Biology 101: Intro to Biology Ch 6. Cell Structure, Organelles & Organelle Functions
1/95
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
96 Terms
nucleus
membrane-bound structure that contains the genetic material of a cell
replication
creates an identical copy of DNA
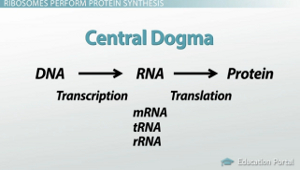
transcription
the process of creating different types of RNA from DNA
translation
process that creates proteins from mRNA; protein synthesis by creating a chain of amino acids linked together by polypeptide bonds
nuclear envelope
double membrane comprised of an outer membrane and an inner membrane
nuclear pores
small openings in the nuclear envelope where the inner and outer membranes come together
chromatin
DNA packaged with the help of specialized proteins
nuclear lamina
attaches to the nuclear envelope and chromatin to help maintain the shape of the nucleus
nucleolus
starting site of ribosomal synthesis from rRNA and proteins
The _____ is a double membrane that shields the nucleus.
nucleolus
DNA
chromatin
nuclear envelope
nuclear envelope
Which of the following does NOT take place in the nucleus?
Ribosome synthesis
Transcription
Replication
All of these take place in the nucleus
All of these take place in the nucleus
Where is the starting point of ribosome synthesis?
Nucleolus
Nuclear localization signal
Nuclear envelope
Nuclear pore
Nuclear lamina
Nucleolus
Which of the following helps maintain the shape of the nucleus?
Nucleolus
Nuclear localization signal
Nuclear pore
Nuclear lamina
Nuclear envelope
Nuclear lamina
How do large proteins enter the nucleus?
With chemical energy
By stretching the nuclear pore
With a nuclear localization signal
Helped by an import protein
All of these
All of these
Central Dogma
Ribosome
cellular structure that performs translation, or protein synthesis/ composed of rRNA and protein
large subunit/small subunit

Which of the following first binds to the mRNA message?
Rough endoplasmic reticulum
Cytoplasm
Large subunit
Small subunit
P site
Small subunit
What are ribosomes comprised of?
rRNA and protein
mRNA and protein
tRNA and protein
mRNA and tRNA
rRNA and mRNA
rRNA and protein
Where can you NOT find ribosomes performing translation?
Attached to the endoplasmic reticulum
Cytoplasm
All of these are places that you can find ribosomes performing translation.
Chloroplasts
Mitochondria
All of these are places that you can find ribosomes performing translation.
Where are the A, P, and E sites located?
rRNA
Large subunit
Small subunit
Rough endoplasmic reticulum
Cytoplasm
Large subunit
Which ribosomal site joins amino acids via a polypeptide bond?
A site
R site
E site
P site
P site
endomembrane system
a series of compartments that work together to package, label, and ship proteins and molecules
Lumen
inside compartment of the endoplasmic reticulum
Smooth endoplasmic reticulum
membranous compartment of smooth tubes; lipid and steroid synthesis; proteins and small molecules can be chemically modified
Rough endoplasmic reticulum
membranous compartments and sacs studded with ribosomes
Golgi apparatus
membranous compartment of flattened sacs; packages, sorts, and sends off proteins from the rough ER;
What type of cell might have more smooth ER?
Heart
Nerve
Liver
Skin
Liver
Which of the following is NOT true of the endomembrane system
It has many folds.
The lumen is not in contact with the cytoplasm.
It releases its contents in vesicles.
It is a continuous part of the cell membrane
Its components work together to make, modify, and package molecules.
It is a continuous part of the cell membrane
Which part of the endomembrane system synthesizes lipids and steroids?
Ribosome
Rough ER
Smooth ER
Golgi
Smooth ER
The following cellular compartment(s) contain a lumen created by their membranes:
Rough and Smooth ER
Golgi
Rough ER, Smooth ER, Golgi
Rough ER
Rough ER and Golgi
Rough ER, Smooth ER, Golgi
Which part of the endomembrane system is a site for protein synthesis?
Smooth ER
Golgi
Rough ER
Nucleus
Rough ER
Cytoskeleton
network of thin fibers; contains some proteins that are similar to the actin and filaments of eukaryotic cells
Microtubules
largest fibers of the cytoskeleton (25 nm in diameter)
Flagella
snake-like whips that drive cell movement
Cilia
multiple short, hair-like structures that beat to move liquid around a cell
Intermediate filaments
mid-sized fibers of the cytoskeleton; diverse role within the cell (8-12 nm in diameter)
Microfilaments
thinnest fibers of the cytoskeleton (7 nm in diameter)
Which of the following is NOT a function of the cytoskeleton?
Anchoring the cell
Transporting of molecules within a cell
Cell movement
Transporting molecules into the cell
Providing cell structure and shape
Transporting molecules into the cell
Which of the following functions is carried out by intermediate filaments but not microtubules?
Cell division
Movement of structures within the cell
Providing nuclear lamina structure
Providing flagella structure
Cell movement
Providing nuclear lamina structure
The following cytoskeleton component(s) can be dynamic, shrinking and growing by adding and subtracting subunits:
Microtubules and Intermediate filaments
Microfilaments only
Microtubules and Microfilaments
Microtubules, Microfilaments & Intermediate filaments
Microtubules only
Microtubules and Microfilaments
Which of the following makes up flagella?
Microtubules in a 9 plus 2 arrangement
Actin dimers in a 9 plus 2 arrangement
Intermediate filaments in a 9 plus 2 arrangement
Microfilaments in a 9 plus 2 arrangement
Microtubules in a 9 plus 2 arrangement
Microfilaments are composed of
alpha and beta tubulin subunits
rope-like twists of proteins
Chains of tubulin in a double helix
Chains of actin in a double helix
Chains of actin in a double helix
cellular respiration
process that converts food into usable chemical energy
mitochondria
membrane-bound structures where cellular respiration occurs
mitochondrion
outer membrane - selectively permeable membrane that surrounds the mitochondria; inner membrane - folds inward to form extra surfaces for cellular respiration
cristae
folds created by the inner membrane
matrix
contains enzymes for cellular respiration as well as its own ribosomes
Which of the following cells might have the most mitochondria?
Skin cell
Bacterium
Cardiac muscle cell
None of these cells have mitochondria
Cardiac muscle cell
Which does NOT describe the inner membrane of the mitochondria?
Selectively permeable
Contains components for cellular respiration
Impermeable
Folds to create cristae
Interior to the outer membrane
Selectively permeable
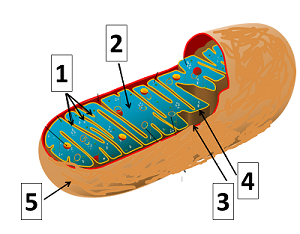
On the following diagram, which number indicates the cristae?
5
4
1
3
2
1
What part of the mitochondria creates more space for cellular respiration?
Outer membrane
Ribosomes
Matrix
Inner membrane
Integral membrane proteins
Inner membrane
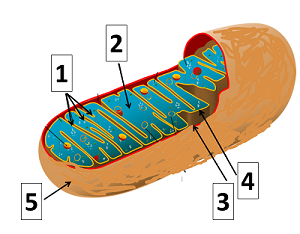
On the following diagram, which number indicates where mitochondrial DNA is located?
1
3
5
4
2
2
Photosynthesis
process that converts energy from sunlight into food in plant cells
Chloroplasts
structural sites of photosynthesis, where light energy is converted into food
Thylakoids
small disk-like compartments composed of membranes that are the sites of sunlight-dependent photosynthesis
Stroma
inner liquid portion of the chloroplast
Grana
stacks of thylakoids within chloroplasts
Chlorophyll
pigment, or compound, that absorbs a specific wavelength of energy from sunlight
Which of the following is true about chlorophyll?
Is broken down into a food source
Absorbs specific light wavelengths
It is a protein
Exists in the stroma
Absorbs specific light wavelengths
Which of the following is NOT contained in a chloroplast?
Nucleus
Chlorophyll
DNA
Ribosomes
Stroma
Nucleus
What process takes place in the chloroplast turning light energy into food?
Protein Synthesis
Chlorophyll
Photosynthesis
Stroma
Photosynthesis
Which part is a granum?

In what singular part is chlorophyll located?

Cell Wall
a protective layer surrounding the cell on the outside of the plasma membrane
Cellulose
a polysaccharide sugar that provides strength to the cell wall
Central vacuole
a large storage compartment in plant cells
The purpose of cellulose is to:
All of these
Store water
Create an acidic environment
Regulate digestive enzymes
Provide strength to the cell wall
Provide strength to the cell wall
Protons pumped into the central vacuole can affect this space by making it:
Waste
Neutral
Acidic
Larger
Basic
Acidic
What is NOT stored in the central vacuole of plants?
Food
Sunlight
Nutrients
Water
Sunlight
A plant cell in a hypotonic solution will respond by:
Shriveling up
Shrinking, but maintain its cell wall shape
Putting pressure on the cell walls through the central vacuole after taking in water.
Bursting
Storing waste in the central vacuole
Putting pressure on the cell walls through the central vacuole
A plant cell surrounded by a hypertonic solution will respond by:
Losing water while maintaining its cell wall shape
Putting pressure on the cell walls through the central vacuole
Storing waste in the central vacuole
Bursting
Losing water while maintaining its cell wall shape
Organelles
membrane-bound compartments; nucleus, mitochondria, chloroplasts, golgi, and endoplasmic reticulum; compartmentalize cellular functions
eukaryote
contain membrane-bound organelles, including a nucleus
prokaryote
do not contain a nucleus or other membrane-bound organelles
Nucleoid
area where DNA exists
Peptidoglycan
polymer of sugar and amino acids that give shape and structure to the bacterial cell wall
What do all eukaryotes have that prokaryotes do not?
Flagella
Cell membrane
Nucleus
Cytoskeleton
DNA
Nucleus
What do both prokaryotes and eukaryotes have that is involved in translation?
DNA
Ribosomes
Nucleus
Peptidoglycan
Endoplasmic reticulum
Ribosomes
Which of the following describes prokaryotic DNA?
They do not have DNA.
It is linear.
It is usually larger than eukaryotic DNA.
It is circular.
It is within a nucleus.
It is circular.
Which is a membrane-bound organelle?
Chloroplasts
Mitochondria
Nucleus
Endoplasmic Reticulum
All answers are correct.
All answers are correct.
The purpose of _____ is to provide separation and compartmentalization of processes in eukaryotes.
organelles
DNA
transcription
cell membrane
translation
organelles
Virus
acellular parasitic particle
consisting of protein and nucleic acid
acellular
NOT made of cells
CAN’T reproduce on their own
CAN’T transport substances between membranes
CAN’T metabolize food
Bacteriophage (Phages)
a virus that infects bacteria
Capsid
viral envelope made of protein
Nucleic Acid
double-stranded or single-stranded DNA or RNA
tail fibers
aid in injecting the viral nucleic acid into the bacterial cell
The Lytic Cycle
bacteriophage will replicate and cause the bacterial cell to burst
The Lysogenic Cycle
phage nucleic acid will integrate into the bacterial genome
Prophage
phage DNA that is integrated into the bacterial DNA
Which of the following is NOT a characteristic of a virus?
Containing nucleic acid
Able to reproduce on its own
Nonliving
Surrounded by capsid proteins
Able to reproduce on its own
After the bacteriophage uses its tail fibers to attach to the bacterial host, what will happen next in the lytic cycle?
Degradation of host DNA
Integration of viral nucleic acid into the bacterial genome
Injection of viral nucleic acid
Lysis of the bacterial cell wall
Assembly of the new viruses
Injection of viral nucleic acid
Which of the following could trigger the lytic cycle of a bacteriophage?
Host cell dividing
Host cell stress
Bacterial protein synthesis
Host cell replicating its genome
Host cell stress
Which of the following describes a process that involves viral integration into the host genome?
Replication
Lytic cycle
Living
Prophage
Lysogenic cycle
Lysogenic cycle
Which of the following describes a process that involves viral replications and assembly within a host, followed by bursting the host cell wall?
Living
Lytic cycle
Lysogenic cycle
Replication
Prophage
Lytic cycle