W3 Cornea I
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
What is the structure of the epithelial cells?
Outer layer of cells are fixed to a basement membrane
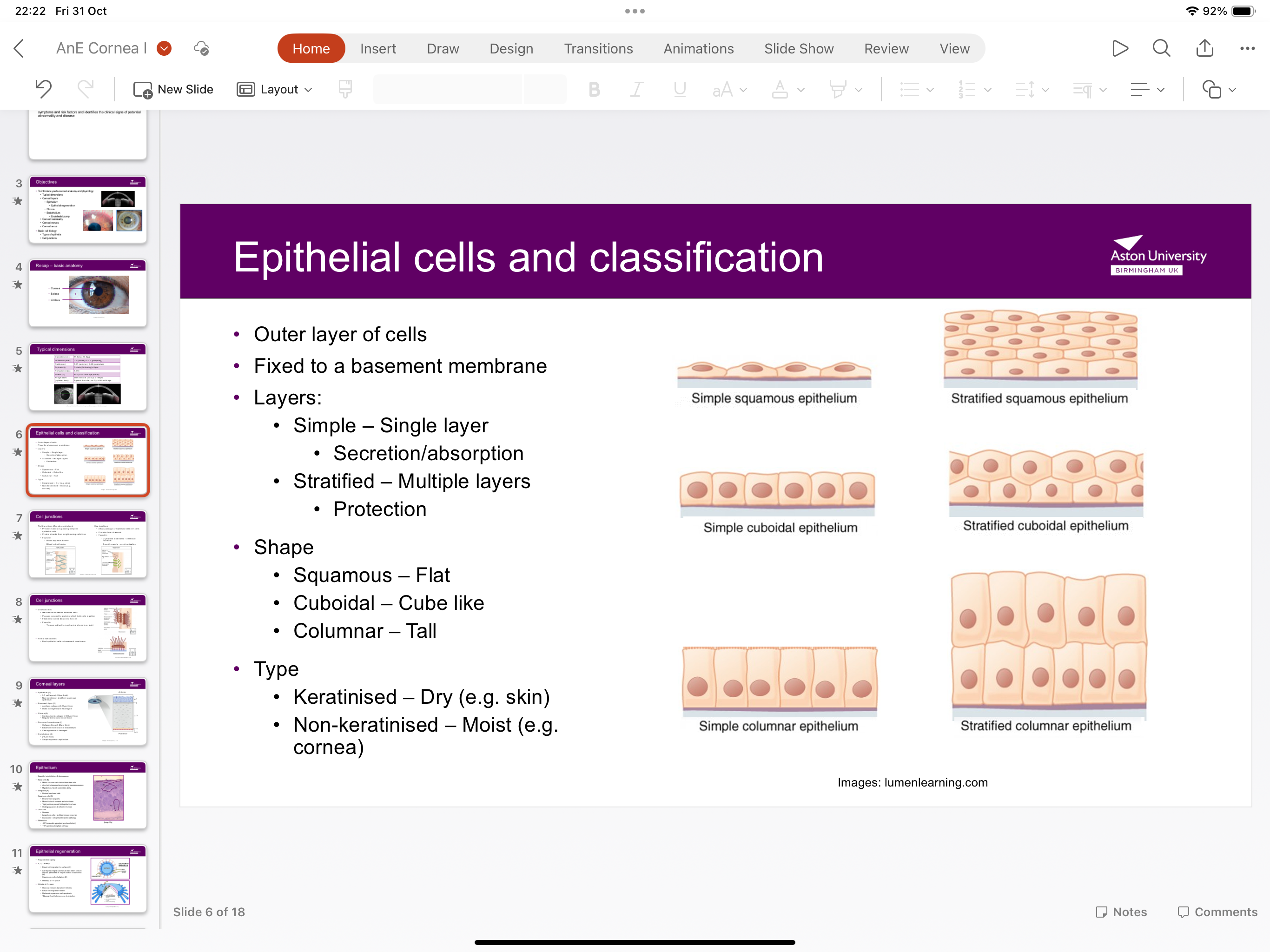
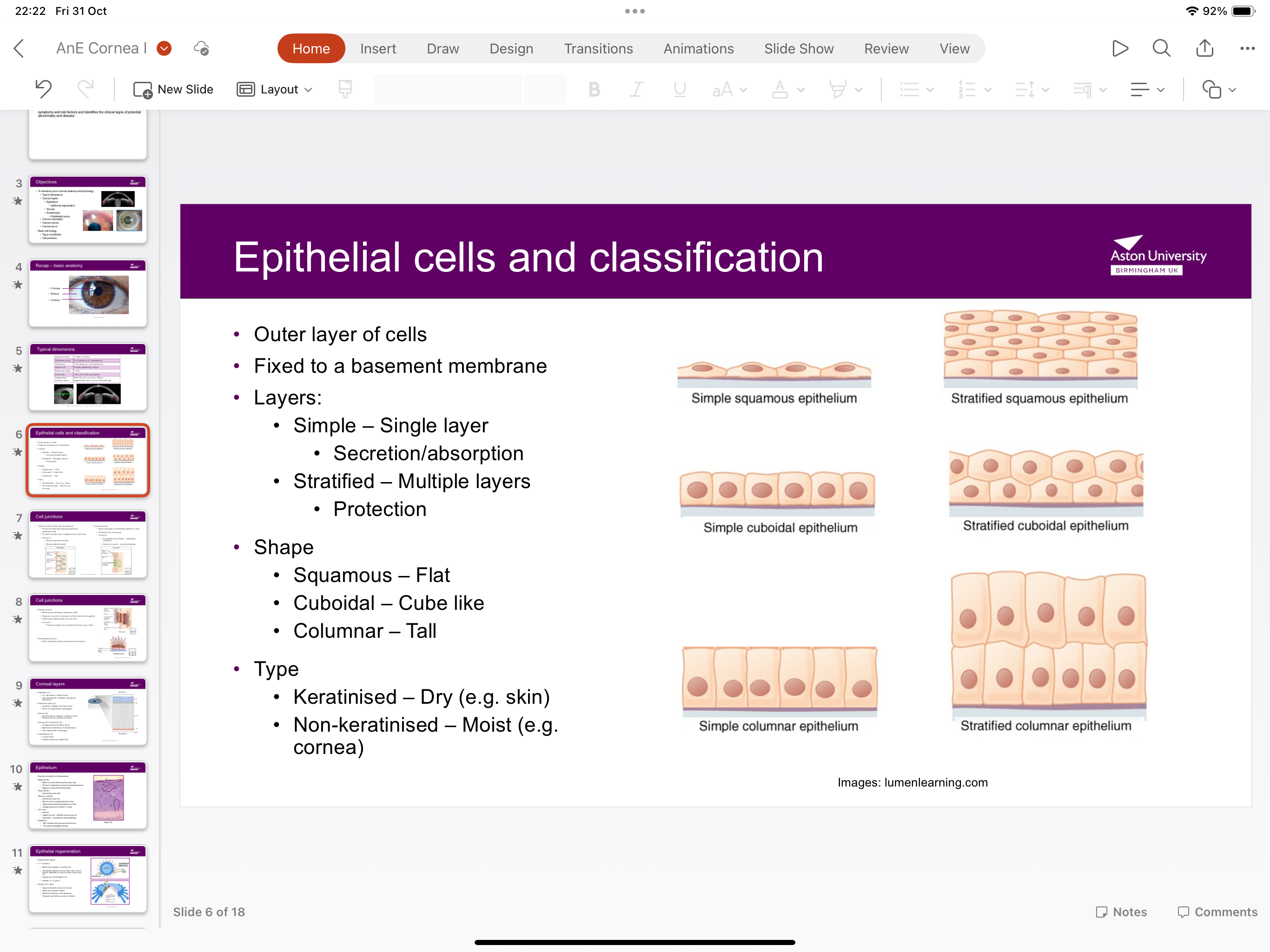
What are the epithelial cell layers?
Simple squamous epithelium has a single layer for secretion and absorption. Stratified squamous epithelium has multiple layers for protection
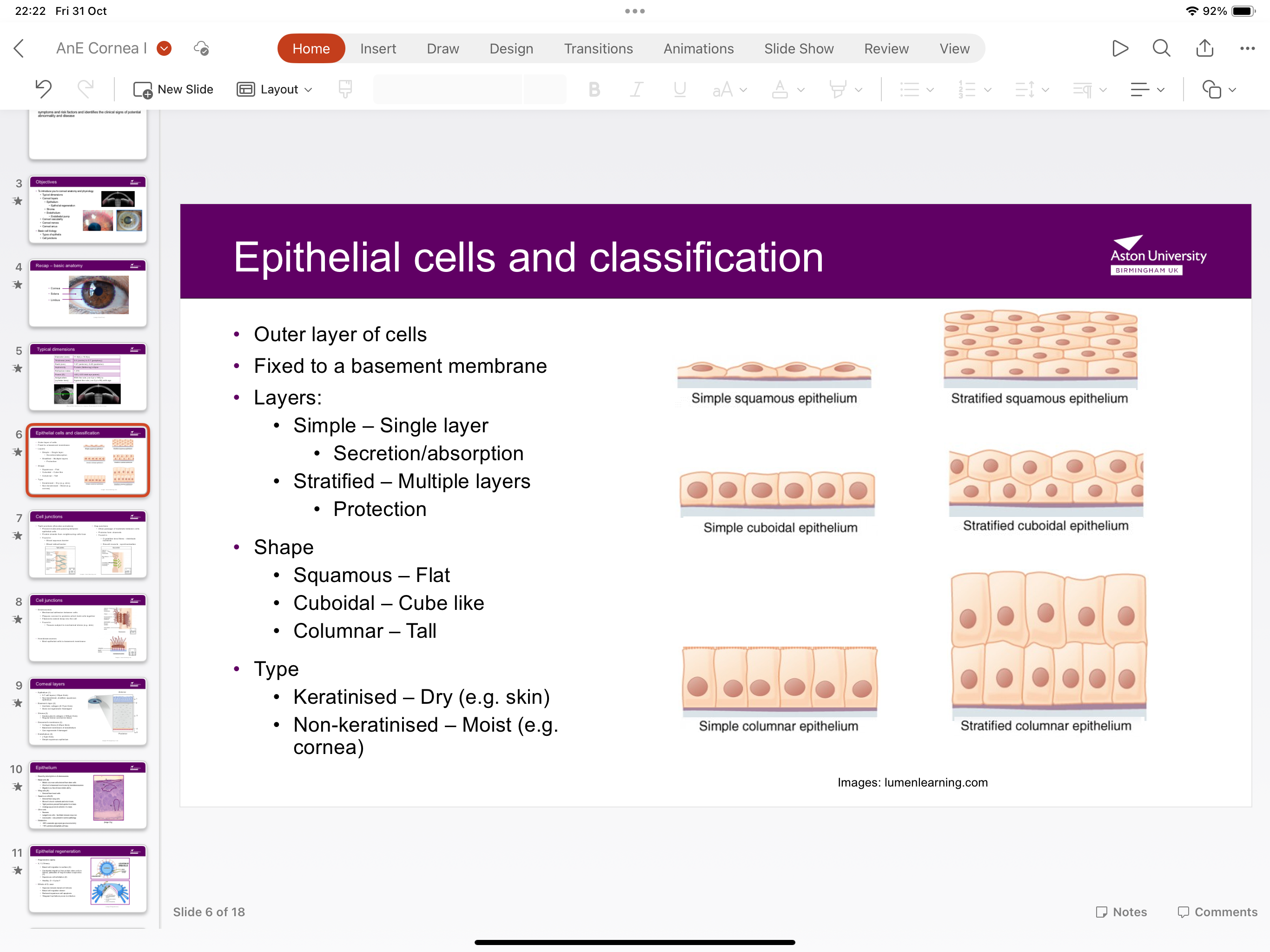
What is the shape of the epithelium?
Squamous epithelium is flat, cuboidal epithelium is shaped like a cube and columnar is tall

Is the cornea keratinised or non-keratinised?
The cornea is non-keratinised so it is moist- skin is keratinised so it is dry
What are tight junctions?
Zonulae occludens prevent molecules passing between epithelial cells as protein strands from neighbouring cells fuse
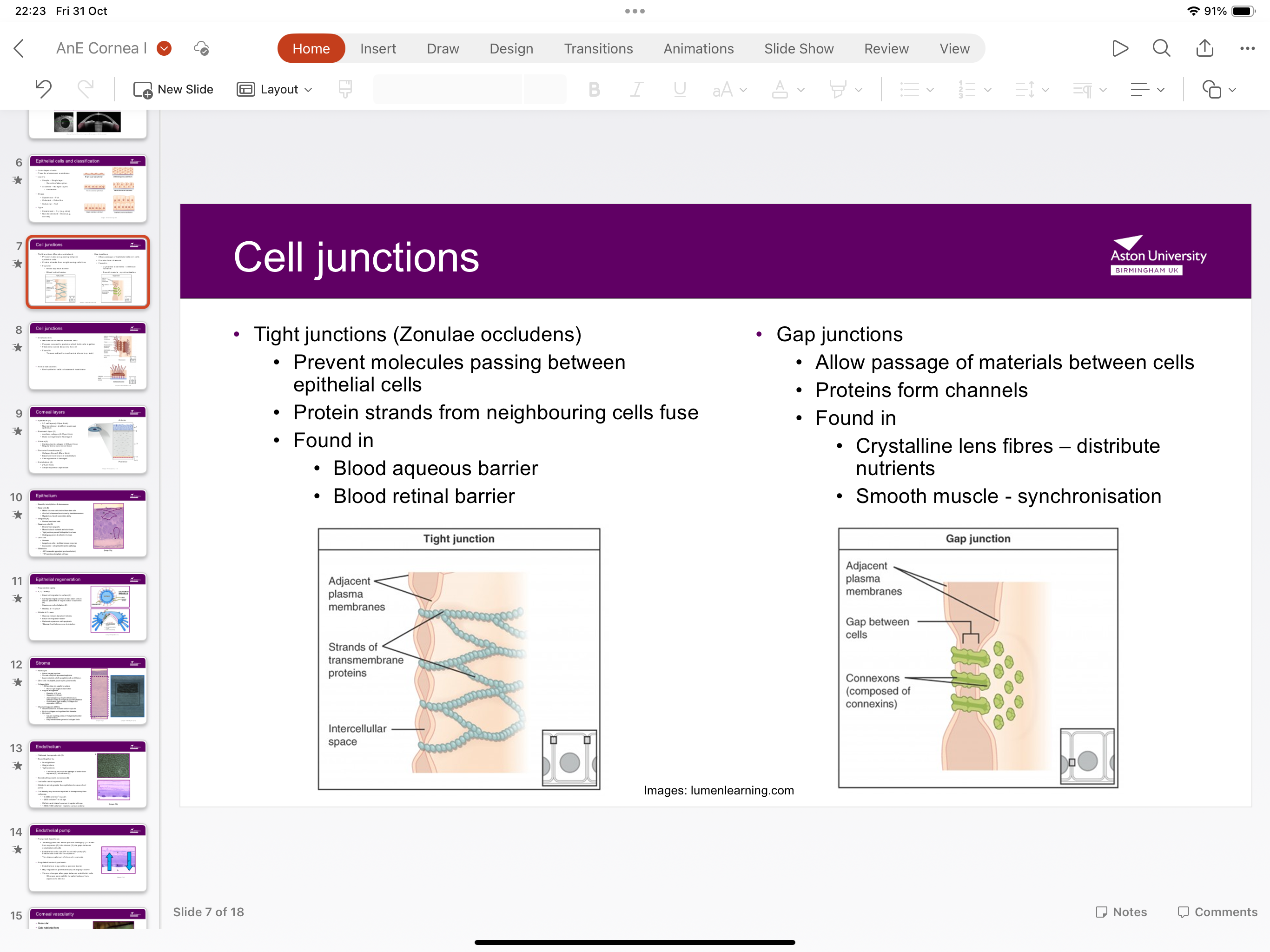
Where are zonulae occludens found?
Blood aqueous barrier and blood retinal barrier
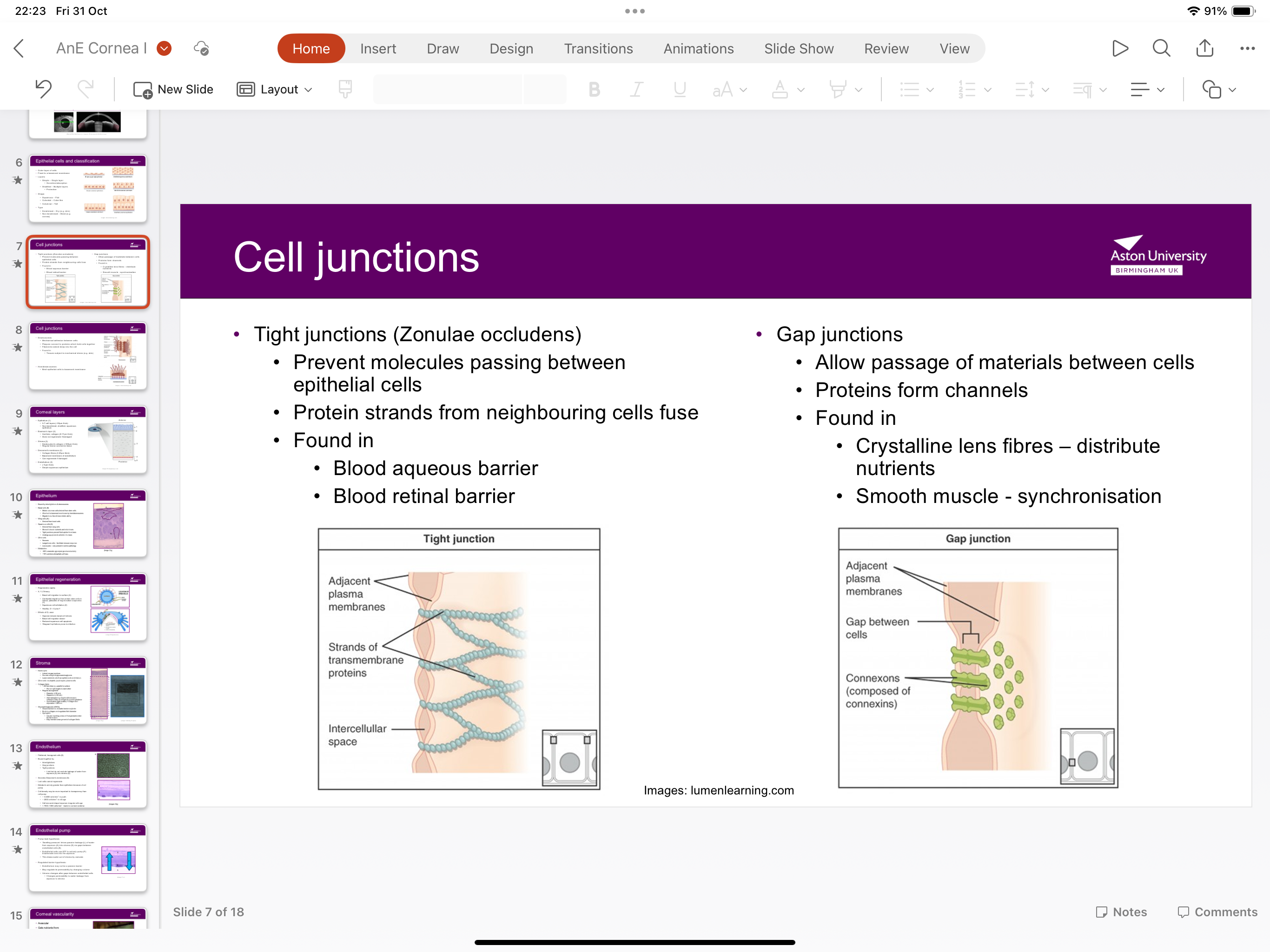
What are gap junctions?
Allows passage of material between cells as proteins form channels
Where are gap junctions found?
Crystalline lens fibres to distribute nutrients and smooth muscle for synchronisation
What are examples of cell junctions?
Desmosomes and hemidesmosomes
What are desmosomes?
Mechanical adhesion between cells- plaque connects to proteins which hold the cell together as filaments extend deep into the cell
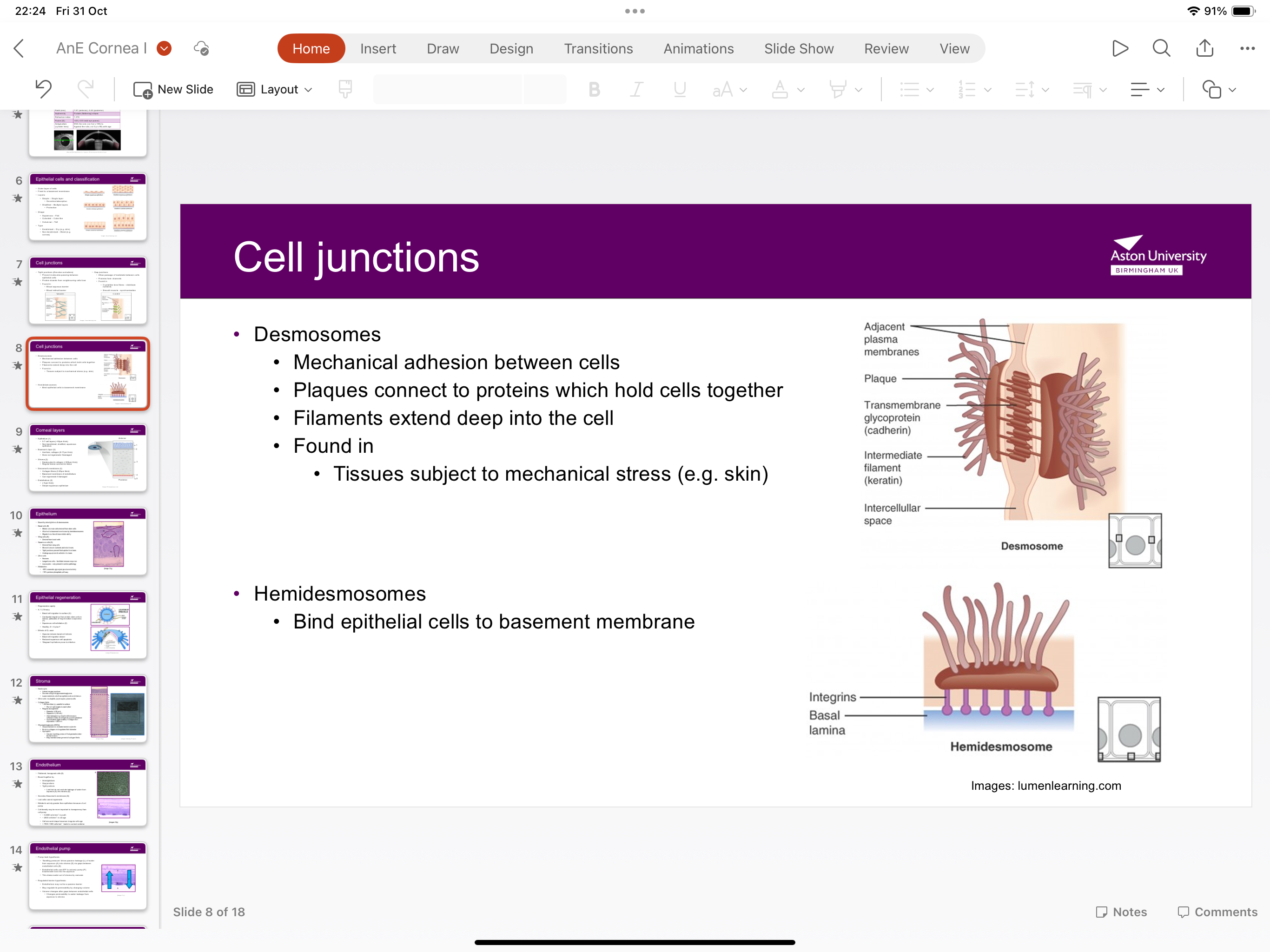
Where are desmosomes found in?
Tissues subject to mechanical stress such as skin
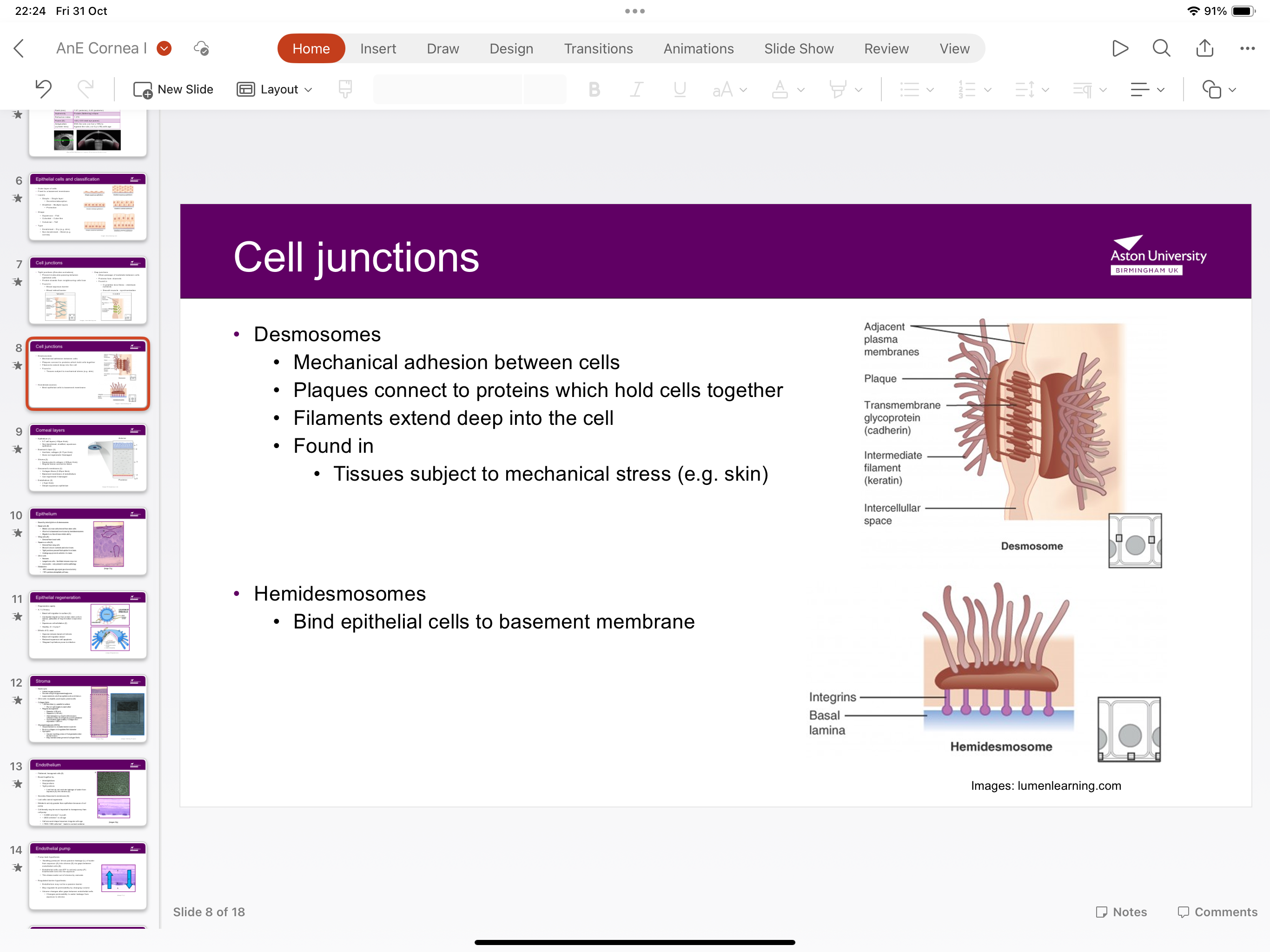
What are hemidesmosomes?
Binds epithelial cells to basement membrane
What are the layers of the cornea?
Epithelium, bowman’s layer, stroma, descement’s membrane and endothelium
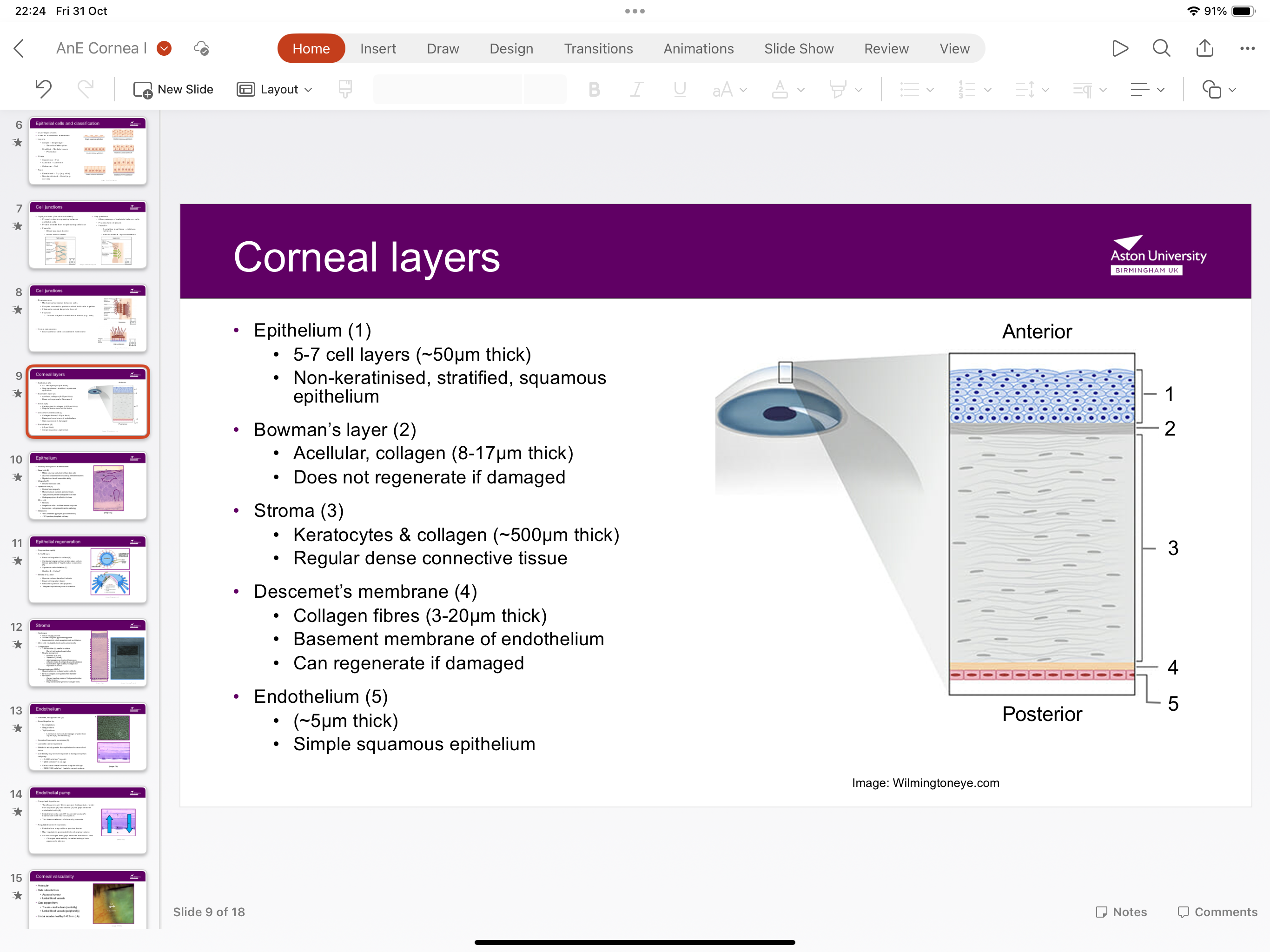
What are features of the epithelium?
5-7 cell layers, 50 micrometres thick
NON-keratinised, stratified, squamous epithelium
What are features of the Bowman’s layer?
Acellular, collagen 8-17 micrometres thick, does not regenerate if damaged
What are features of the stroma?
Keratocytes and collagen 500 micrometres thick, regular dense connective tissue
What are features of the descements membrane?
Collagen fibres 3-20 micrometres thick, basement membrane of endothelium, CAN regenerate if damaged
What are features of the endothelium?
5 micrometres thick, implement squamous epithelium
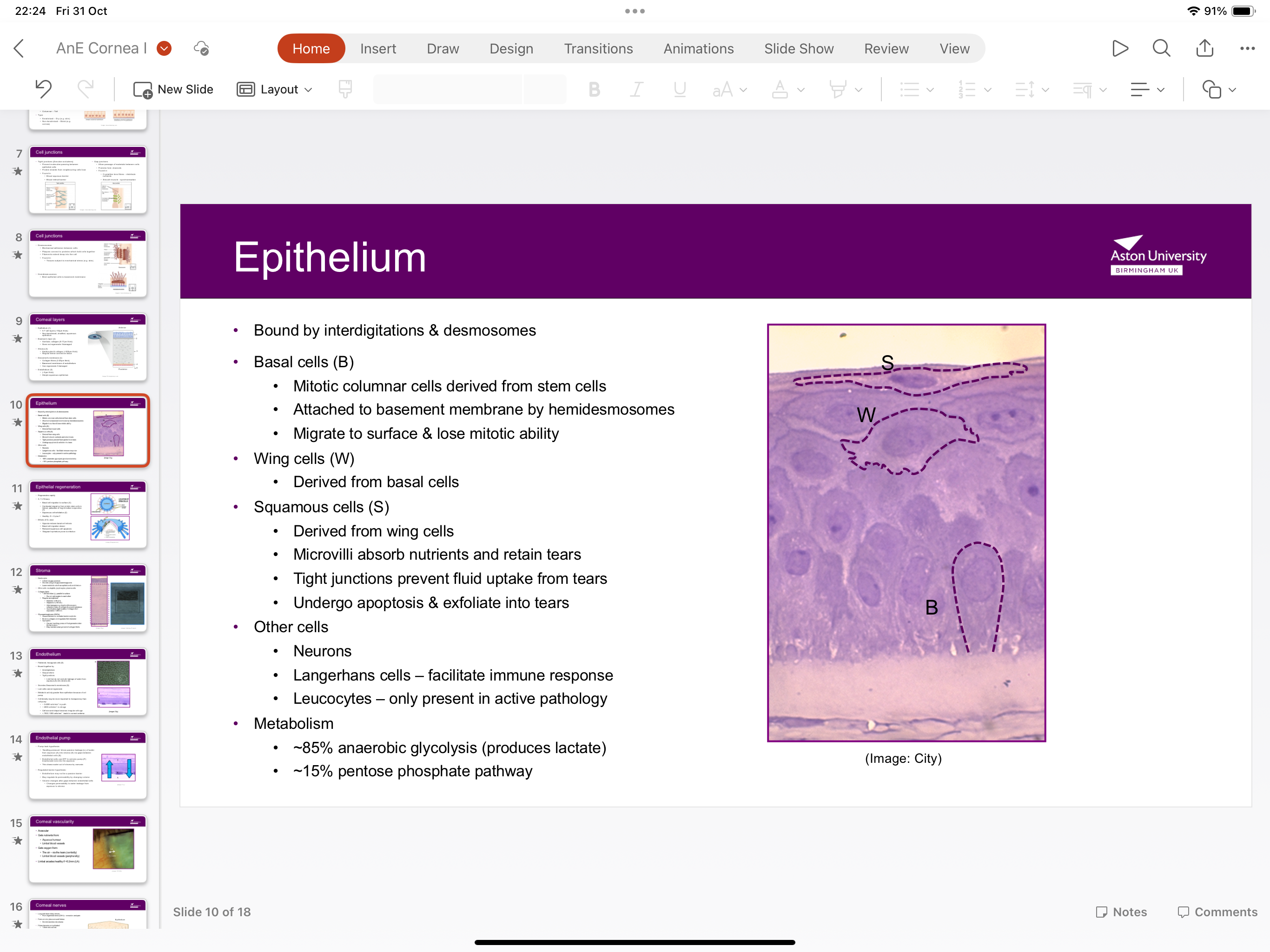
What is the structure of epithelium?
Has basal cells, wing cells, squamous cells langerhans cells, leukocytes, bound by interdigitations and desmosomes
What are basal cells?
Mitotic columnar cells derived from stem cells inch are attached to basement membranes by hemidesmosomes which migrate to surface and lose mitotic ability
What are wing cells?
Derived from basal cells
What are squamous cells?
Derived from wing cells, microvilli absorbs nutrients and retains tears, tight junctions prevent fluid uptake from tears
What do langerhans cells do?
Facilitates the immune response
What is the metabolism in the epithelium?
85% anaerobic glycolysis (producing lactate) and 15% pentose phosphate pathway
What is epithelial regeneration?
Daughter cell migrates from basal cells layer to the surface of epithelium as cells moves from conjunctiva to cornea as surface cells desquamate (come off in flakes)
What is the effect of wearing contact lenses on epithelial regeneration?
Hypoxia reduces basal cell mitosis, basal cell migration slower, ducted squamous cell apoptosis as stagnant prone to infection
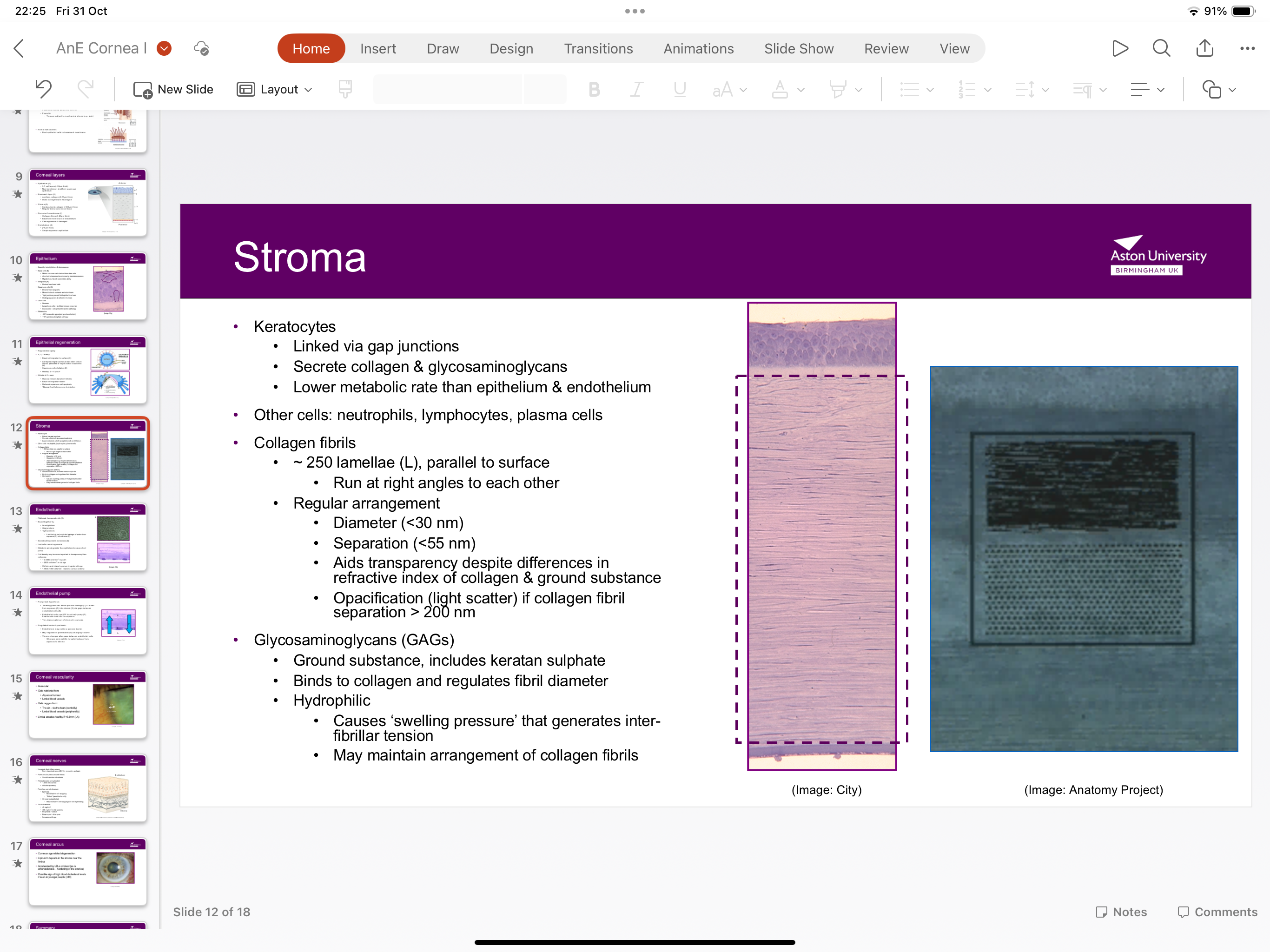
What does stroma contain?
Keratocytes collagen fibrils, GAG’s.
HM: neutrophils, lymphocytes, plasma cells
What are keratocytes within stroma?
Linked via gap junctions, secretes collagen and GAG’s, has lower metabolic rate than epithelium and endothelium
What are GAG’s?
Glycosaminoglycans bind to collagen and regulate fibril diameter- they are hydrophilic cause swelling pressure that hat generates interfibrillar tension and may maintain arrangement of collagen fibrils
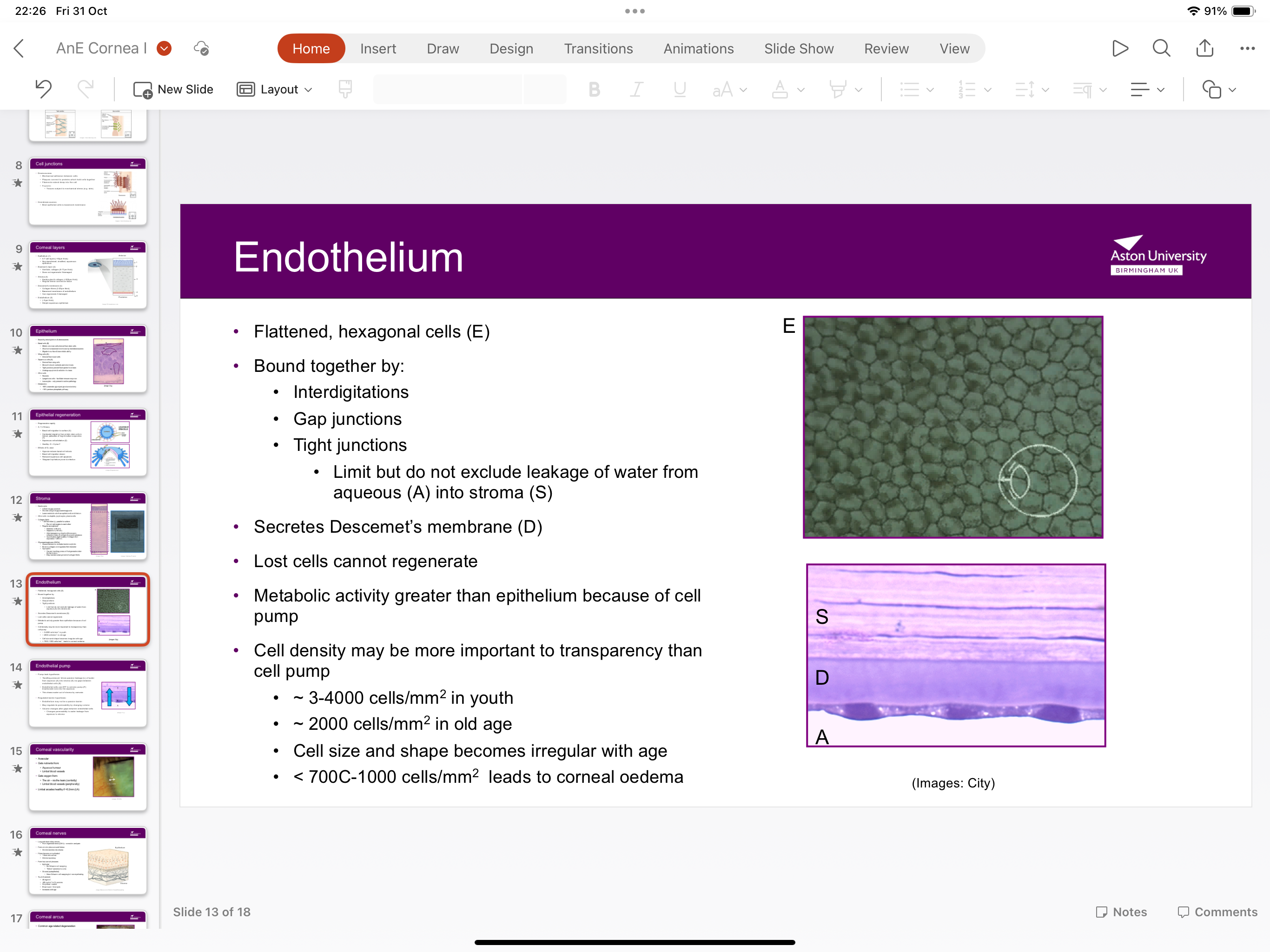
What is the structure of endothelium?
Flattened hexagonal cells which are bound together by gap junctions and tight junctions
What is the function of endothelium?
Limits leakage of water from aqueous into stroma, secretes descements membrane- lost cells cannot regenerate and tabolic activity greater than epithelium because of pump
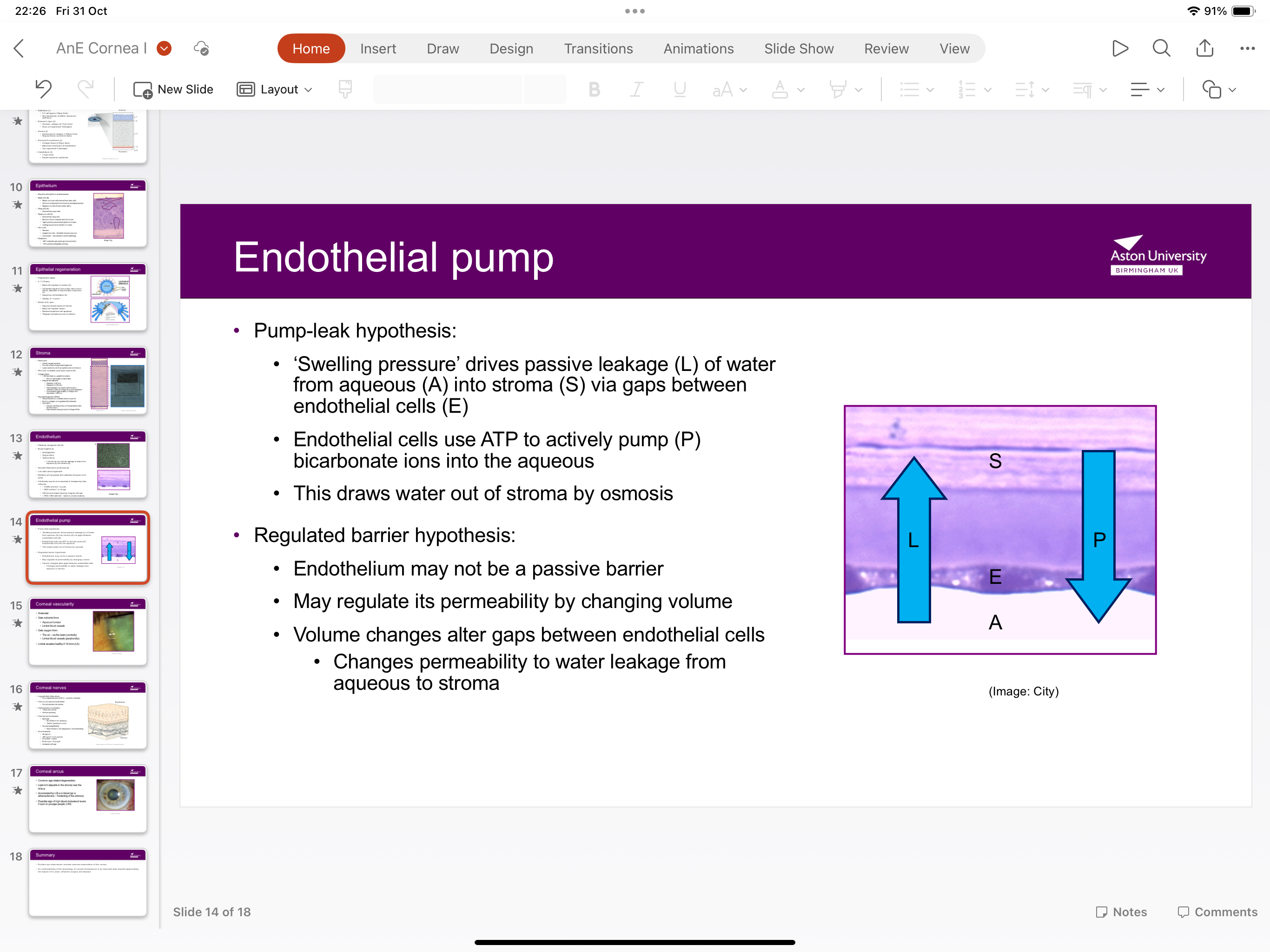
What is the endothelial pump?
Swelling pressure drives passive leakage of water from aqueous into stroma via gaps between endothelial cells as endothelial cells use ATPto actively pump bicarbonate ions into the aqueous, drawing water out the stroma by osmosis
What does avascular mean?
Lack of blood vessels- the cornea is avascular and obtains nutrients from aqueous humour and limbal blood vessels and oxygen from the air via the tears and limbal blood vessels
What is corneal arcus?
Lipid rich deposits in the stroma near the limbus amusing rings in the peripheral cornea
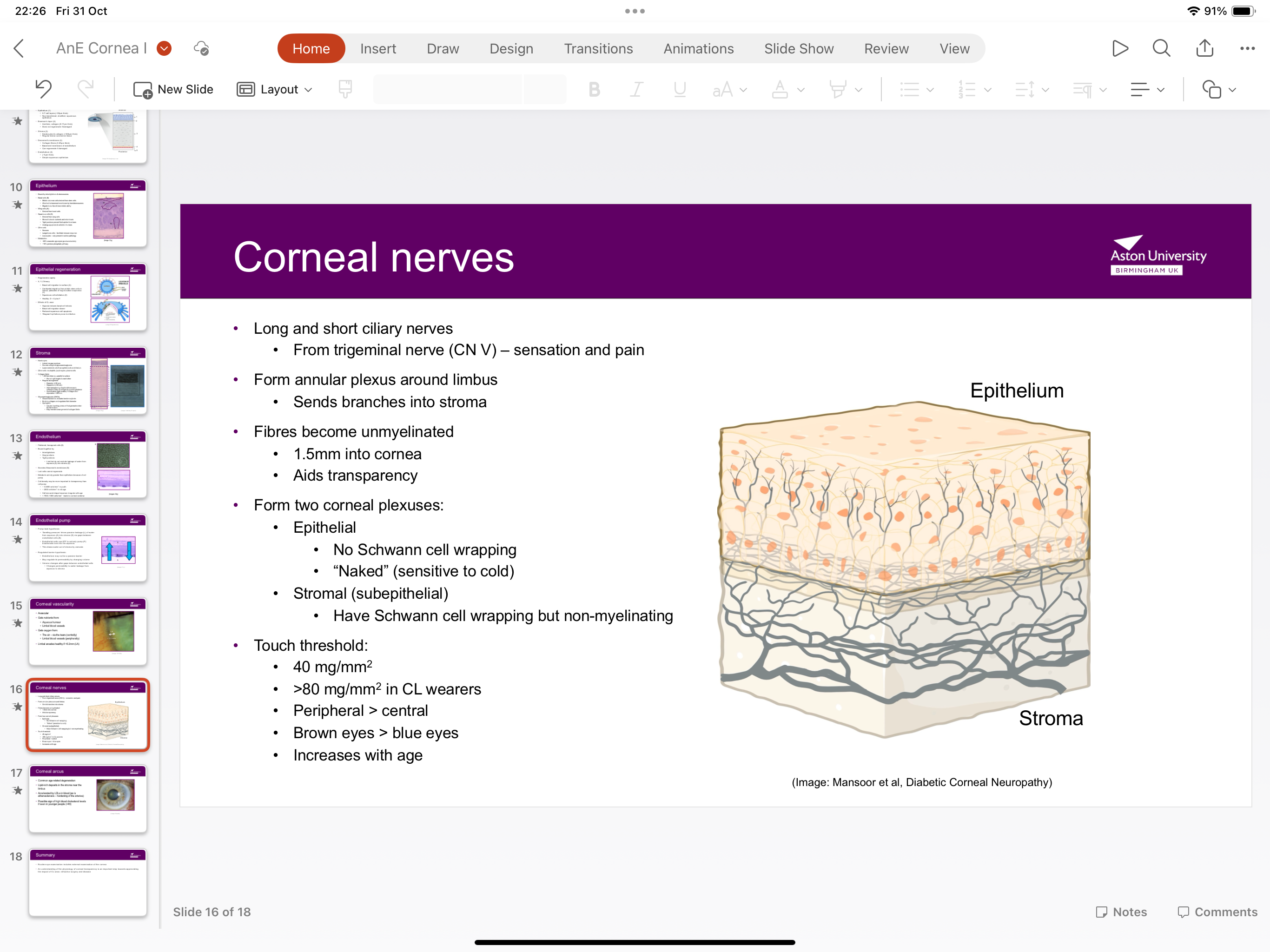
What is the difference between epithelial and stromal plexuses?
Epithelial has no shcwann cell wrapping but stromal has Schwann cell wrapping but non-myelinating
Which nerve is involved in corneal nerves?
CN 5- responsible for sensation and pain
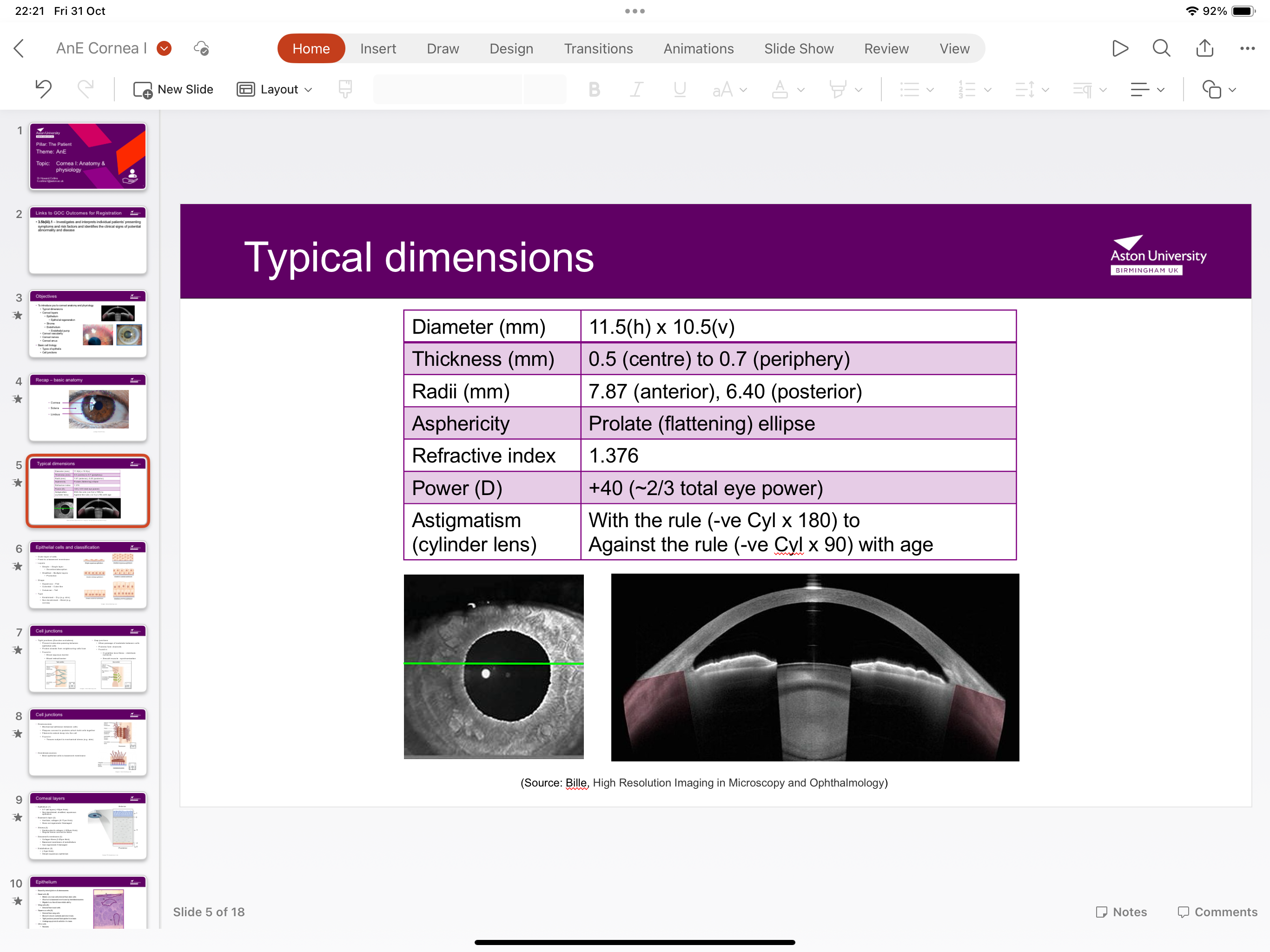
What are the dimensions of the cornea?
enclosed