PK liver-2
1/212
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
213 Terms
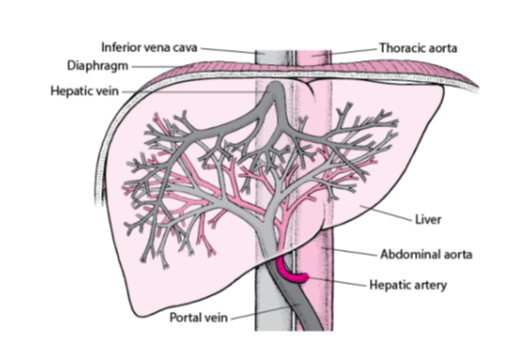
What is the main vein that carries deoxygenated blood from the liver to the heart?
Inferior vena cava.
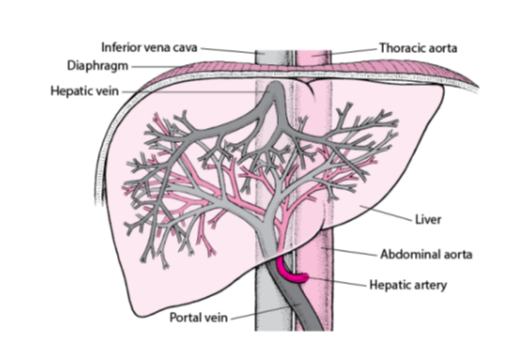
Which vein carries blood from the liver back into the inferior vena cava?
Hepatic vein.
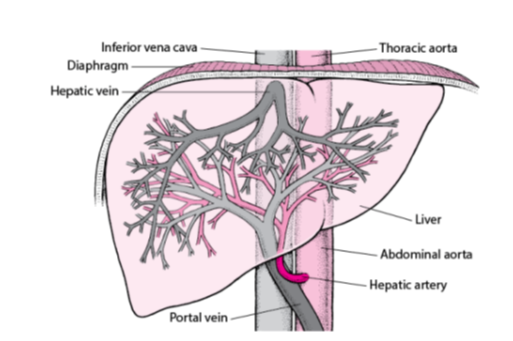
What is the large artery labeled that supplies oxygenated blood to the body from the heart?
Thoracic aorta.
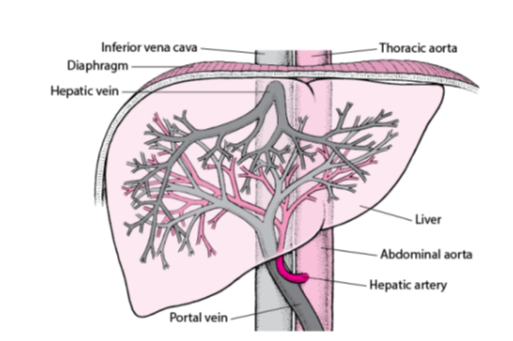
Name the organ shown in the diagram responsible for detoxification, protein synthesis, and the production of biochemicals necessary for digestion.
Liver
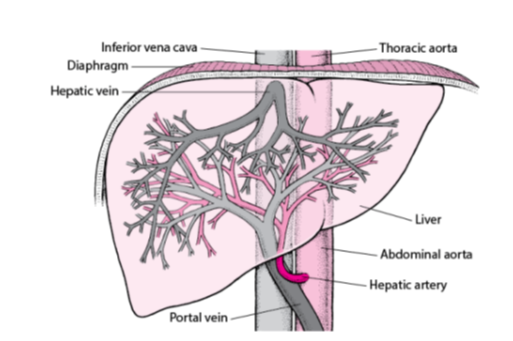
Which artery carries oxygen-rich blood from the abdominal aorta to the liver?
Hepatic artery.

Which vein delivers nutrient-rich blood from the digestive organs to the liver?
Portal vein.
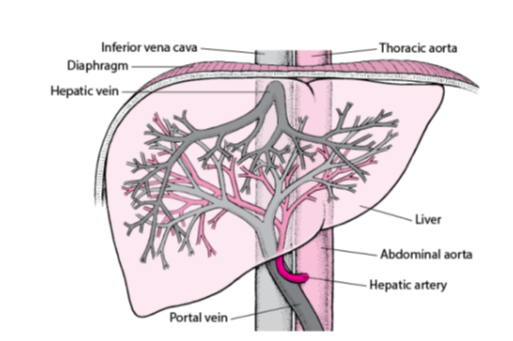
What is the main artery that continues from the thoracic aorta into the abdominal cavity?
Abdominal aorta.
What is the central vessel that collects blood from liver sinusoids?
Central vein.
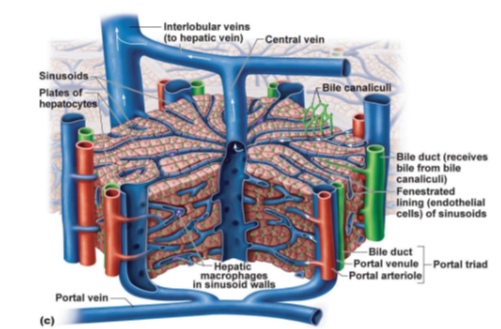
What are the specialized capillaries in the liver that allow exchange between blood and hepatocytes?
Sinusoids.
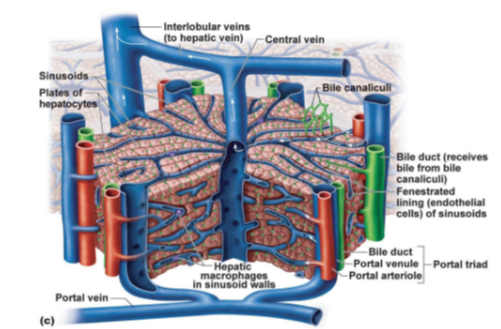
What liver cells are arranged in plates and are responsible for metabolism, detoxification, and protein synthesis?
Hepatocytes.
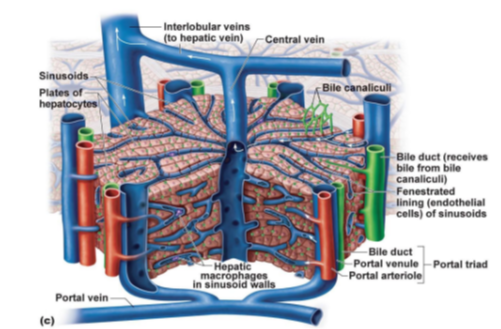
What tiny channels collect bile from hepatocytes?
Bile canaliculi.
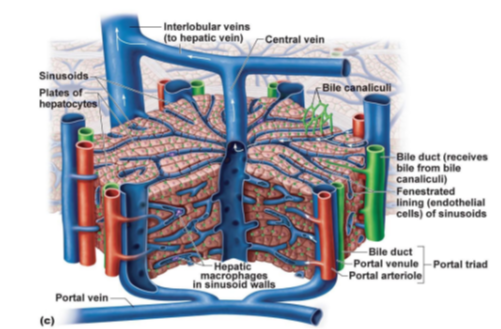
Which structure receives bile from bile canaliculi and sends it to the bile duct system?
Bile duct
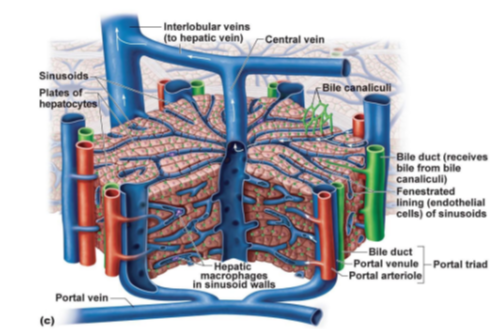
What type of cells line the sinusoids to allow large molecules to pass through?
Fenestrated endothelial cells.
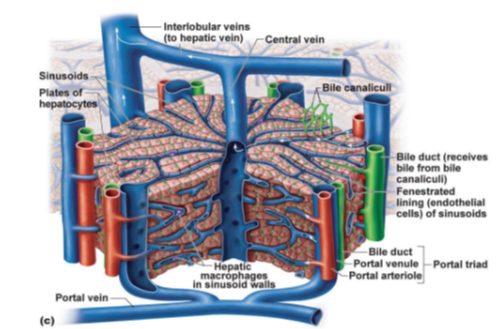
What immune cells are found in the walls of sinusoids, responsible for phagocytosis?
Hepatic macrophages (also known as Kupffer cells).
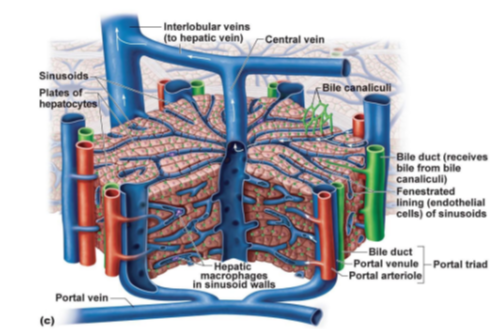
Which vein delivers nutrient-rich blood from the intestines to the liver?
Portal vein.
What three structures make up the portal triad in the liver?
Portal venule, Portal arteriole, and Bile duct.
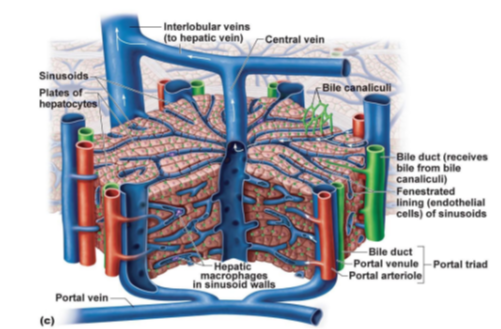
Which veins transport blood from the liver lobules to the hepatic vein?
Interlobular veins.
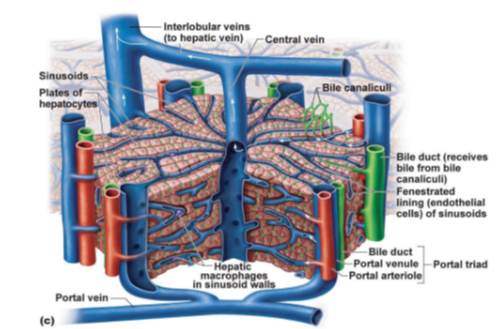
What structures make up the portal triad in the liver?
Portal vein, hepatic artery, and bile duct.
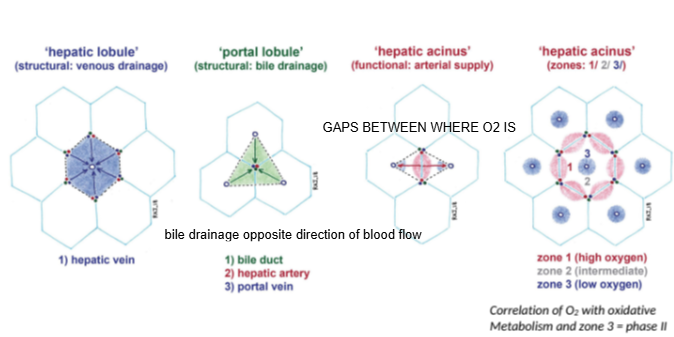
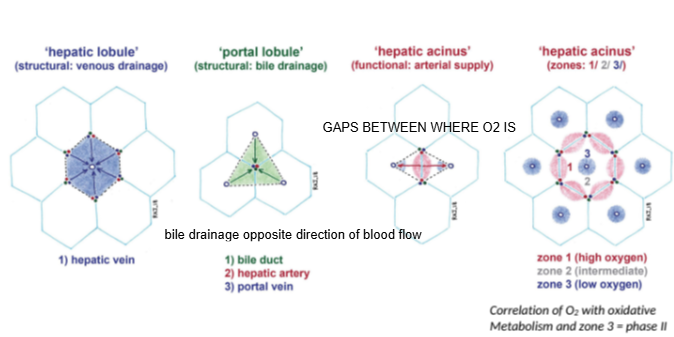
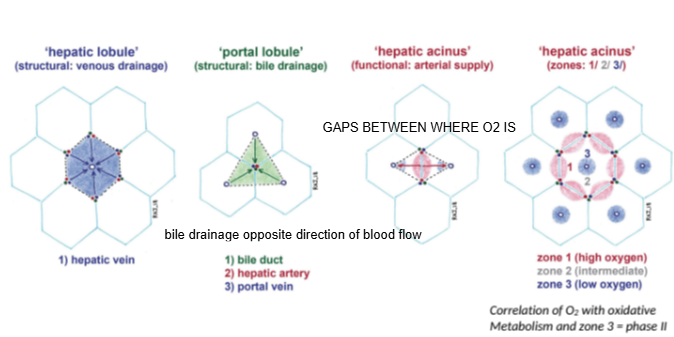
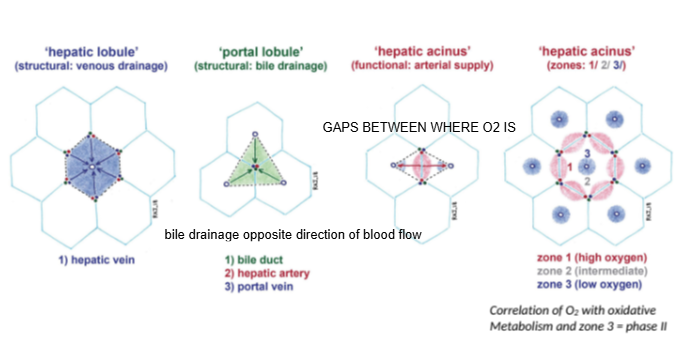
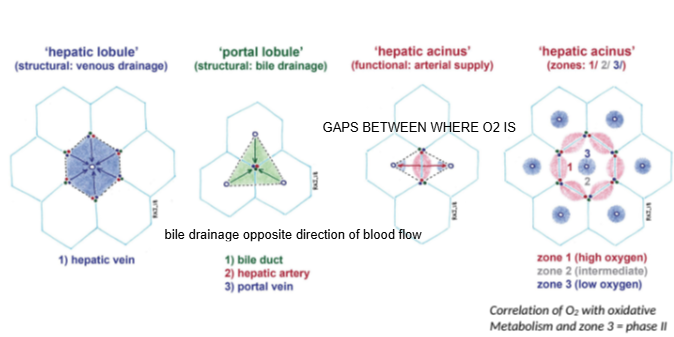
In the hepatic lobule model, blood flows from the portal triad toward which structure?
The central (hepatic) vein.
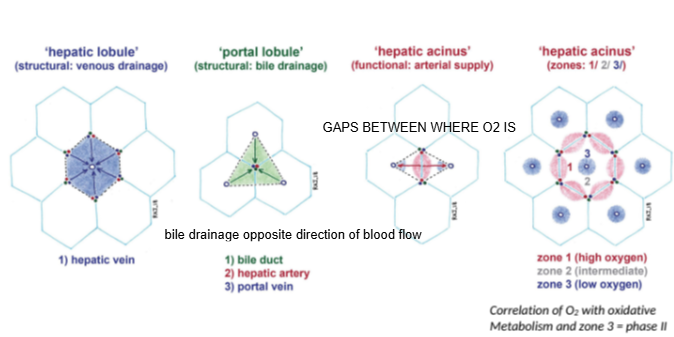
In the portal lobule model, bile drains toward which structure?
The bile duct located at the center of the lobule.
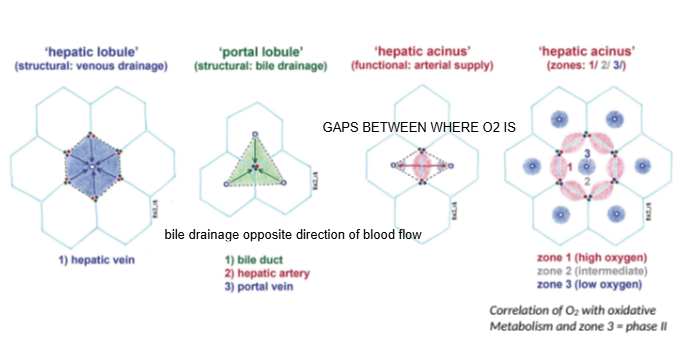
How does bile drainage flow compared to blood flow in the liver?
Bile drainage flows in the opposite direction to blood flow.
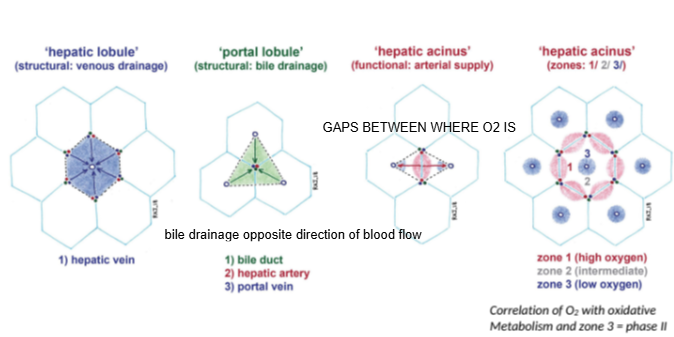
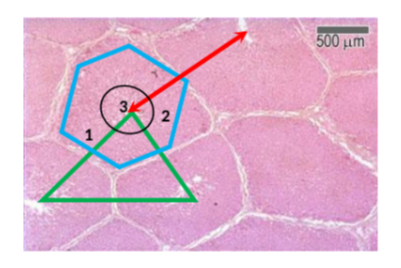
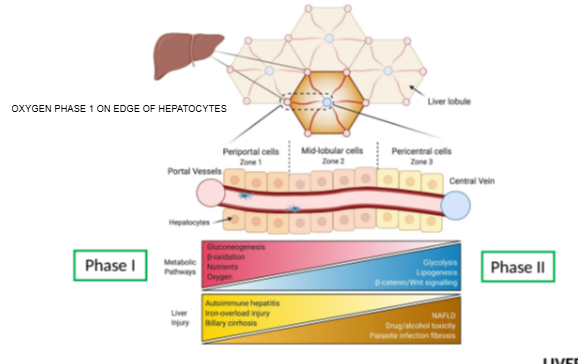
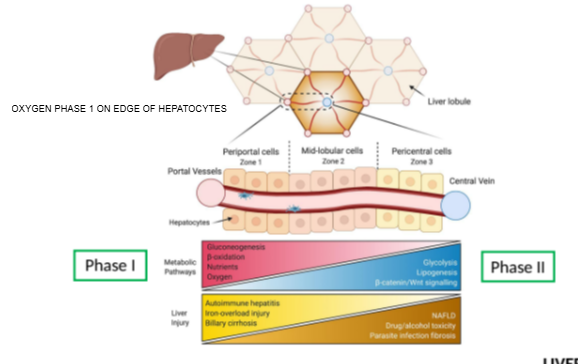
What is the hepatic acinus model primarily used to describe?
Functional zones of oxygen supply and metabolism within hepatocytes.
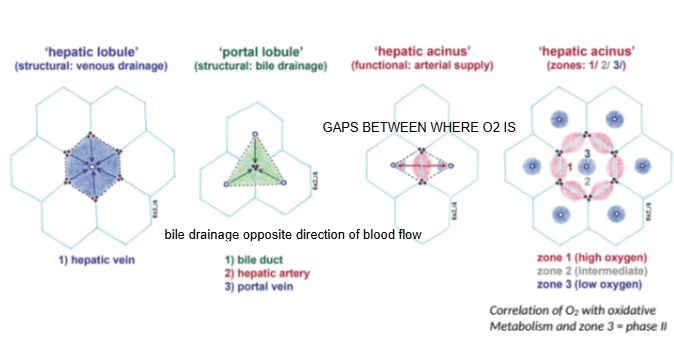
In the hepatic acinus, which zone has the highest oxygen concentration?
Zone 1, closest to the portal triad.
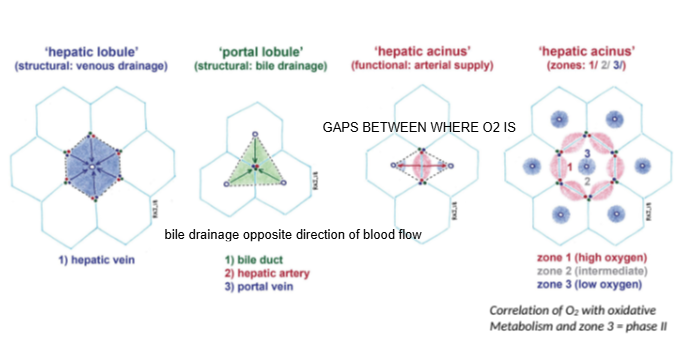
Which metabolic phase relies heavily on oxygen and occurs mainly in Zone 1?
Phase I metabolism (oxidative reactions).
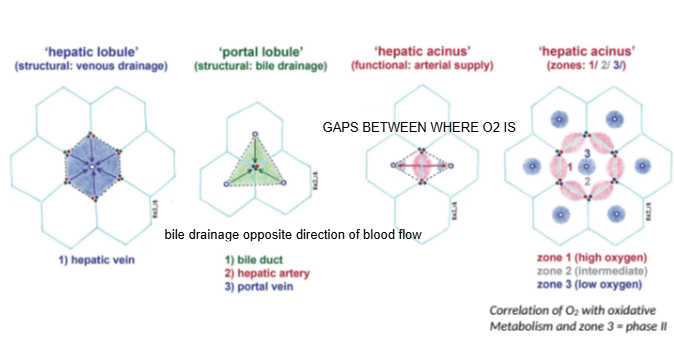
Which metabolic phase is less dependent on oxygen and can occur throughout the liver?
Phase II metabolism.
Which metabolic phase is less dependent on oxygen and can occur throughout the liver?
Phase II metabolism.
Why is the hepatic acinus considered important for understanding drug metabolism?
Because oxygen and nutrient gradients affect how hepatocytes process substances during first-pass metabolism.
What happens to substances absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract in the liver?
They enter through the portal vein, get metabolized in hepatocytes, and either exit into bile for excretion or pass into the central vein for systemic circulation
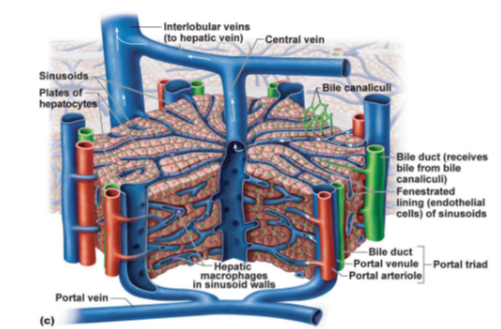
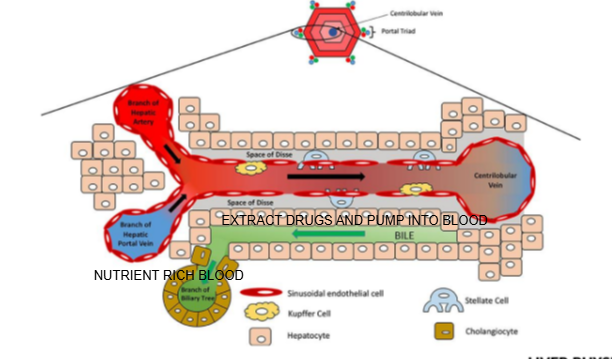
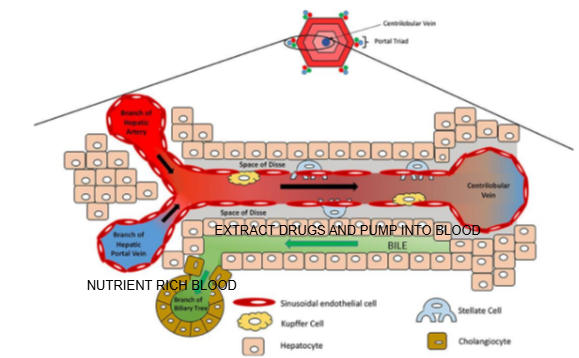
Liver lobule diagram
What is the function of the central vein in the liver lobule?
It collects blood from the sinusoids and drains it into the hepatic vein for return to the systemic circulation.
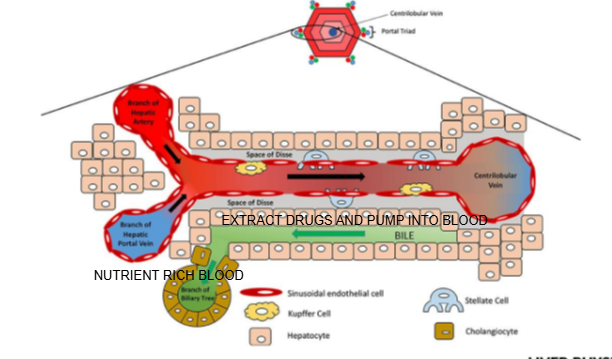
What are the components of the portal triad?
Branch of the hepatic artery, branch of the hepatic portal vein, and bile duct.
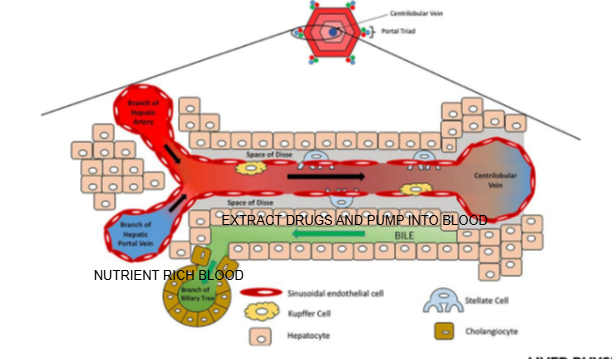
What type of blood does the hepatic artery bring to the liver lobule?
Oxygen-rich blood.
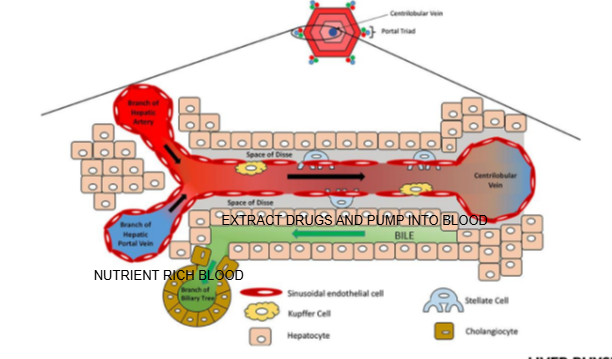
What type of blood does the hepatic portal vein bring to the liver lobule?
Nutrient-rich blood from the digestive tract.
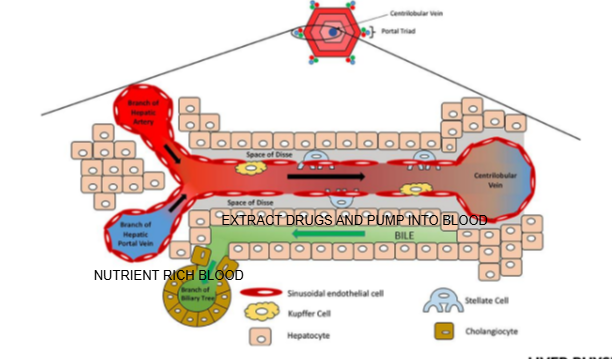
In which direction does bile flow compared to blood flow in the liver lobule?
Bile flows in the opposite direction to blood flow, from the center toward the bile ducts in the portal triad.
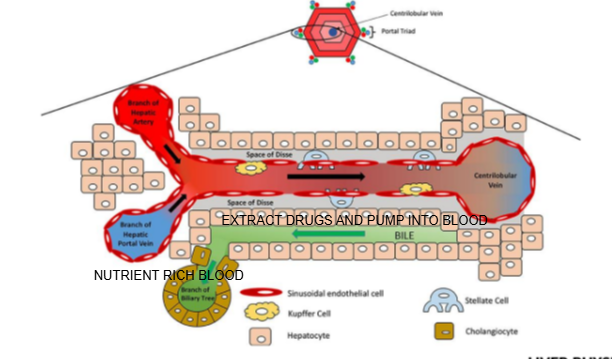
What is the role of cells lining the Space of Disse in drug metabolism?
They can extract drugs from the blood in the sinusoid and pump them into the bile for excretion
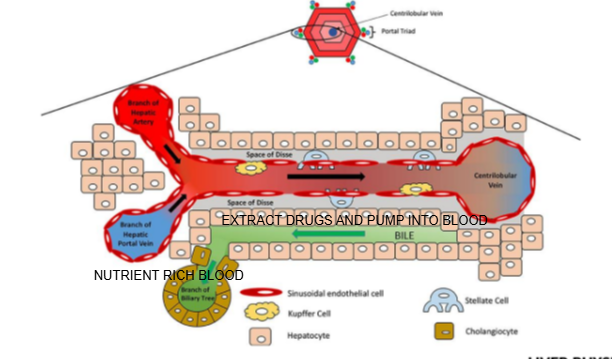
Name two types of specialized cells located in the Space of Disse.
Kupffer cells and stellate cells.
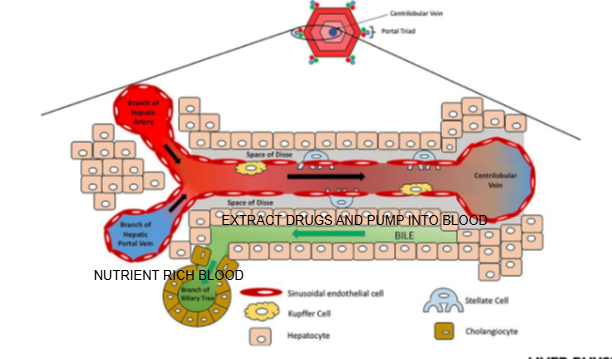
What is the function of Kupffer cells?
They are liver-resident macrophages involved in immune response and clearing pathogens.
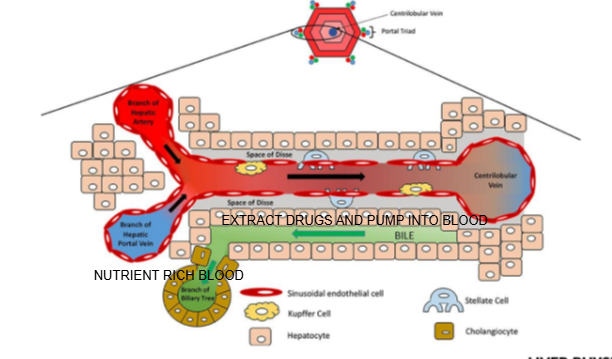
What is the role of stellate cells in the liver?
They store vitamin A and regulate fibrosis; they can become activated during liver injury.
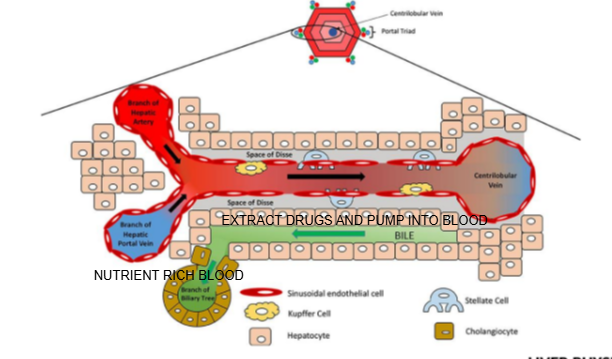
How do hepatocytes contribute to drug metabolism?
Hepatocytes contain enzymes that metabolize drugs, often making them more water-soluble for excretion via bile or urine.
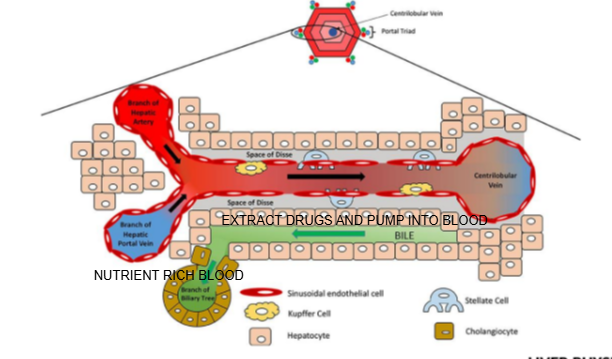
What is the role of cells near the Space of Disse in drug handling?
These cells can extract drugs from the blood in the sinusoid and pump them into bile, aiding in drug elimination.
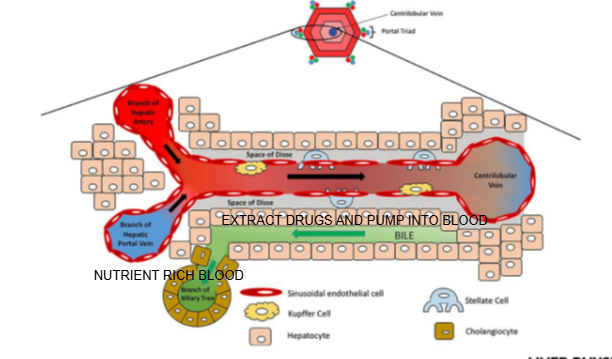
Why is the liver a primary site for drug detoxification?
The liver receives blood rich in absorbed drugs via the hepatic portal vein and has specialized enzymes (like cytochrome P450) for detoxification
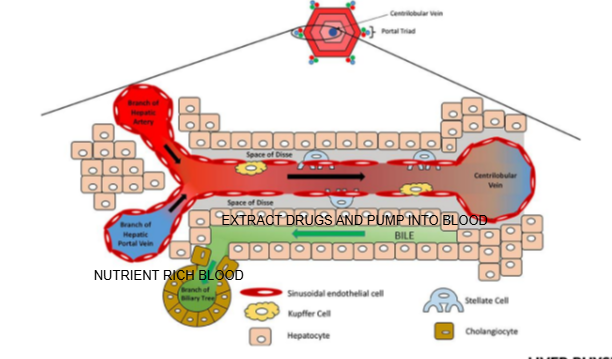
What happens to some drugs after being metabolized by hepatocytes?
They are secreted into bile and excreted into the intestine, where they may be eliminated or reabsorbed (enterohepatic circulation).
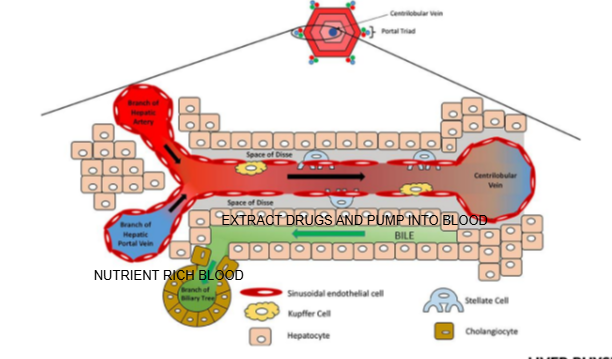
What is the role of Kupffer cells in drug handling?
Kupffer cells can capture and degrade some drug-containing particles or damaged cells, contributing to detoxification.
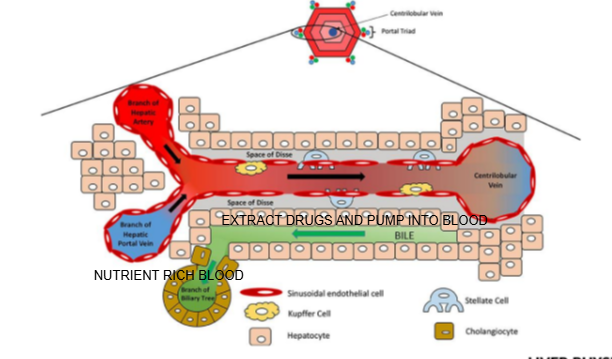
How do drugs enter the liver for metabolism?
Drugs enter through the hepatic portal vein (from the gut) or hepatic artery (from systemic circulation).
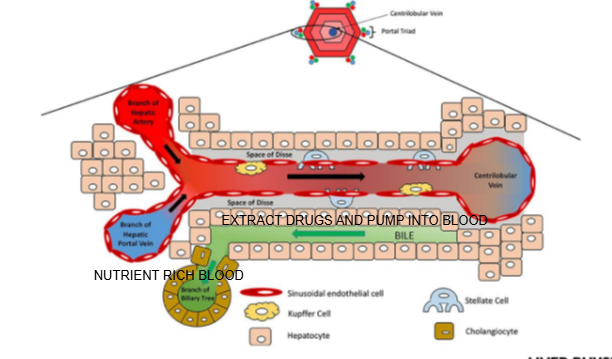
How do bile canaliculi relate to drug excretion?
Metabolized drugs from hepatocytes are pumped into bile canaliculi, which direct them toward bile ducts for excretion
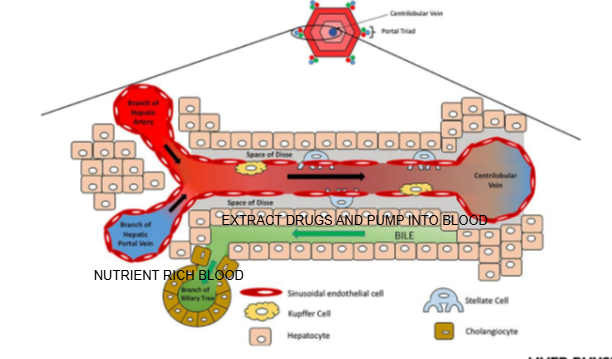
Why is understanding liver structure essential in pharmacology?
Drug absorption, metabolism, detoxification, and excretion all depend on the liver’s blood flow, hepatocyte enzyme activity, and bile secretion pathways.
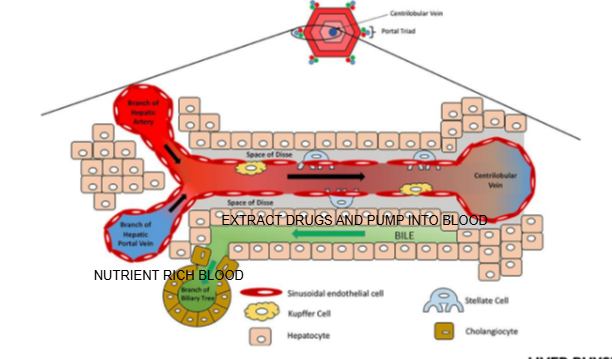
Why do some drugs undergo first-pass metabolism in the liver?
Because nutrient and drug-rich blood from the digestive system passes through the liver via the portal vein before entering systemic circulation.
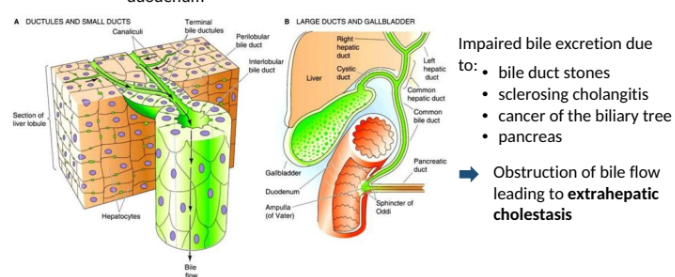
Biliary excretion
Active secretion of endogenous and exogenous drugs/substances from the hepatocytes into the bile and duodenum
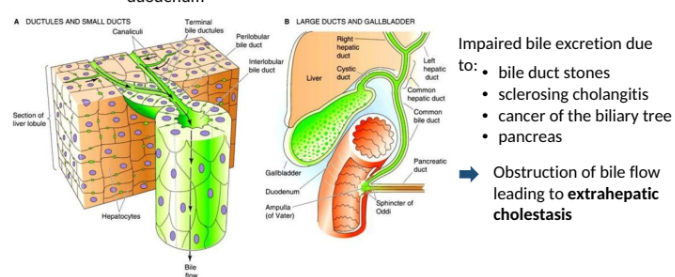
Impaired bile excretion due to:
Bile duct stones
sclerosing cholangitis
Cancer of the biliary flow leading to extrahepatic cholestasis
What is the function of the bile duct in the liver?
The bile duct carries waste products and drug metabolites from hepatocytes to the gastrointestinal tract for excretion
Which cells pump substances like drugs into the bile duct?
Hepatocytes, the liver’s functional cells, pump drugs and waste into the bile duct for excretion.
Name two conditions that can impair bile excretion.
Bile duct stones and decompensated liver failure.
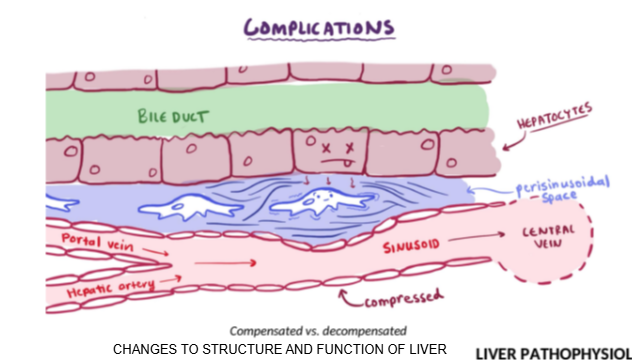
What is the difference between compensated and decompensated liver failure?
In compensated liver failure, the liver is damaged but still functions; in decompensated liver failure, structural damage prevents the liver from performing its normal functions.
In compensated liver failure, how is drug metabolism affected?
Drug metabolism can still occur, although liver function tests may be elevated.
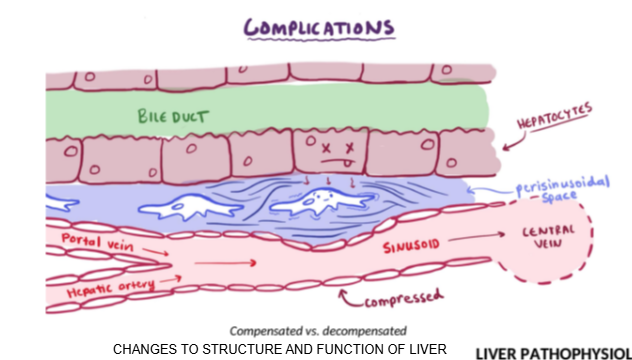
What happens to drug metabolism in decompensated liver failure?
Drug metabolism is severely reduced due to structural damage and impaired blood and bile flow.
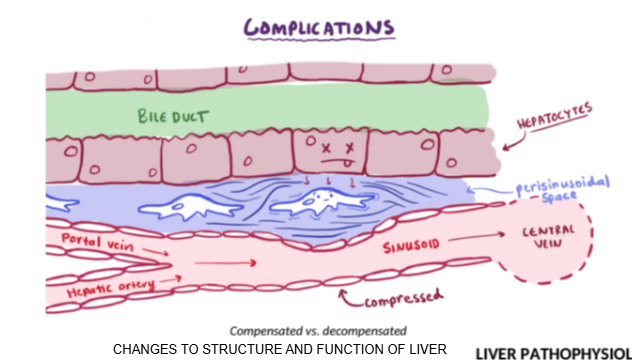
Which two immune-related cells accumulate in the Space of Disse during liver inflammation?
Kupffer cells and stellate cells.
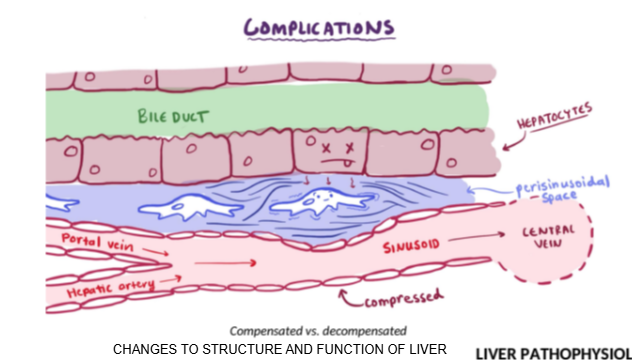
How does inflammation in the Space of Disse affect bile and blood flow?
Inflammation causes fluid buildup and pressure, blocking bile flow through ducts and blood flow through sinusoids to the central vein.
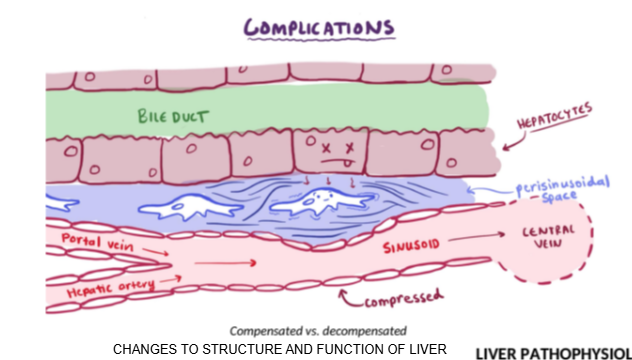
Why is it important to adjust drug doses in patients with decompensated liver failure?
Because impaired bile and blood flow slows drug metabolism and excretion, increasing the risk of toxicity.
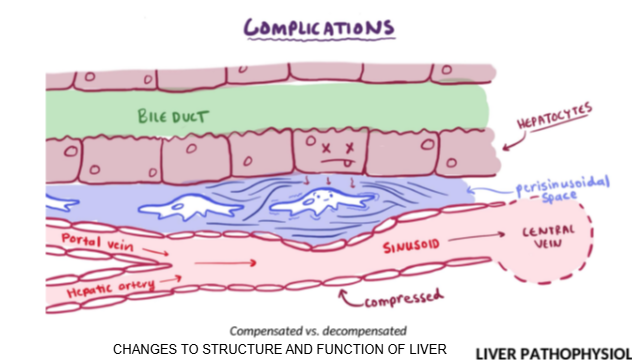
What is the clinical consequence of blocked bile ducts or sinusoid flow in liver failure?
Reduced clearance of drugs, nutrients, and waste, leading to buildup in the body.
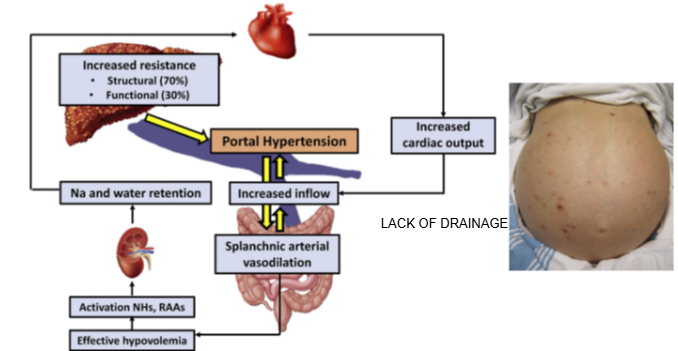
What is portal hypertension?
Portal hypertension is increased pressure in the portal vein due to blocked or impaired blood flow through the liver.

What causes portal hypertension in liver disease?
Damaged liver tissue prevents proper drainage of blood from the portal vein into the liver.
How does portal hypertension affect nutrient and drug absorption?
It reduces the liver’s ability to absorb and process nutrients and drugs from the blood.

What is ascites and how is it linked to portal hypertension?
Ascites is the buildup of fluid in the abdominal cavity, often caused by portal hypertension.
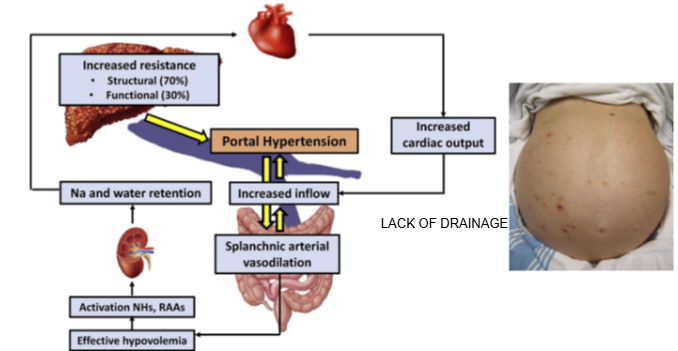
Why does ascites develop in liver disease?
Increased portal vein pressure forces fluid out of blood vessels into the abdominal cavity, leading to swelling
How does liver damage affect hepatocyte function?
Blocked blood flow limits hepatocytes' ability to metabolize nutrients, drugs, and waste.
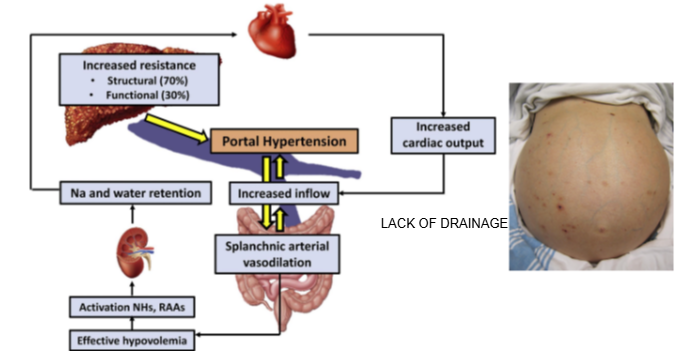
What is a visible clinical sign of portal hypertension?
A swollen abdomen due to ascites.
What is the functional unit of the liver responsible for drug metabolism?
The hepatocyte
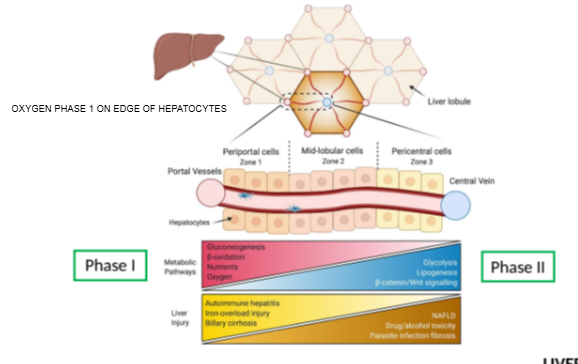
Where do Phase I metabolic reactions mainly occur in hepatocytes?
At the edges of the hepatocyte, near the smooth endoplasmic reticulum.
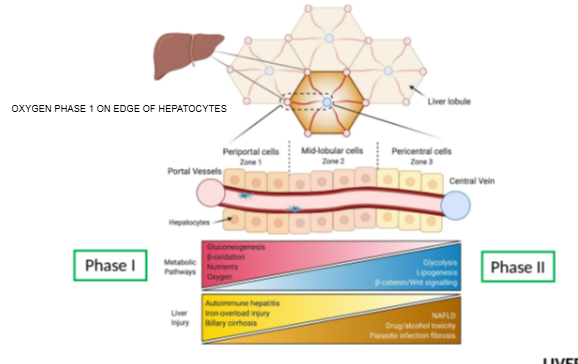
Give an example of a Phase I metabolic reaction.
Oxidation

Where do Phase II metabolic reactions occur in hepatocytes?
Throughout the cell, not restricted to specific areas.
How does liver dysfunction affect Phase II reactions compared to Phase I?
Phase II reactions are less affected by liver dysfunction until severe decompensation occurs.
Until what stage are Phase II reactions relatively unaffected by liver dysfunction?
Until the liver reaches significant decompensation.
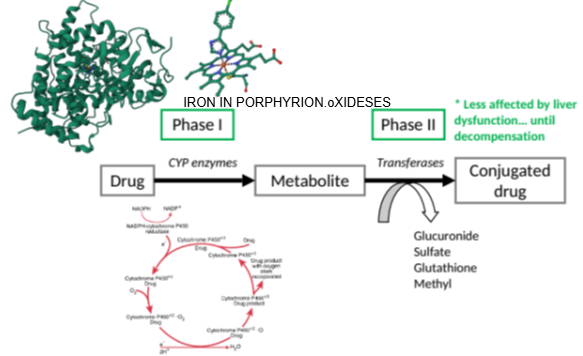
Which enzyme family is responsible for oxidation in Phase I metabolism?
Cytochrome P450 enzymes (CYP enzymes).
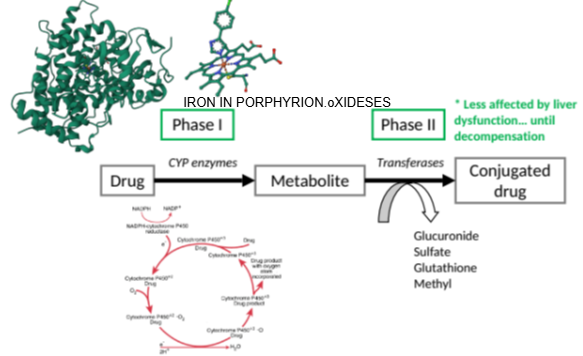
What important structure is found at the core of a cytochrome P450 enzyme?
A porphyrin unit with an iron atom at its center.
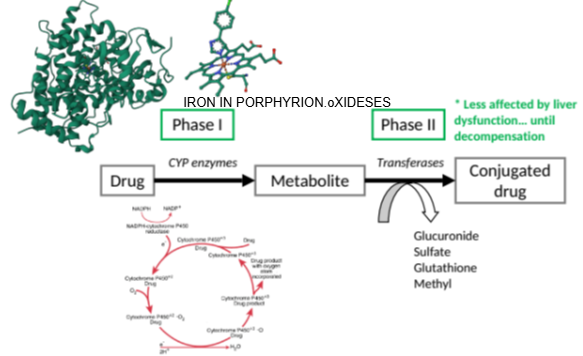
What role does the iron-containing porphyrin unit play in cytochrome P450 enzymes?
It facilitates the oxidation of substances.
What does the cytochrome P450 enzyme require to perform oxidation?
Oxygen.
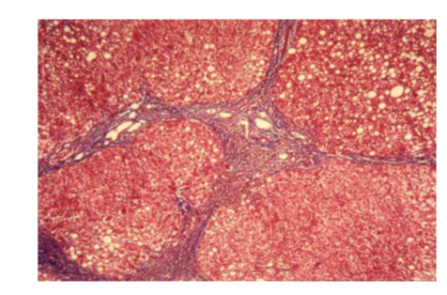
What healthy liver is?
Pink cells
well defined borders
Allow substances to be metabolised as it moves from triad into portal vein
Liver cirrhosis or fatty liver disease
See fat globules
Disruption in the triad
Border lining of each of these hepatocytes are not very clear
Structural changes will affect function
Potential changes in drugs disposition in cirrhotic patients
Liver cirrhosis
Portosystemic shunts (e.g. TIPS)
Impaired renal excretion
Reduced hepatic blood flow
Hypoalbuminemia
Ascites
Portal gastropathy
Reduced cytochrome activity
Portosystemic shunts (e.g. TIPS)
Partial/complete loss of first pass metabolism → increased bioavailibitlity (caution in using medication known to prolong QTc interval)
Reduced hepatic flow
Higher bioavailibility & serum levels
Hyperalbuminemia
Reduced protein binding → increased serum concentration of the free drug
Ascites
Effect on elimination half life
Impaired renal excretion
Increased serum concentrations
Portal gastropathy
Altered drug absorption
Reduced cytochrome activoty
Reduced first pass metabolism or clearance
Bowel edema
Impaired absorption
Intracellular liver enzymes
AST
ALT
GGTP
Alkaline Phosphatase
Increased levels indicate liver damage however paracetamol maximum dose for 2 weeks show increased AST level
Elevated ALT
Indicate liver damage however could be short-term
Mainly found in liver, and so alt tends to be more sensitive for liver damage versus those other ones which can be found elsewhere
Liver can compensate for damage
Alcohol liver damage sign
However, an AST/ALT ratio of 2:1, with elevated GGTP