Overview of the Vestibular System and Hair Cells
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
24 Terms
What are hair cells in the vestibular system?
Special sensory receptors of the inner ear that act as mechanoreceptors.
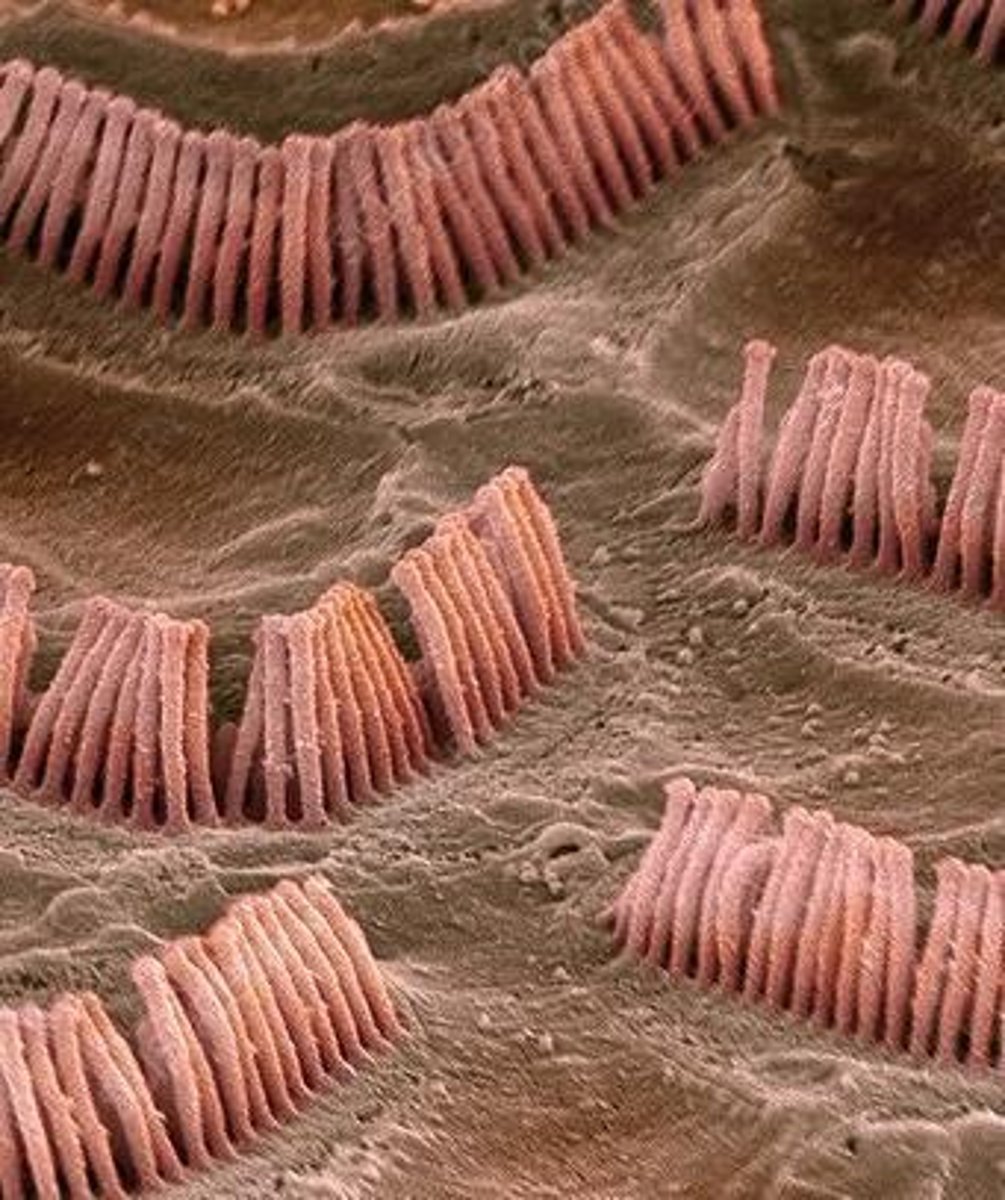
How do hair cells respond to head movement?
Head movement is converted to bending forces on the hairs.
Where do hair cells synapse in the vestibular system?
At the dendritic ending of the vestibular afferents.
What is the role of efferent input to hair cells?
To control sensitivity of the hair cells.
Where are hair cells located in the semicircular canals?
In the cristae.
Where are hair cells located in the utricle and saccule?
In the maculae.
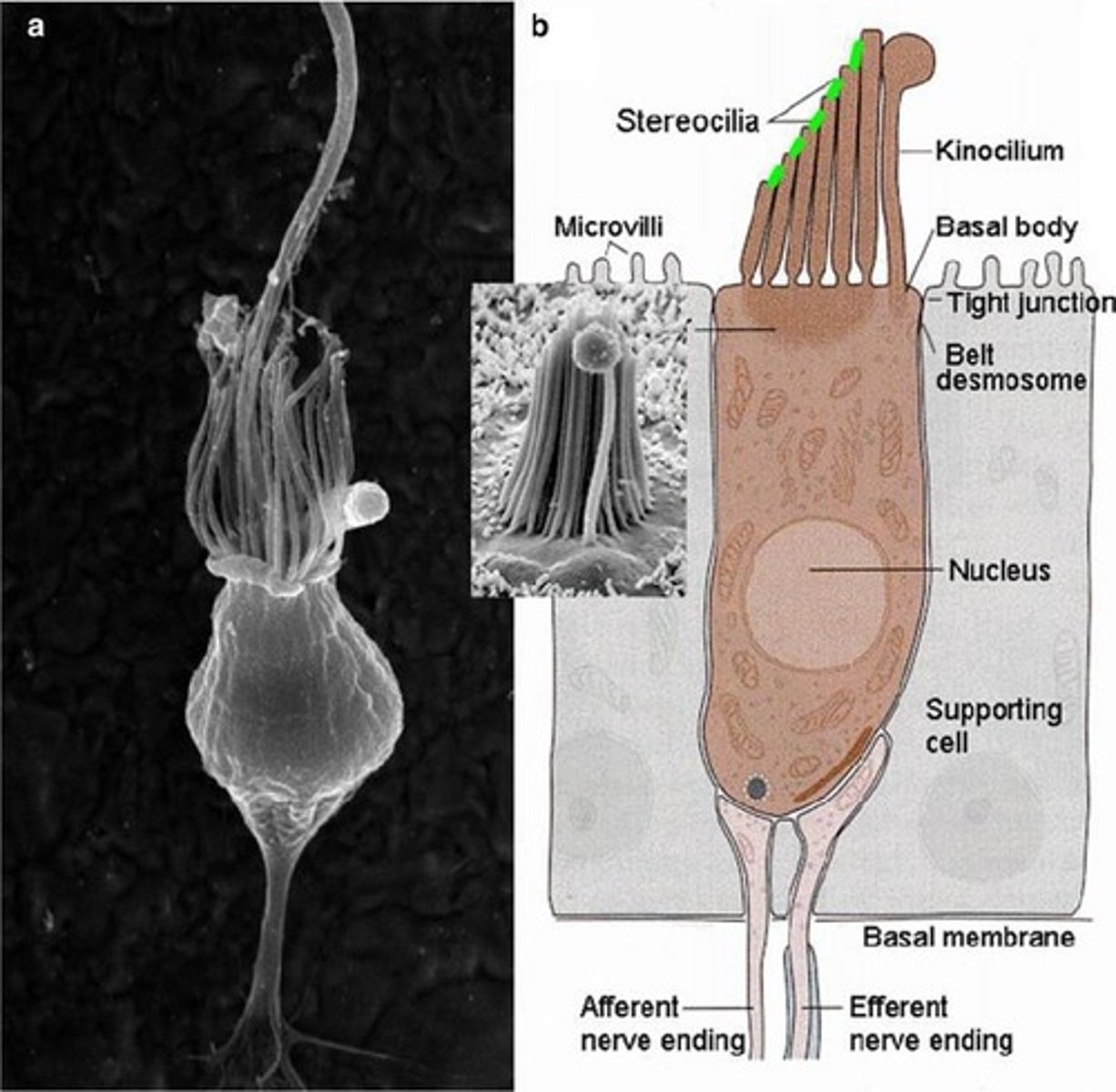
What structures are found at the apical end of hair cells?
30-50 microvilli (stereocilia) and 1 kinocilium.
What happens when stereocilia bend towards the kinocilium?
There is depolarization and neurotransmitter release.
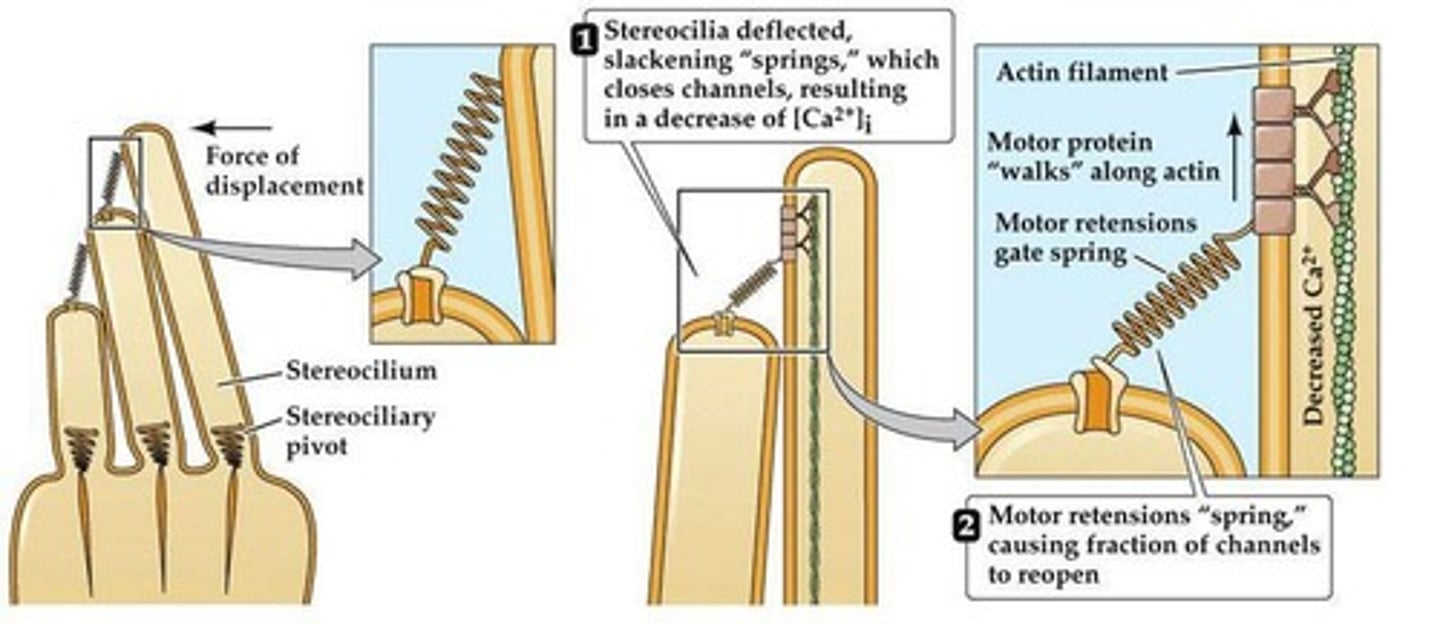
What occurs when stereocilia move away from the kinocilium?
There is inhibition or hyperpolarization of the cell.
What do the semicircular canals respond to?
Rotational accelerations.
What is the function of the semicircular canals?
To coordinate eye and head movement to maintain focus.
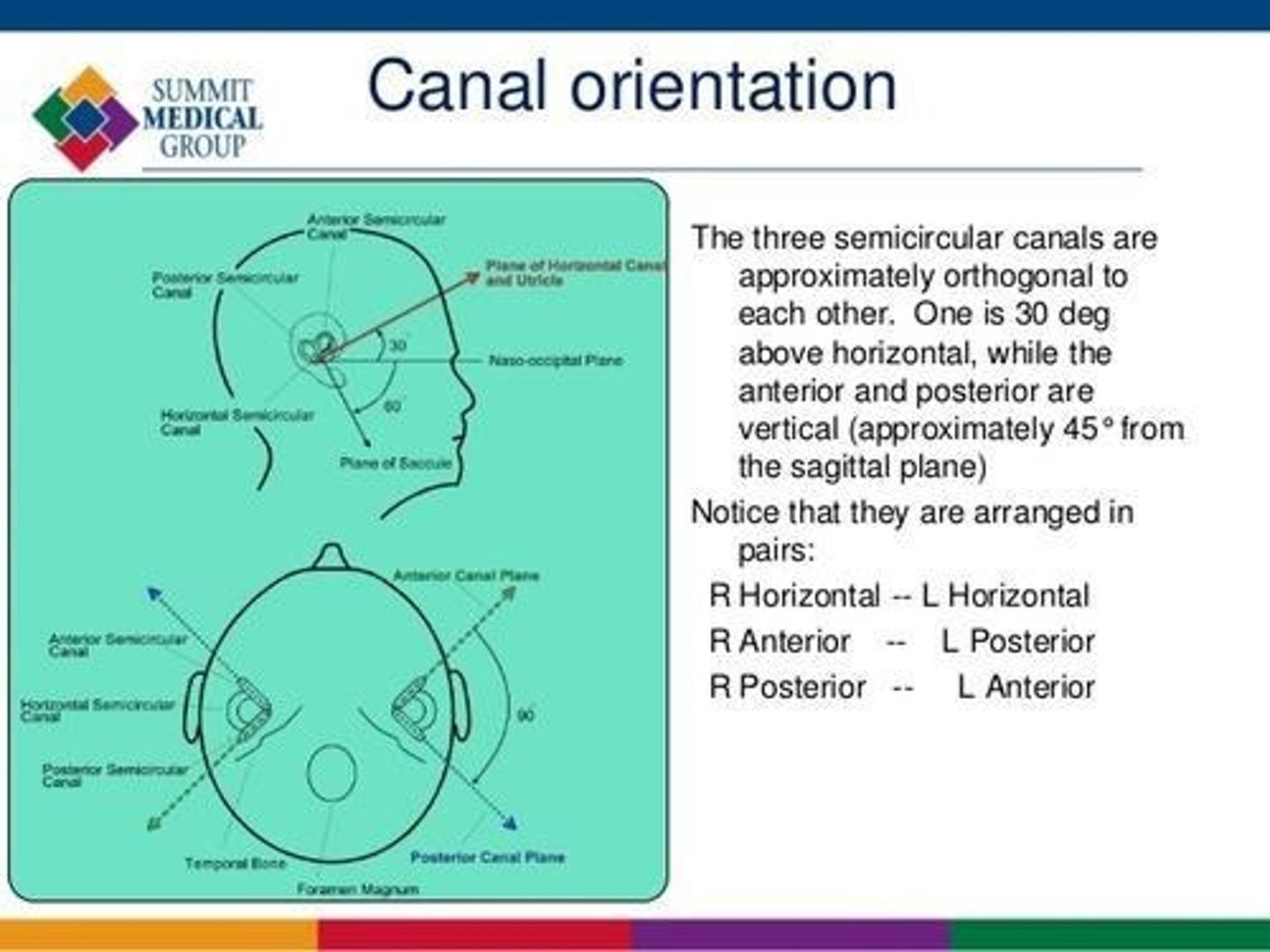
What are the three types of semicircular canals?
Anterior (inferior), posterior (superior), and horizontal (lateral).
What is the ampullae in the context of semicircular canals?
The opening of the canal into the utricle.
What is the sensory organ located in the ampullae?
Cristae (hair cells).
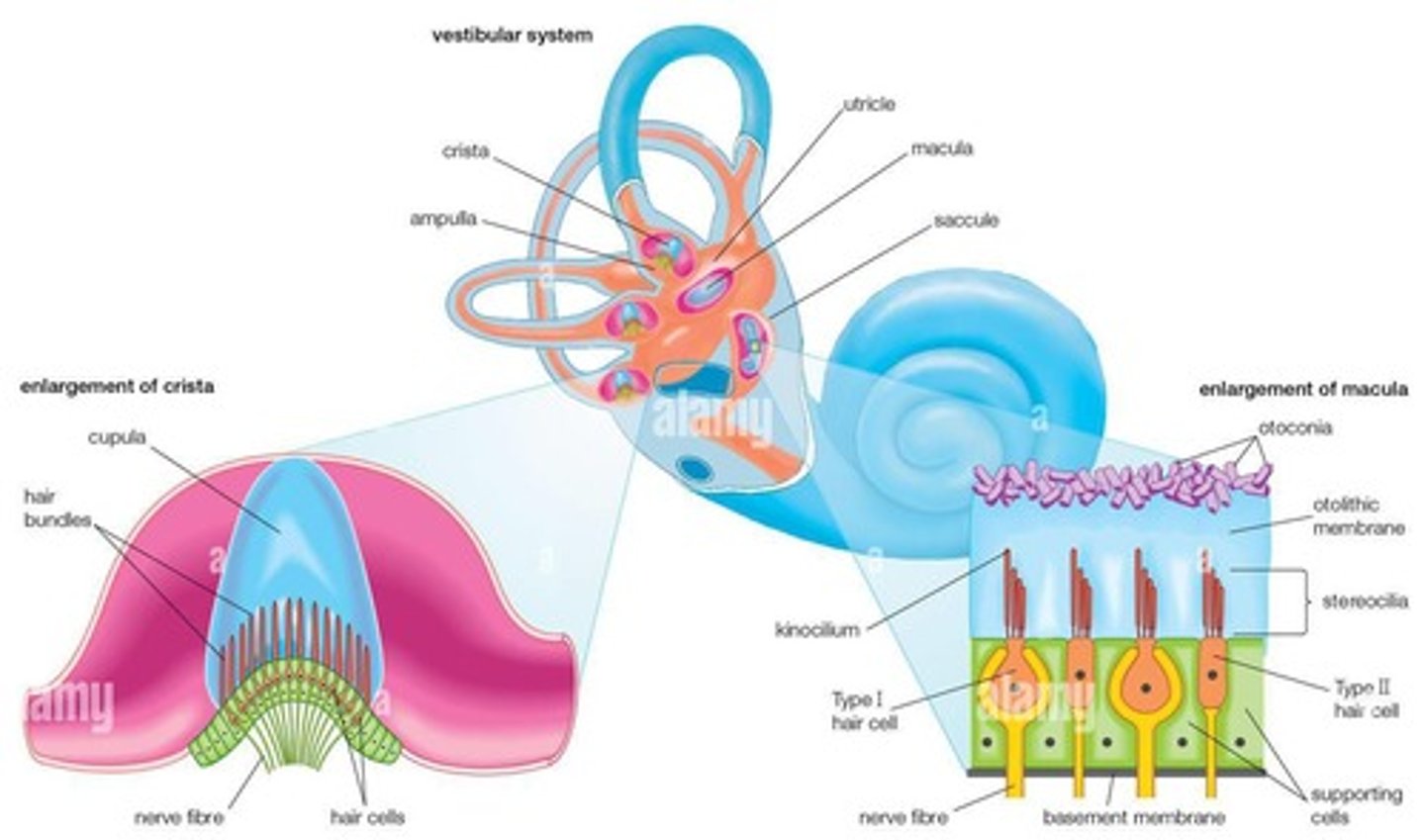
What is the cupula in the vestibular system?
A gel that hair sensory cells are embedded in, which moves when the head rotates.
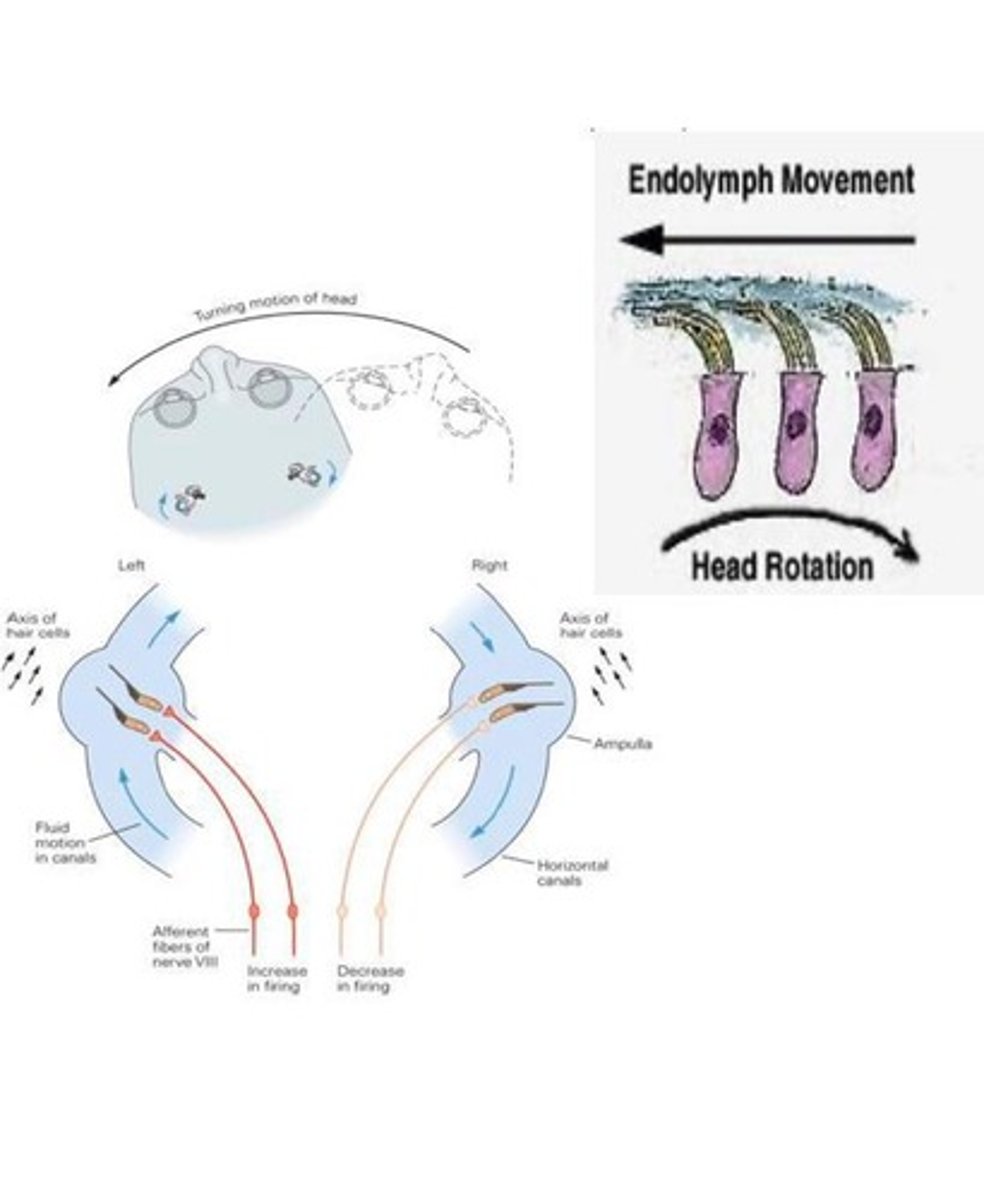
How does endolymph movement relate to head rotation?
Endolymph moves in the opposite direction of head rotation.
What happens to the vestibular nerve when the head turns left?
The left vestibular nerve is stimulated while the right is inhibited.
How are the semicircular canals paired?
With corresponding canals on the opposite side of the head.
What is the role of the vestibular nuclei in the CNS?
To integrate information from the right and left vestibular systems.
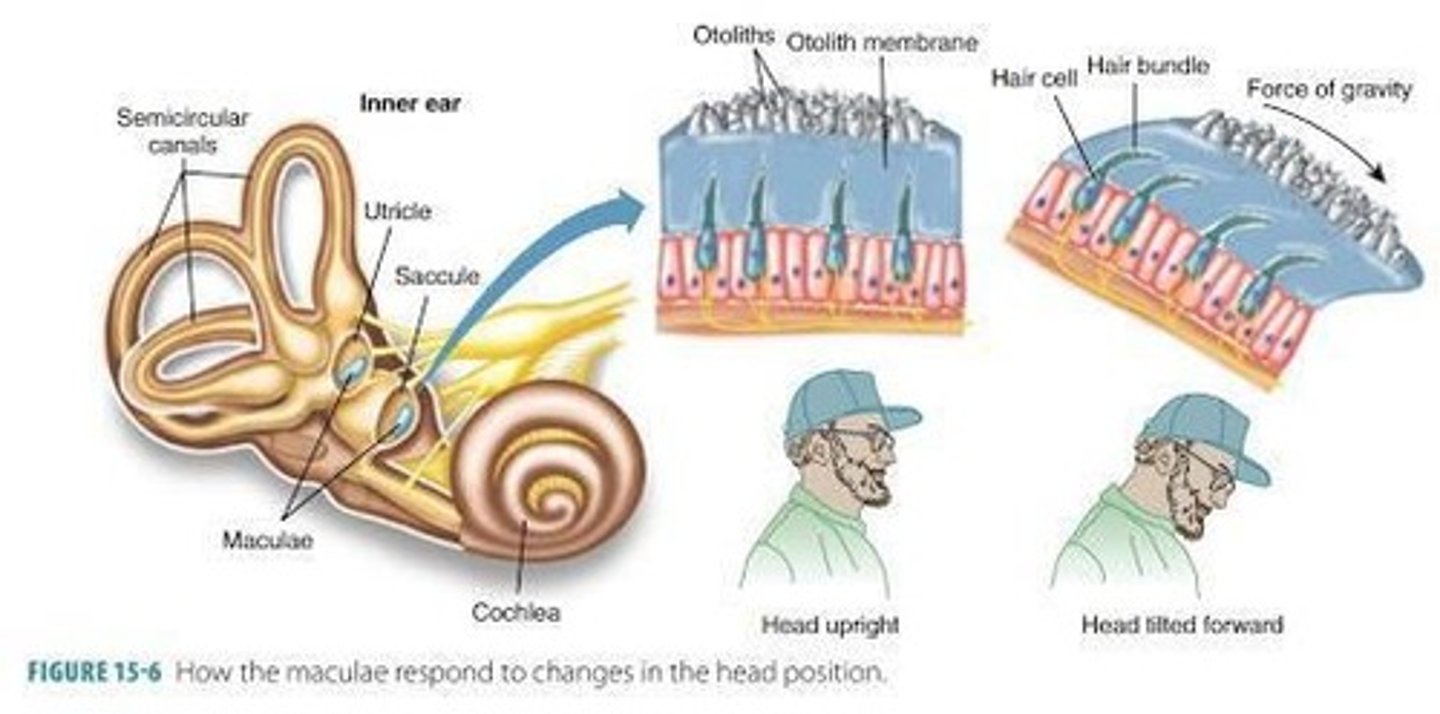
What do the utricle and saccule detect?
Static head position relative to gravity and linear acceleration.
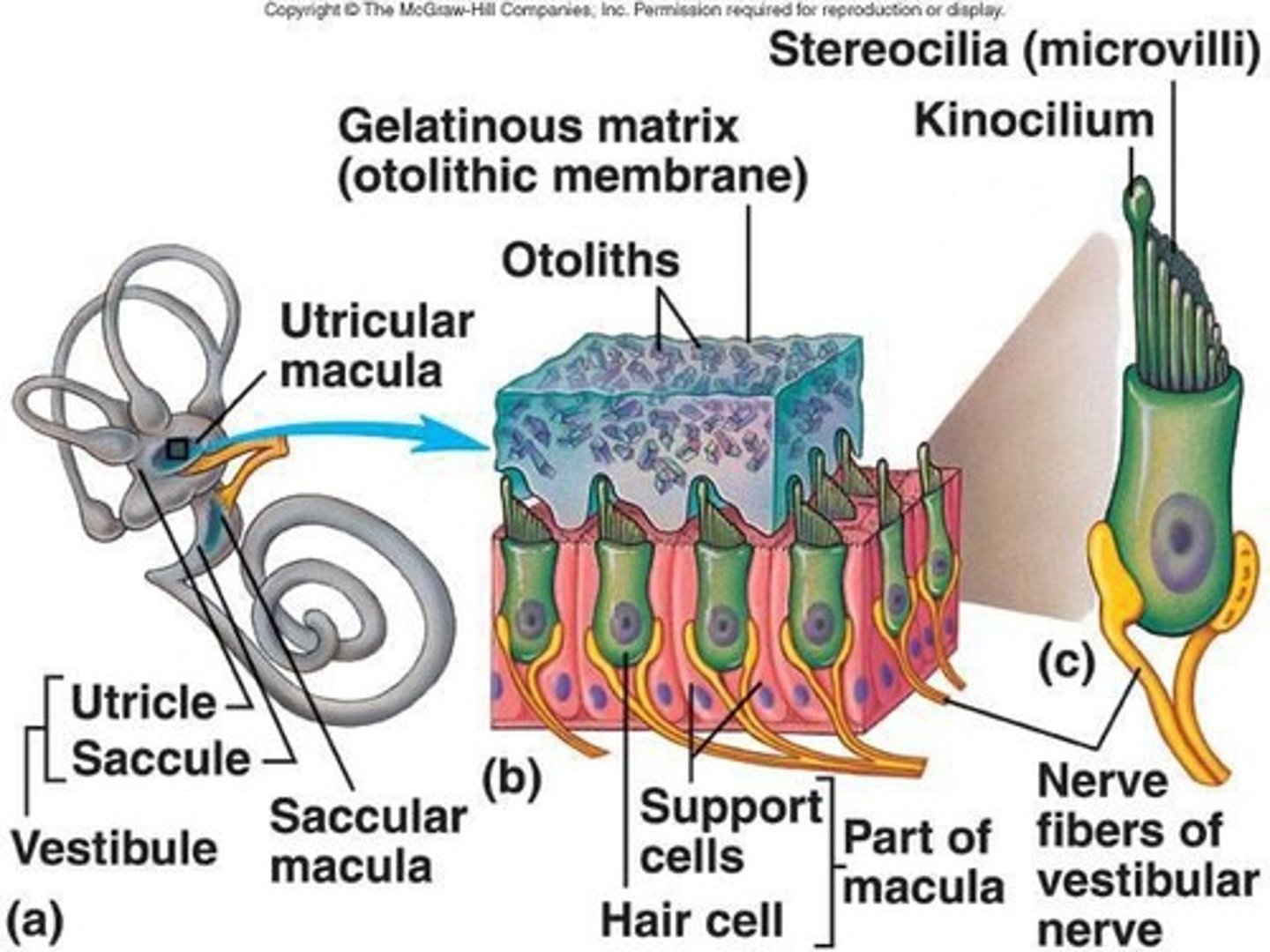
What are the maculae in the context of the utricle and saccule?
The sensory organ of the saccule and utricle.
How does the orientation of the maculae differ between the utricle and saccule?
Utricle maculae is in the horizontal plane; saccule maculae is in the vertical plane.
What is the function of otoliths in the vestibular system?
They provide static information and respond to linear or vertical acceleration.
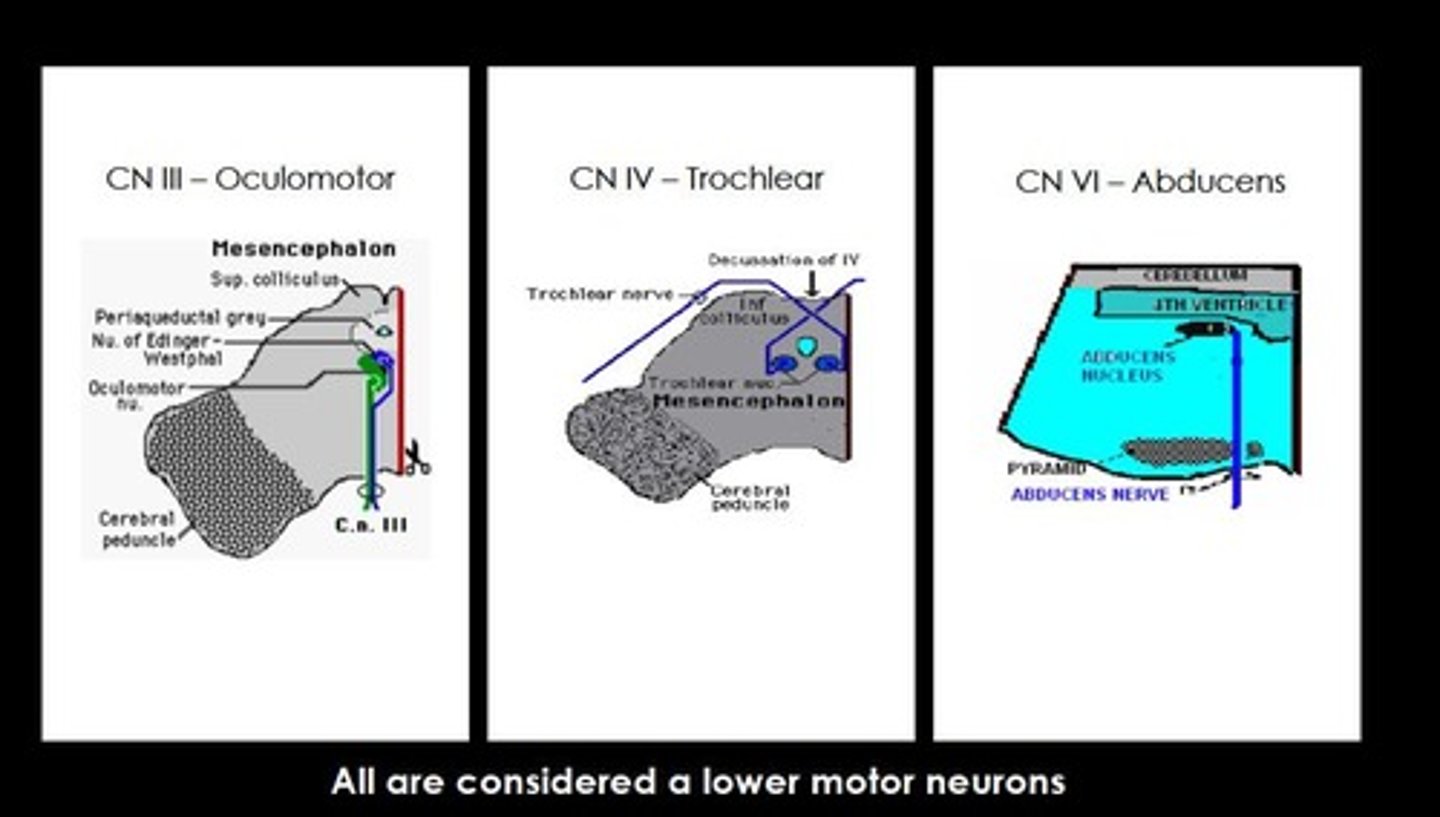
What is the medial longitudinal fasciculus (MLF)?
An ascending tract that carries fibers from the vestibular nuclei to the lower motor neurons of cranial nerves III, IV, and VI.