Chemistry Unit 1 and 2 Test
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
58 Terms
Atom
Smallest unit of matter. Has protons, neutrons, electrons.
Element
Pure substance made of only one type of atom.
Compound
Pure substance of 2+ different elements chemically bonded.
Molecule
Group of atoms bonded together (can be same element or different).
Pure substance
Either an element or a compound, has fixed composition.
Mixture
Physical combo of substances, no fixed ratio.
Homogeneous mixture
Uniform (ex: salt water).
Heterogeneous mixture
Not uniform (ex: oil + water).
Physical properties
Observed without changing substance (melting point, density, color).
Chemical properties
Observed by changing substance (flammability, reactivity).
Physical changes
Doesn't change identity (melting, cutting, dissolving).
Chemical changes
New substance formed (burning, rusting, reacting).
Intensive properties
Don't depend on amount (density, boiling point).
Extensive properties
Depend on amount (mass, volume).
Phase diagram
Graph of pressure vs. temperature showing states of matter.
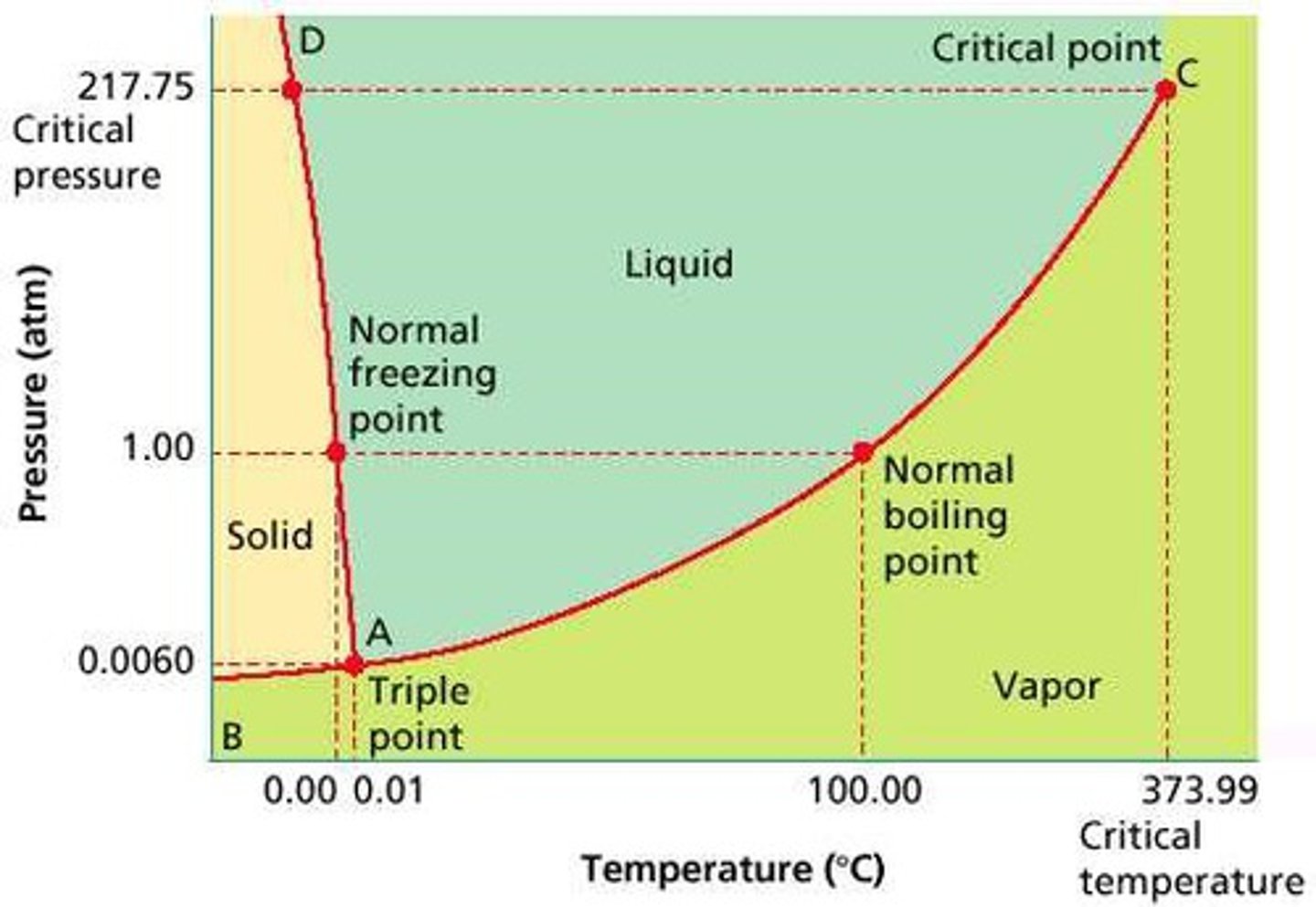
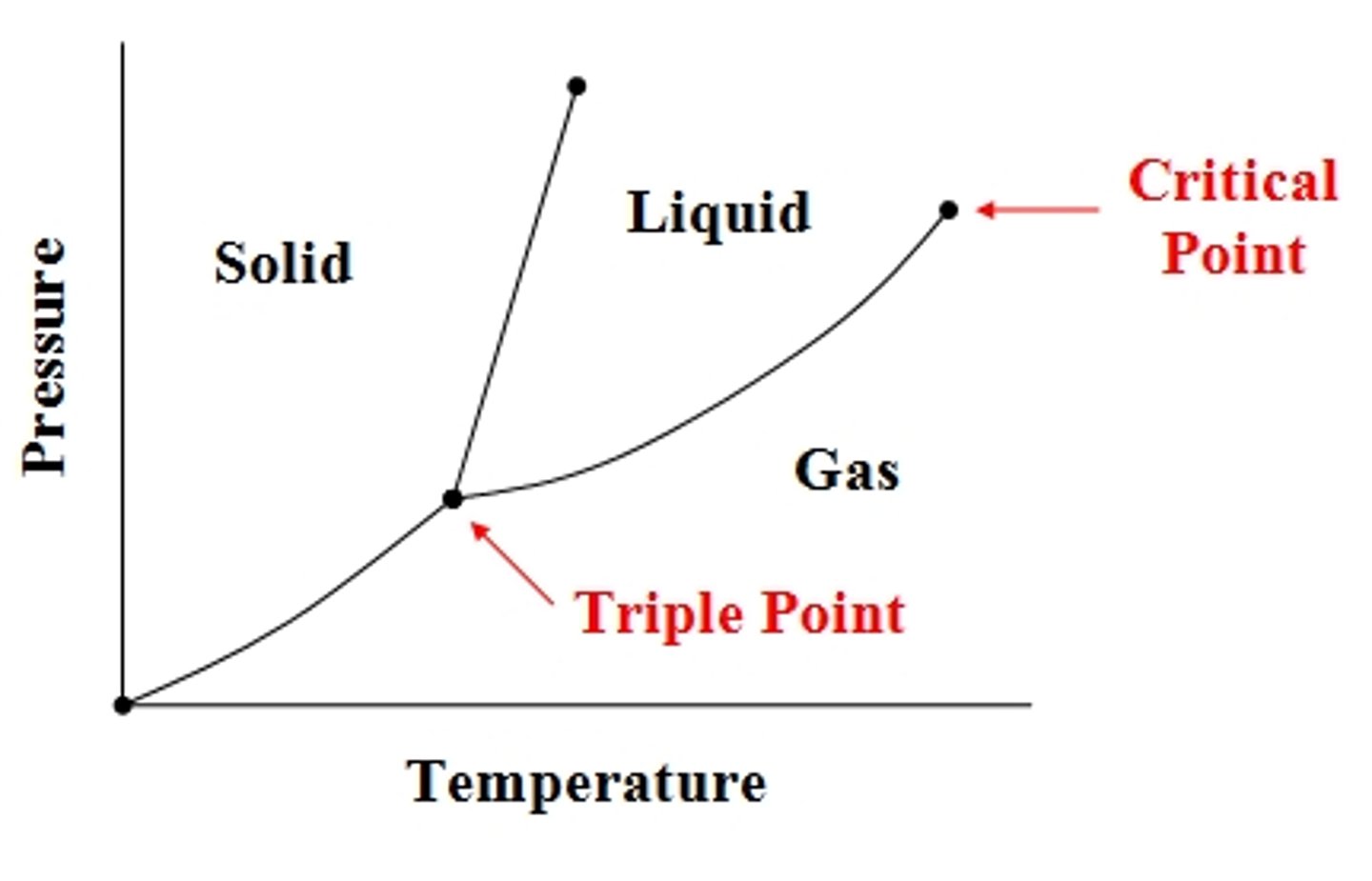
Triple point
Temp + pressure where solid, liquid, gas coexist.
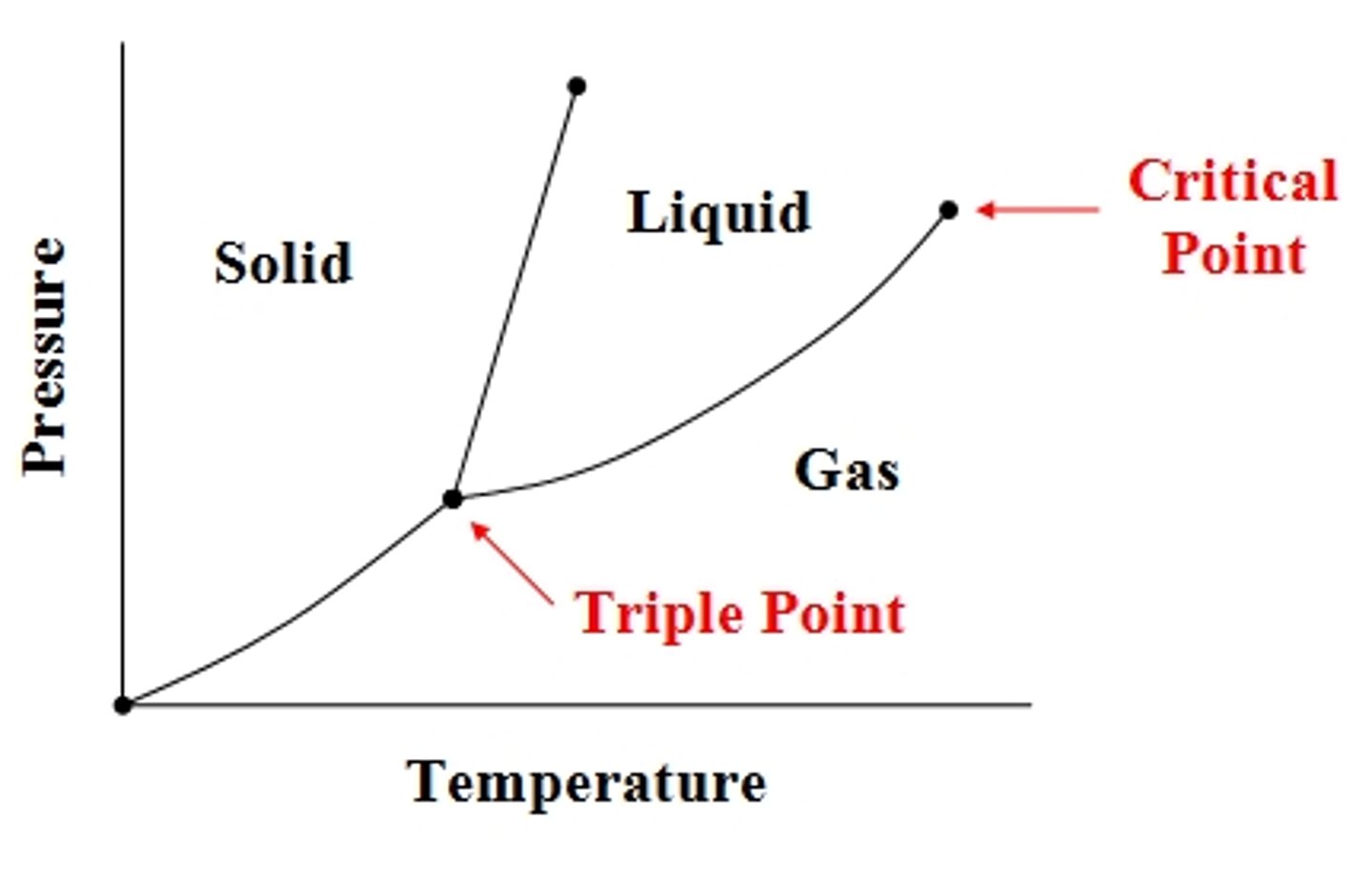
Critical point
End of liquid-gas line; above it you can't tell liquid/gas apart.
Democritus
First idea of atom (indivisible).

Dalton
Atomic theory (atoms of same element are identical, atoms combine in whole ratios).

Thomson
Discovered electron, "plum pudding model."
Rutherford
Gold foil → discovered nucleus (dense + positive).
Bohr
Electrons in fixed energy levels (like orbits).
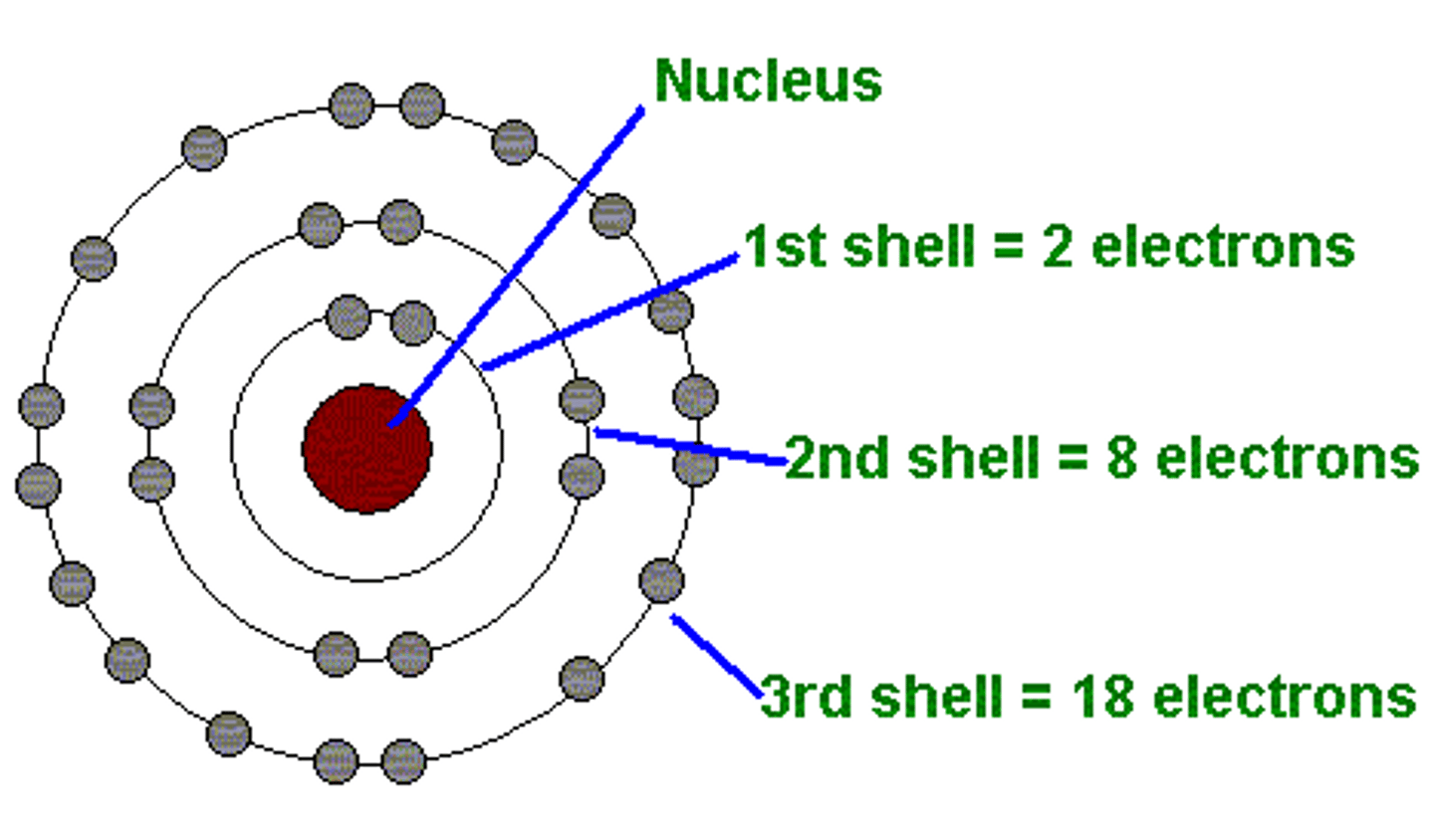
Schrödinger
Electron cloud model (probability regions, not fixed paths).
Chadwick
Discovered neutron.
Atomic number (Z)
# of protons (defines element).
Mass number (A)
Protons + neutrons.
Average atomic mass
Weighted average of isotopes.
Protons
+ charge, in nucleus.
Neutrons
Neutral, in nucleus.
Electrons
- charge, orbit nucleus.
Isotopes
Same element, different # neutrons (different mass).
Ions
Charged atoms (gain/lose electrons).
Cation
Positive ion (lost electrons). (Pawsitive...)
Anion
Negative ion (gained electrons).
Valence electrons
Outer shell electrons → control reactivity.
Periodic table notation
Nuclear notation: A/Z Hyphen notation: Name-mass # (Carbon-12).
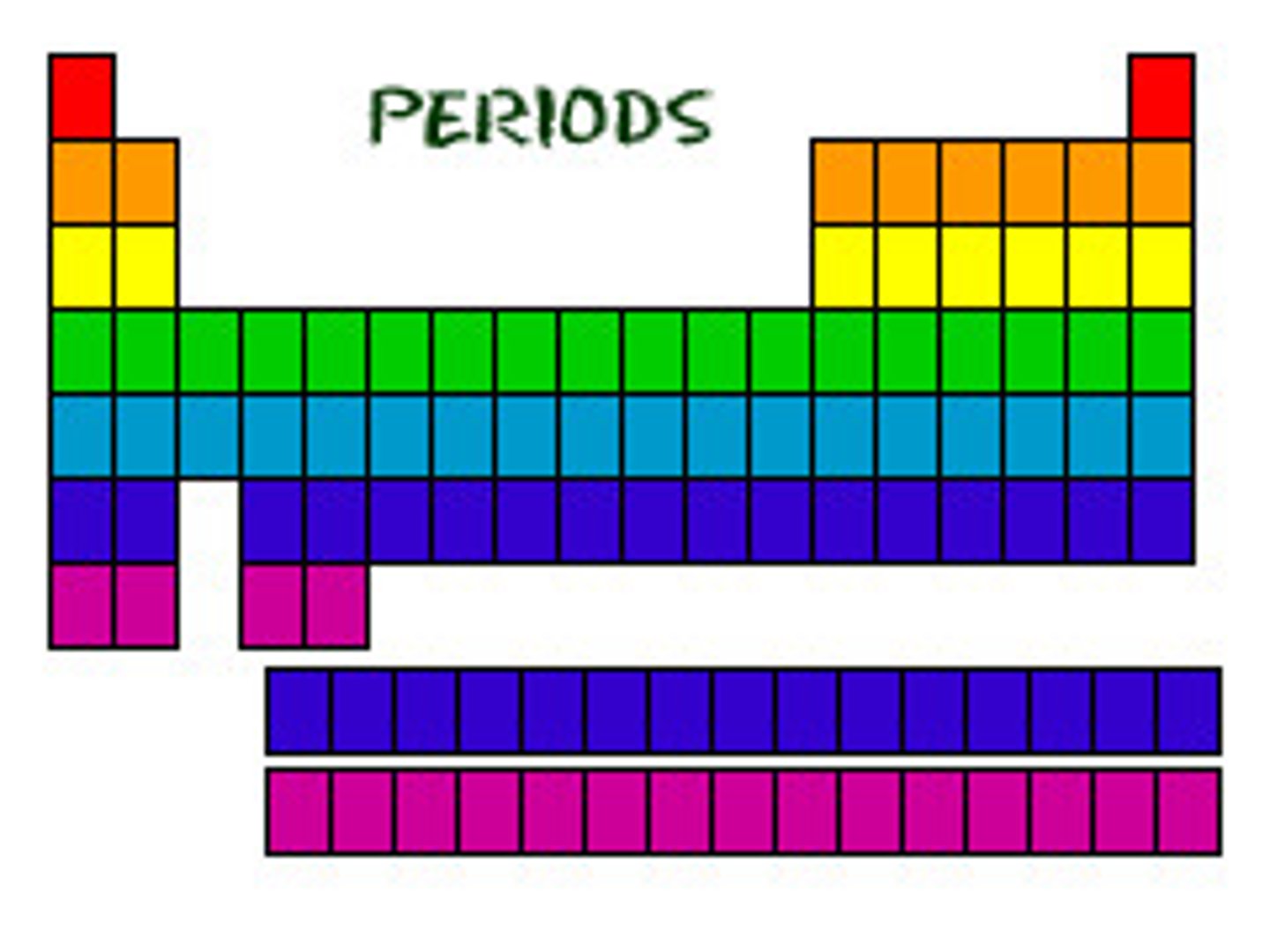
Periods
Rows (same # energy levels).
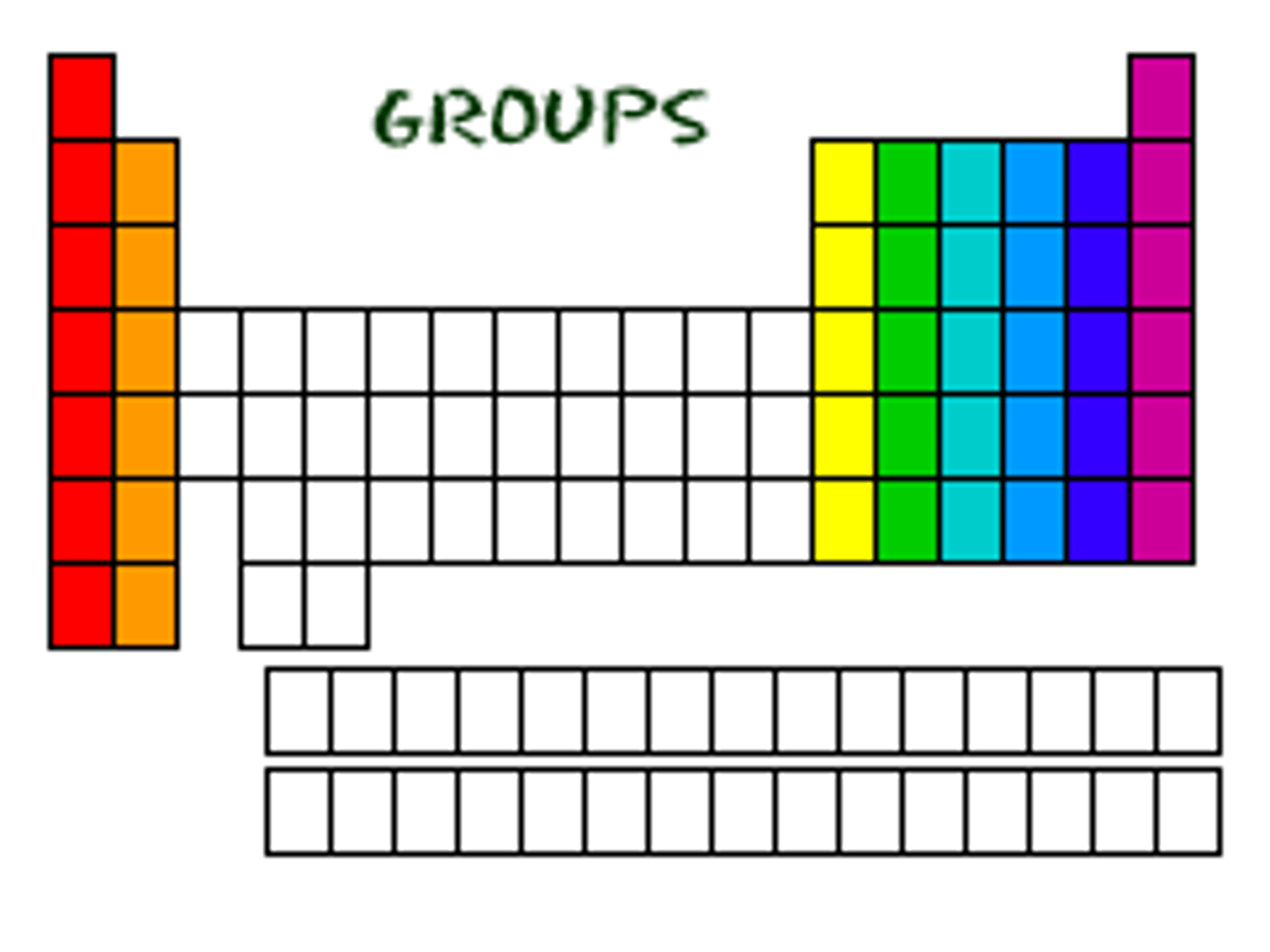
Groups
Columns (same # valence electrons).
Representative elements (Groups 1-2, 13-18)
Show predictable valence trends.
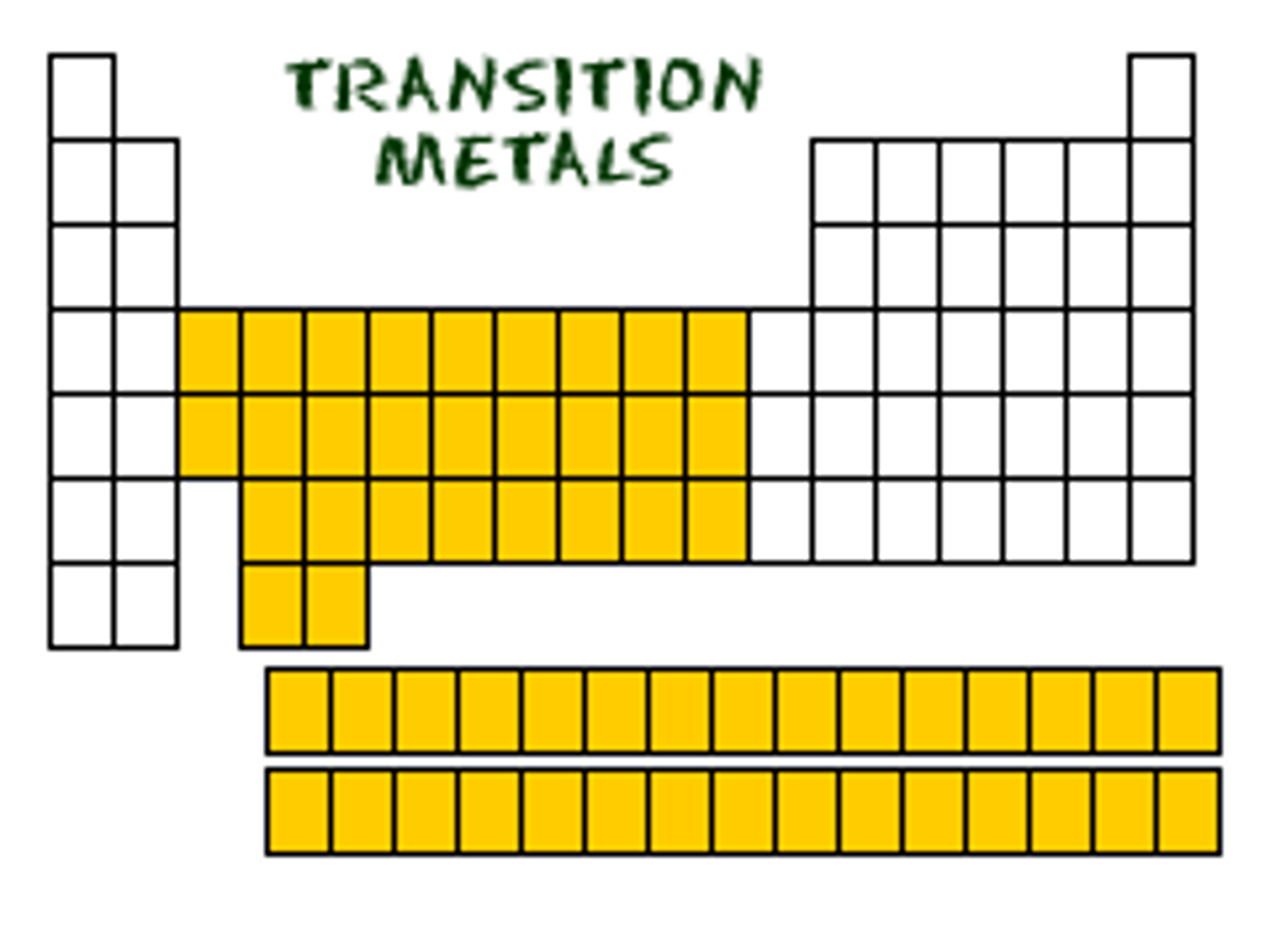
Transition elements (Groups 3-12)
Metals, variable charges.
Alkali metals (Group 1)
Very reactive, 1 valence e⁻.
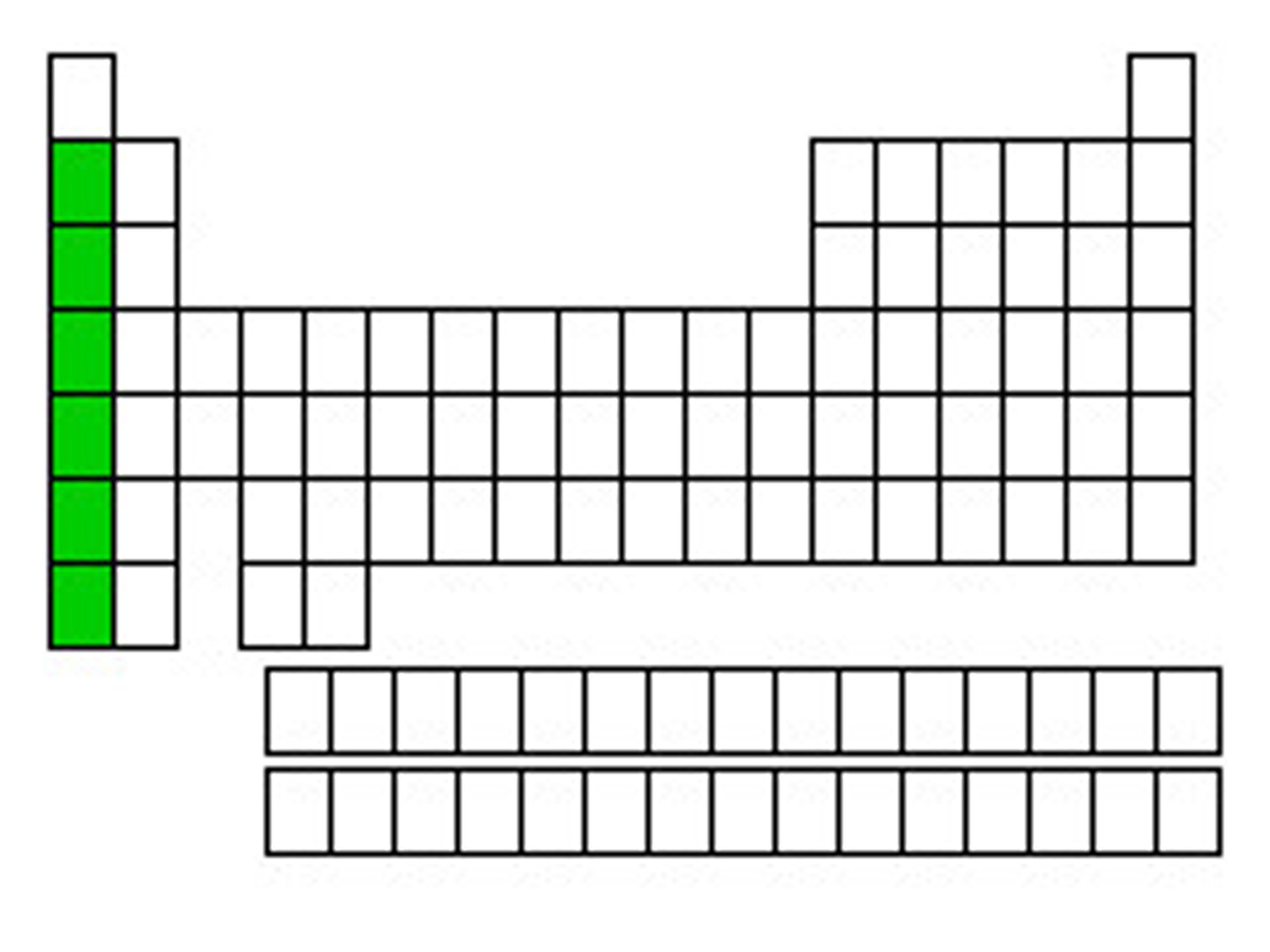
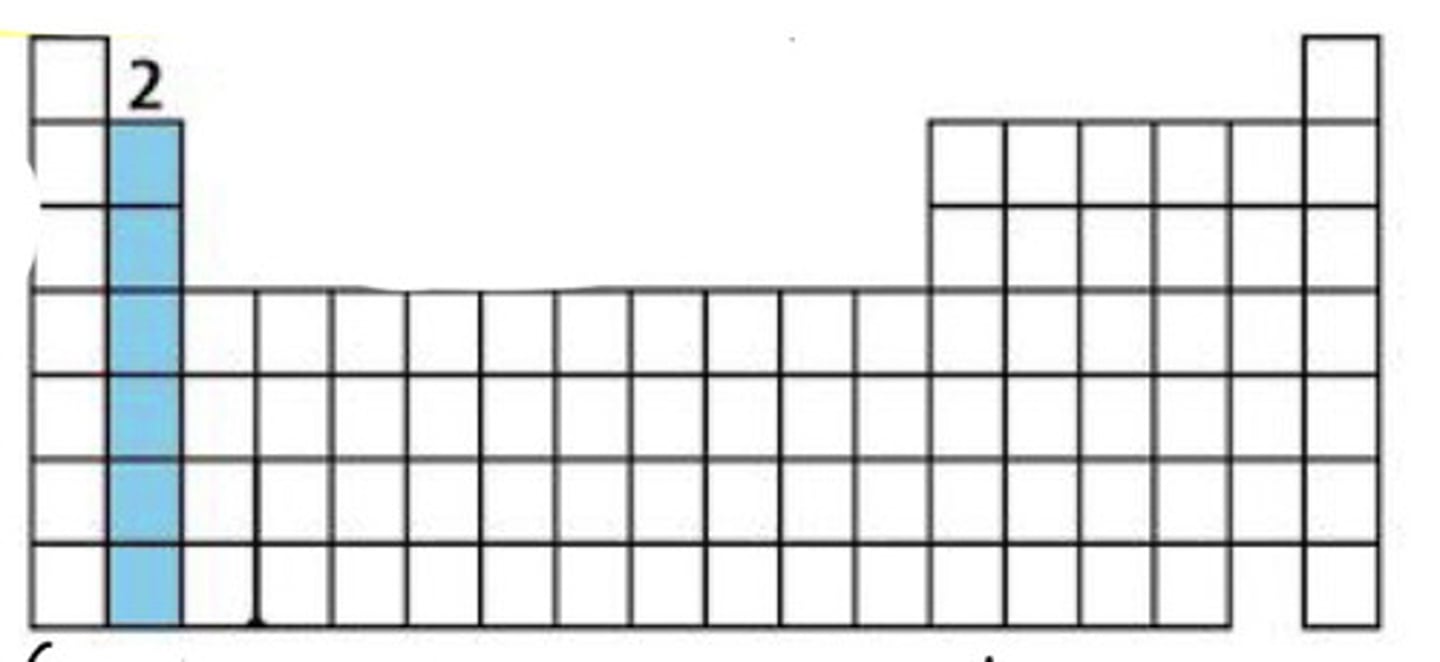
Alkaline earth metals (Group 2)
Reactive, 2 valence e⁻.
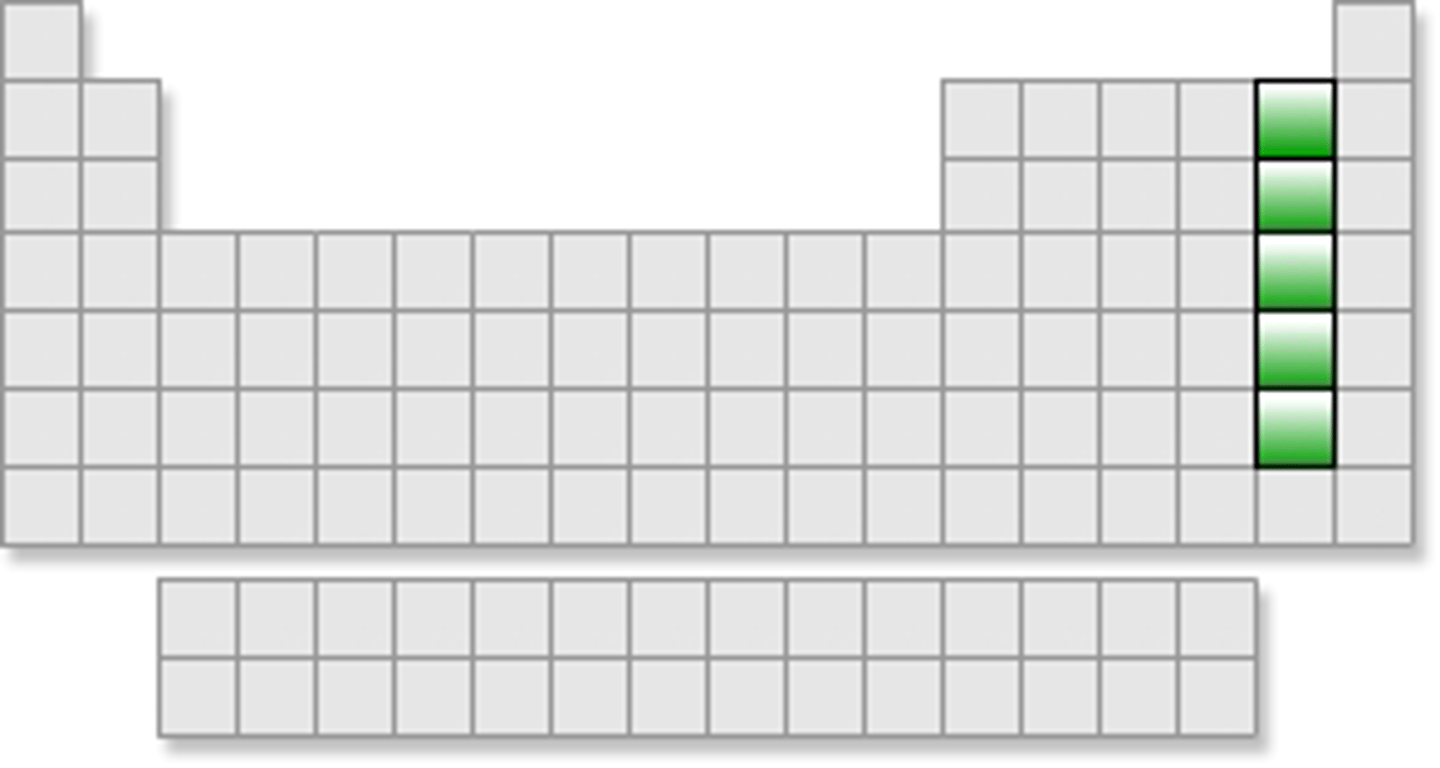
Halogens (Group 17)
Very reactive nonmetals, 7 valence e⁻.
Noble gases (Group 18)
Inert, full valence shell.
Rare earth elements
Lanthanides + actinides.
Post-transition metals
Softer, lower melting points (ex: Al, Pb).
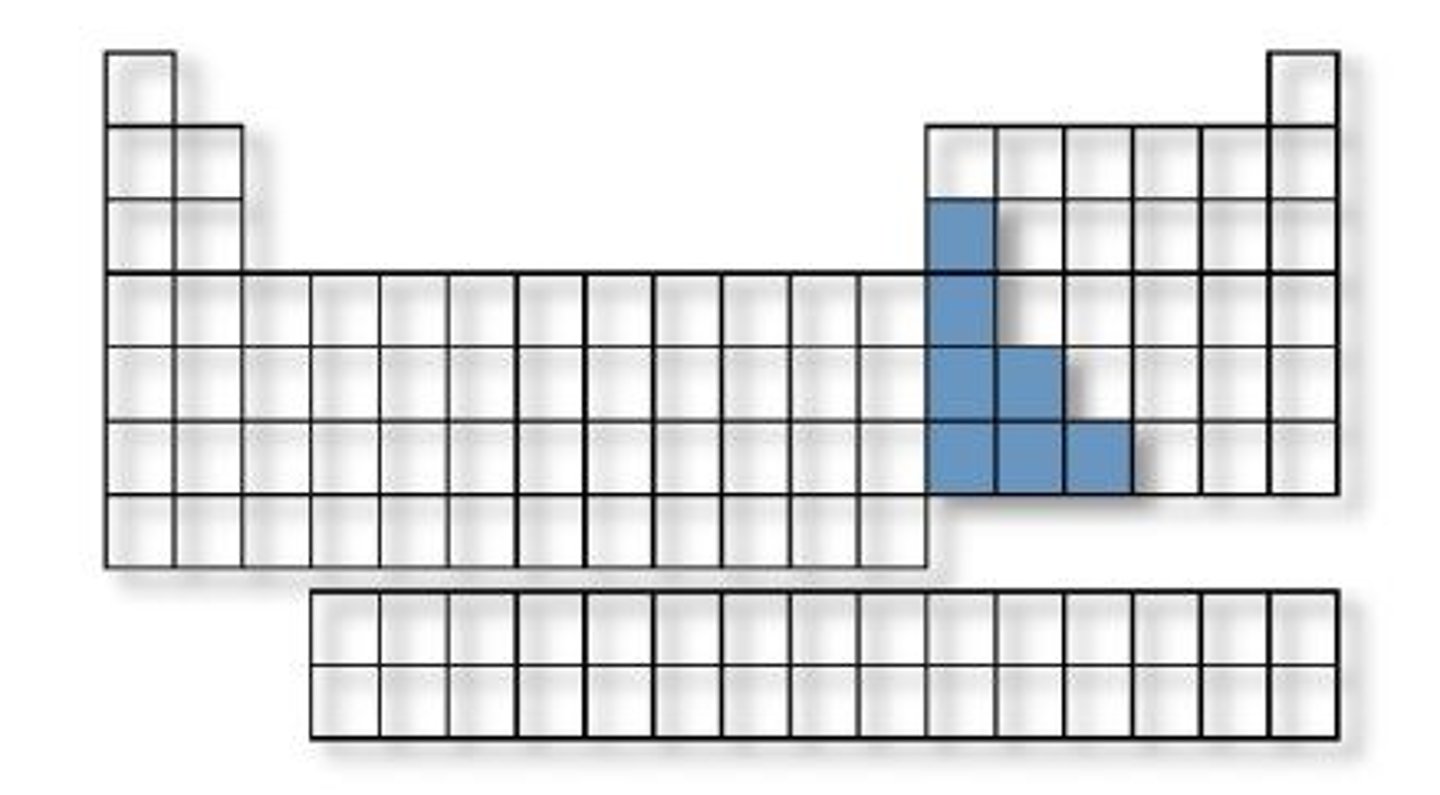
Metals
Shiny, malleable, conductors.
Nonmetals
Dull, brittle, poor conductors.
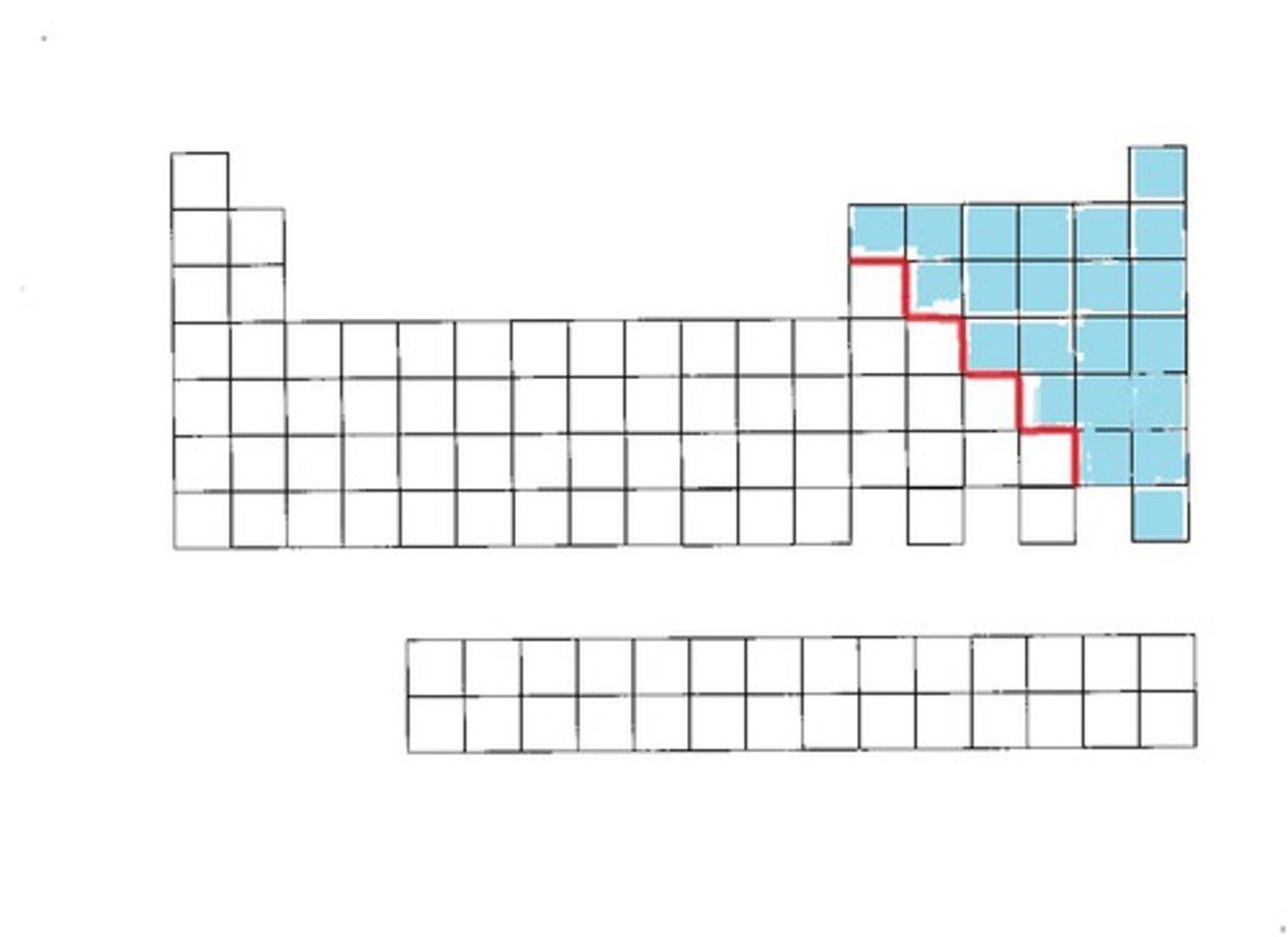
Metalloids
Have properties of both (ex: Si, As).
Mendeleev
Made first periodic table, arranged by atomic mass → predicted missing elements.
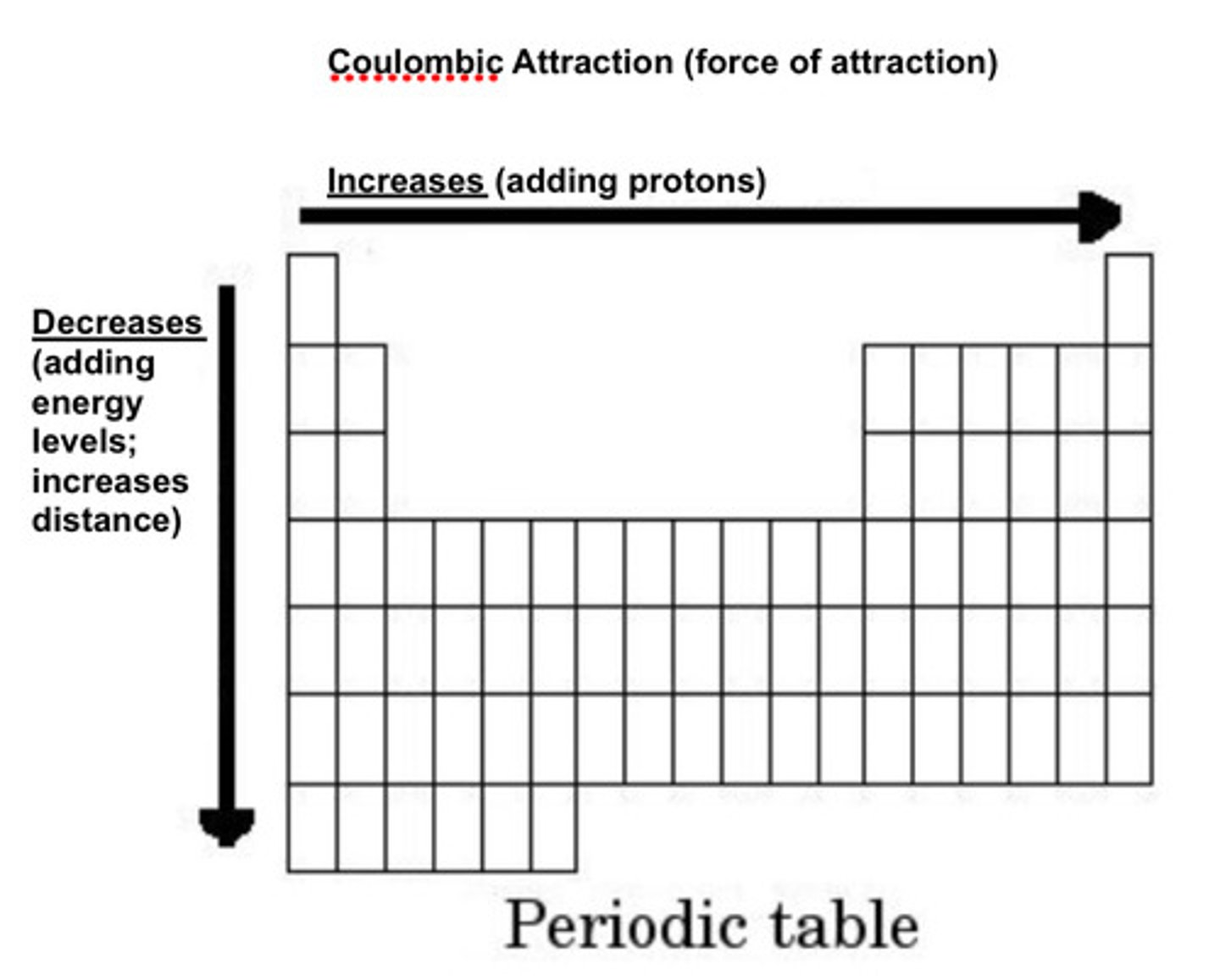
Coulombic attraction + Trend
Attraction between + nucleus and - electrons. Stronger when: More protons (higher nuclear charge). Electrons are closer (fewer energy levels).
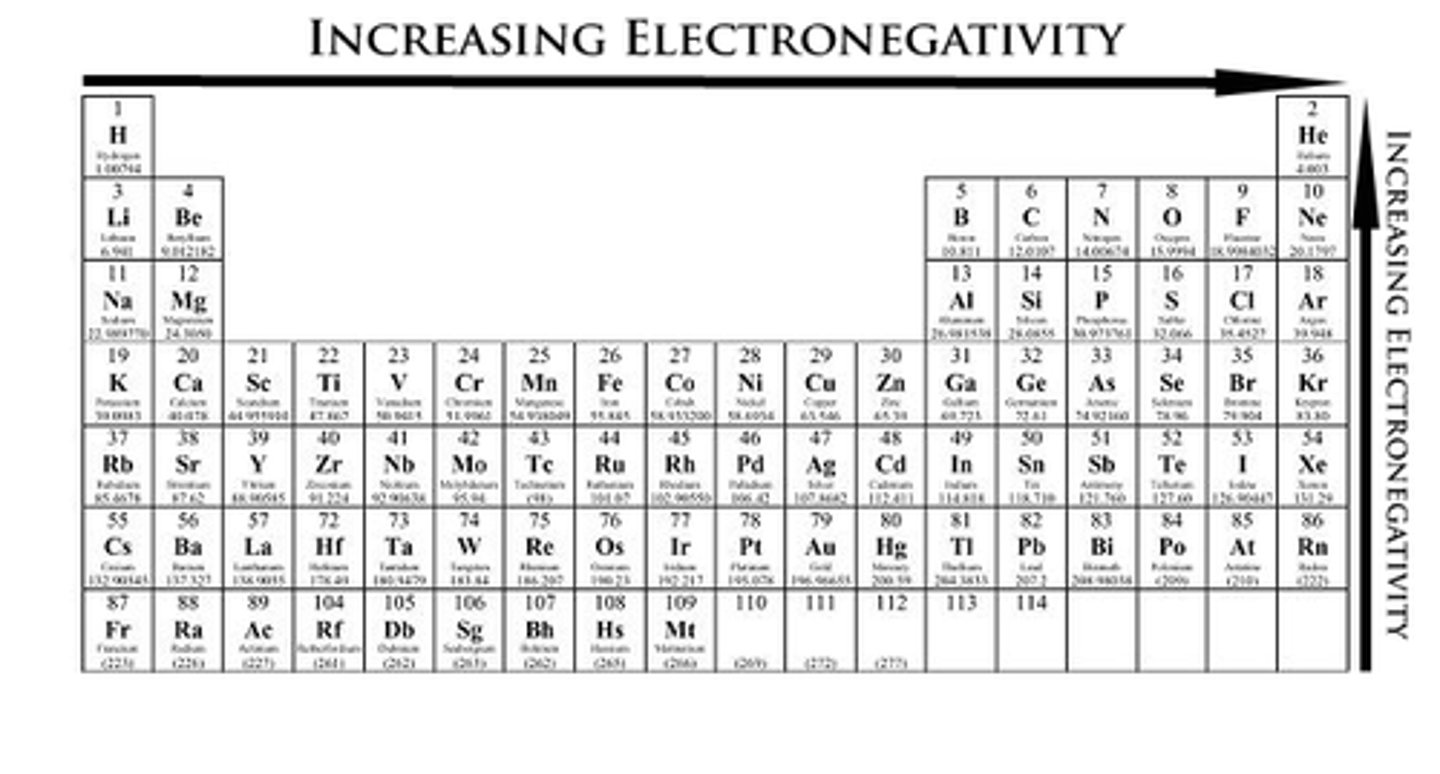
Electronegativity + Trend
Ability to attract electrons in a bond.
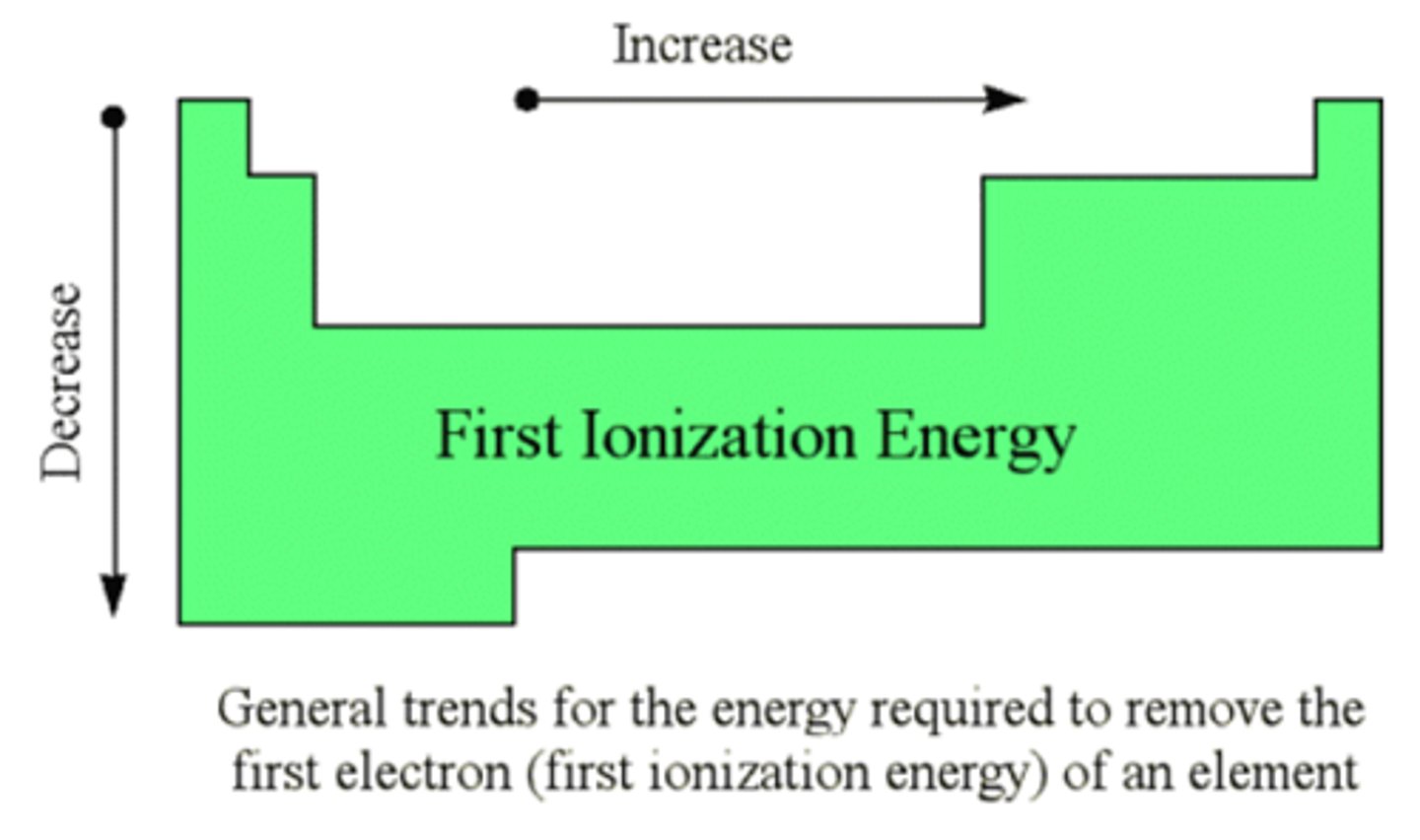
Ionization energy + Trend
Energy needed to remove e⁻.
Atomic radius + Trend
Left and down....

Ionic radius + Trend
Nuclear charge
# protons → effective pull on electrons.
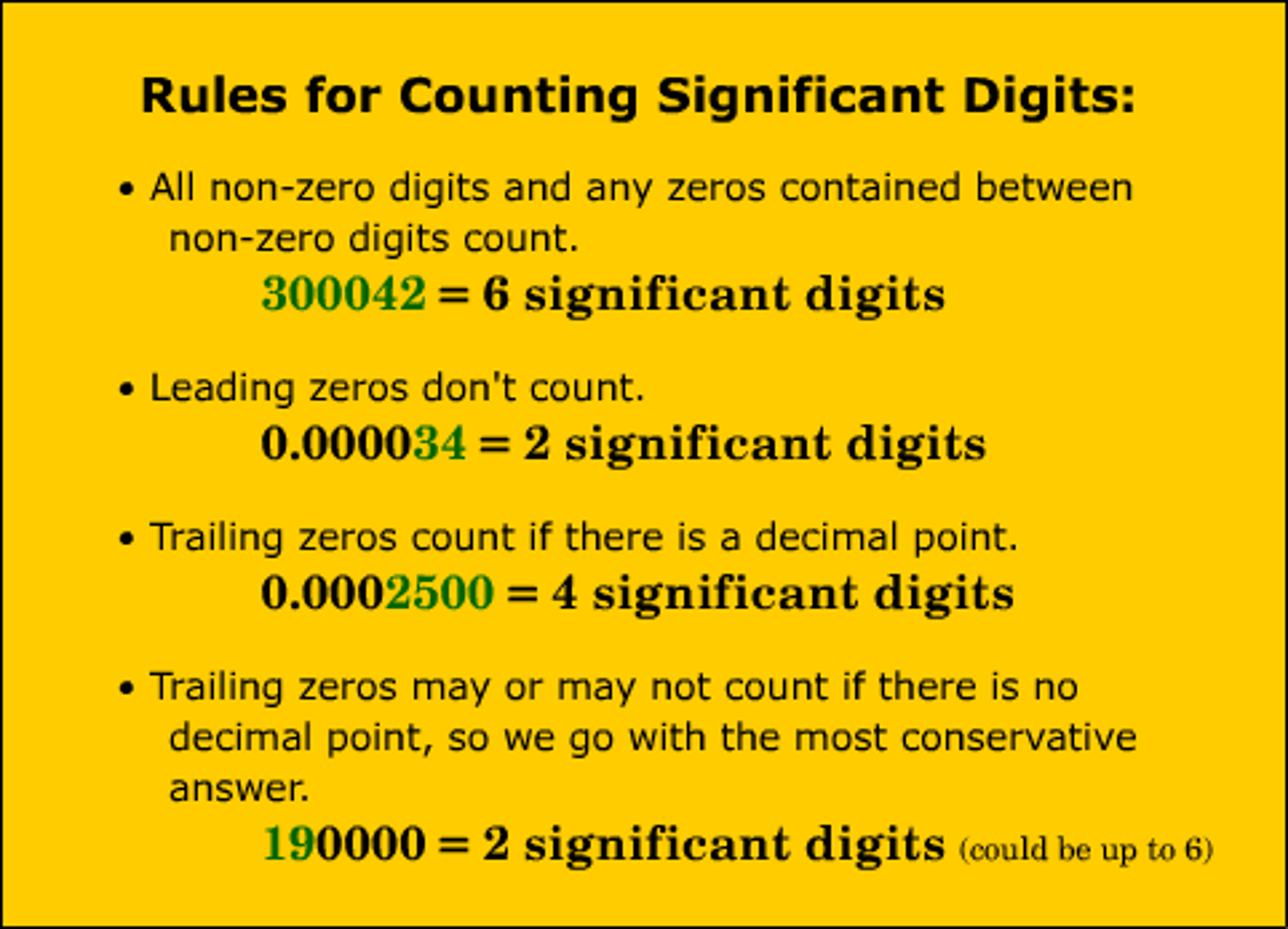
Significant figures
Rules for reporting precision in measurements.
Metallic character
bottom-left strongest.