SQL Overview: DML, Data Types, and Integrity Constraints
1/99
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
100 Terms
Relational Algebra
Procedure-based data manipulation language.
Relational Calculus
Non-procedural data manipulation language using logic.
SQL
Structured Query Language for database manipulation.
4GLs
Fourth-generation languages for user-friendly applications.
5GLs
Fifth-generation languages using natural language.
DDL
Data Definition Language for database schema.
DML
Data Manipulation Language for data operations.
ISO Standard
International standard for SQL compliance.
SEQUEL
Original name for SQL, developed in 1974.
Integrity Enhancement Feature
Enhancements for data integrity in SQL.
Integrity Constraints
Rules ensuring data validity in databases.
Primary Key
Unique identifier for table rows.
Foreign Key
Column linking child table to parent table.
Referential Integrity
Ensures foreign key values match primary keys.
Domain Constraints
Rules defining valid values for a column.
CHECK Constraint
Ensures values meet specific conditions.
CREATE DOMAIN
Defines a custom data type in SQL.
DROP DOMAIN
Removes a previously defined domain.
Tuple Relational Calculus
Uses tuples to express queries in logic.
Domain Relational Calculus
Uses domain variables to express queries.
SQL3
SQL version supporting object-oriented features.
SELECT Statement
Retrieves data from a database.
INSERT Statement
Adds new records to a database.
UPDATE Statement
Modifies existing records in a database.
DELETE Statement
Removes records from a database.
Views
Virtual tables based on SQL queries.
View Updatability
Ability to modify data through views.
ISO Transaction Model
Defines ACID properties for transactions.
Literals
Constants used in SQL statements.
Reserved Words
Fixed keywords in SQL syntax.
FOREIGN KEY
Establishes a relationship between two tables.
ON DELETE SET NULL
Sets foreign key to NULL on deletion.
CREATE ASSERTION
Defines a condition that must hold true.
SQL DDL
Defines database schema and objects.
CREATE SCHEMA
Creates a new database schema.
DROP SCHEMA
Deletes a schema and its objects.
RESTRICT
Prevents deletion if schema is not empty.
CASCADE
Deletes all associated objects automatically.
CREATE TABLE
Defines a new table structure.
PRIMARY KEY
Uniquely identifies each row in a table.
UNIQUE Constraint
Ensures all values in a column are distinct.
ALTER TABLE
Modifies an existing table structure.
DROP TABLE
Removes a table and its data.
INSERT INTO
Adds new rows to a table.
INSERT ... SELECT
Copies rows from one table to another.
UPDATE
Modifies existing records in a table.
DELETE
Removes rows from a table.
DISTINCT
Eliminates duplicate rows in query results.
GROUP BY
Groups rows sharing a common value.
HAVING Clause
Filters groups based on a condition.
ORDER BY
Sorts query results by specified columns.
DEFAULT
Specifies a default value for a column.
CONSTRAINT
Limits the type of data in a column.
VARCHAR
Variable-length character string data type.
DECIMAL
Fixed-point number data type for precision.
SMALLINT
Integer data type with small storage size.
Date Format
Specifies date representation in SQL.
SELECT
Command to retrieve data from a database.
FROM
Specifies the table to select data from.
AS
Renames a column in the result set.
WHERE
Filters records based on specified conditions.
BETWEEN
Tests if a value falls within a range.
IN
Checks if a value matches any in a list.
LIKE
Pattern matching operator for string comparisons.
IS NULL
Tests for null values in a column.
COUNT
Returns the number of items in a column.
SUM
Calculates the total of a numeric column.
AVG
Calculates the average of a numeric column.
MIN
Finds the smallest value in a column.
MAX
Finds the largest value in a column.
HAVING
Filters groups based on aggregate conditions.
Subquery
A SELECT statement nested within another query.
Calculated Fields
Columns derived from expressions in SELECT.
Compound Condition
Combines multiple conditions using AND/OR.
NULL Search Condition
Condition to find records with null values.
Pattern Matching Symbols
Special characters for LIKE queries: % and _.
Aggregate Functions
Functions that perform calculations on multiple rows.
Single Column Ordering
Sorts results by one specified column.
Multiple Column Ordering
Sorts results by multiple specified columns.
Negated Version
Opposite condition using NOT in SQL queries.
Viewing
Table containing records of property viewings.
Branch
Table representing different office locations.
Aggregate Function
Calculates a single result from multiple rows.
AVG()
Returns the average value of a numeric column.
SalDiff
Difference between salary and average salary.
WHERE Clause
Filters records based on specified conditions.
ORDER BY Clause
Sorts the result set by specified columns.
Single Column Subquery
Subquery returning only one column of data.
EXISTS
Checks for existence of rows in subquery.
ANY
Condition true if satisfied by any subquery value.
ALL
Condition true only if satisfied by all values.
IN Operator
Checks if a value exists in a set.
JOIN
Combines rows from two or more tables.
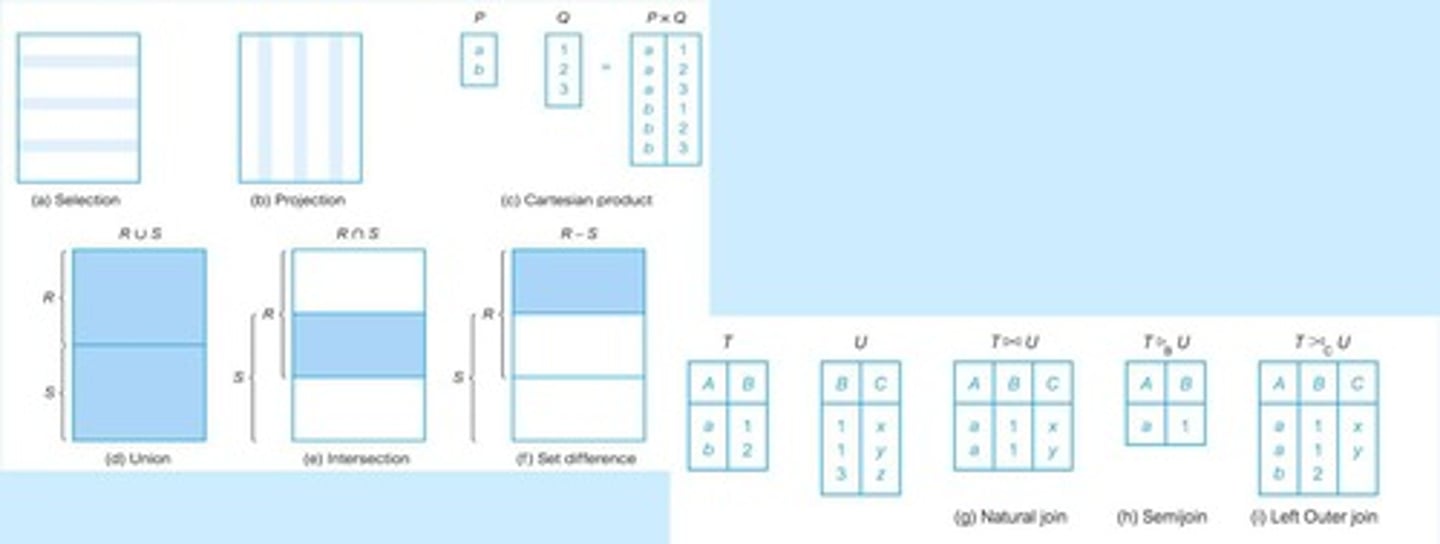
Equi-Join
Join based on equality condition between columns.
LEFT OUTER JOIN
Includes unmatched rows from the left table.
RIGHT OUTER JOIN
Includes unmatched rows from the right table.
FULL OUTER JOIN
Includes unmatched rows from both tables.
CROSS JOIN
Produces Cartesian product of two tables.
GROUP BY Clause
Groups rows sharing a property for aggregation.
COUNT()
Returns the number of rows that match a query.