Economics & Business Topic Test
4.7(7)
Card Sorting
1/59
Earn XP
Last updated 11:38 PM on 6/13/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
60 Terms
1
New cards
Why do we measure the economy
to see if we are on the right track, to compare with other countries (influence trade, currencies, power relationships), visualising where to make improvements (budgeting and redirecting money)
2
New cards
What are economic indicators for
measure people’s consumption of goods and services and gather data
3
New cards
What does the economy need to do?
To grow at a sustainable rate to meet the needs of its growing population and their changing life stages
4
New cards
What are the 3 economic growth indicators
GDP, inflation, unemployment
5
New cards
Outline what GDP is
Gross Domestic Product - total value of all goods and services of a country over a year, measured quarterly (ever 3 months), sustainable growth is 2-3% annually
6
New cards
What is a recession
if quarterly GDP figures record negative growth for two consecutive quarters (6 months)
7
New cards
What are some reasons for growth in an economy
mining sector (abundance of material, trading), spending money, labour force, injection of money from government (stimulus money), greater education
8
New cards
What is the difference between a recession and depression?
Depressions are a much greater severity and lasts for over 8 quarters (2+ years)
9
New cards
Outline the Global Financial Crisis
between 2007-2008. referring to extreme pressure in global financial markets and banking systems. the crashing of the US housing market and spread globally through leakages in the global financial system
10
New cards
What are some effects of a depression
unemployment, decline in industrial production, deflation, increase of poverty
11
New cards
Outline inflation
inflation measures the increase in the general level of prices paid for goods and services over a certain period of time.
12
New cards
What is the sustainable range of inflation
2-3%
13
New cards
Define cost pull factors
cost pull inflation is caused by the producers putting additional cost on the consumers to cover their extra expenses
14
New cards
Define demand pull factors
an increase in prices due to an increase in the demand for goods and services
15
New cards
Define cost of living
referring to how much it costs to purchase necessities
16
New cards
How is inflation an economic indicator
* high inflation can signal an overheated economy
* moderate inflation is associated with economic growth
* if economic growth accelerates very rapidly, demand grows even faster and producers raise prices continually
* moderate inflation is associated with economic growth
* if economic growth accelerates very rapidly, demand grows even faster and producers raise prices continually
17
New cards
Why can’t we just print more money?
printing money increases inflation
18
New cards
How can an increase in supply of money occur?
* government can print more notes
* the currency in circulation can be devalued
* government bonds can be purchased, loaning new money into existence through the banking system
* the currency in circulation can be devalued
* government bonds can be purchased, loaning new money into existence through the banking system
19
New cards
Outline CPI
CPI measure the price change of a typical basket of goods and service purchased by Australian household every quarter. The change in prices in each quarter is the inflation rate
20
New cards
What are the groups in a CPI basket
87 categories, 11 groups weighted differently on how likely they are used by the average Australian family
* transport
* alcohol and tobacco
* clothing and footwear
* communication
* recreation and culture
* education
* insurance and financial services
* food and non-alcoholic beverages
* housing
* health
* furnishing, household equipment and services
* transport
* alcohol and tobacco
* clothing and footwear
* communication
* recreation and culture
* education
* insurance and financial services
* food and non-alcoholic beverages
* housing
* health
* furnishing, household equipment and services
21
New cards
Define unemployment
the percentage of people in the labour force who are unemployed.
22
New cards
What are the types of unemployment
Structural, Cyclical, Frictional, Frictional, Seasonal
23
New cards
Define structural unemployment
is a type of unemployment that can last for many years due to changes in technology or changing demographics
24
New cards
Define cyclical unemployment
caused by economic downturns or is relates to changes in business conditions that affect the demand for workers
25
New cards
Define frictional unemployment
when people move between jobs in the labour market, as well as when people transition into and out of the labour force
26
New cards
Define seasonal unemployment
occurs at different points over the year because of seasonal patterns that affect jobs
27
New cards
List some causes of unemployment
* When production or GDP is weak/decreased spending in the economy - business cutback on employment to save money
* Increased competition overseas
* Businesses may take their operations offshore or close down
* Labour saving technology introduced
\
* Increased competition overseas
* Businesses may take their operations offshore or close down
* Labour saving technology introduced
\
28
New cards
Define labour force
total number of people in Australia working and willing and able to work
29
New cards
Consequences of high unemployment
Economic spending is low, government collects less revenue from tax and must pay more to direct it towards social benefits, reduced standard of living, loss of skills from workforce, possible psychological effects
30
New cards
Define material living standards w/ examples
Refers to access to physical goods and services and is assessed or measured by the GDP - groceries, transport, maintenance
31
New cards
Define non-material living standards w/ examples
Refers to things that cannot be measured in dollar terms and are intangible, but affect enjoyment of life
* freedom of speech
* free elections
* low levels of crime and discrimination
* preservation of the environment
* adequate leisure time
* freedom of speech
* free elections
* low levels of crime and discrimination
* preservation of the environment
* adequate leisure time
32
New cards
5 policies uses to increase living standard by government
Budgetary (gov budget)
Monetary (bank)
Microeconomics (company)
Productivity (improvement)
Training and Workforce
Migration (migrant criteria - age, skills, education, language, family, humanitarian)
Monetary (bank)
Microeconomics (company)
Productivity (improvement)
Training and Workforce
Migration (migrant criteria - age, skills, education, language, family, humanitarian)
33
New cards
Define macroeconomic policy
economic policy that focuses on an industry or market segment, focuses on improving production over the medium to long term.
34
New cards
Define monetary policy
actions by the Reserve Bank of Australia that affect the money supply and interest rates
35
New cards
What is the trend of a business cycle over time
follows a wave like pattern
36
New cards
What do the expansions of an economy signify
economic growth is growing
unemployment is falling
inflation is likely rising
unemployment is falling
inflation is likely rising
37
New cards
What do contractions of an economy signify
economic growth is too low
unemployment is too high
inflation is low
unemployment is too high
inflation is low
38
New cards
Define fiscal policy
is the use of government revenue collection and expenditure to influence a country's economy
39
New cards
Define budget surplus
revenue minus spending is positive number - government collected more money than spent
40
New cards
Define budget deficit
if government revenue minus spending creates a negative number - spent more than collected
41
New cards
What type of budget should the government use during a economic boom? Why?
budget surplus. a boom will have an unsustainable inflation rate >3%. they can reduce this by lowering spending and raising taxes
42
New cards
What type of budget should the government use during economic trough? Why?
budget deficit. The government should spend more money towards stimulating the economy through injections (social benefits) and lowering taxes, as spending is low during this time
43
New cards
Define disposable income
income remaining after the deduction of taxes and social security charges, available to be spent or saved as one wishes
44
New cards
Define income
money received, especially on a regular basis, for work or through investments
45
New cards
Define equity
equity is impartiality, fairness and justice for all people in social policy. Social equity takes into account systemic inequalities to ensure everyone in a community has access to the same opportunities and outcomes
46
New cards
Define taxation
compulsory payment to the government (from current income or consumption) from the private sector to finance government spending
47
New cards
Outline tax
* tax is money charged by the government on items such as wages, goods and services you provide money to government services
* in a time of the strong economics business cycle, the government can try reduce inflation by lowering spending and raising taxes
* taxes go towards education, infrastructure, transport, health, etc.
* in a time of the strong economics business cycle, the government can try reduce inflation by lowering spending and raising taxes
* taxes go towards education, infrastructure, transport, health, etc.
48
New cards
Outline direct taxes
* direct taxes are tax you pay directly to the government
* direct taxes cannot be paid by anyone else
* the amount of tax you pay depends on how much money you earn
* other factors also include
* whether you have children or other dependents
* whether you are single or married
* direct taxes cannot be paid by anyone else
* the amount of tax you pay depends on how much money you earn
* other factors also include
* whether you have children or other dependents
* whether you are single or married
49
New cards
Outline indirect taxes
* indirect taxes are taxes on goods and services
* this is because tax has been imposed on producers and is then shifted to the consumer
* they are usually included in the price of the item, making them less visible to consumers
* examples of indirect taxes include sales tax and value added tax (VAT)
* indirect taxes can be regressive, meaning they take a larger percentage of income from low-income individuals than from high-income individuals
* this is because tax has been imposed on producers and is then shifted to the consumer
* they are usually included in the price of the item, making them less visible to consumers
* examples of indirect taxes include sales tax and value added tax (VAT)
* indirect taxes can be regressive, meaning they take a larger percentage of income from low-income individuals than from high-income individuals
50
New cards
List purposes of taxes
raise revenue - money for government services
* e.g. welfare, hospitals, school
redistribute income - people who earn more money pay more tax
resources allocation - used to encourage or discourage the use of certain resources
* e.g. carbon tax, cigarette tax
stabilise economic activity - reducing fluctuations
* e.g. welfare, hospitals, school
redistribute income - people who earn more money pay more tax
resources allocation - used to encourage or discourage the use of certain resources
* e.g. carbon tax, cigarette tax
stabilise economic activity - reducing fluctuations
51
New cards
List examples of government spending
* investing on infrastructure (roads, bridges, public transport, power, water)
* providing healthcare services and funding medical research
* supporting education through funding schools and university
* providing social welfare programs (unemployment benefits and food assistance)
* funding scientific research and development
* supporting environmental protection and conservation efforts
* providing public safety services (police and fire departments)
* funding public parks and recreation facilities
* maintain defense and military services
* providing healthcare services and funding medical research
* supporting education through funding schools and university
* providing social welfare programs (unemployment benefits and food assistance)
* funding scientific research and development
* supporting environmental protection and conservation efforts
* providing public safety services (police and fire departments)
* funding public parks and recreation facilities
* maintain defense and military services
52
New cards
define externalities
a consequence of an industrial or commercial activity which affects other parties not directly related to the activity, without this being reflected in market prices. can either have positive or negative effects
53
New cards
How can the government increase positive externalities
promoting policies (walking to school - reduces traffic congestions)
54
New cards
How can the government reduce negative externalities
increasing taxes on items or practices to deter people from buying or engaging in action - cigarettes, mining
55
New cards
Define income
money received, especially on a regular basis, for work or through investments
56
New cards
Define wealth
an abundance of valuable possessions or money
57
New cards
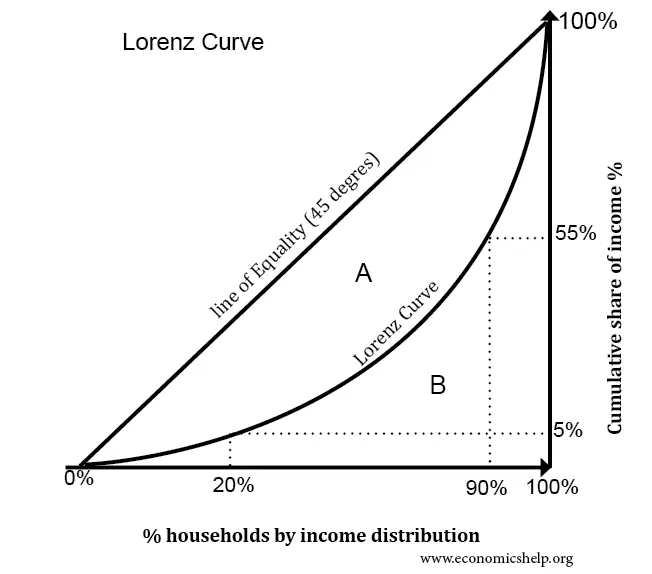
Outline the Lorenz Curve
* the Lorenz curve is a way of showing the distribution of income (or wealth) within an economy
* the Lorenz curve shows the **cumulative** share of income from different sections of the population
* if there was perfect equality (everyone has same salary) the poorest 20% of the population would gain 20% of the total income; the poorest 60% of the population would get 60% of the income
* the Lorenz curve shows the **cumulative** share of income from different sections of the population
* if there was perfect equality (everyone has same salary) the poorest 20% of the population would gain 20% of the total income; the poorest 60% of the population would get 60% of the income
58
New cards
What is the realistic income distribution in comparison to the cumulative share of income (probs don’t need remember, given graph)
\
* the poorest 90% of the population holds 55% of the total income; the richest 10% of income earners gain 45% of total income
\
* the poorest 90% of the population holds 55% of the total income; the richest 10% of income earners gain 45% of total income
\
59
New cards
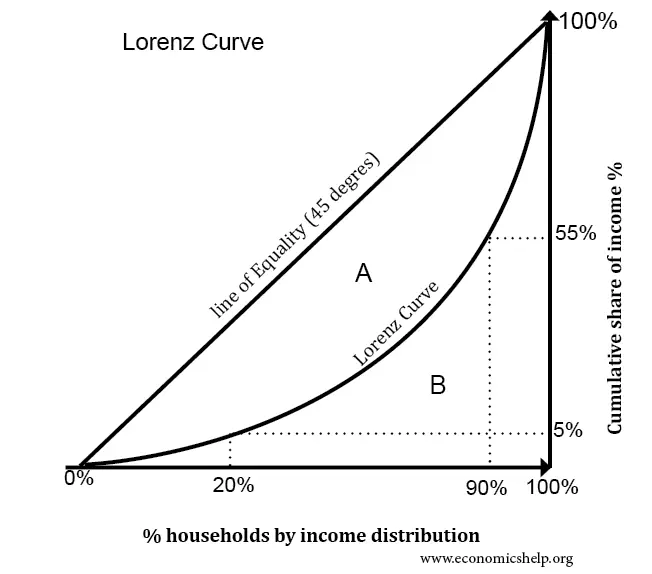
Outline the Gini coefficient
it is between 0 and 1 - the closer the number is to 0, the more income is distributed amongst the population; the closer to 1 the more inequitable the distribution of income
* the closer the Lorenz curve is to the line of equality, the smaller area A is - the Gini coefficient will be low
* if there is high degree of inequality, then area A will be a bigger percentage of the total area
* **a rise in the Gini coefficient shows a rise in equality - it shows the Lorenz curve is further away from the line of equality**
* the closer the Lorenz curve is to the line of equality, the smaller area A is - the Gini coefficient will be low
* if there is high degree of inequality, then area A will be a bigger percentage of the total area
* **a rise in the Gini coefficient shows a rise in equality - it shows the Lorenz curve is further away from the line of equality**
60
New cards
How do you calculate the Gini Coefficient
***G = A/(A+B)***
the area **above** the Lorenz curve but below the line of perfect equality is **A,** the remaining area is **B**
we divide A by (A+B) to determine the Gini coefficient
the area **above** the Lorenz curve but below the line of perfect equality is **A,** the remaining area is **B**
we divide A by (A+B) to determine the Gini coefficient