cellular respiration: pyruvate oxidation and citric acid/krebs cycle
1/9
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
10 Terms
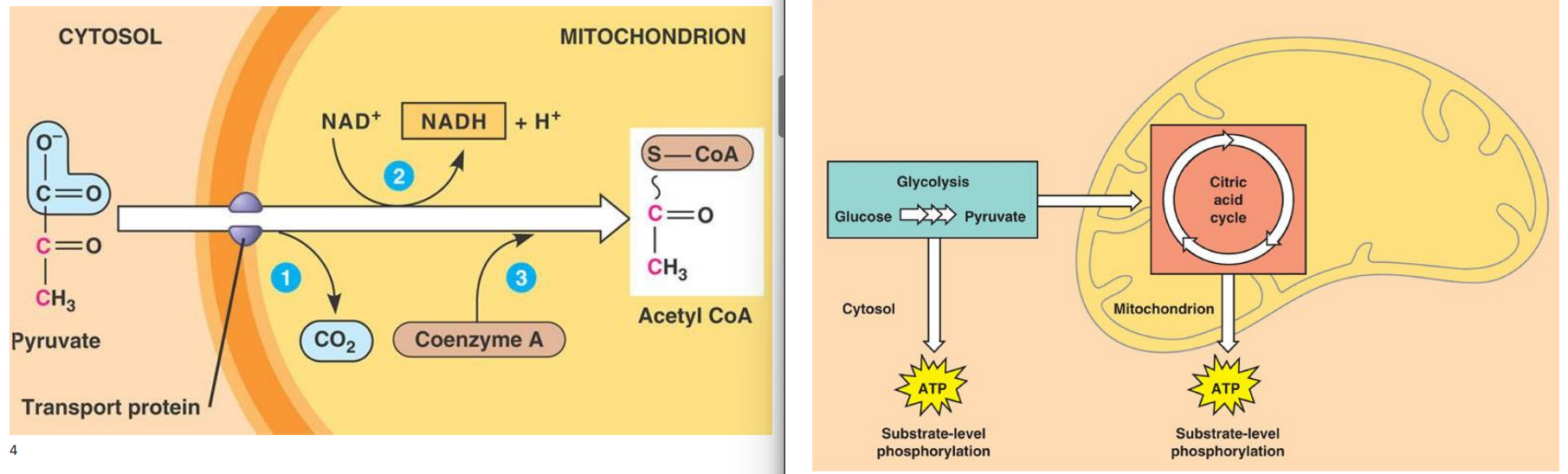
pyruvate oxidation overview
linking stage between glycolysis (anaerobic) and citric acid/krebs (aerobic)
oxygen required
one pyruvate molecule turned into one acetyl group
acetyl group attaches to coenzyme A (carrier molecule) to be acetyl CoA, used in krebs cycle
NAD+ reduced to NADH
occurs in intermembrane space to matrix
stage 2 of cellular respiration
fates of pyruvate
there are many pathways that pyruvate can take
very common molecule
anaerobic yeast: pyruvate decarboxylase, makes alcohol
aerobic yeast: makes acetyl coA, energy or fat
other anaerobic substances: makes lactate (sore muscles)
other aerobic: oxidative decarboxylation of pyruvate into acetyl coA, energy or fat
pyruvate to acetyl-coA formula per one glucose molecule
2 pyruvate + 2NAD+ + 2 CoA → 2 acetyl-CoA + 2 NADH + 2H+ + 2 CO2
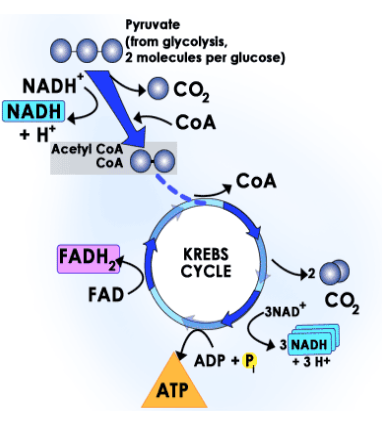
krebs cycle overview
also called citric acid cycle
stage 3 of cellular respiration
aerobic
completes breakdown of glucose
consists of 8 enzyme catalyzed reactions
uss acetyl coA to produce energy in the form of NADH, FADH2, ATP and releases CO2
Hydrogen ions and electrons are stripped and loaded onto NAD+ and FAD to produce NADH and FADH2
2 cycles per one molecule of glucose
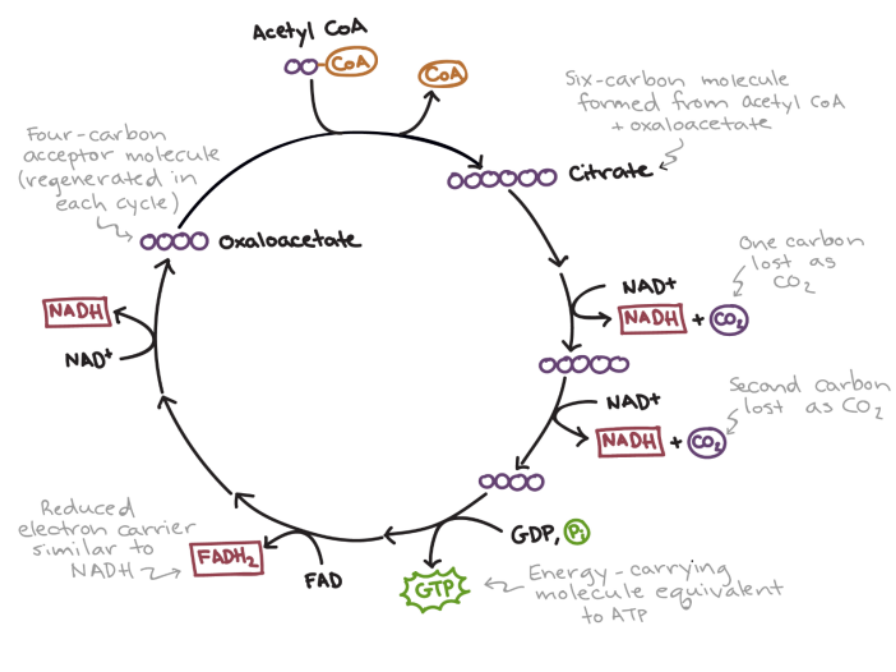
krebs cycle steps
every step includes an enzyme catalyzed reaction that forms a new molecule
enrgy released from ^ reaction used to reduce NAD+ to NADH
2 carbons acetyl coA bond with oxaloacetate form citrate (6 carbon)
citrate loses carbon and produces CO2 + NADH, forms 5 carbon molecule
loses another carbon, prodces CO2 and NADH, forms 4 carbon molecules
GDP, similar to adp, forms gtp, = to atp
FAD reduced to FADH2, electron carrier similar to NADH
NAD+ reduced to NADH
forms oxaloacetate, 4 carbon molecule
acety coA completly changed to CO2 and H2O
end result of krebs cycle per one molecule of glucose
per 1 molecule of glucose
two full turns
2 atp
6 NADH
2 FADH2
FADH2 and NADH electron carriers will make abundance of ATP for ETC
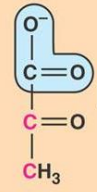
what molecule is this?
pyruvate
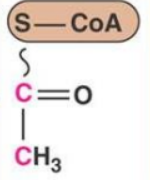
what molecule is this?
acetyl coA
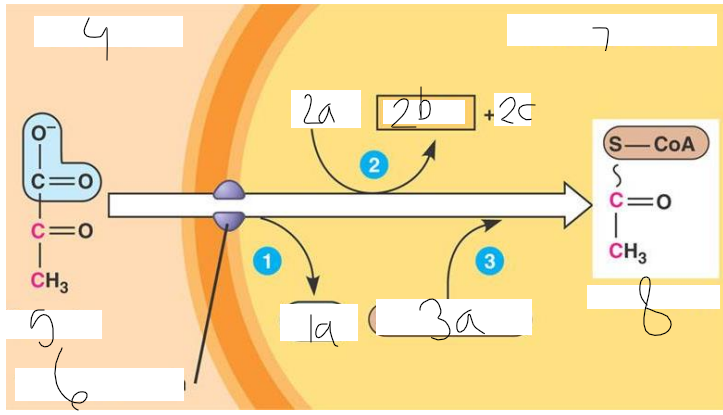
label
pyruvate oxidation
1: carbon dioxide (1a) is released
2: NAD+ (2a) is reduced to NADH (2b) and hydrogen ions are produced (3c)
3: coenzyme A (3a) is added
4: cytosol
5: pyruvate
6: transport protein
7: mitochondrion
8: acetyl coA
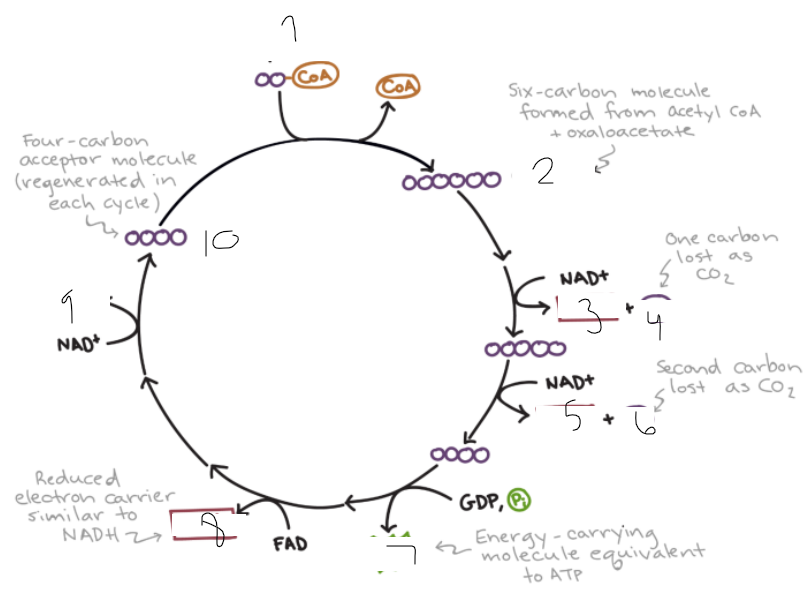
label
krebs cycle
1 = acetyl coA
2 = citrate
3= NADH
4 = CO2
5 = NADH
6 = CO2
7 = GTP, equivalent to ATP
8 = FADH2, similar to NADH
9 = NADH
10 = oxaloacetate