of the two factors can produce unique outcomes.
Distinguish a mixed PxE factorial from simple PxE factorial designs
Simple PxE factorial designs can either manipulate both factors as between-subjects or both as within-subjects.
Mixed PxE factorial designs manipulate the Person factor as a between-subjects factor and the Environment factor as a within-subjects factor.
simple between subject design
Number of participants = Levels of P×Levels of E×Participants per cell
simple within subject design
Number of participants=Participants per condition(same participants for all conditions)
mixed PxE design
Number of participants=Levels of P×Participants per cell (P)