Blastocyte formation and implantation unfinished
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
12 Terms
Fetal Development:
The first week of pregnancy
1.Ovulation
2.Fertilisation
3.Cleavage
4.Morula
5.Early Blastocyst
6.Late Blastocyte
Cleaveage (Harry Ate Apples Easily)
splitting without cell growth
Series of mitotic divisions of the zygote (occurs in fallopian tube) to form small daughter cells called blastomeres.
Holoblastic: Complete cleavage that divides the whole egg into distinct and separate blastomeres due to absence of yolk. In hen’s egg the cleavage is incomplete (meroblastic) due to presence of large amount of yolk.
Asymmetrical: Blastomeres are unequal in size (unequal cytoplasm distribution)
Asynchronous: Occurring at different times
Each cleavage takes around 12 to 24 hours to complete.
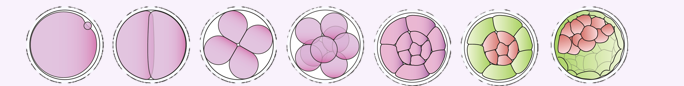
Cleavage ( what happens before it?)
Approximately 24 hours after fertilization in the fallopian tube, the zygote travels down the fallopian tube and begins to divide by mitosis in a process called cleavage
morula
By day 3/4, cleavage results in the formation of a solid, spherical mass of cells known as a morula.
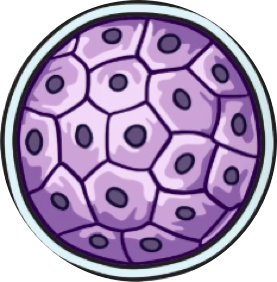
blastocyst
By day 5 a blastocyst has been formed and reaches the uterus
A blastocyst is a hollow ball of cells that is surrounded by a fluid filled cavity
Inner cell mass (embryoblast)
Group of 30 or so stem cells that will differentiate into the different body cells to form the embryo
trophoblasts
cells that surround the blastocyst
what happens after blastocyst remains free for 2-3 days?
implants into then sinks into the soft endometrium (uterine lining)
allows it to gain nourishment for growth and development by absorbing nutrients from the glands and blood vessels of the uterine lining
outer layer of cells forms the placenta and embryonic membranes
role of hormones in this process?
After implantation, trophectoderm release the pregnancy hormone hCG (human chorionic gonadotrophin).
hormone detected by pregnancy tests to confirm pregnancy
maintains the corpus luteum, continues secrete progesterone which maintains the uterine lining (no period)
ectopic pregnancy
Implantation anywhere outside the uterus =embryo won’t be develop to term
Growth inside uterine tube can rupture=fertility problems for the woman
necessary to remove the embryo asap for mother’s immediate health/ long-term fertility.
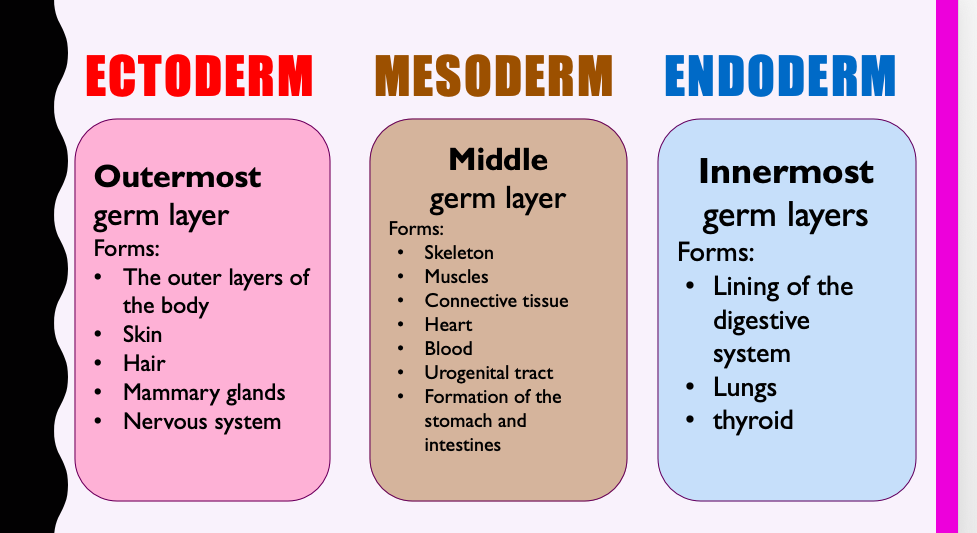
what are primary germ layers?
•While the blastocyst is implanting in the uterus, the inner cell mass changes = formation of three cell layers
• ectoderm, mesoderm and endoderm = embryonic tissues, will differentiate into tissues and organs of the body
what organs/tissue does each form?