physics test 1 quizlet
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
ultrasound waves
• beyond the audible range, used to evaluate soft tissue
• Infrasound - less than 20 Hz
• Audible sound- between 20 Hz & 20kHz
• Ultrasound- greater than 20 kHz
• Diagnostic ultrasound rang 1-10 MHz
• lower frequency Probe for deeper structures.
• Higher frequency Probe for surface structures.
• low frequency probe receives greater depth penetration but less axial resolution.
• high frequency probe receives less depth penetration but increases the axial resolution.
Metric System Powers of 10
• Scientific Engineering Notation
• 1,000,000=1.0 x 106
• 0.000000124=1.24 x 10-7
• 1742=1.742 x 103
Frequency is directly related to
axial resolution
Frequency is inversely related to
period and depth
Sound waves:
• Sound is a mechanical wave in which particles in the medium move
• As sound travels through mediums molecules are alternately compressed (squeezed together) and rarefied (stretched apart)
Three acoustic variables
pressure, density, distance
Density-
: Concentration of mass in volume. (kg/cm³)
pressure
• Pressure: Concentration of force in area. (Pa)
distance
• Distance: measure of particle motion. (m, mm, cm.....)
àTransverse waves particles move in a direction that is perpendicular to the direction the wave propagates
àLongitudinal waves particles move in the same direction that the wave propagates
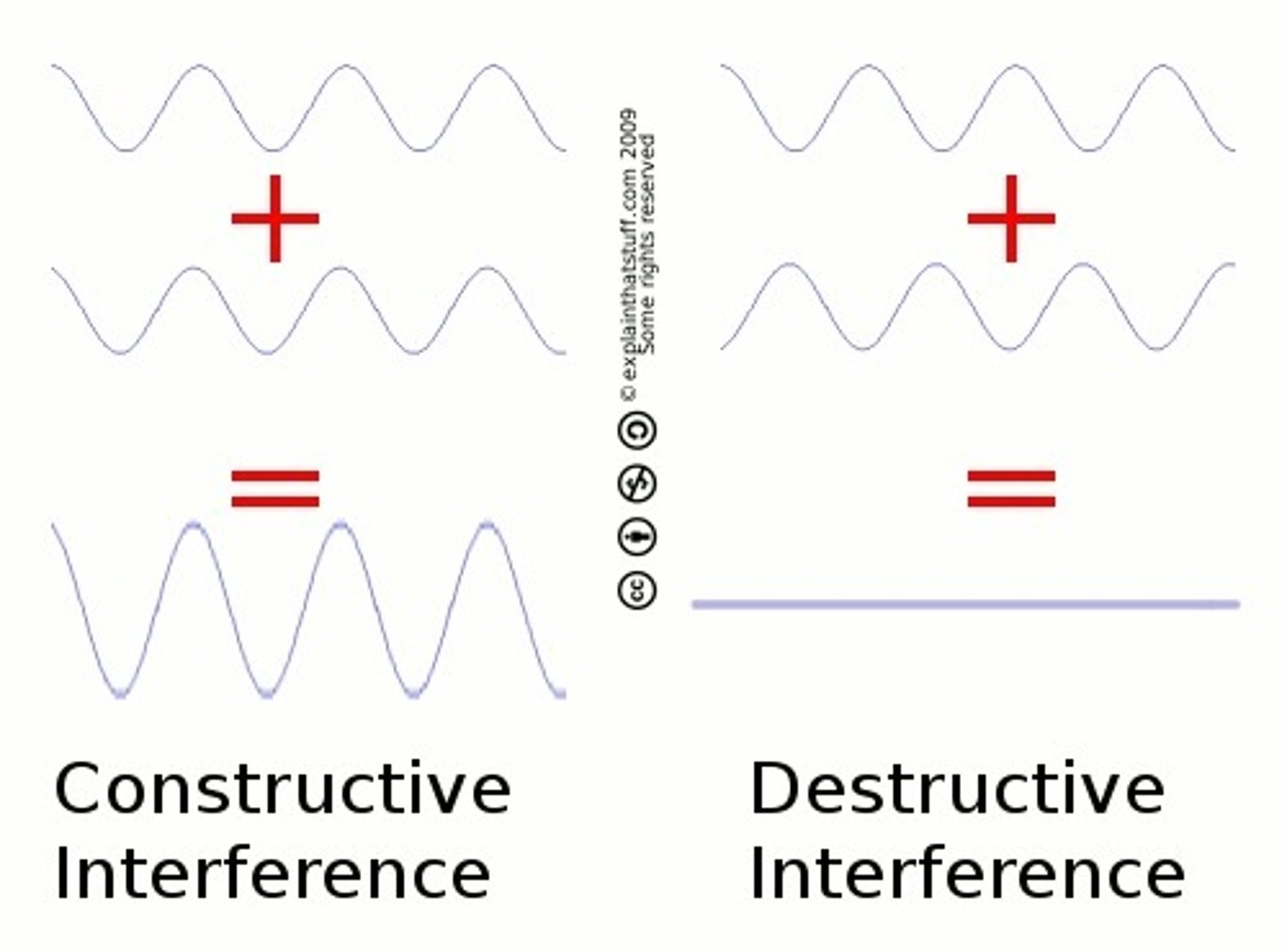
Constructive interference
• In phase waves form a single wave of greater amplitude than either of its components
• The resulting wave is larger
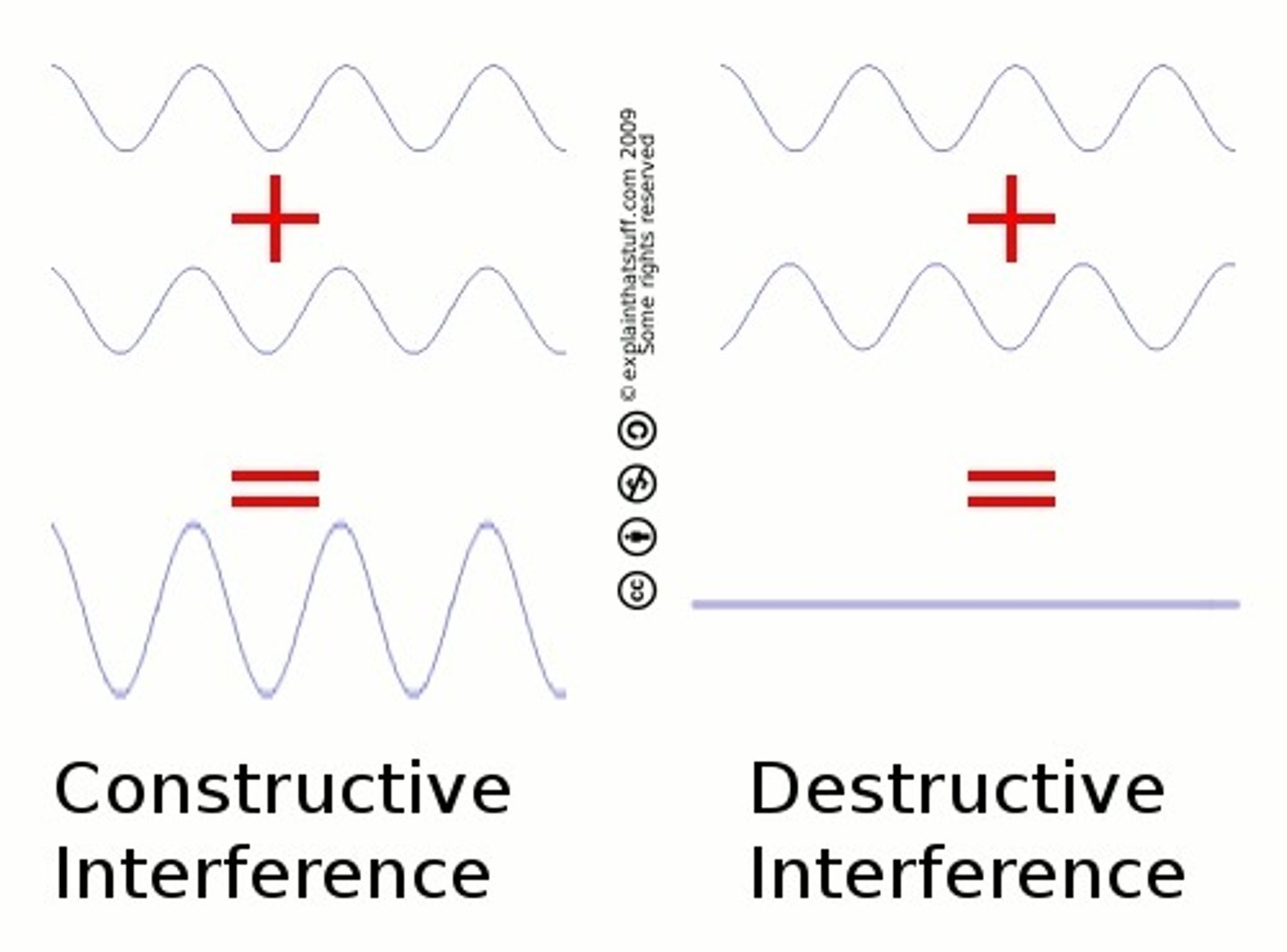
Destructive interference
Out of phase waves form a single wave of lesser amplitude than at least one of its components
• Resultant wave is smaller
Speed of Sound:
In Soft tissue speed is 1540m/sec or 1.54 mm/ μs.
• In Fat speed is 1450 m/sec.
• Bone speed is3,500 m/sec.
• Air speed is 330 m/sec.
1.Period:
à Time start from one cycle to start another cycle.
• Unit: μs
• Determined by Sound source.
• Not adjustable
• Period inversely related to Frequency.
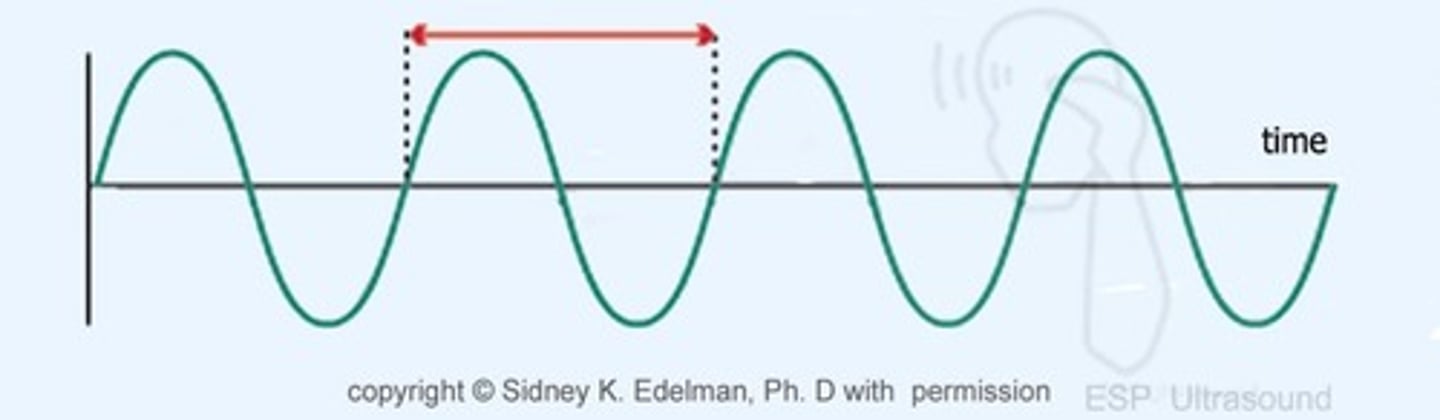
2.Frequency:
àNumber of cycles in one Sec.
• Unit: Hz
• Determined by Sound source.
• Not adjustable
• frequency inversely related to Period.
• frequency inversely related to Depth.
• frequency directly related to Axial Resolution.
• frequency inversely related to Wavelength.
Amplitude:
• Unit: dB
• Determined by Sound source.
• It's adjustable
• Amplitude directly related to Power.
power
Unit: Watts
• Determined by Sound source.
• It's adjustable
• Amplitude directly related to Power.
5.Intensity:
Unit: W/cm2
• Determined by Sound source.
• It's adjustable
• Intensity directly related to Amplitude directly related to Power.
6. Wavelength
à Length of One complete cycle.
• Unit: m / mm
• Determined by both Sound source and medium.
• It's not adjustable.
• frequency inversely related to Wavelength.
• Wavelength (mm) = Speed (mm/ μs)/ Frequency (Hz).
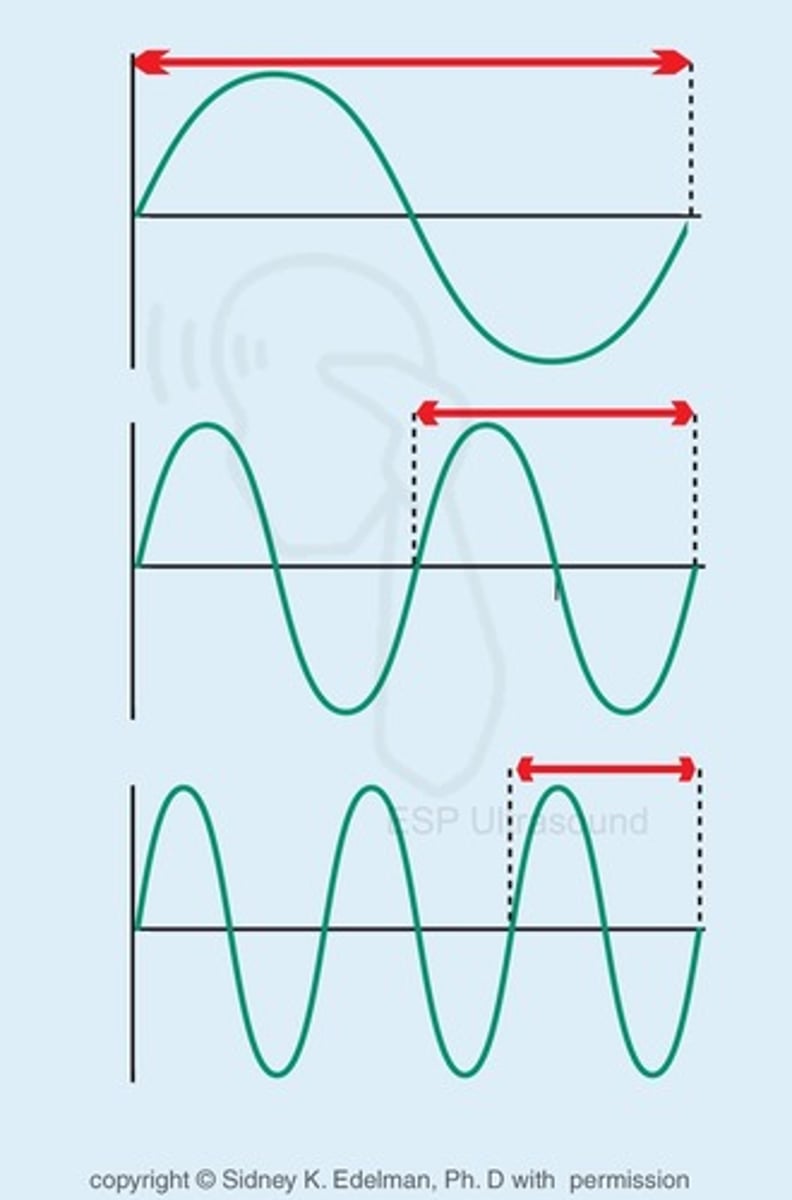
7. Propagation Speed:
• Unit: mm/ μs.
• Determined by Medium only.
• It's Not adjustable
• Speed directly related to Stiffness.
• Speed inversely related to Density.
transducer settings
•Set in certain increments: 2.0,2.5,4.0,5.0,7.0,10.0
deeper structures
abdominal aorta, kidney, heart are set at the lower frequencies
superficial structures
The surface structures such as: vascular (arteries and veins), and thyroid are set at higher frequencies
universal probe
4.0
METRIC SYSTEM POWERS OF 10
•Positive exponent greater than 10
•Negative exponent less than 1
•Multiply by the appropriate power of 10
•See page 6 chapter one
1,000,000=1.0 x 106
•0.000000124=1.24 x 10-7
•1742=1.742 x 103
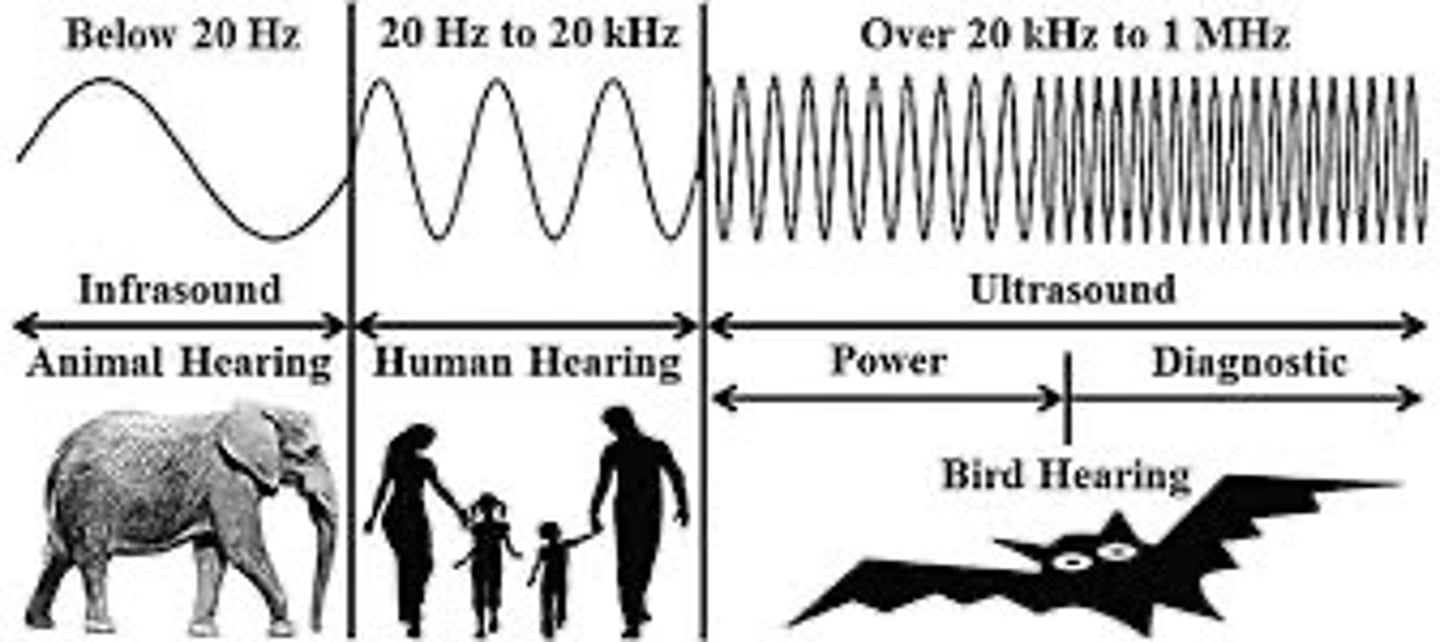
Infrasound
less than 20 Hz
audible sound
between 20 Hz and 20 kHz
Ultrasound
Sound waves with frequencies above 20,000 Hz.
PULSED WAVES
5 Parameters describe pulsed sound
•Pulse duration
•Spatial pulse length
•Pulse repetition period
•Pulse repetition frequency
•Duty factor
PULSE DURATION "TIME"
•Pulse duration is the actural time from the start of a pulse to the end of that pulse
•When the pulse is "on" not "off"
•Measured in units of time in ultrasound typically microseconds 0.3us
•Determined by the sound source
•Fixed duration for the particular transducer cannot be manipulated
DIRECTLY PROPORTIONAL
Directly proportional means that if one item increases the other item increases
•Directly proportional = Directly related
•Frequency is directly related to axial resolution
INVERSELY PROPORTIONAL
decreases
•Inversely proportional = Inversely related
•Frequency is inversely related to period
TRANSVERSE WAVES VS. LONGITUDINAL WAVEs
•Transverse waves particles move in a direction that is perpendicular to the direction the wave propagates
•Longitudinal waves particles move in the same direction that the wave propagates
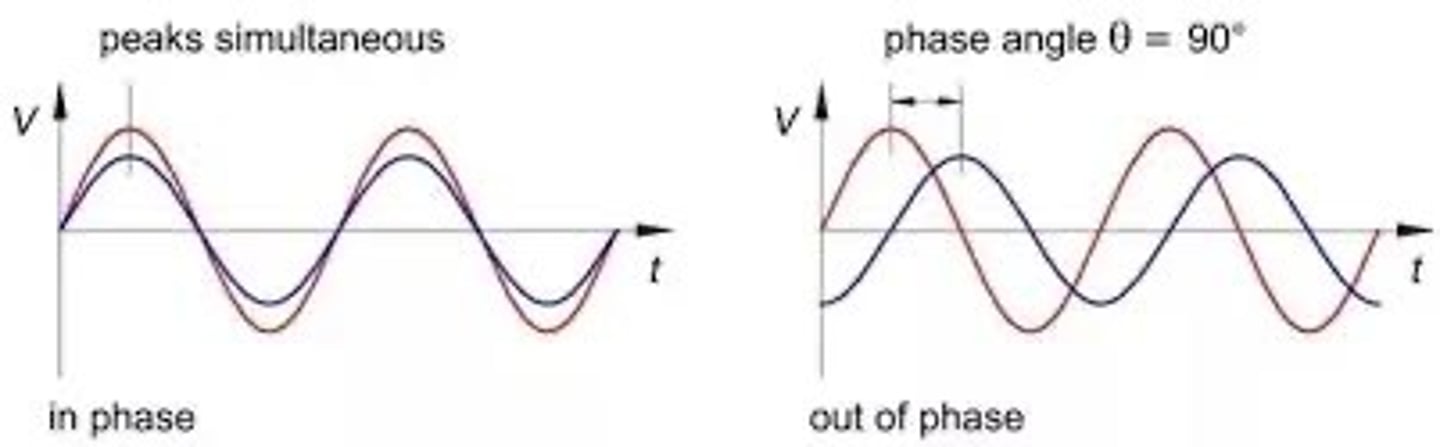
IN PHASE WAVES VS. OUT OF PHASE WAVES
In phase when their peaks (max values) occur at the same time and location
•Out of phase their peaks occur at different times
RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN PERIOD AND FREQUENCY
Increased transducer frequency from 2.0hz to 10.0hz decreases the period
•Decreased transducer frequency from 10.0hz to 2.0hz increases the period
What is a kilohertz?
A kilohertz is 1000 Hz, which means 1000 waves per second.
What is a megahertz?
1 million waves per second
What is a hertz?
one cycle per second
Piezoelectric effect
The sound beam used in diagnostic ultrasound are produced from a transducer by the piezoelectric effect.
•The transducer is a means of converting one form of energy into another, from a electrical wave to a mechanical wave upon transmission
•Reception is from mechanical to electrical
Stiffness and speed are ______ related.
directly
Density and speed are _____ related.
inversely