Session 8: Anxiety
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
Physical symptoms of anxiety
Increase in arousal ( heart rate, sweating, butterflies in stomach, more blood to muscles) in preparation for flight/ fight
When does anxiety become a problem?
- Danger is imagined
- Anxiety is out of proportion to the danger, is persistent, and disabling
- Worrying about normal aspects of daily life or no identifiable trigger
- Panic attacks
- Prolonged and affects functioning
Anxiety is often experienced concurrently with ___ (60%)
Depression
Anxiety disorders
A group of mental disorders characterized by feelings of anxiety and fear
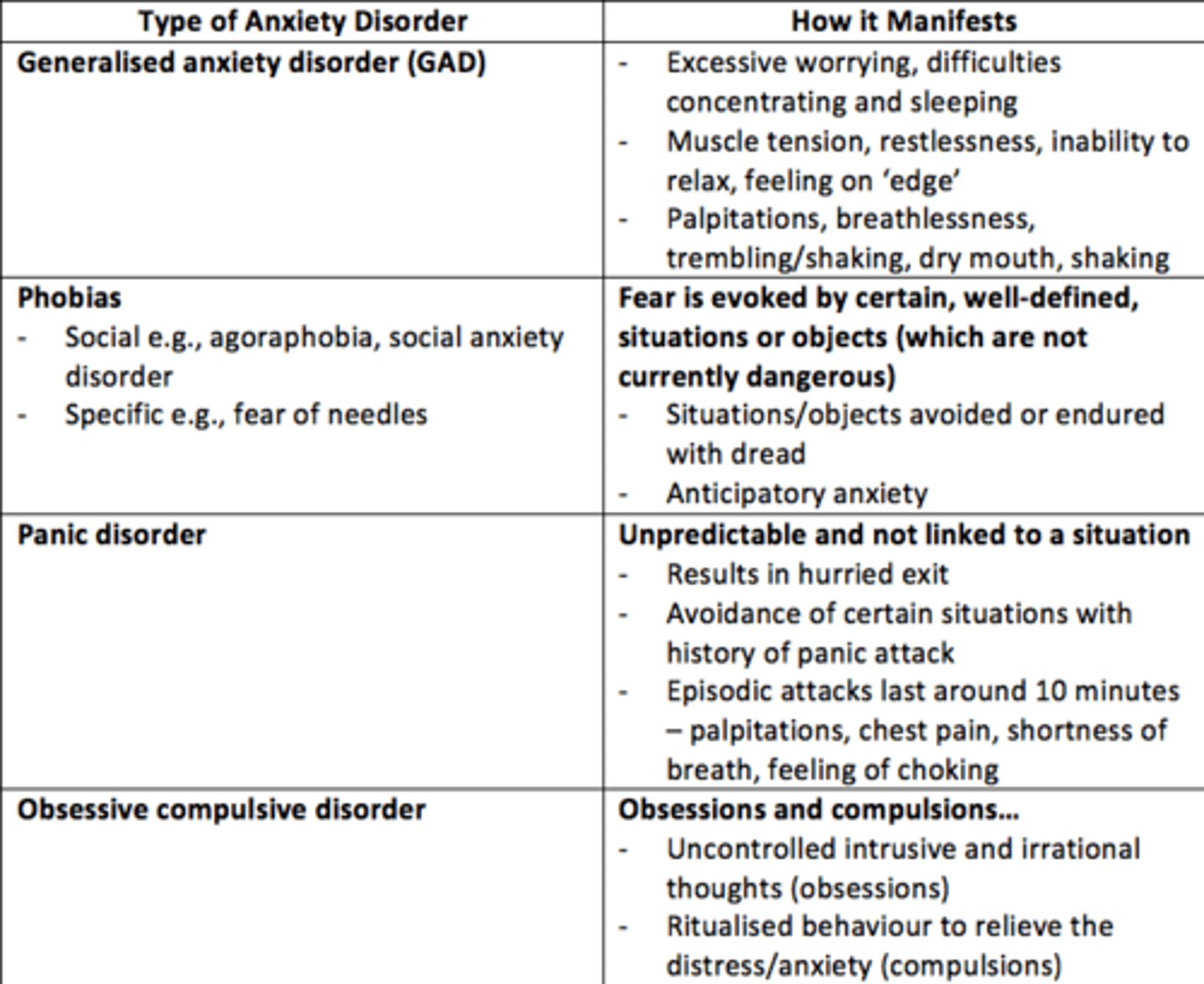
List some anxiety disorders
- Generalised Anxiety Disorder
- Obsessive Compulsive Disorder
- Social phobia
- Post-traumatic stress disorder
- Panic disorder
- Specific phobias
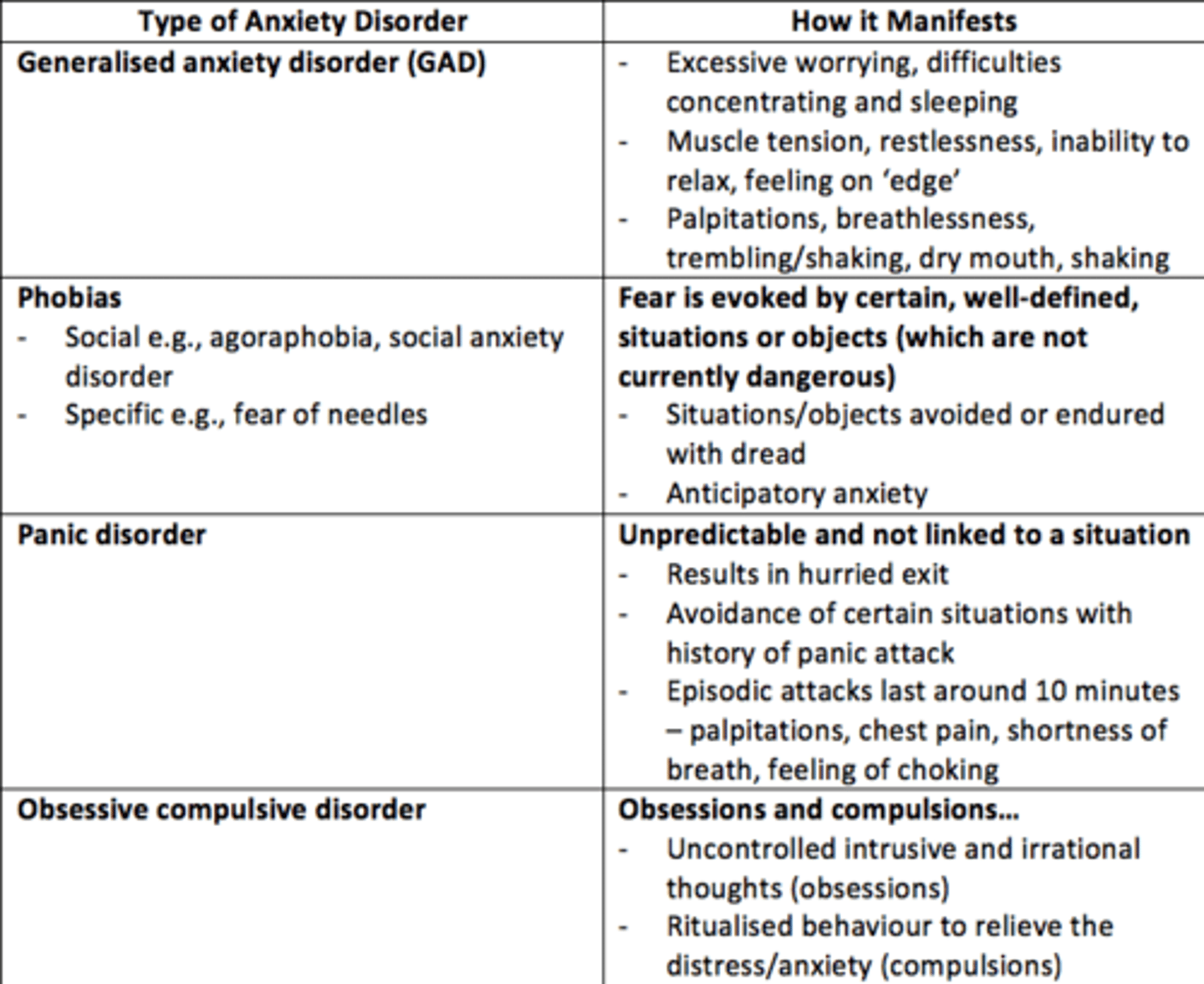
Generalised Anxiety Disorder
• An anxiety disorder in which a person is continually tense, apprehensive, and in a state of autonomic nervous system arousal
• Feeling anxious most days for at least several weeks at a time, and usually for at least 6 months

Three main features of Generalised Anxiety Disorder (GAD)
• Excess worrying, difficulty concentrating, sleeping
• Muscle tension, inability to relax, feeling on edge
• Palpitations, breathlessness, trembling/shaking, dry mouth, sweating
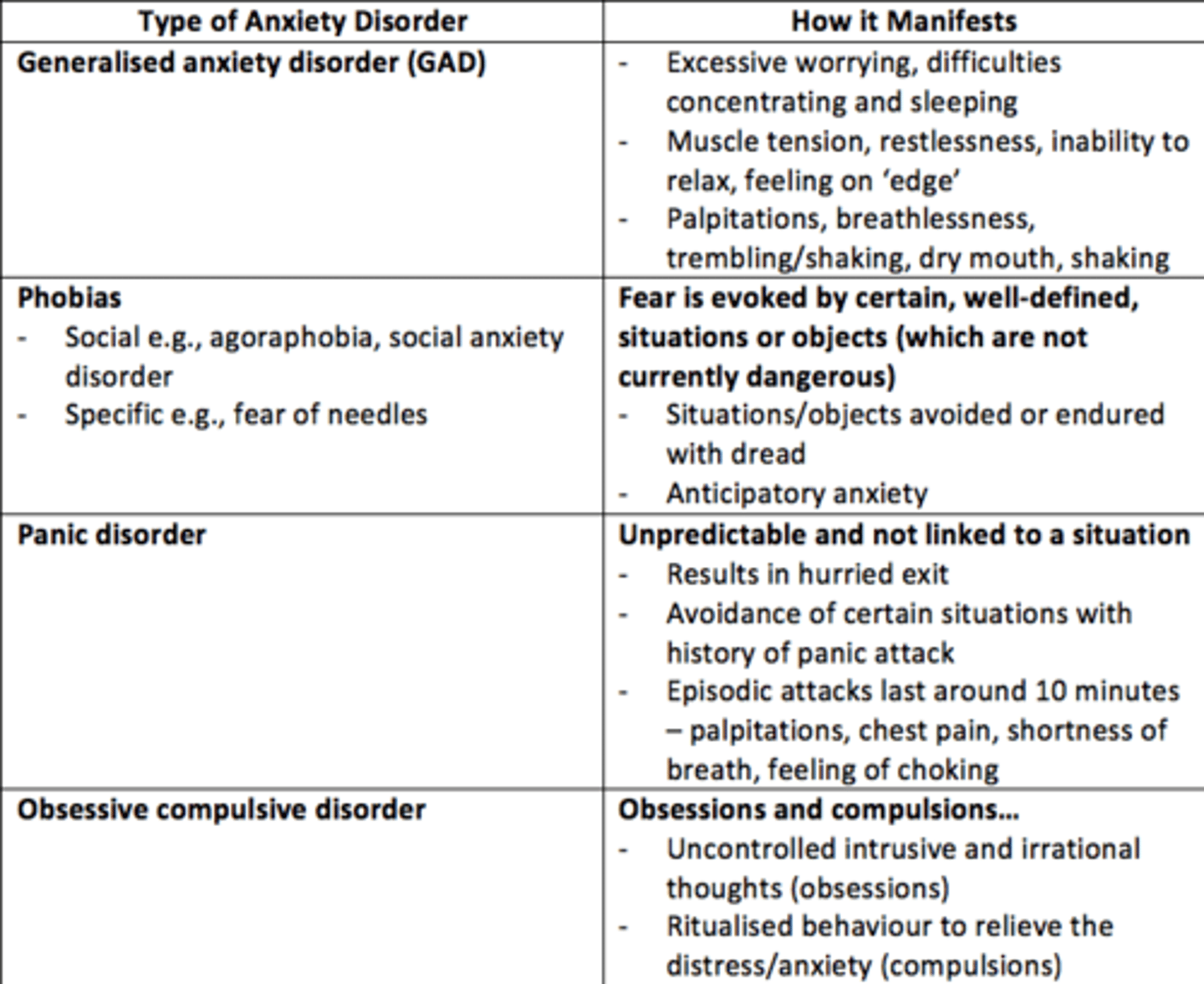
What are the two types of phobia?
- Social = agoraphobia, social anxiety disorder
- Specific = e.g., dental, fear of needles/injections
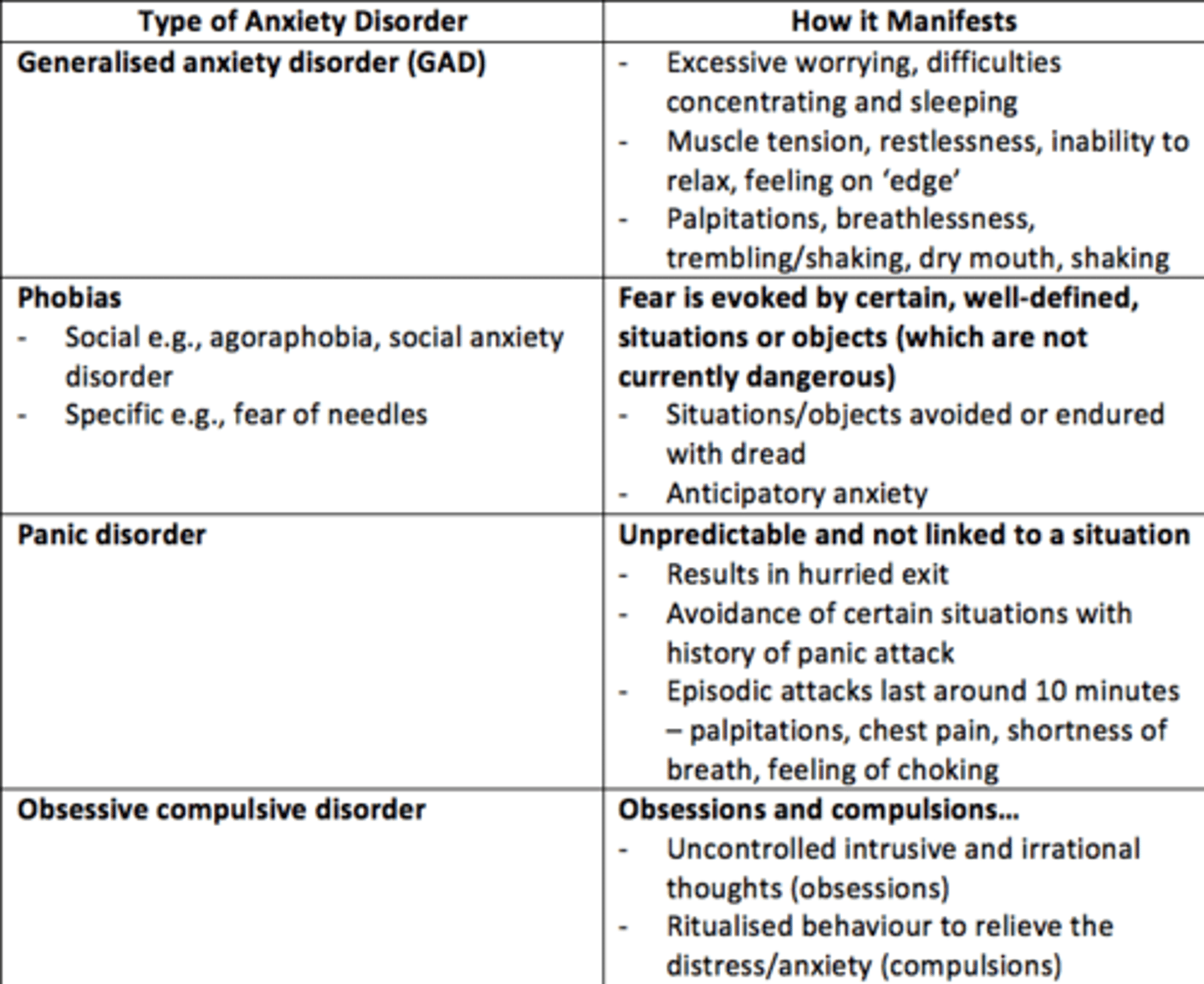
Phobia
Phobias are a disruptive fear that is severe enough to induce distress and/or interfere with the patient’s job or social life, thus leading to avoidance of the stimuli.
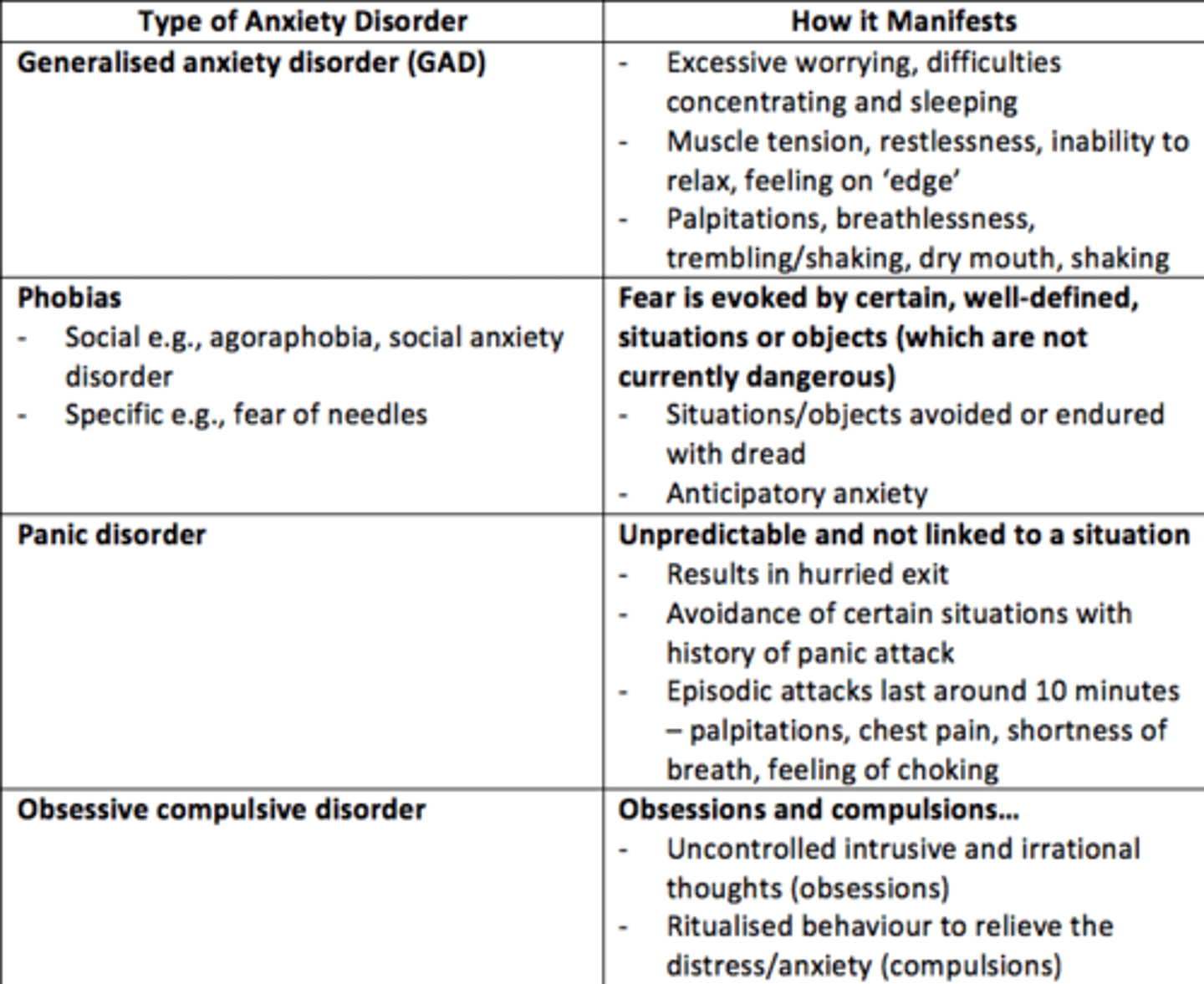
Panic disorder
• Recurrent attacks of sudden, severe anxiety
• May lead to avoidance of certain situations
• Persistent fear of having another attack
Panic attack
Episodic attacks lasting around 10 minutes typically, palpitations/chest pain/shortness of breath/choking sensations/feeling dizzy.
Obsessive Compulsive Disorder (OCD)
• Uncontrolled intrusive and irrational thoughts (obsessions)
• Ritualised behaviors to relieve the distress/anxiety or to “stop” harm (compulsions)
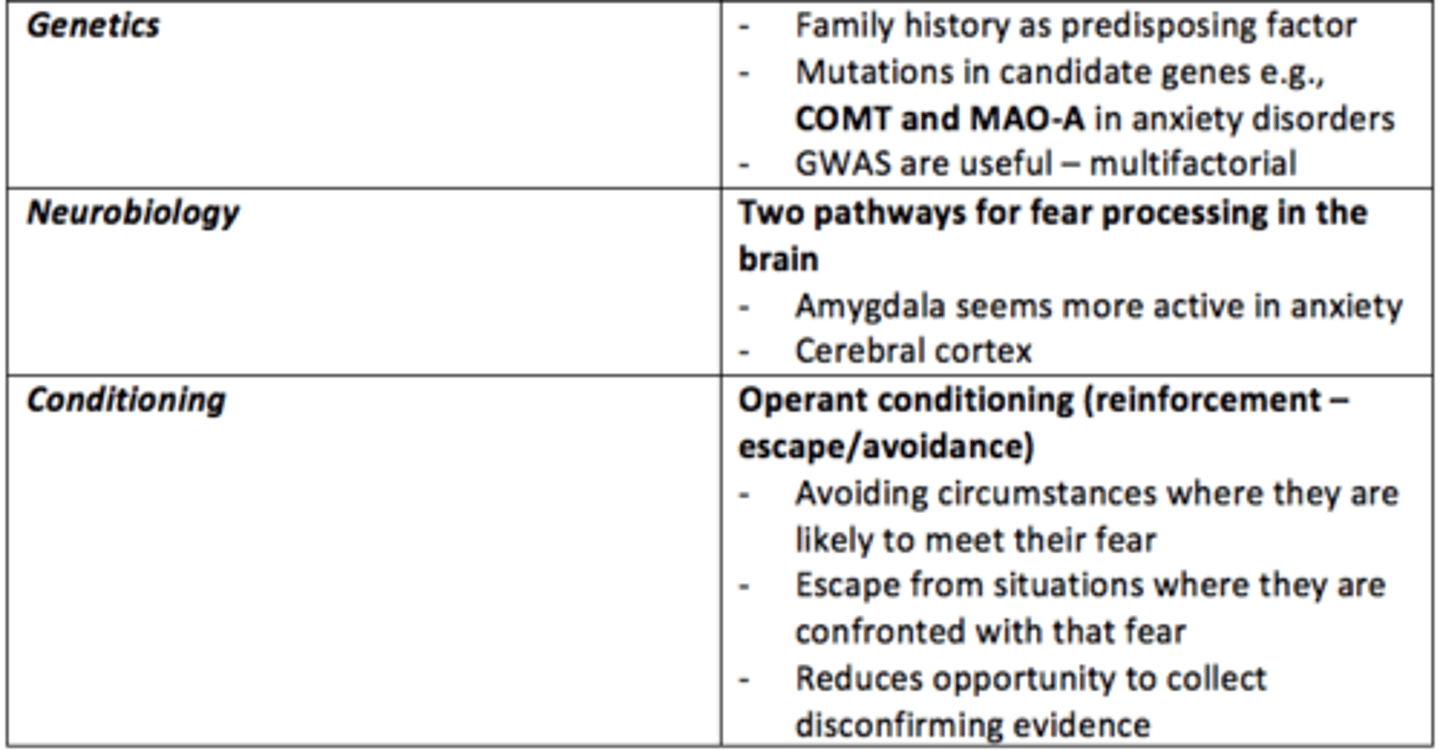
What causes some anxiety disorders?
• Unique to individuals - traumatic experiences
• Genetics
• Neurotransmitters, neurobiology
• Conditioning
• Cognitive distortions and cognitive bias
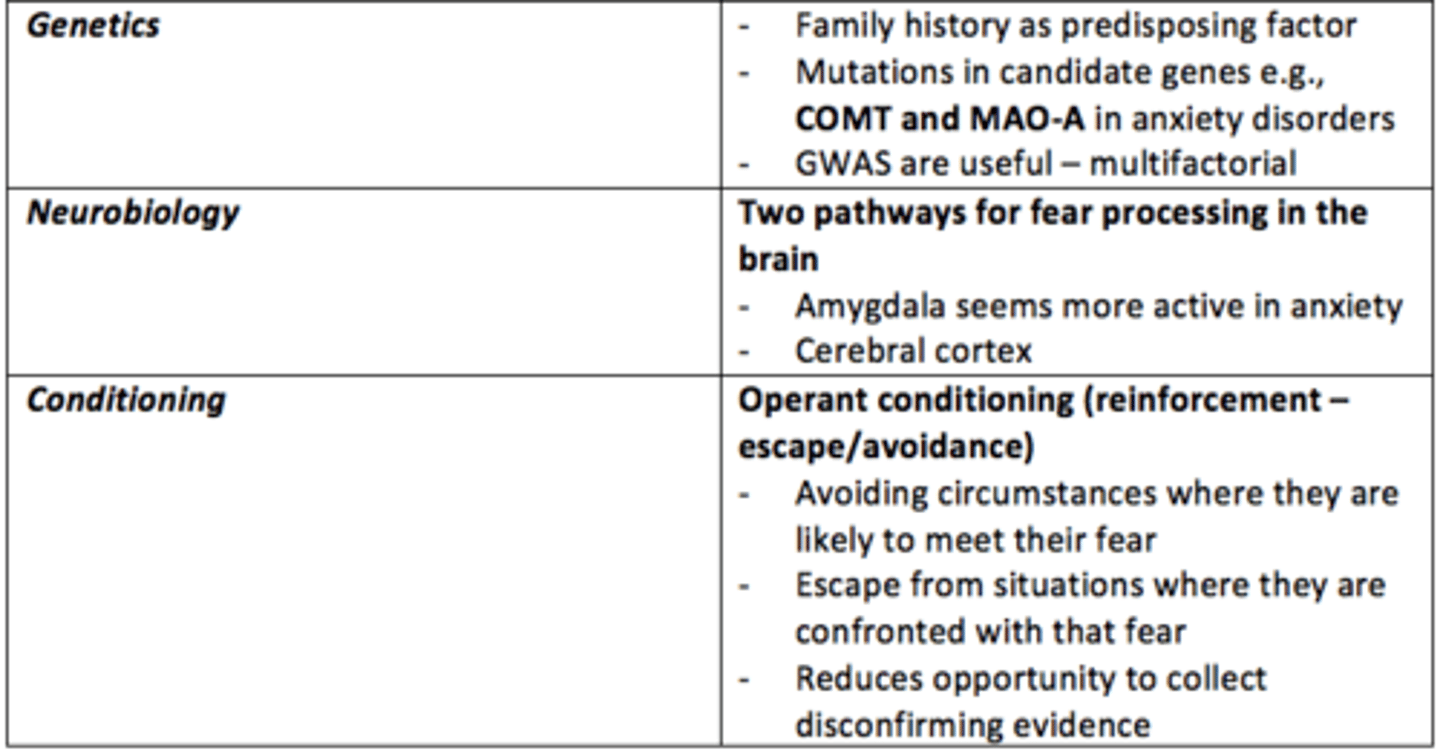
___ history is a predisposing factor to developing anxiey disorders
Family

What are the two major pathways for fear processing in the brain?
1) Cerebral cortex = slow
2) Amygdala = fast
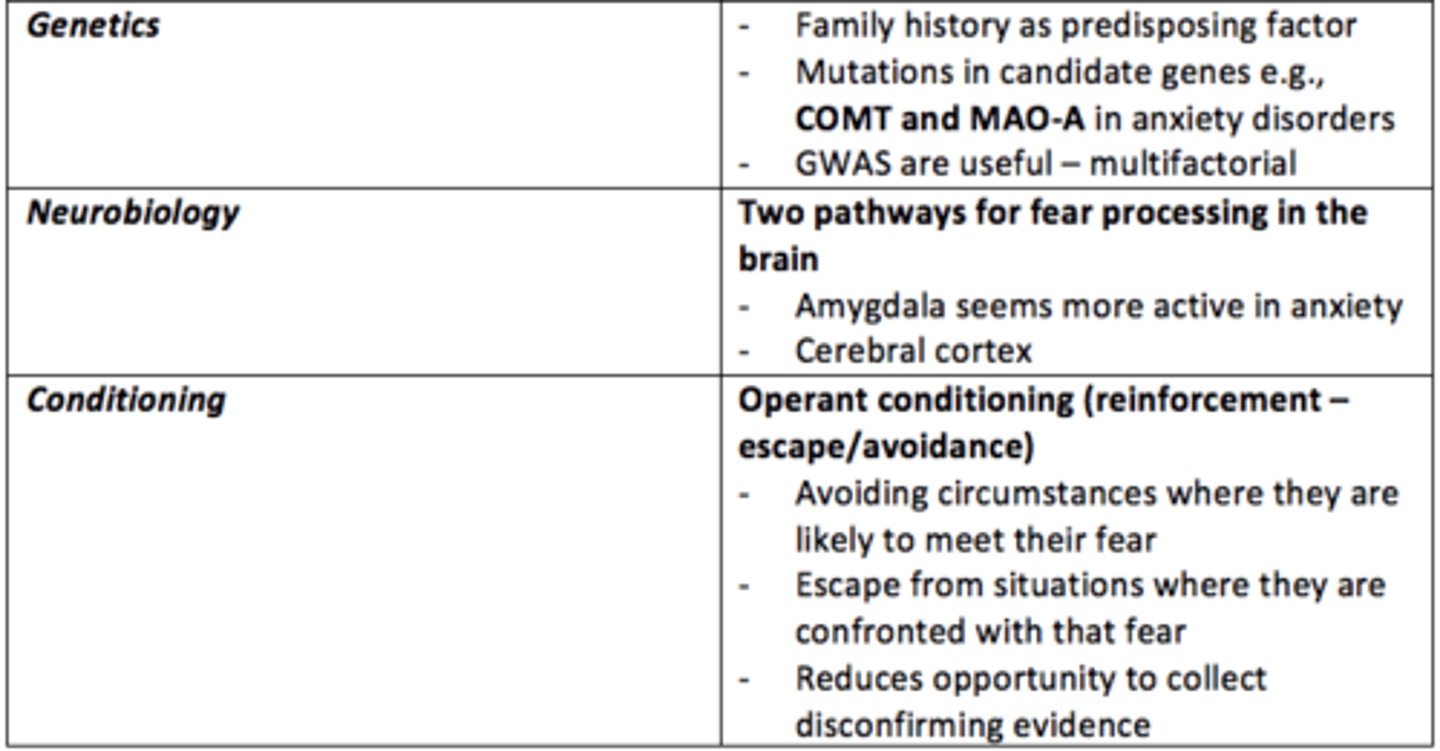
The ___ seems more active in anxious individuals
Amygdala
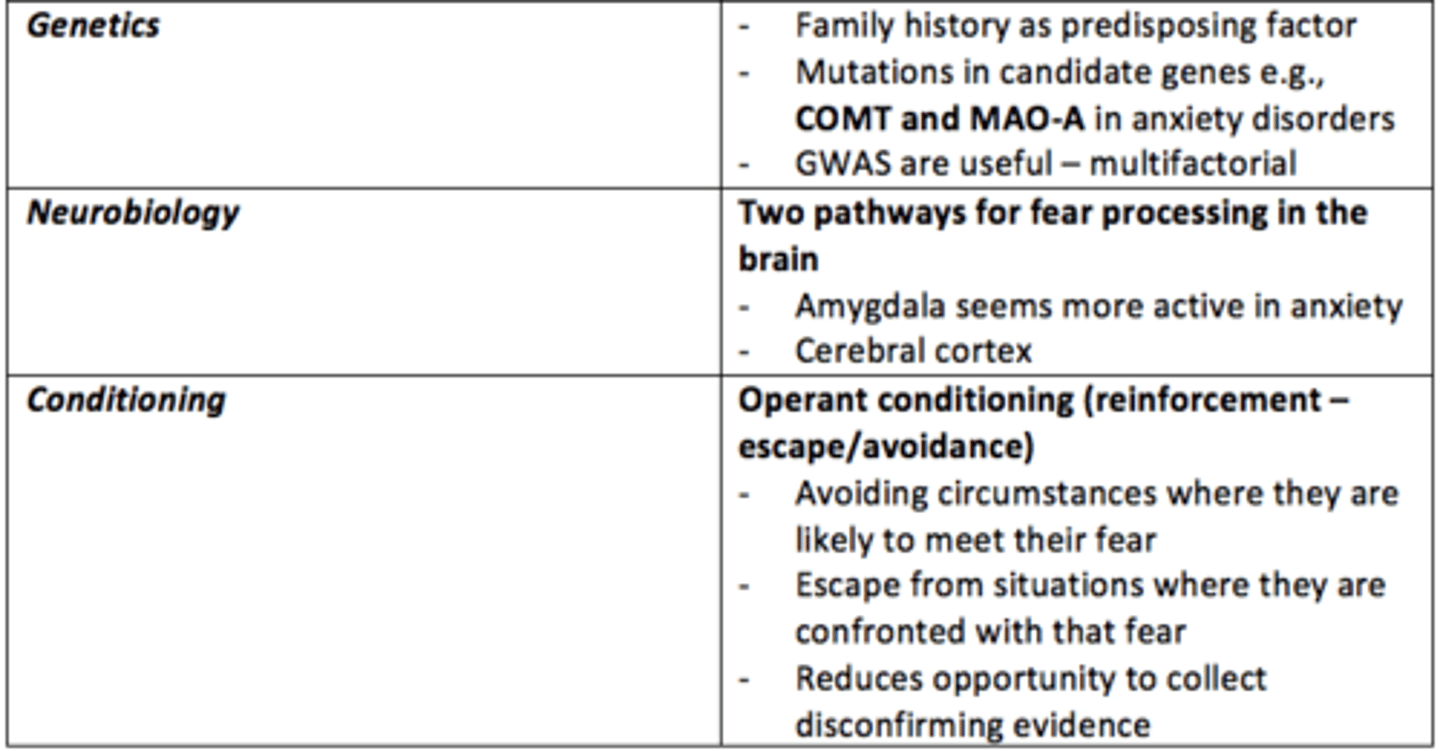
What neurobiological differences can be observed in the brain of individuals with anxiety?
- Amygdala more active
- Inadequate suppression by prefrontal cortex (PFC)
- Reduced GABA
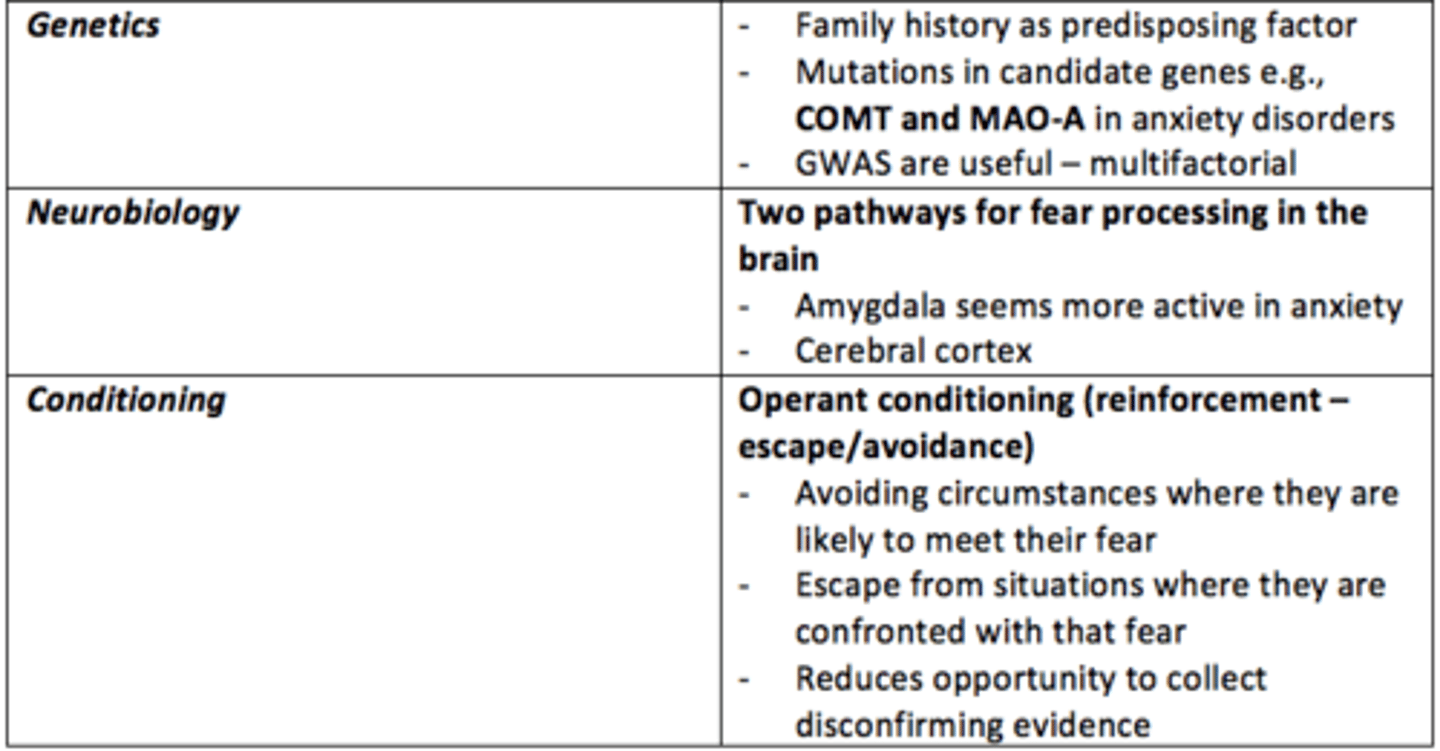
Operant conditioning
a type of learning in which behavior is strengthened if followed by a reinforcer or diminished if followed by a punisher
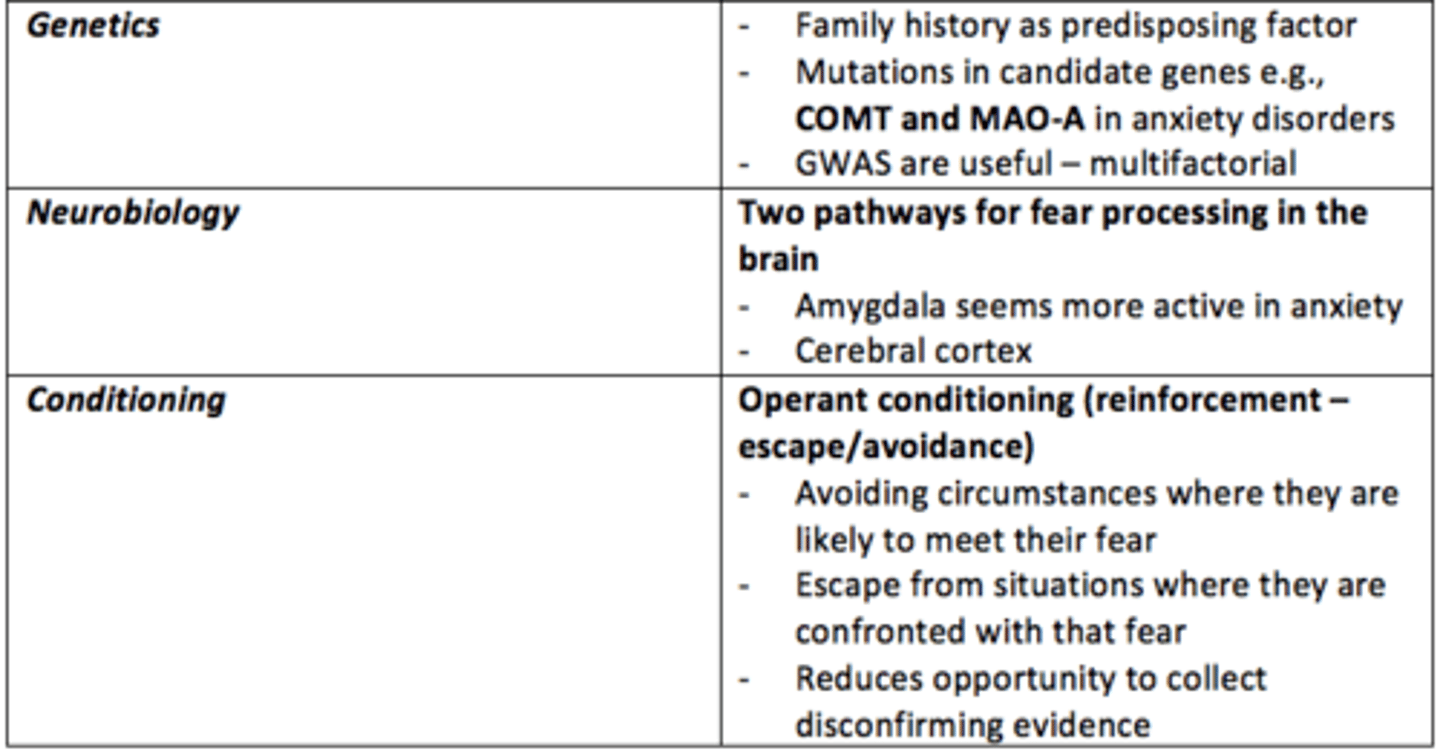
Give an example of negative reinforcement which exacerbates anxious behaviours or thoughts?
- Avoidance of circumstances where they are likely to confront their fear
- Escaping from situations where they are confronted with that fear
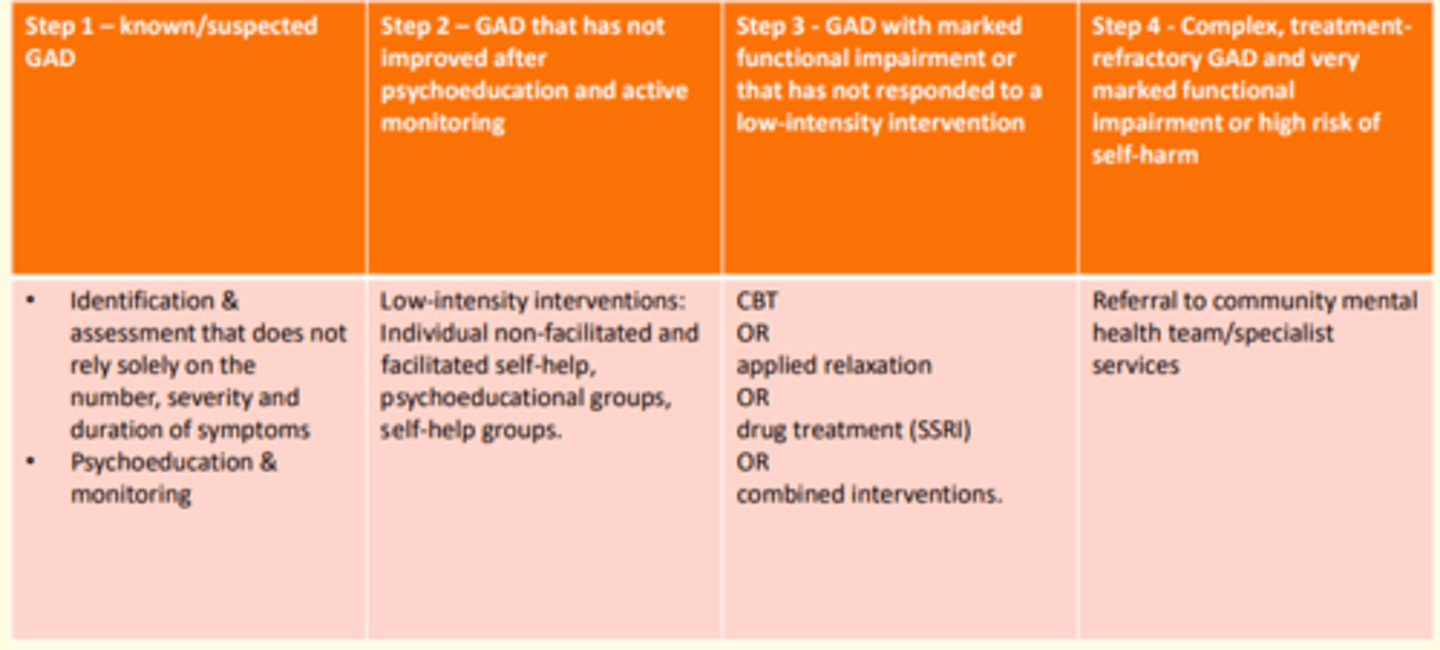
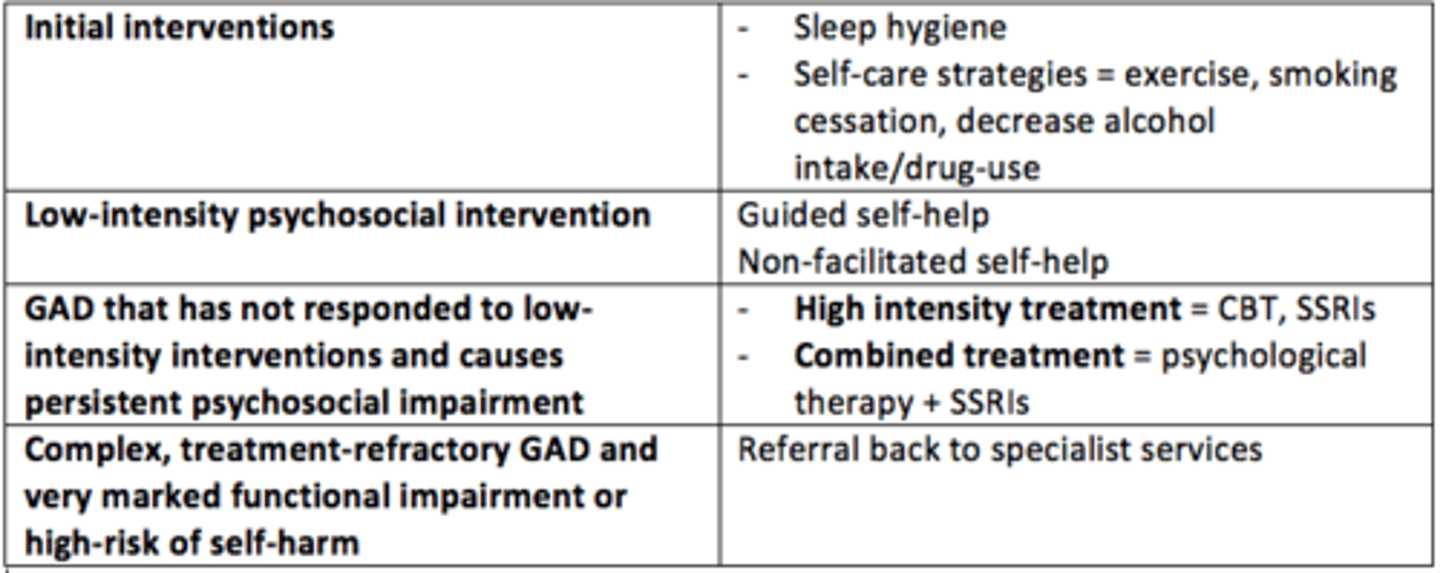
Treating patient with suspected/known GAD
- Identification & assessment that does not solely rely on number, severity & duration of symptoms
- Psychoeducation, monitoring
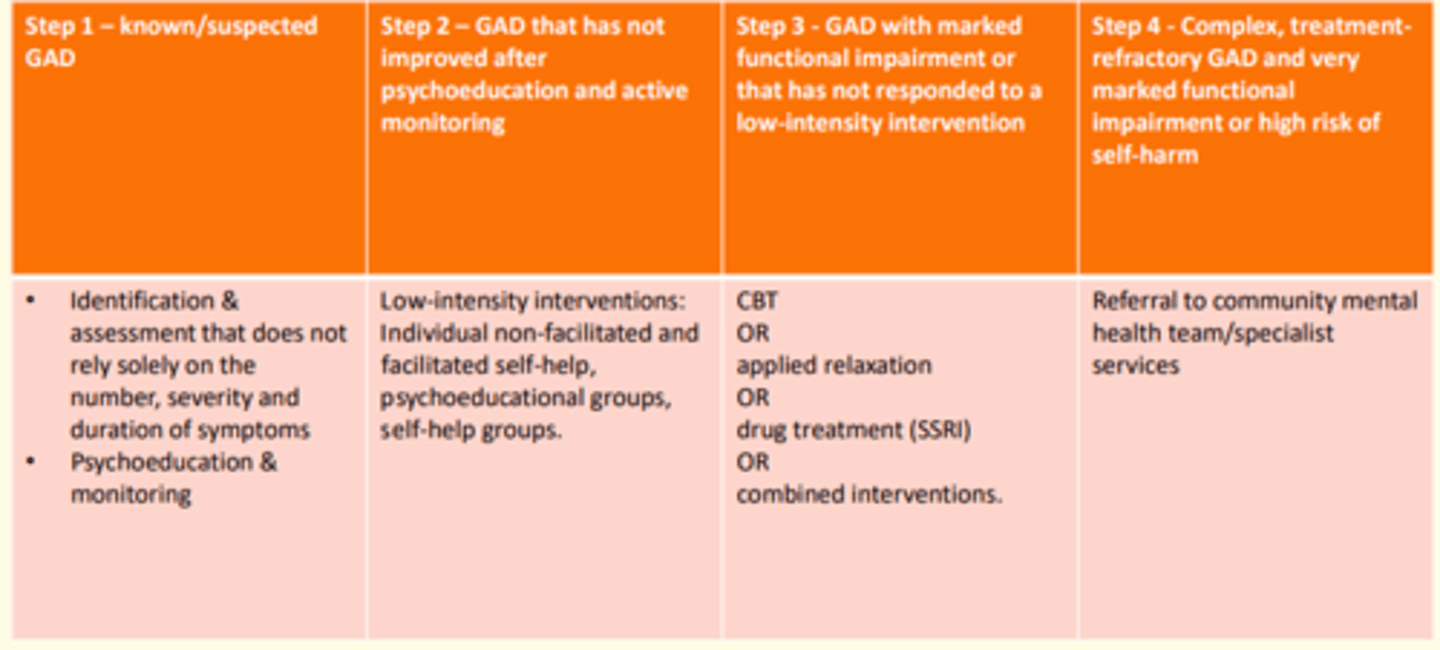
Treating patient with GAD that has not shown improvement after psychoeducation & active monitoring
- Low-intensity interventions: Individual non-facilitated and facilitated self-help
- Psychoeducational groups
- Self-help groups
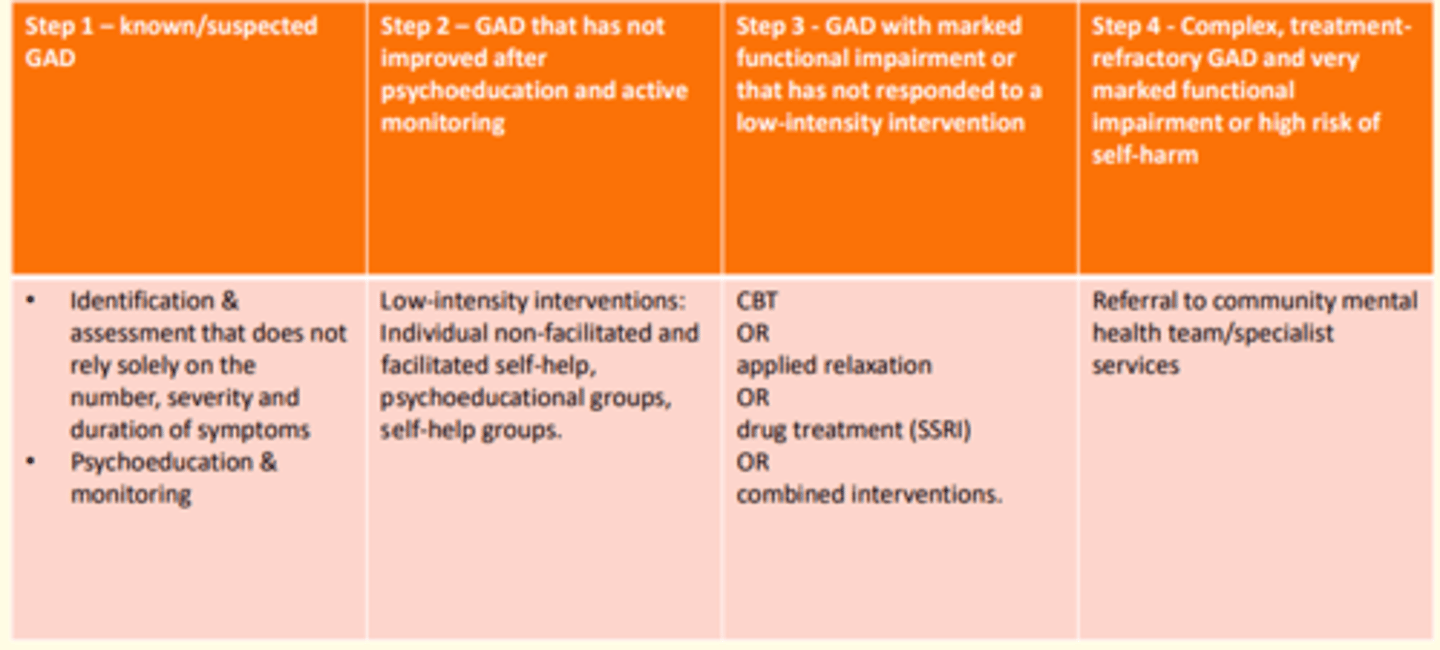
Patient with marked functional impairment due to GAD that has not responded to low-intensity interventions
- CBT
or
- Applied relaxation
or
- Drug treatment (SSRI)
or
- Combined approach
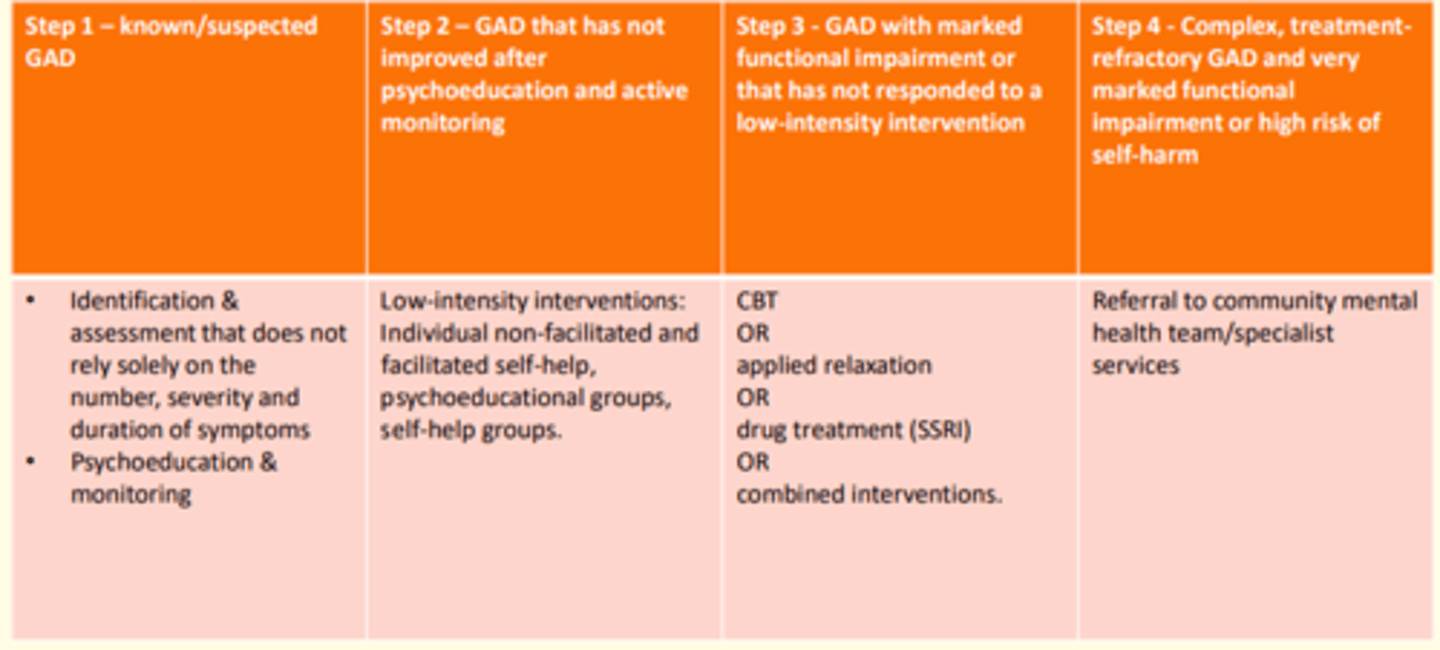
Patient with complex, treatment-resistant GAD and very marked functional impairment +/- high-risk of self-harm
- Referral to community mental health services/specialist services
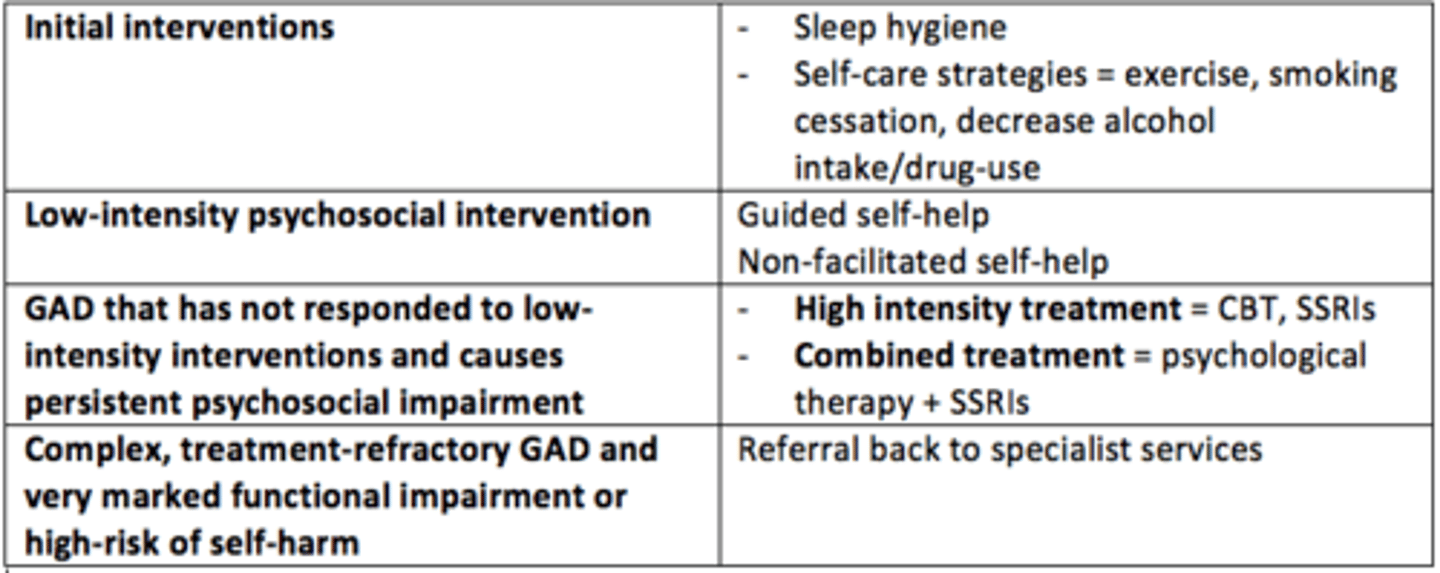
Initial low-intensity interventions (self-care strategies) for anxiety
Sleep hygiene, smoking/drug cessation, alcohol reduction, self-help, exercise
What are 'high-intensity' treatments for anxiety?
- CBT
- Medications = SSRIs
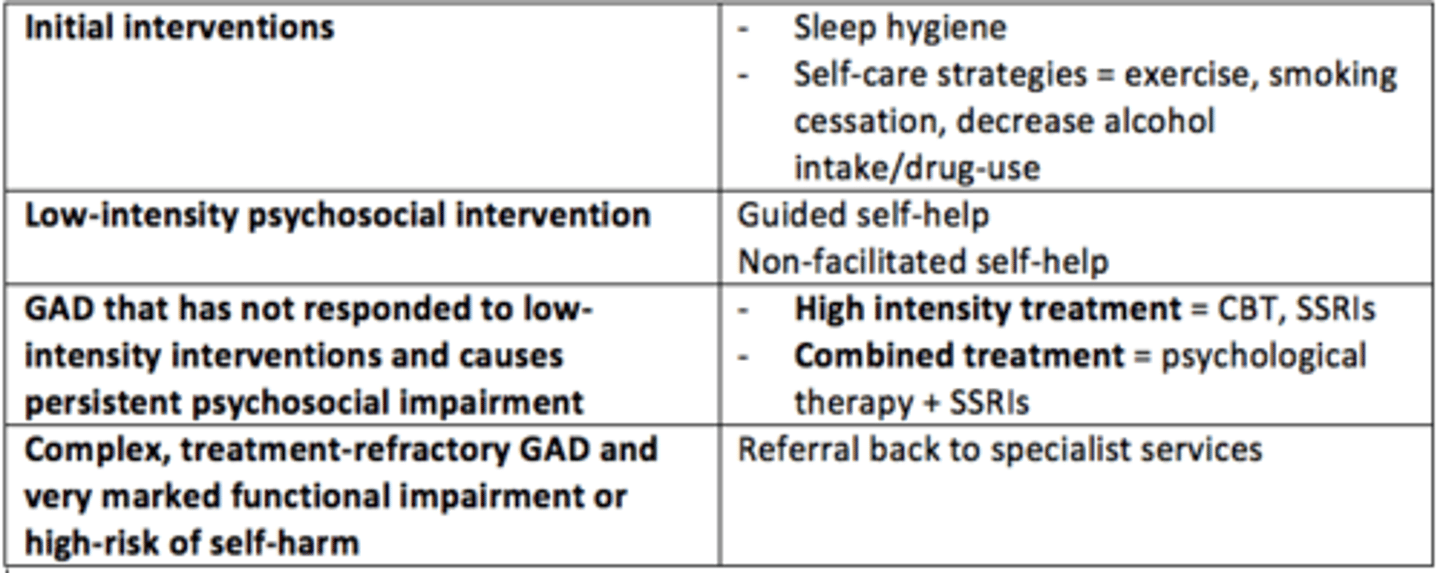
What is 'combined' approach to treating anxiety?
- Psychological therapies AND SSRIs
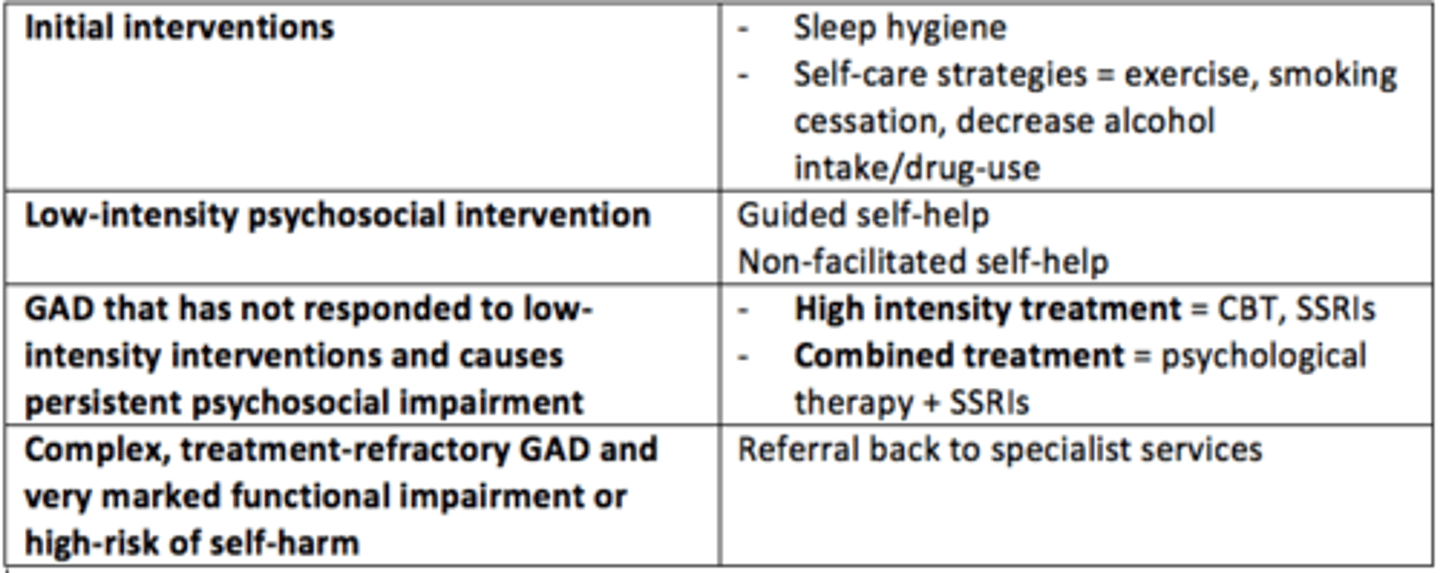
Complex, treatment-refractory GAD and very marked functional impairment or high risk of self-harm
Referral to specialist services
What is one type of intervention for OCD specifically?
Exposure-response prevention
What tool is used to identify anxiety disorders in patient?
GAD-2
- If GAD is >3 = continue to GAD-7 for assessment of severity
- If GAD is <3 = ask 'Do you find yourself avoiding places or activities and does this cause you problems?’
If yes, consider GAD
