Econ Test 2
1/86
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
87 Terms
True or False
Tax incidence is determined entirely by the legal assignment of the tax burden?
False
When supply is more elastic than demand, which group bears the larger share of the tax burden?
Buyers
Sellers
The tax incidence is equal
The government
Buyers
If demand for a good is more elastic than supply, the majority of the tax burden falls on:
Buyers
The government
Sellers
Neither, as both share it equally
Sellers
If a tax is imposed on buyers of a good, the demand curve will:
Shift right (increase in demand)
Become steeper
Remain unchanged
Shift left (decrease in demand)
Shift left (decrease in demand)
When a tax is imposed on sellers, what happens to the supply curve?
It becomes horizontal
It remains unchanged
It shifts left (decrease in supply)
It shifts right (increase in supply)
It shifts left (decrease in supply)
True/False
A price floor set below equilibrium has no effect on the market.
True
A common unintended consequence of rent control (a price ceiling) is:
Housing shortages and longer wait times for apartments
Increased quality of rental apartments
Increased supply of rental housing
Higher rental prices
Housing shortages and longer wait times for apartments
True or False
A tax imposed on a good will always reduce the equilibrium quantity of the good.
True
A price ceiling is a:
Minimum legal price a seller can charge
Maximum legal price a seller can charge
Government-mandated minimum wage
Tax imposed on consumers
Maximum legal price a seller can charge
A binding price floor leads to:
A shortage
More demand than supply
No change in the market
A surplus
A surplus
If a tax is imposed on a good, who bears the burden of the tax?
Only buyers
Only the government
Both buyers and sellers
Only sellers
Both buyers and sellers
Which of the following is an example of a price floor?
The price of gasoline being subsidized
A cap on interest rates for student loans
Rent control in New York City
The federal minimum wage
The federal minimum wage
If a price ceiling is set above the equilibrium price, it is:
Binding and causes a shortage
Not binding and has no effect
Binding and causes a surplus
Not binding and still changes the market
Not binding and has no effect
Which of the following correctly describes willingness to pay (WTP)?
The maximum price a consumer is willing to pay for a good
The price that maximizes total revenue
The price a seller is willing to accept for a good
The lowest price a consumer is willing to pay for a good
The maximum price a consumer is willing to pay for a good.
If price increases, what happens to consumer surplus?
It depends on the elasticity of demand
It stays the same
It increases
It decreases
It decreases
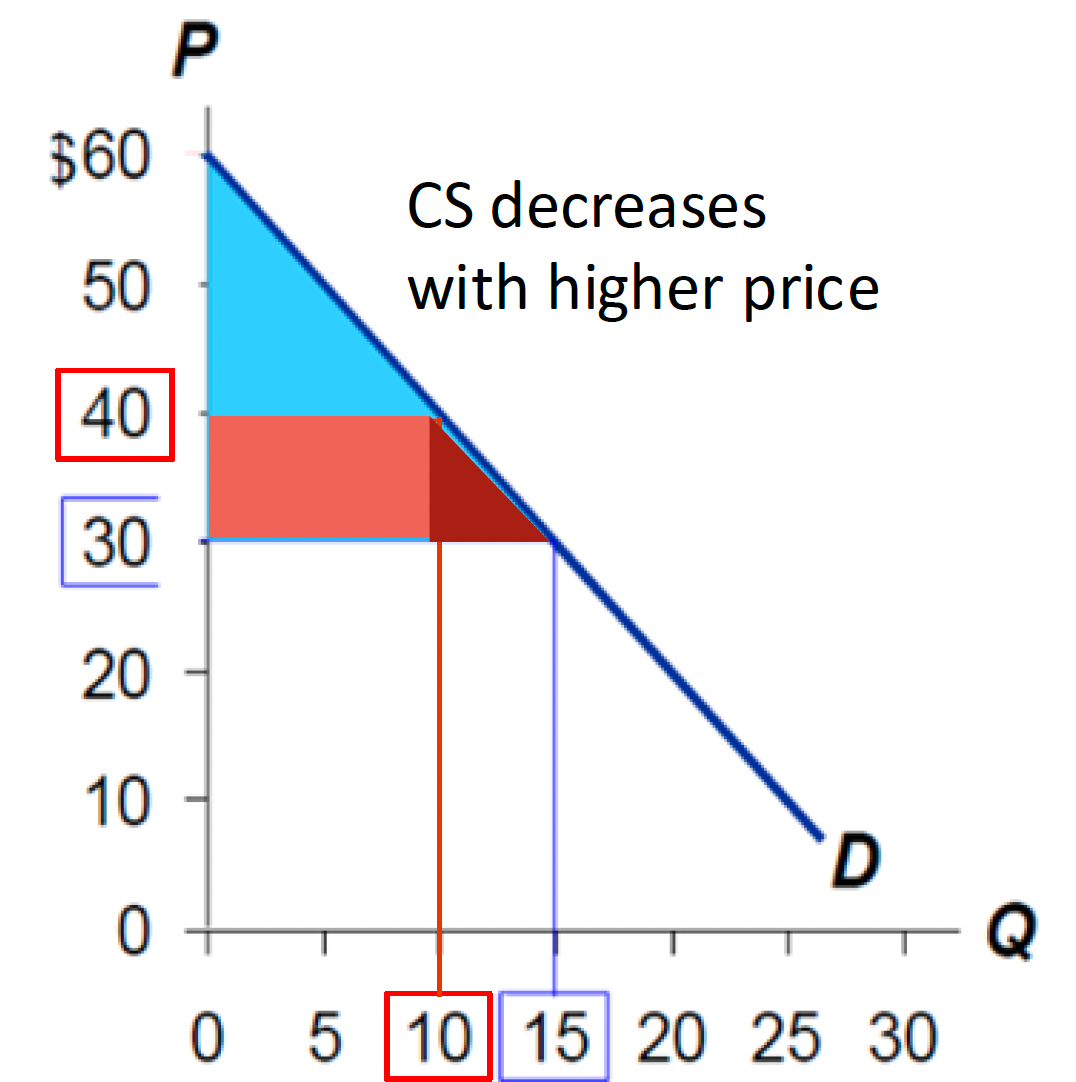
How much do we lose in Consumer Surplus if Price goes up from $30 to $40 and Quantity fall from 15 to 10?
$125
$175
$150
$100
$125
If market price equals WTP for all buyers, consumer surplus is:
Infinite
Negative
Maximized
Zero
Zero
If demand for a good is more elastic than supply, the majority of the tax burden falls on:
Buyers
The government
Sellers
Neither, as both share it equally
Sellers
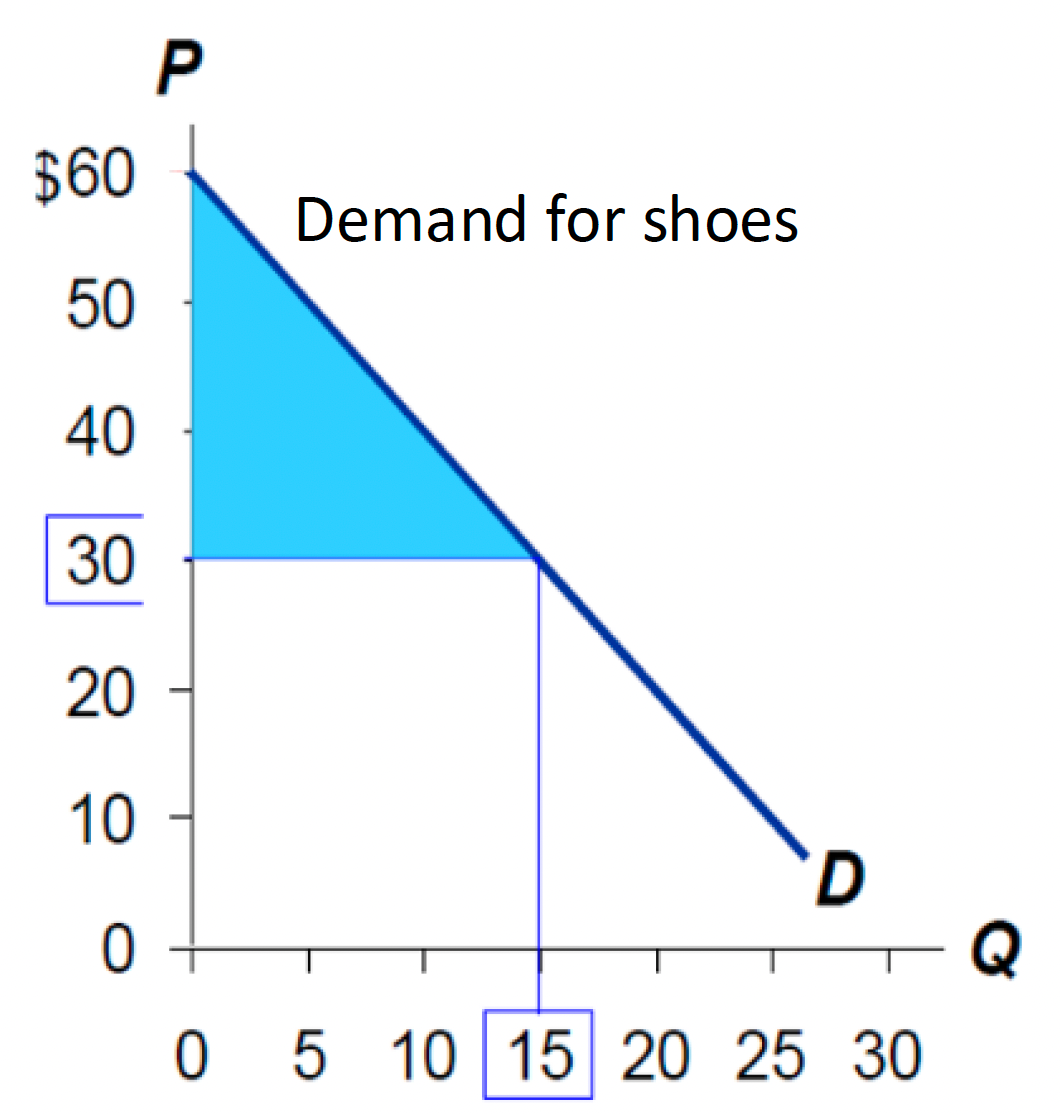
Calculate Consumer Surplus from this diagram if market equilibrium price is $30 and market equilibrium quantity is 15.
$200
$275
$250
$225
$225
Which of the following best represents consumer surplus on a demand curve?
The area below the demand curve but above the price line
The area above the supply curve but below the price line
The area above the price line but below the supply curve
The area below both the demand and supply curves
The area below the demand curve but above the price line.
Consumer surplus is defined as:
The total amount paid by consumers for a good
The price consumers are willing to pay minus the price they actually pay
The difference between total revenue and total cost
The total benefit that producers receive
The price consumers are willing to pay minus the price they actually pay.
If Anthony’s WTP for a concert ticket is $250, but he buys it for $200, what is his consumer surplus?
$200
$0
$50
$250
$50
When supply is more elastic than demand, which group bears the larger share of the tax burden?
Sellers
The tax incidence is equal
The government
Buyers
Buyers
If the market price of a good is higher than a consumer’s WTP, then the consumer will:
Not purchase the good
Demand more of the good
Increase their WTP
Purchase the good anyway
Not purchase the good
Which market would likely experience the largest deadweight loss from a tax?
A market with a perfectly inelastic supply curve
A market where both supply and demand are elastic
A market where supply and demand are both inelastic
A market where supply is elastic and demand is inelastic
A market where both supply and demand are elastic
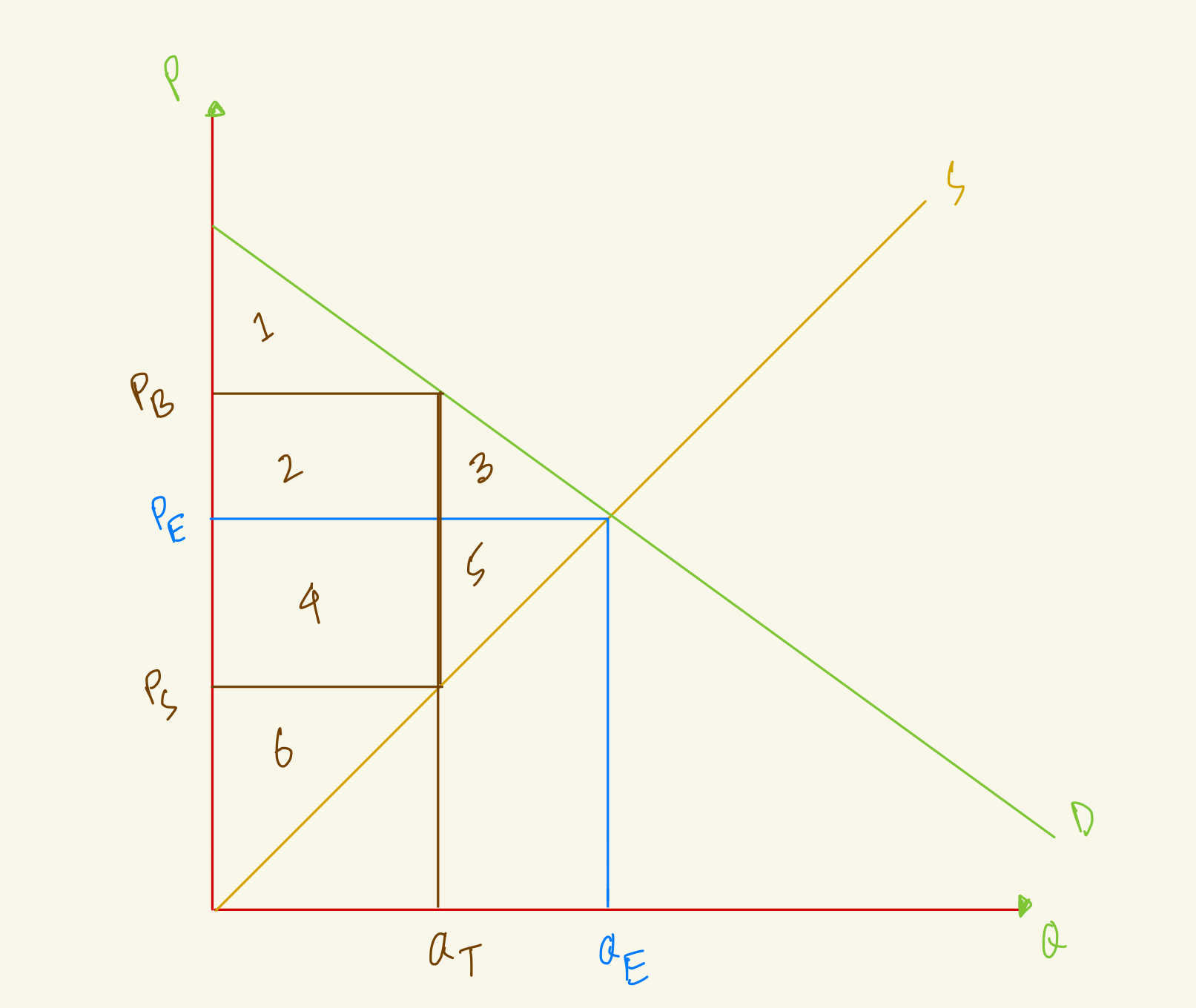
At the equilibrium, price is PE and quantity is QE. After tax, quantity in the market falls to QT, the amount that buyers pay rises to PB and the amount that sellers receive falls to PS. What's the deadweight loss in this market with tax?
2+4
3+5
1+2
4+6
3+5
What determines the size of deadweight loss in a market?
The number of buyers and sellers
The price level of the good
The elasticity of supply and demand
The government’s budget deficit
The elasticity of supply and demand.
What is deadweight loss (DWL)?
A reduction in total surplus due to a tax
Government revenue collected from a tax
An increase in consumer surplus from lower prices
The additional surplus gained from taxation
A reduction in total surplus due to a tax
What happens to consumer surplus when a tax is imposed?
It decreases
It turns into producer surplus
It remains unchanged
It increases
It decreases
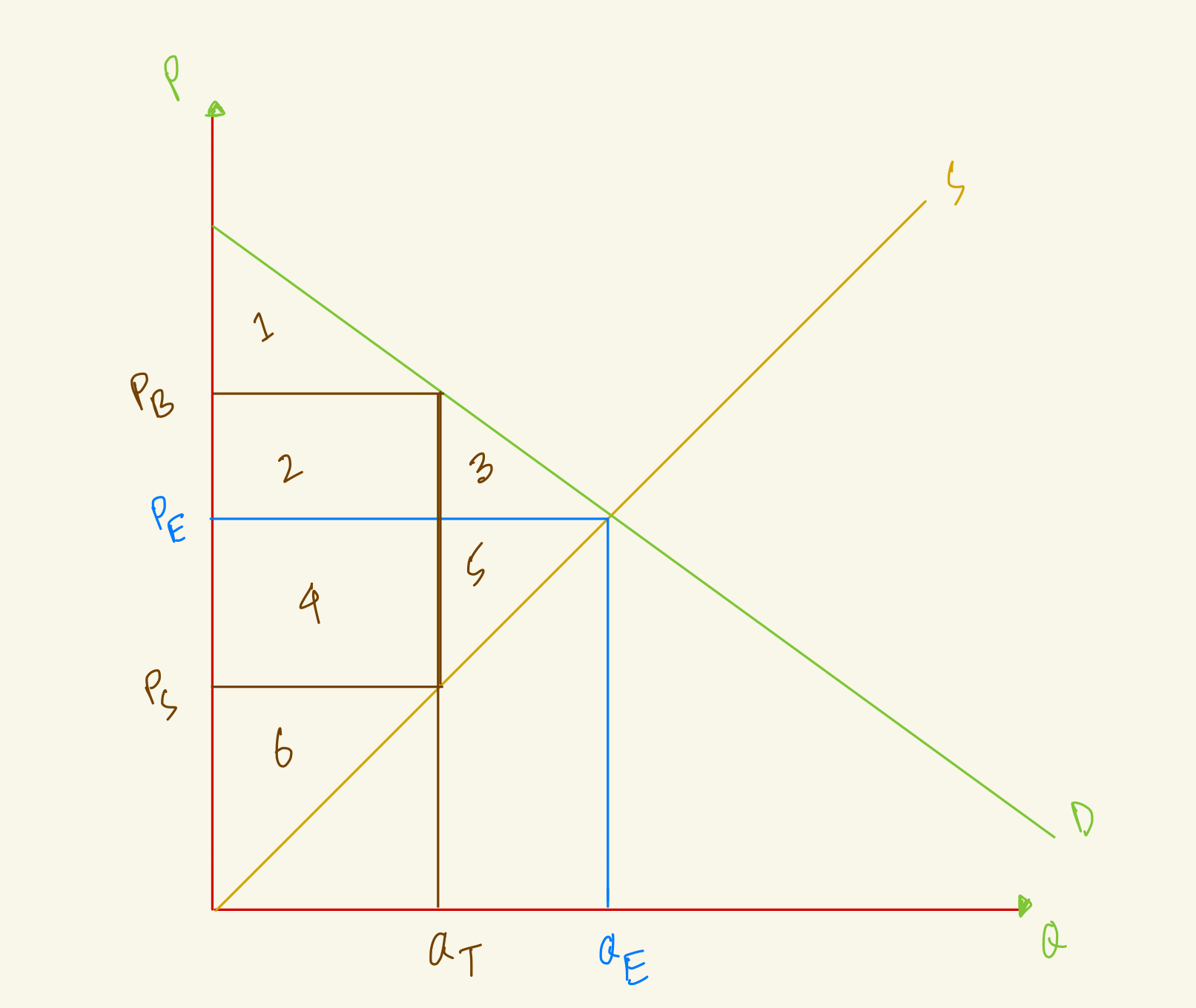
At the equilibrium, price is PE and quantity is QE, what's the consumer surplus in this market?
1+2
1+2+3
1+4
1
1+2+3
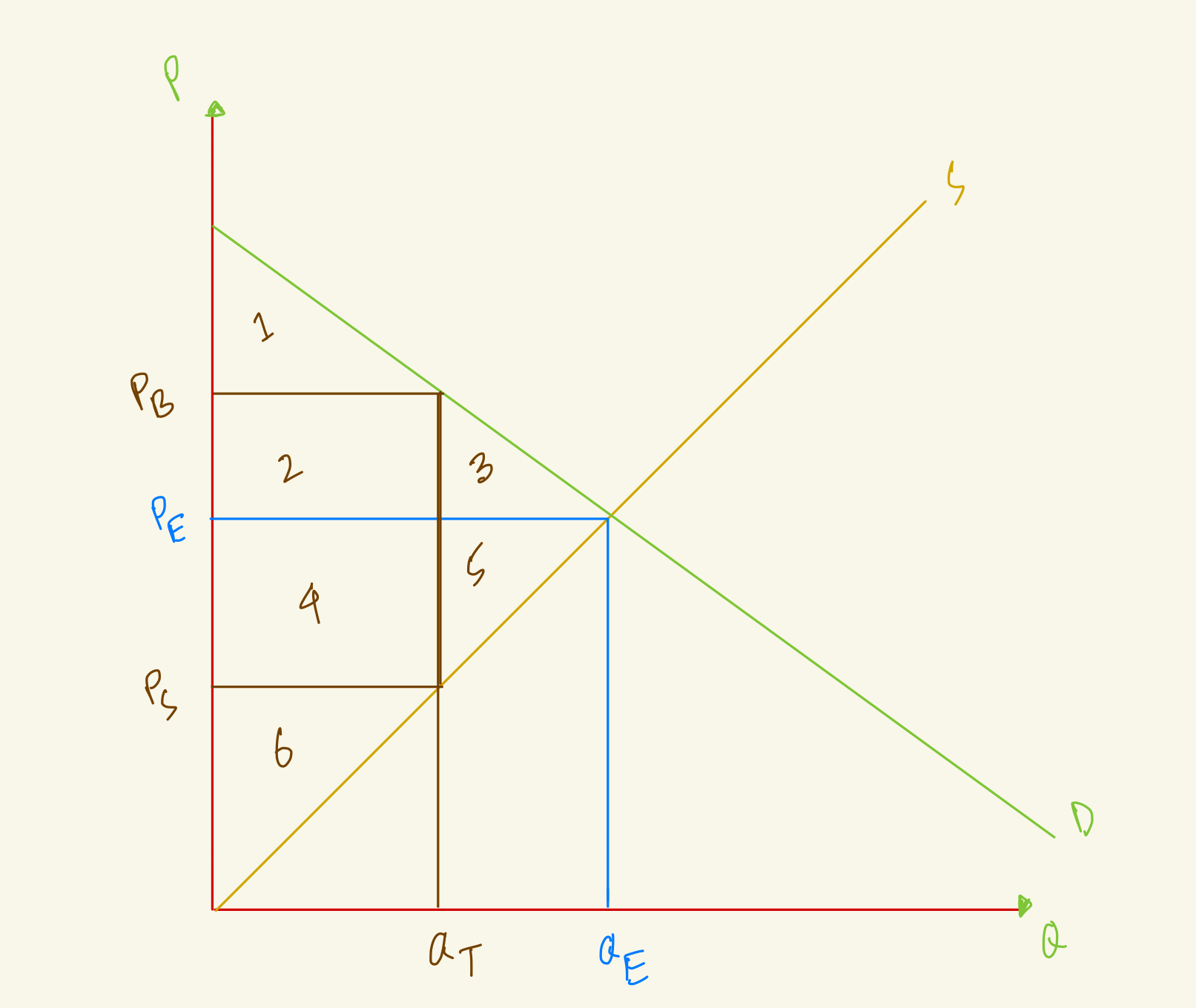
At the equilibrium, price is PE and quantity is QE. After tax, quantity in the market falls to QT, the amount that buyers pay rises to PB and the amount that sellers receive falls to PS. What's the total surplus in this market with tax?
1+2+4+6
1+3+4+5
1+3+5+6
1+2+3+4
1+2+4+6
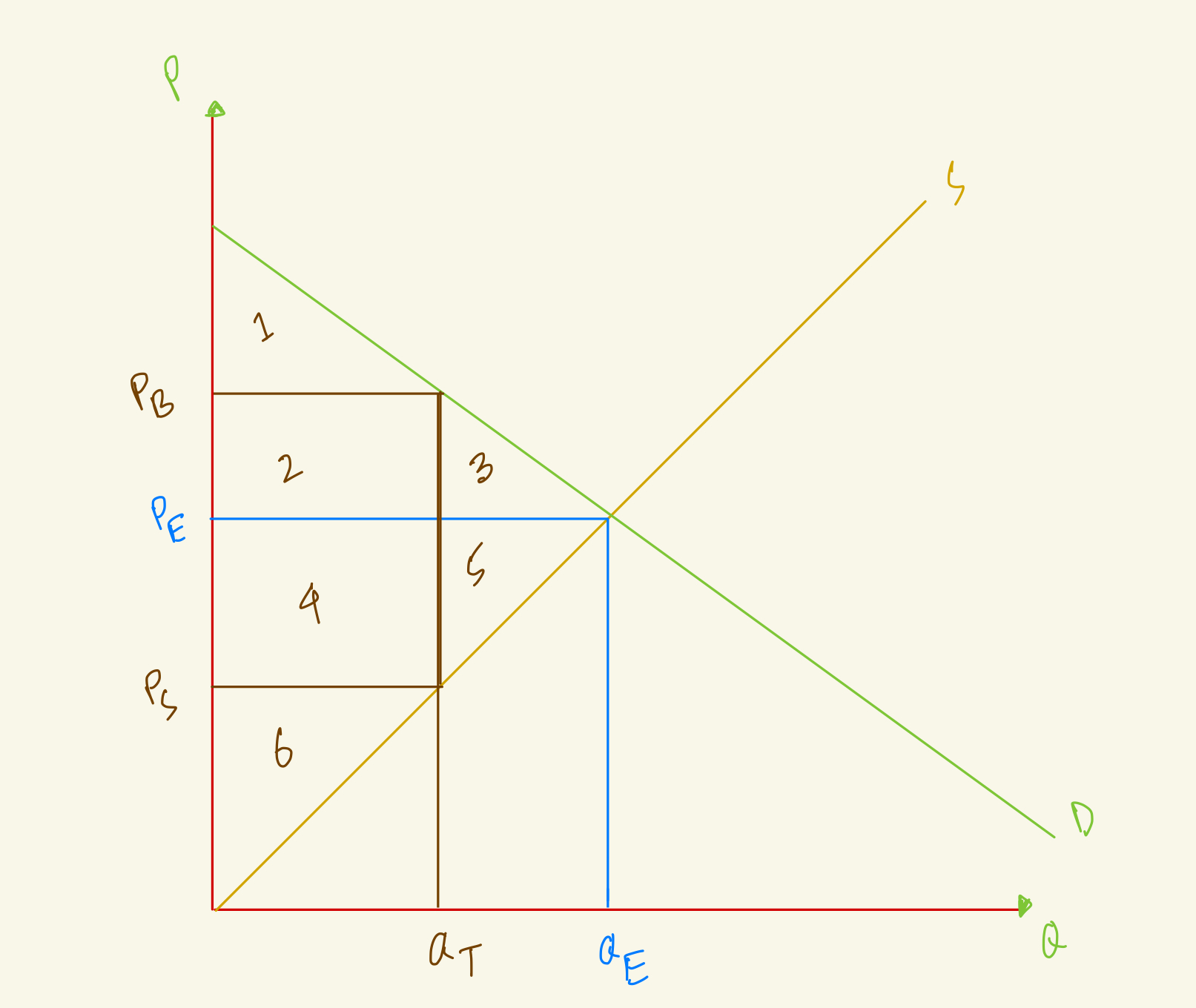
At the equilibrium, price is PE and quantity is QE. After tax, quantity in the market falls to QT, the amount that buyers pay rises to PB and the amount that sellers receive falls to PS. What's the producer surplus in this market with tax?
5
3
6
4
6
At the equilibrium, price is PE and quantity is QE, what's the producer surplus in this market?
4+5
2+3
2+4+6
4+5+6
4+5+6
If a $5 per unit tax is imposed and the new quantity sold is 200 units, what is the total tax revenue?
$500
$2000
$1500
$1000
$1000
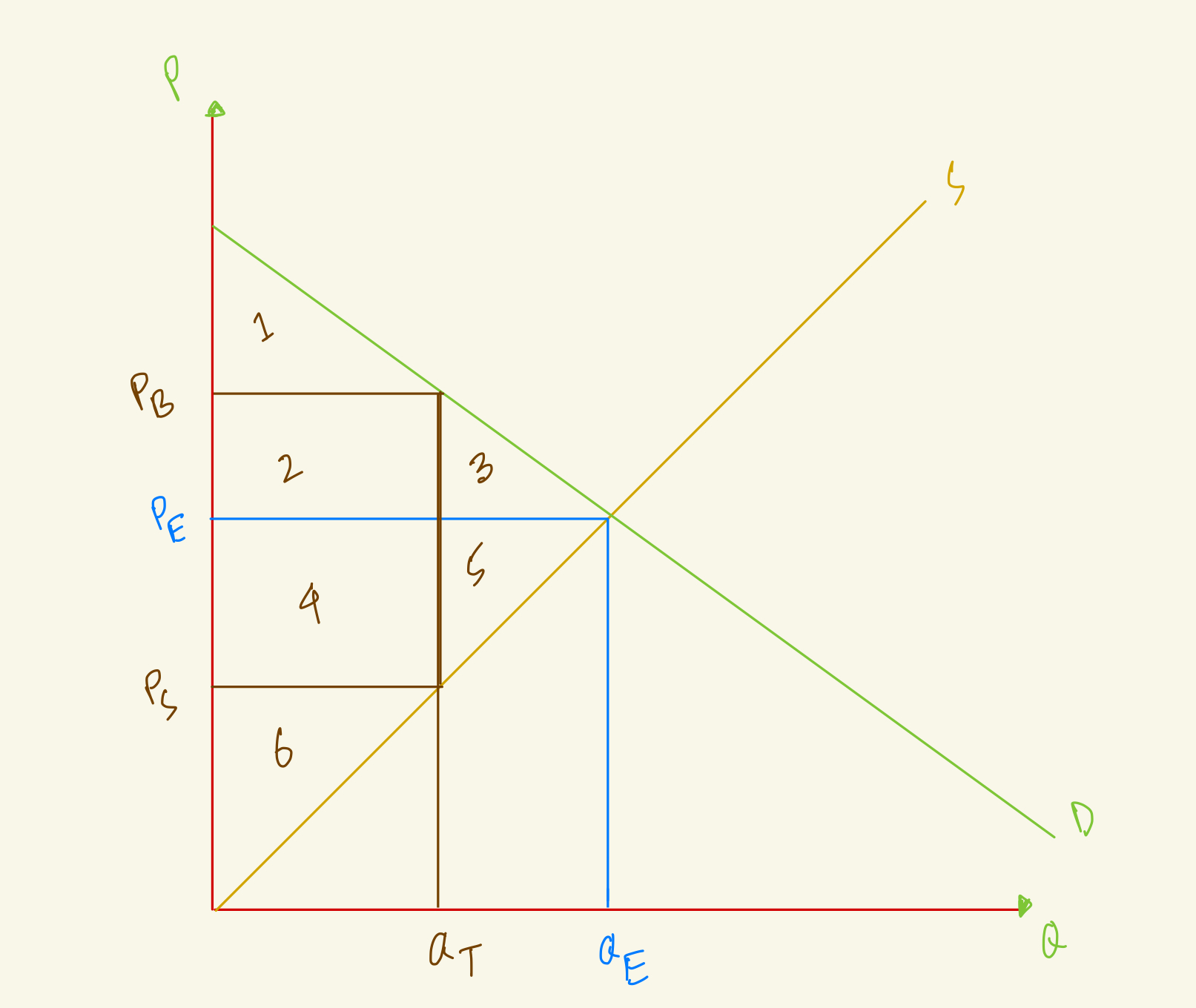
At the equilibrium, price is PE and quantity is QE, what's the total surplus in this market?
1+2+3+4+5
3+4+5+6
1+2+3+4
1+2+3+4+5+6
1+2+3+4+5+6
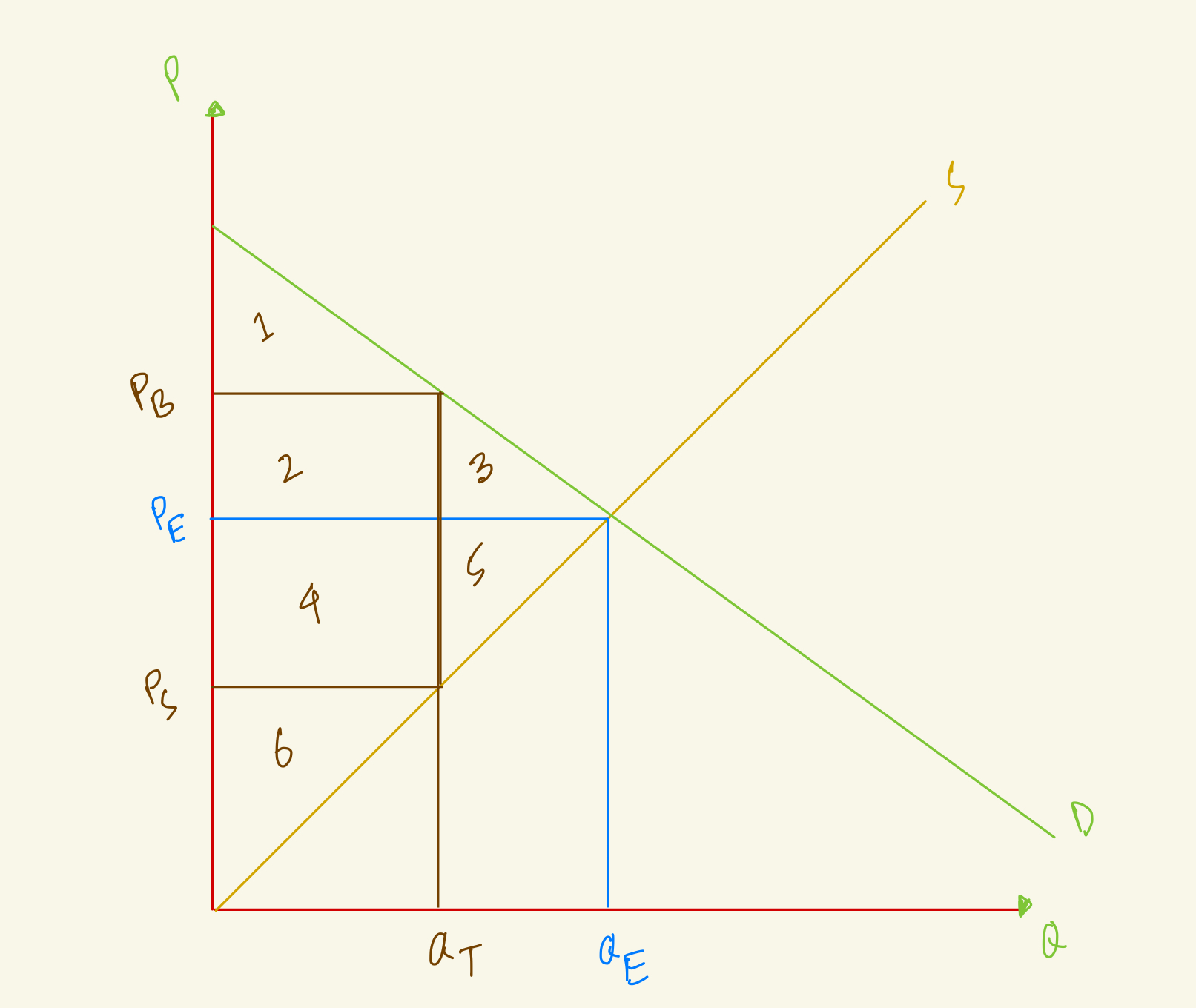
At the equilibrium, price is PE and quantity is QE. After tax, quantity in the market falls to QT, the amount that buyers pay rises to PB and the amount that sellers receive falls to PS. What's the consumer surplus in this market with tax?
2
1
1+2+3
1+2
1
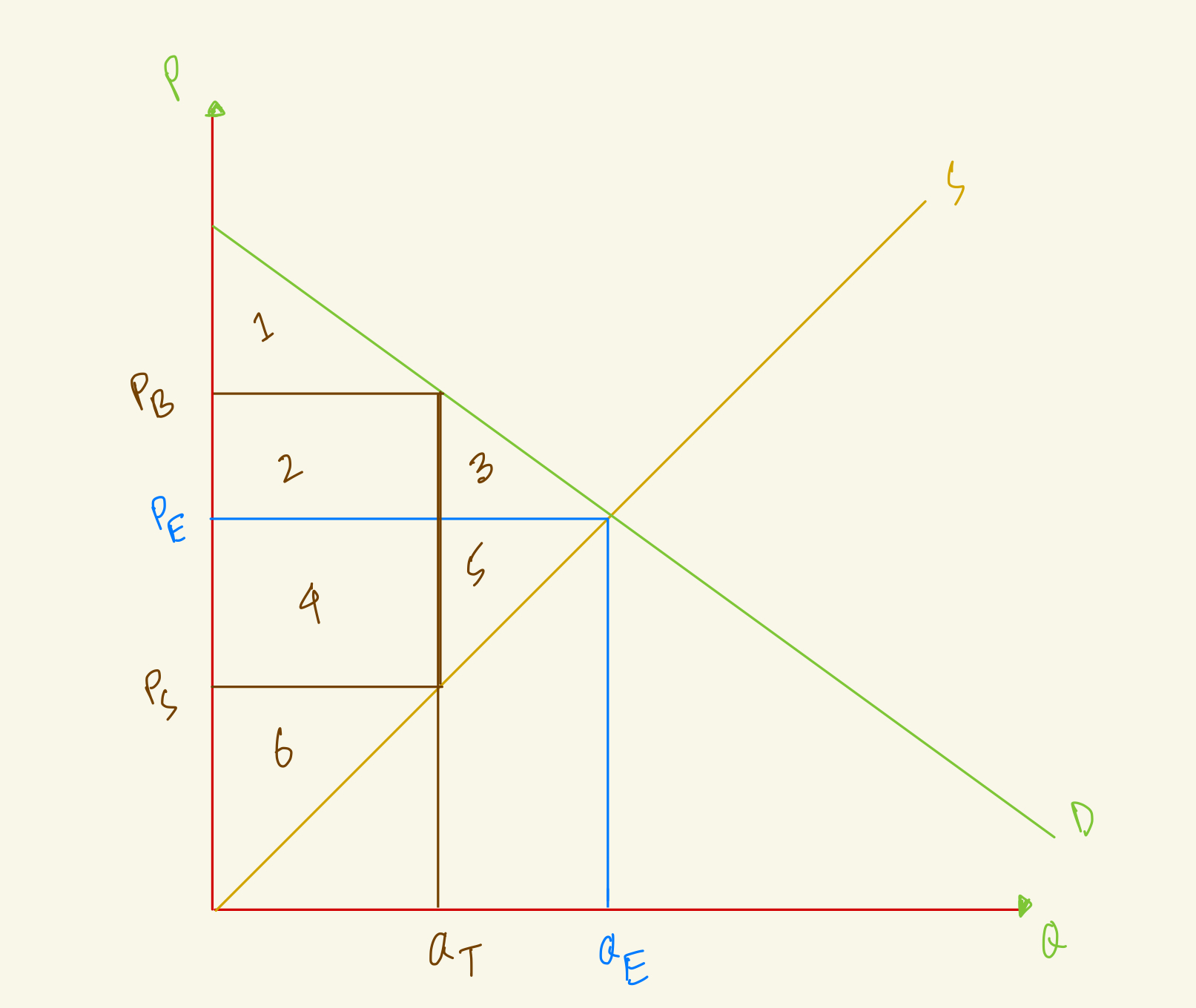
At the equilibrium, price is PE and quantity is QE. After tax, quantity in the market falls to QT, the amount that buyers pay rises to PB and the amount that sellers receive falls to PS. What's the government revenue in this market with tax?
2+4
4+6
1+2
3+5
2+4
When a tax is imposed on a good, what happens to total surplus?
It decreases
It becomes negative
It remains unchanged
It increases
It decreases
A producer’s surplus is:
The total revenue received from selling goods
The equilibrium price multiplied by quantity
The area between the supply and demand curves
The amount a seller is paid minus their cost of production
The amount a seller is paid minus their cost of production
If a consumer is willing to pay $200 for a good but buys it for $150, their consumer surplus is:
$50
$0
$200
$150
$50
Consumer surplus is maximized when:
Price is low
There are few buyers in the market
Demand is perfectly inelastic
Price is high
Price is low
If price increases, what happens to consumer surplus?
It depends on the elasticity of demand
It increases
It stays the same
It decreases
It decreases
If the price of a good increases, producer surplus generally:
Remains unchanged
Becomes zero
Decreases
Increases
Increases
Suppose Stanley’s willingness to pay for a good is $250, and the price is $220. Darryl’s willingness to pay is $300, and the price remains $220. What is the total consumer surplus for Stanley and Darryl combined?
$190
$250
$110
$80
$110
When the price of a good rises from $100 to $150, how does producer surplus change assuming the cost of production remains constant at $90?
It decreases by $50 for each unit sold
It cannot be determined from the given information
It increases by $50 for each unit sold
It remains constant because the cost of production does not change
It increases by $50 for each unit sold
If the demand curve is a straight downward-sloping line, the consumer surplus at equilibrium is represented by:
A circle
A trapezoid
A triangle
A rectangle
A triangle
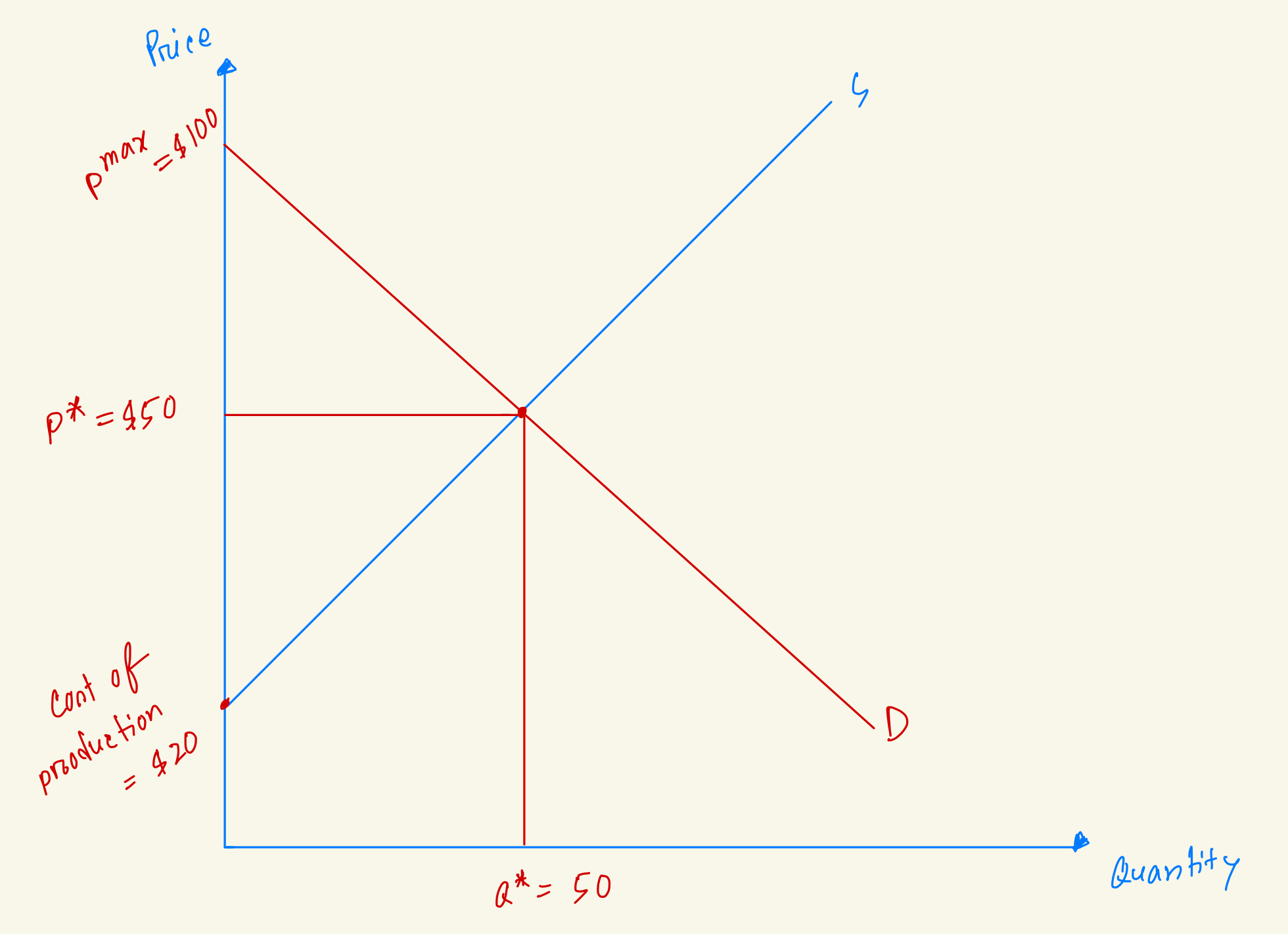
Calculate Consumer Surplus in the market from this diagram.
$1000
$1500
$1250
$2500
$1250
True or False
When price decreases, consumer surplus always decreases.
False
Market efficiency occurs when:
Total surplus is maximized
Only producers benefit from the market
Producer surplus is maximized at the expense of consumers
Consumer surplus is minimized
Total surplus is maximized.
If Michael’s cost of cutting lawns is $10, Jim’s is $20, and Dwight's is $35, and the market price for cutting lawns is $25, how much is the total producer surplus?
$20
$15
$25
$5
$20
Which of the following best represents consumer surplus on a demand curve?
The area above the price line but below the supply curve
The area below the demand curve but above the price line
The area below both the demand and supply curves
The area above the supply curve but below the price line
The area below the demand curve but above the price line.
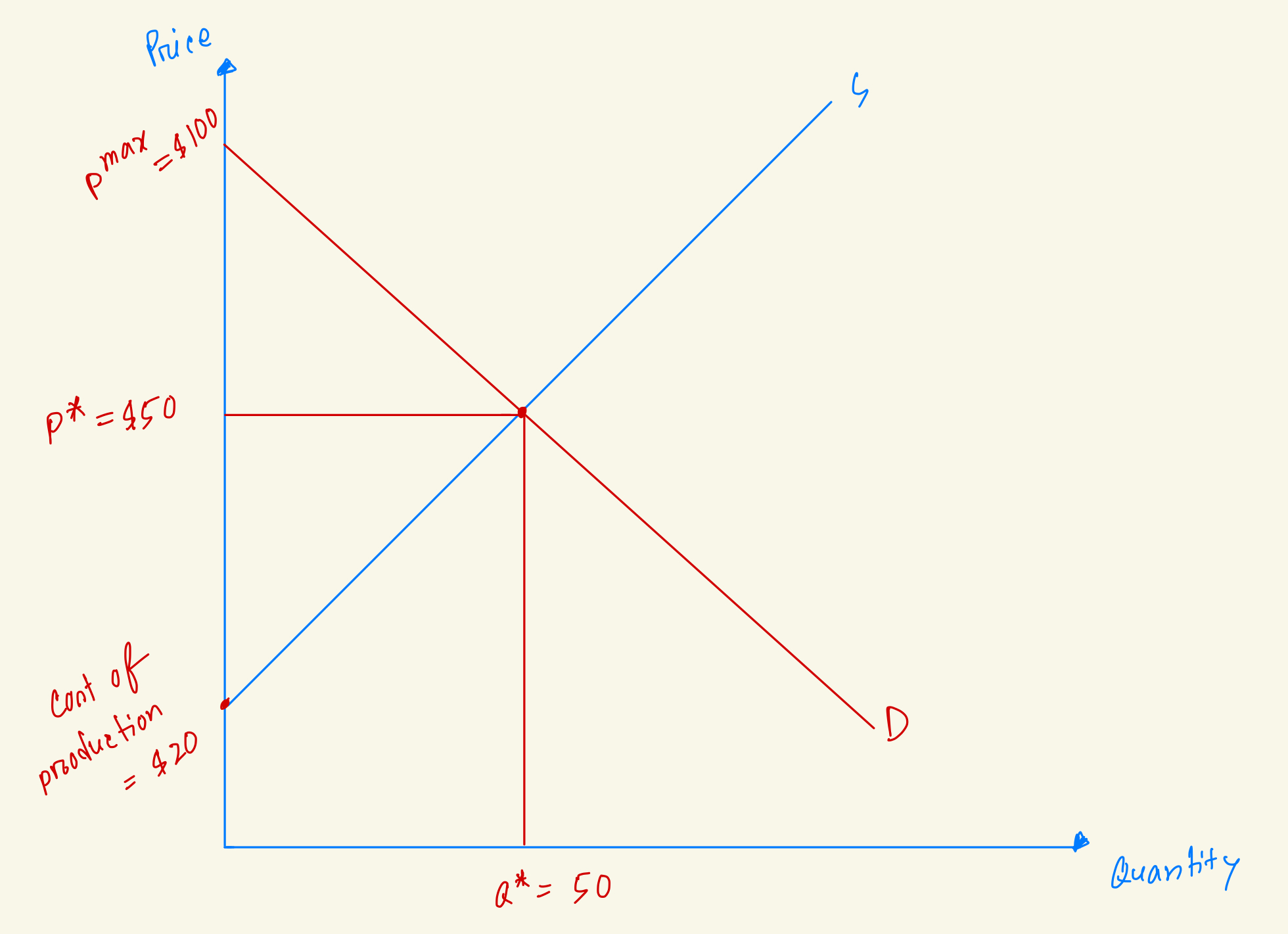
Calculate Total Surplus in the market from this diagram.
$2500
$1750
$4000
$2000
$2000
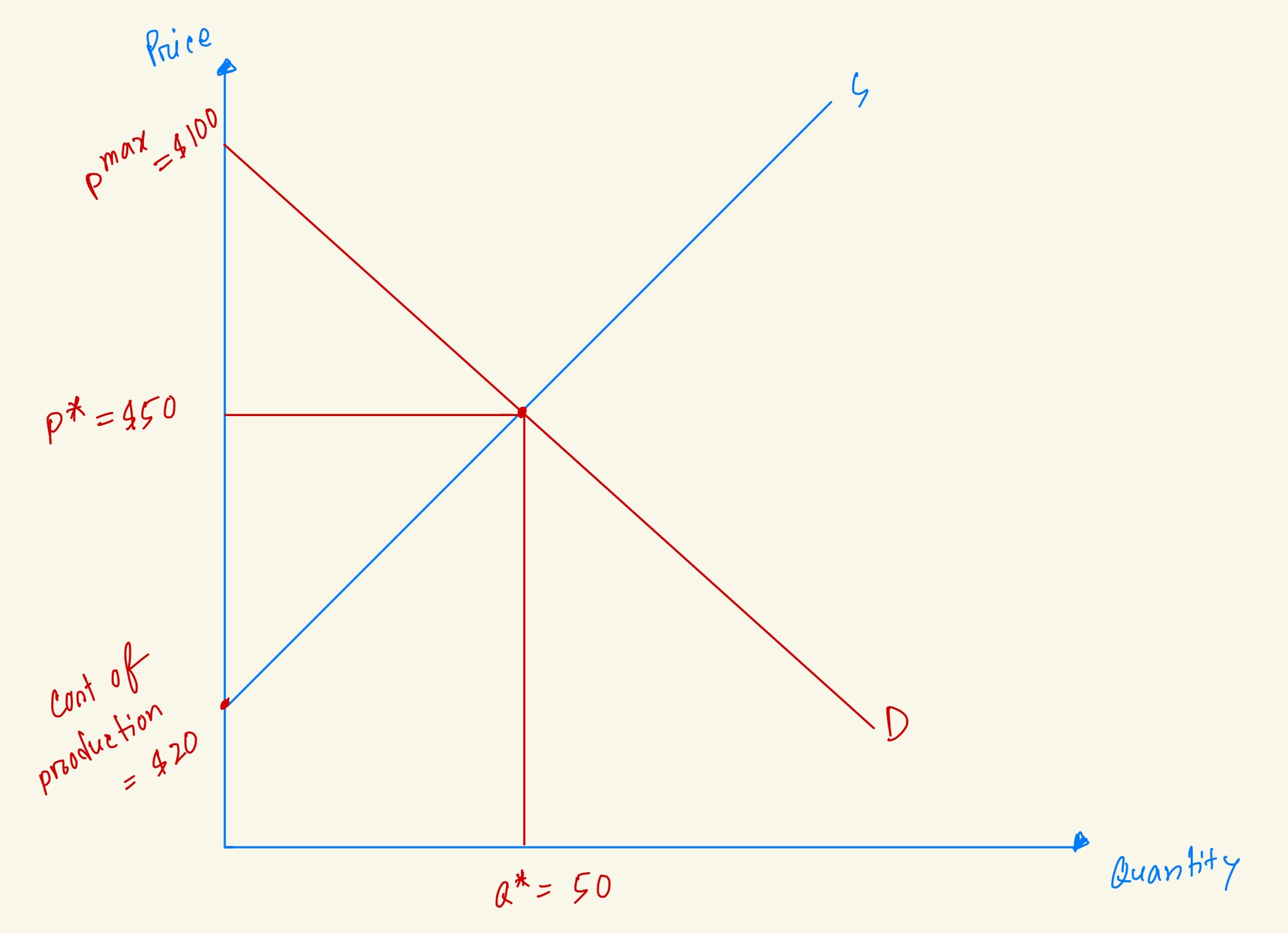
Calculate Producer Surplus in the market from this diagram.
$1250
$1500
$1000
$750
$750
True or False
Accounting profit always exceeds economic profit.
True
Which of the following is an example of an implicit cost?
Utilities paid monthly
Rent for office space
Wages paid to employees
Foregone salary by owner
Foregone salary by owner
If explicit costs are $37,000 and implicit costs are $28,000, and total revenue is $75,000, what is economic profit?
$10000
$28000
$47000
$38000
$10000
Angel’s fixed cost is $18. If she produces 6 scarves, what is her AFC?
$3.2
$2.8
$3.6
$3.0
$3.0
Jelani’s gelato shop makes 15,000 pints per year at $5 each. Her costs are $65,000. What’s her profit?
$15000
$75000
$60000
$10000
$10000
In the short run, which cost is always fixed?
VC
MC
FC
OC
FC
Kurt invested $80,000 in the factory and equipment to start the business last year: $30,000 from savings and borrowed $50,000 (interest 10% for saving and borrowing). Calculate the explicit costs.
$5000
$6000
$3000
$8000
$5000
Jelani owns a small gelato shop on campus. Jelani pays $20,000 a year for raw materials, and $12,000 in rent. Jelani can work at the local coffee shop for $25,000 a year. What's Jelani's implicit costs?
$57000
$25000
$32000
$60000
$25000
In the long run:
Fixed costs dominate
No cost curves exist
Firms cannot exit
All costs are variable
All costs are variable
Jelani owns a small gelato shop on campus. Jelani pays $20,000 a year for raw materials, and $12,000 in rent. Jelani can work at the local coffee shop for $25,000 a year. What's Jelani's explicit costs?
$25000
$32000
$60000
$57000
$32000
If ATC = $10 and AFC = $2, what is AVC?
$20
$2
$8
$12
$8
A firm’s total revenue is $60,000 and accounting profit is $10,000. If implicit costs are $12,000, what are explicit costs?
$38000
$22000
$48000
$50000
$50000
True or False
If marginal cost exceeds average total cost, ATC is falling.
False
When marginal cost is less than average total cost:
ATC is falling
Marginal product is zero
ATC is rising
ATC is constant
ATC is falling
True or False
In the long run, there are no fixed costs.
True
Total cost equals:
Accounting profit plus economic profit
Fixed cost plus variable cost
Implicit cost only
Total revenue minus fixed cost
Fixed cost plus variable cost.
Which curve always intersects ATC at its minimum?
MC
AVC
AFC
TC
MC
Kurt invested $80,000 in the factory and equipment to start the business last year: $30,000 from savings and borrowed $50,000 (interest 10% for saving and borrowing). Calculate the implicit costs.
$3000
$8000
$2000
$5000
$3000
True or False
In long-run equilibrium, P = MC = min ATC.
True
A competitive firm shuts down in the short run if:
Price < AVC
TR > TC
PRICE = MR
Price > ATC
Price < AVC
In a perfectly competitive market, individual firms:
Take prices as given
Set their own prices
Face downward-sloping demand
Can influence market supply
Take prices as given
Why is the long-run market supply curve horizontal in perfect competition?
Sunk costs dominate
Decreasing returns to scale
Firms face downward-sloping demand
Identical cost structures among firms
Identical cost structures among firms
For a competitive firm, which of the following is true?
MR = Price = AR
MR < Price
AR < Price
MR > Price
MR = Price = AR
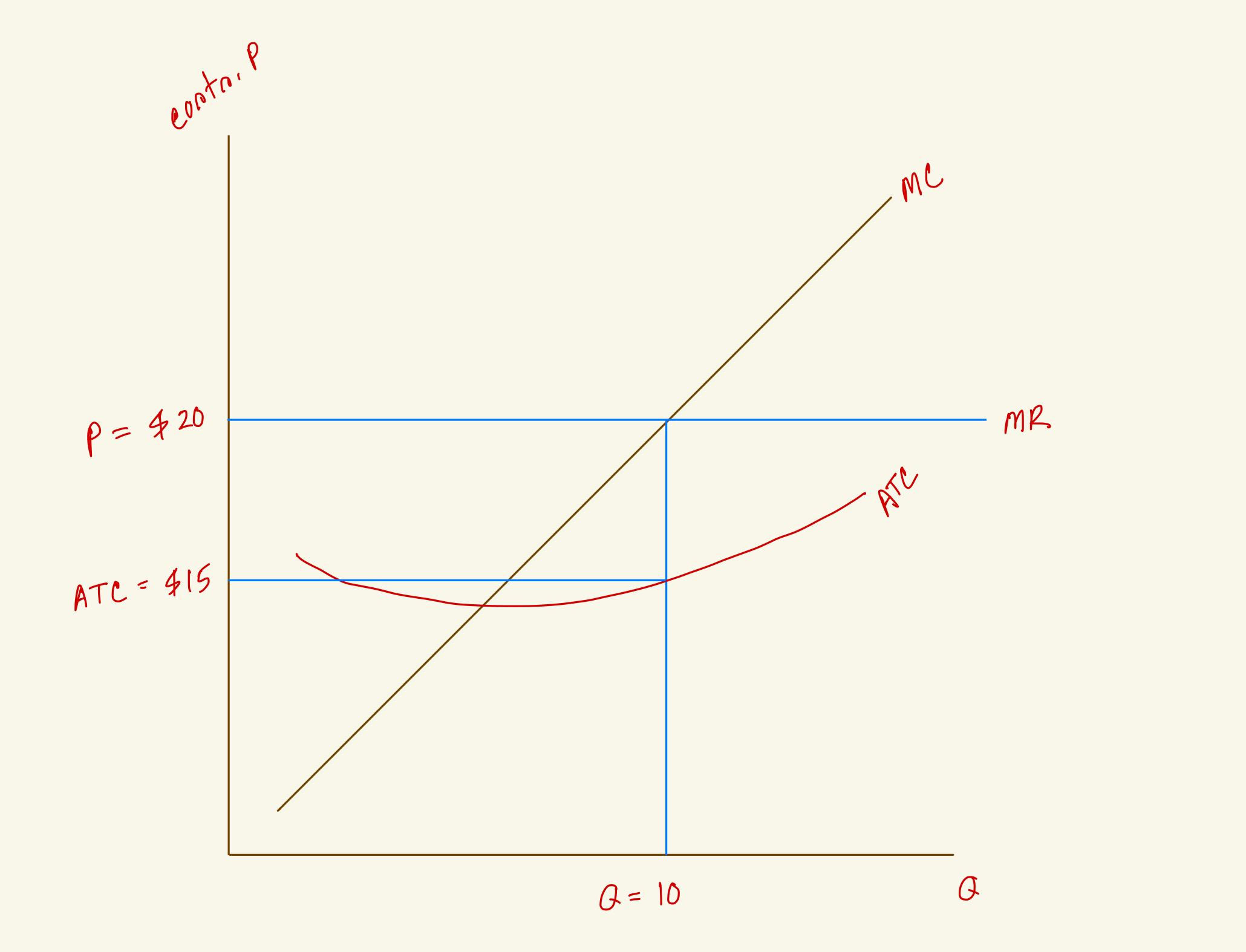
What's the profit for this firm in the diagram?
$150
$50
$75
$100
$50
If P = min ATC and firms earn zero economic profit:
Entry continues
Firms exit
Long-run equilibrium is reached
AVC is maximized
Long-run equilibrium is reached
True or False
Firms can avoid paying fixed costs by shutting down in the short run.
False
A firm exits the market in the long run when:
P > ATC
TR < TC
TR > VC
P = MR
TR < TC
A firm’s supply curve in the short run is the portion of its:
AVC above AFC
ATC above MR
MC below ATC
MC above AVC
MC above AVC
The profit-maximizing condition for a competitive firm is:
MR = MC
P = AFC
MR = AVC
MC = ATC
MR = MC
Which of the following is a sunk cost?
Lease that can be canceled anytime
Past advertising expense
Interest on a loan
Future wage payments
Past advertising expense
The firm’s MC curve intersects ATC at:
Its maximum
Maximum TR
Minimum AVC
Its lowest point
Its lowest point
If marginal cost is less than marginal revenue:
Raise price
Increase output
Shut down
Decrease output
Increase output
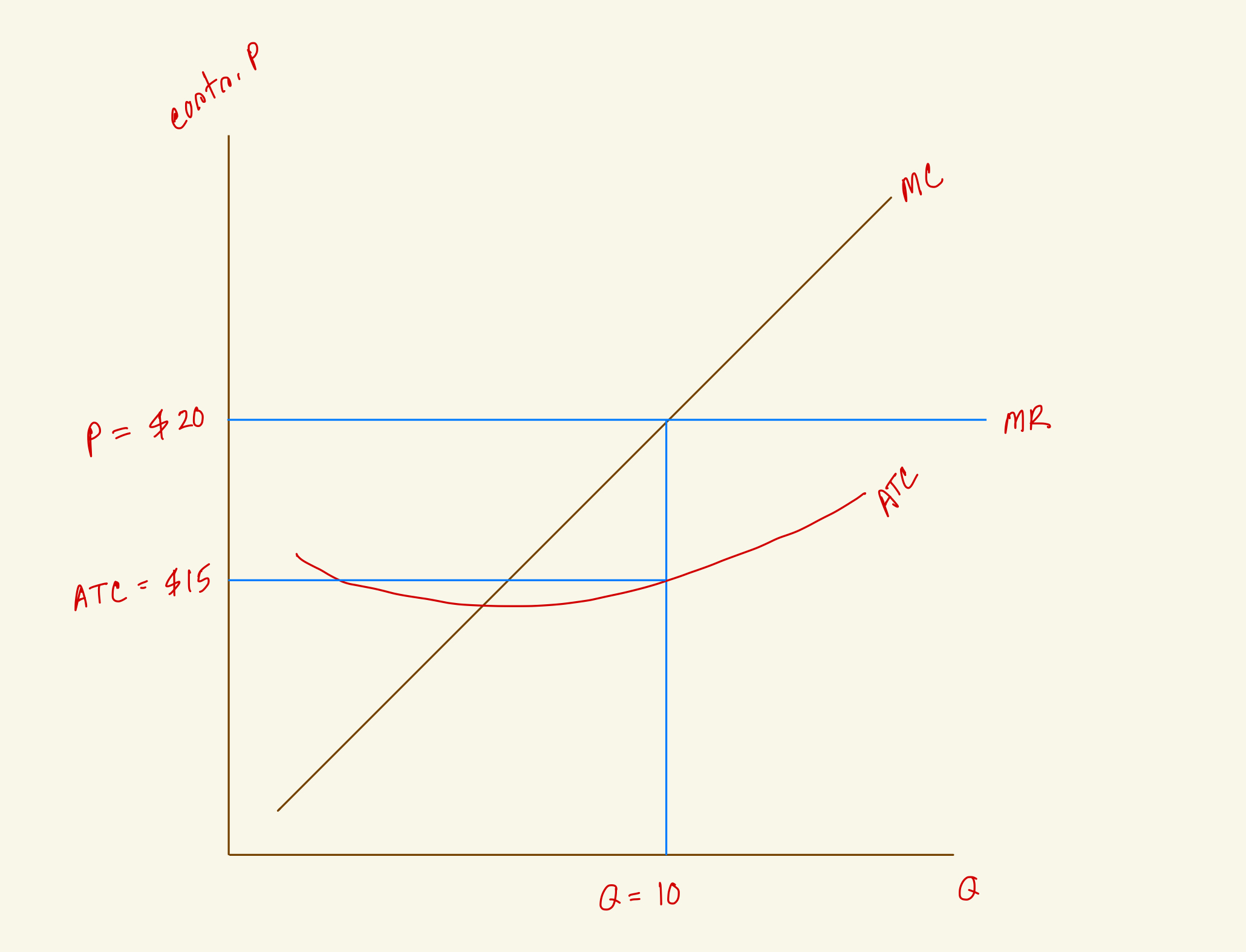
What's the total cost for this firm in the diagram?
$200
$150
$120
$100
$150
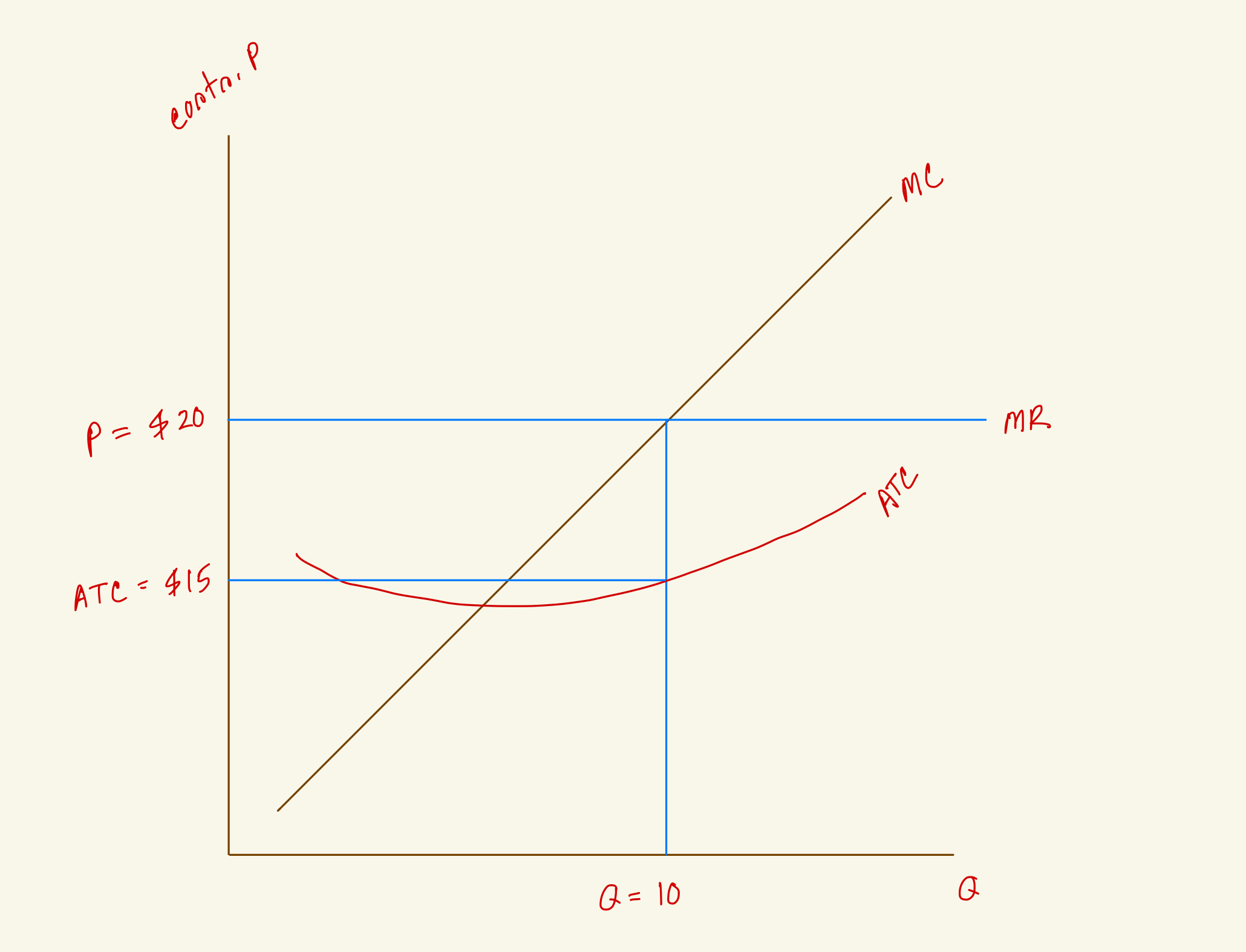
What's the total revenue for this firm in the diagram?
$170
$200
$100
$150
$200