Atomic Structure
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
smallest particle of an element that takes part in a chemical reaction
Atom
The basic structure of an atom includes a tiny, relative massive nucleus, containing __
at least one proton and usually one or more neutrons
Outside of the nucleus are __ which contain one or more electrons
energy levels (also called shells)
The _ have the greatest mass and have no charge.
neutrons
The _ have slightly less mass than the neutrons and are positively charge
protons
The _ have almost no mass and are negatively charged.
electrons
The _ move around the nucleus in energy levels
electrons
3 smaller sub-atomic particles of an atom:
Proton (p+)
Neutron (n0
Electron (e-)
positively charge particle of an atom with a relative mass of 1.0073 amu.
Proton (p+)
neutral particle of an atom with a relative mass of 1.0087 amu
Neutron (n0)
negatively charge particle with a mass of 0.00055 amu
Electron (e-)
Atom can be an _, _, or _
isotopes, isotones, or isobars
two or more atoms with the same atomic number but different mass number
Isotopes
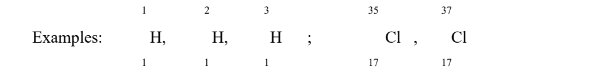
what is this?
Isotopes
any of two or more species of atoms or nuclei that have the same number of neutrons but different number of protons
Isotones

what is this?
Isotones
Aluminum and silicon are _ since they have the same number of neutrons, 14; phosphorus and sulfur have 16 neutrons.
Isotones
two or more atoms with the same mass number but different atomic number
Isobars

what is this?
Isobars
Cobalt and nickel are _ since they have the same mass of 59; whereas bismuth and polonium, the mass number is both 209.
Isobars
The _ and _ are found inside the nucleus which is the central part of the atom.
protons; neutrons
The _ are found outside the nucleus in shells or energy levels.
electrons
The number of protons in an atom is defined as the __
atomic number
The _ is a very small part of an atom in terms of size, but it contains most of the atom’s mass
nucleus
The number of protons + the number of neutrons is defined as the __ which is essentially equal to the atomic mass in amu
mass number
hence, the __ is = the mass number - the number of protons
number of neutrons
An atom is _ _ since it contains the same number of protons inside the nucleus as there are electrons outside the nucleus.
electrically neutral
The _____ is the representation of the arrangement of electrons distributed among the orbital shells and subshells.
electron configuration of an atom
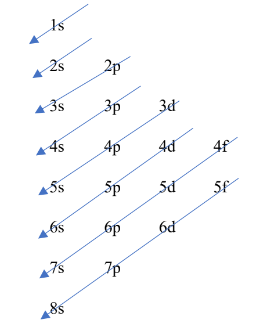
What is this?
Mnemonics in Organization of Electrons
The electron configuration of each element is unique to __
its position on the periodic table
The __ is determined by the period number and the number of electrons is given by the atomic number of the element where we can determine the number of valence electrons (electrons in the outermost shell).
energy level
The limit of two electrons per orbital is based on ___ which states that electrons occupying the same orbital must have their spins in opposite directions
Pauli’s Exclusion Principle
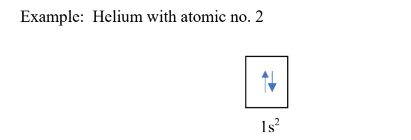
what principle is this?
Since helium has two electrons only based on the atomic number, electrons will occupy the first energy level, and on the same orbital, its electrons are arranged in opposite direction.
Pauli’s Exclusion Principle
states that electrons entering a subshell containing more than one orbital must be spread out over the available orbitals with their spins in the same direction.
Hund’s Rule of Maximum Multiplicity