myelination
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
42 Terms
how to increase speed of action potential conduction
increase in axon diameter-giant axons-invertebrates not in vertebrates because of physical constraints imposed on the CNS by the skull
increased body temperature→faster diffusion
fatty insulation- myelin sheaths- vertebrates
what is myelin
insulates axons from each other, speeds conduction of nervous impulse (saltatory conduction between nodes)
what are node of ranvier
gaps in between myelin. action potential can jump between the nodes and increase the speed
myelination of PNS vs CNS
PNS- schwann cells
CNS- oligodendrocytes active
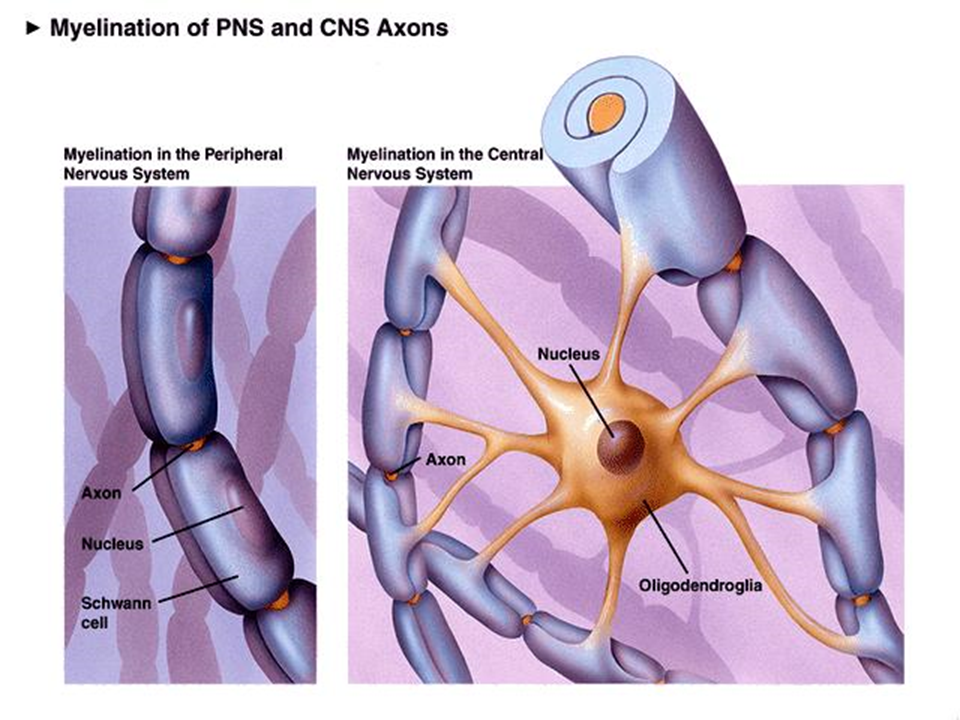

where are schwann cells derived from
neural crest and migrates and differentiates under control of peripheral axons
where are oligodendrocytes derived from
progenitors that reside in ventricular zone of neural tube
what controls schwann cell migrate and differentiate
peripheral axons
what is the oligodendrocyte precursor cell
a bipotential cell that arises after birth- o2A cell (also NG2)
oligodendrocytes vs schwann cells
a single myelin sheath is formed by schwann cells in the peripheral nervous system (PNS)
multiple myelin sheaths are formed by oligodendrocyte in the central nervous system (CNS)
increase in vertebrate axons
myelin sheath increases the local resistance of the axon and reduces membrane capacitance by several orders of magnitude. Voltage-gated sodium channels are concentrated at nodes of Ranvier and are downregulated along the axon plasma membrane between the nodes, ensuring that current flow is spatially restricted to the nodal region. Paranodal junctions function as an electrical seal that limits current leakage underneath the sheath
what determines whether axons in the PNS are myelinated
if they express threshold levels of neuregulin 1 a membrane-tethered member of the epidermal growth factor.
what determines whether axons in the CNS are myelinated
default pathway for oligodendrocytes
other roles of myelin
also provides a substrate for additional control of the timing of inputs during development and in adult neural circuits. energy conservation, insulation and regulation of ion movement
what does neuronal activity promote
proliferation of oligodendrocyte progenitors and stabilizes axon–oligodendrocyte interactions
the number of oligodendrocytes
excess dies by apoptosis. more progenitors are produced than there are mature oligodendrocytes after myelination
oligodendrocytes and progenitors competing
progenitors and newly-differentiated oligodendrocytes compete for limiting amounts of mitogens and survival factors (from astrocytes and neurons) if they don’t get enough they die
can mature oligodendrocytes migrate
no only the precursors can so they need to move where it’s necessary.
what does oligodendrocytes progenitors need to migrate
require cell adhesion molecules (integrins, PSA-NCAM)
where does the oligodendrocytes precursors go
Follow radial glia (outwards from ventricular zone).
Follow developing axon pathways (dorso-ventral and longitudinal).
what enhances myelin gene transcription
signals from neurons (thicker axons get thicker myelin)
signalling between oligodendrocytes and axons
Axons are not passive in myelination….
They provide mitogenic signals for O2A (NG2) cells - PDGF, neuregulin.
Electrical activity stimulates O2A proliferation (poss. via increasing production of mitogens by astrocytes).
how is myelin sheath generated
CONTINUED MIGRATION OF PROCESS LEADING EDGE AROUND AXON
While the leading glial process continues to encircle the axon, the earlier-formed loops undergo compaction to form the contact myelin sheath
schwann cell development
neural crest cell→schwann cell precursor→immature schwann cell→ myelinating/non-myelinating schwann cell
when does migration of schwann cell progenitors stop
when they encounter axons and their signals tell the cells what to do
neuregulins
eg. Glial growth factor (GGF) expressed by motor neurones and in neurones of peripheral ganglia. Stimulates differentiation and proliferation of Schwann cell precursors.
Neuregulins also contribute to survival of Schwann cell precursors
Krox20
zinc-finger transcription factor. Knockout - no myelinating Schwann cells.
Signals from axons (neuregulins) upregulate Krox20 in Schwann cell precursors that contact them.
not expressed in oligodendrocytes lineage
pax3
paired domain transcription factor.
Inhibits Schwann cell differentiation.
Expressed in SC progenitors and downregulated as myelination starts.
Controls expression of e.g., MBP.
not expressed in oligodendrocyte lineage
L1
NCAM and L1 (another Ig-class cell adhesion molecule) expressed in Schwann cell progenitors, and downregulated after myelination starts.
L1 is required for initiation of myelination in Schwann cells, but not present in oligodendrocytes.
Oligodendrocytes express a closely related cell adhesion molecule, neurofascin-155, at start of myelination - may ‘replace’ L1.
MAG and periaxin
Myelin-associated Glycoprotein MAG and a cytoskeletal-linking protein, periaxin, are initially located in Schwann cell membranes in contact with axon. May modulate interaction, but periaxin not in oligodendrocytes.
autocrine survival of mature schwann cells
can schwann cells and oligodendrocytes make myelin on their own
SC only in presence of axons. oligodendrocytes can make in culture on their own
specialised myelin proteins
P0 (Schwann cells only) A cell adhesion molecule (Ig family).
Proteolipid protein PLP (almost entirely oligodendrocytes only).
Myelin Basic Protein MBP (both cell types)
Myelin-associated Glycoprotein (MAG) (both cell types)
peripheral myelin protein-22 (PMP-22)
many others.
P0 and PLP are required in Schwann cells and oligodendrocytes respectively for compaction/stability of myelin - unrelated molecules doing very similar jobs.
the most common protein in CNS myelin
PLP
most common protein in PNS myelin
PO
shiverer mutant
almost complete absence of myelination, due to a failure of precursor cells to differentiate into oligodendrocytes (MBP)
other mutations
impair myelination are mutations in the major protein components of the myelin sheath
mutation in PLP
causes hypomyelination in CNS
regions of the nodes of ranvier
1.Node - voltage-sensitive Na+ channels
2.Paranodal regions – specialized transmembrane proteins that prevents movement of Na+ and K+ channels in axon plasma membrane
•Contactin
•Caspr (contactin associated protein)
•Schwann cells have nuerexin – thought to interact with contactin–
3.Juxtaparanodal regions – K+ channels are highly concentrated
what is the site of tight axon-glial adhesions
paranode
sodium channels in immature notes
Sodium channels cluster early at wide immature nodes. As nodes narrow and
mature, sodium channel density increases.
potassium channels in nodes
Potassium channels cluster later and shift their position. They first appear at nodes,
But move to paranode and then juxtaparanode as structure matures.

slides 33-35