OPERATIVE FINAL
1/94
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
95 Terms
coupling agents, fillers, resin matrix
major constituents of common dental composites
lower amount of residual monomer (ideal)
composite with HIGHER degree of conversion will have
TEGDMA
dimethacrylate monomer added to composites with better cross linking than PMMA
long working time, high degree of conversion, low abrasive wear
properties desired for light cured composites
true
T/F When dimethacrylate monomer molecules polymerize, the distance between the formed units (or intermolecular distance) becomes smaller and results in volumetric shrinkage.
polymerization shrinkage
major shortcoming of current direct composites
1% to 5% volumetric (3%)
polymerization shrinkage of most composites
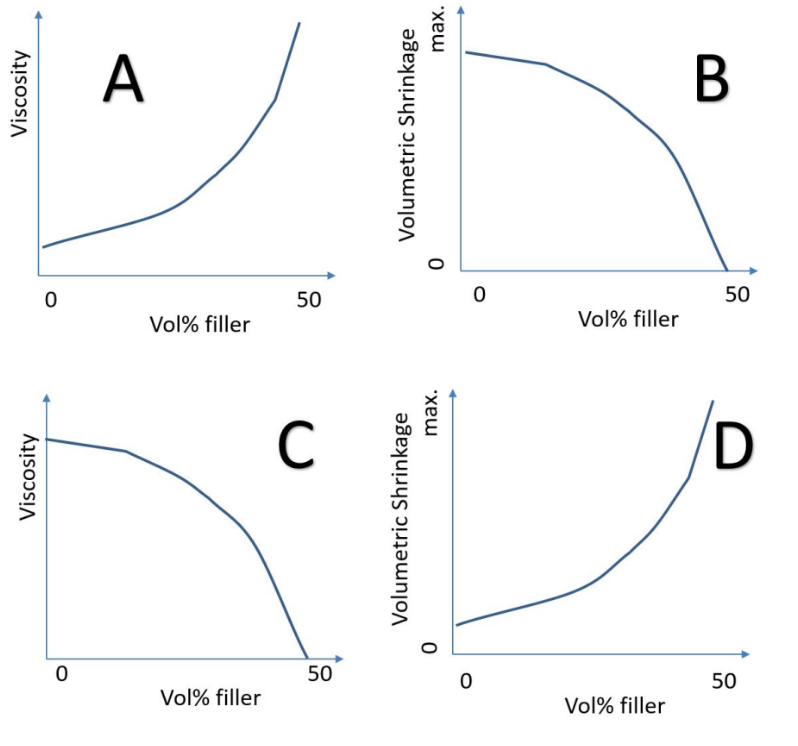
A
which represents the effect of filler content on composite properties
visible blue light
most composites are intended to be cured using
narrower emitting spectra
potential disadvantage of LED light curing units compared to conventional (QTH)
phosphoric etching, rinse and dry, bonding, light cure
Bonding to enamel using a two step etch and rinse 5th generation adhesive system follows the following order:
all in one adhesive (7th gen)
this bonding agent is best described as

phosphate
functional group of MDP
suitable dentin primer
Enamel bonding was introduced as early as 1950's but successful
bonding to dentin lagged for decades because _____ was not
available.
false
T/F The primer in three-step bonding agent is a highly hydrophobic component that penetrates into the demineralized dentin.
air turbine
which handpiece are lighter in weight
electric slow speed
which hand piece has the highest torque
air driven high speed
which hand piece produces the highest pitch noise
2, 1, 3, 4
What is the appropriate sequence of cavity preparation stages?
1) Establishing retention and resistance form
2) Establishing an outline form
3) Deep caries removal
4)Application of Cavity Cleanser
latch type
type bur shank is limited to slow-speed handpieces?
deep pulpal floor, pulpal health, DEJ
Caries at the ______ may be left in consideration of prioritizing
______, while a caries-free _____ is a requirement for a
composite restoration.
caries extent, existing pit and fissure (groove) pattern
The primary guides for establishing an initial cavity outline for a
modern composite restoration is/are:
black and green
which diamond bur bands are coarser
true
T/F caries lesion activity cannot be determined by radiographic appearance except for sequential radiographic images of the same lesion over time
active caries
in normal Stephen response curees, plaque pH would be below critcal level for an extended perior of times in which situation
initial
visually non-cavitated enamel surface with shallow demineralization of dentin
mostly inorganic
human enamel is
striae of retzius
incremental growth lines or bands on tooth enamel
demineralized by acid, reduced permeability zone, remineralizable
features of caries-affected dentin
true
T/F caries lesions represent a continuum of net mineral loss
visual and radiographic exam
proximal carious lesion are best detected using
lactic acid
most potent cariogenic acid produced by strep mutans
refers to intended restoration outcome
G.V. black caries classification primarily
change in enamel opacity
earliest clinical sign of carious lesion
tactile hardness
factor commonly used to distinguish caries affected vs infected dentin
moderate
visible signs of localized enamel breakdown or signs of dentin demineralization by gray shadow under enamel
true
T/F it is unlikely to have infected dentin in initial lesion (ADA criterria)
fluoro apatite
crystal with lower solubility isotherm and better acid resistance
true
T/F lesion activity should be considered when making a decision regarding treatment
restore of individual tooth, prevention, restore of genetic abnormality, esthetic restore
conditions that fall within the scope of operative dentistry
sensory, defense, reactionary
roles of pulp
false
T/F carious lesion excavation and filling eliminates the caries process
yes
should clinical judgement be a part of assessing caries risk
moderate
radiolucency to middle 1/3 of dentin
initial
radiolucency up to outer 1/3 of dentin
bacterial penetration to dentin and enamel surface integrity loss
determinants of moderate caries lesion
true
T/F resin infiltration is based on blocking diffusion of acid
caries free DEJ
goal of restoration
initial
E1- D1 lesions
initial
resin infiltration is indicated for what lesion stage
soluble in low saturation of carbonated or other apatites
human enamel is:
specificity
diagnosing non-carious lesions as non-carious
sensitivity
diagnosing carious lesions as carious
hunter schreger bands
alternate light and dark bands in enamel, due to alternating enamel crystal orientation
dry mouth due to radiotherapy
what could cause enamel to dissolve at a higher pH than 5-5.5
hard
implies lesion on smooth surface may be arrested
food impaction, tooth and restore fracture, periodontal problems, pulp inflammation
incorrect restoration contour can lead to
polymerization shrinkage
incorrect restoration contour does NOT lead to
deep
dentin with higher permeability
S. mutans, S. sobrinus, lactobacilli
major cariogenic bacteria
false (only fluoride)
T/F carbonate and fluoride BOTH increase acid resistance
lining, small defects, PRR restoration
indication for flowable composites
water
constituent found in primer/bonding but not resin composites
higher viscosity (thicker)
higher filler load results in
addition by free radical initiation
how are dental composites polymerized
true
T/F dentin must be kept moist to allow resin infiltration
MDP
acidic monomer for decalcification and smear layer modification
smaller volume, smaller surface area, decreased C factor
concept behind incremental filling to reduce polymerization stress
radiopacity
main function of filler
2 step 6th gen adhesive
In which technique is RINSING WITH WATER NOT required after the first step of bonding to dentin?
wet bonding technique
which bonding concept is challenging in terms of “technique sensitivity”
QTH
curing unit with wider emission spectra
heat-curing
composite curing mechanism not appropriate for intraoral use
pit and fissure sealant
resin with LOWEST viscosity
true
T/F composite shrinkage is a function of di-methacrylate polymerization chemistry
TEGDMA (small structure)
composition more suitable for caries infiltration system such as icon
volume %, shrinkage
degree of composite fillers by _____ is MORE relevant, since it directly affects _____
older composites did not have radiopaque fillers
radiolucency of old, existing composites confirms
improve wear, lower solubility, increase modulus, increase strength
why is the formation of cross-linking chains important in dental composites
filler
the phase that does not react as part of the polymerization reaction
40nm to 50µm
size of fillers used today
higher volume of filler
what property of composite reduces shrinkage
higher viscosity
higher filler load results in:
coupling agent
chemically links filler particle to resin matrix
wear resistance, stain resistance, reduce crack propagation, surface integrity
functions of coupling agents
camphorquione
a photoinitiator commonly used in dental materials that enables polymerization when exposed to light.
470 nm
at what wavelength does camphorquinone absorb light to initiate polymerization
enamel
which dental surface is easier to bond to
high surface energy, rough, dryable
features of enamel that make it easier to bond to
increase surface energy for bonding
role of acid etching
37%
ideal concentration of phosphoric acid for etching enamel
link wet dentin to hydrophobic composite
role of bonding agent
true
T/F initial outline form may be different depending on the type of restorative material
convenience form
extending the outline to improve access to caries and ease of material placement
pulpal health
in deep caries what should be prioritized over complete caries removal