Symbiosis
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
22 Terms
Symbiosis
Adaptations of microbes to the intimate presence of other species
Types of symbiotic relationships
Mutualism
Synergism
Commensalism
Amensalism
Parasitsm
mutalism
Two organisms grow in an intimate species relationship in which both partner species benefit and may fail to grow independently
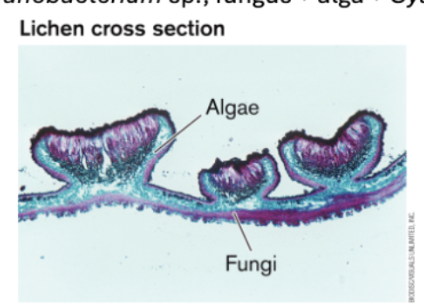
ex) lichens consist of fungi and algea growing together in a complex layered structure. Each species requires the presence of the other.
Synergism
Both species benefit through growth, but the prtners are easily seperated, and either partner can grow indepently of the other
ex) human colon bacteria ferment releasing hydrogen and carbon dioxide which methanogens convert to methane. The methanogens gain energy, and the bacteria benefit energetically from the removal of their fermentation products.
Commensalism
one species benefits, while the other species is neither harmed nor benefits.
ex) beggiatoa bacteria oxidize H2S for energy. removal ofH2S enables growth of other microbes for whom H2S is toxic. The other micorobes dont benefit bggiatoa.
Amensalism
One species benefits by harming another. Nonspecific relationship.
Streptomyces secrete antibiotics that lyse other species, that streptomyces consumes for energy
Parasitism
the parasite benefits at the expense of the other, a specifc host. the relationship is usually obligatory for the parasite.
ex)legionella pneumophelia parasitizes amebas, and infects lung macrophages causing Legionarie’s disease.
Extreme example of mutualism
Lichens
fungus + algea or fungus + cyanobacterium or all three
where fungi provide protective cup for algea while the photobiont produces carbohydrates.
the partner species may require each other
Mutualism checklist
Removal of one partner leads to death or reduced growth of the other
The genomes of each species show advanced degeneration
Products produced by one partern are utilized by the other
Cow rumen microbiome
Rumen bacteria in the cow gut ferment complex polysaccharides from grass producing H2and CO2, methanogens convert these gases into methane preventing the accumulation of H₂, which would otherwise inhibit bacterial fermentation and methanogens use these gases as energy sources.
synergism
Checklist for synergism
Each partner benefits from the other
partners are easily separated and grown indepently of each other
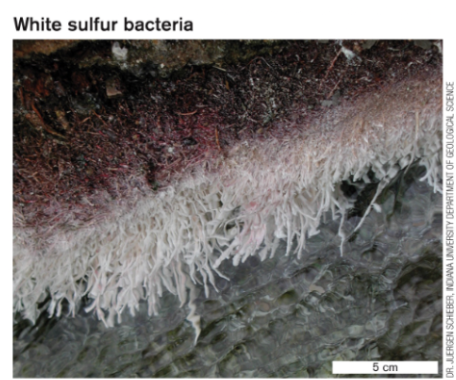
Beggiatoa and other sulfer spring microbes
In ecosystems with high concentrations of toxic H2S microbial mats containing sulfer oxidizers like Beggiatoa reduce ecosystem toxicity and allow growth of other species
Beggiatoa is not doing this out of the goodness of their heart, they are doing it to get energy.
this is commensalism
Streptomyces and other soil bacteria
streptomyces produces natural antibitoics to kill and lyse other bacteria in the soil, releasing their nutrients and the streptomyses consume these.
Streptomyces is bacteria but carries out its life cycle in a fungal way. They make spores.
Amensalism
Checklist for amensalism
one species benfits
the other species is harmed by the interaction
The interaction is non specific
Checklist for parasitism
One species benfits
the other species is harmed by the interaction
The interaction is specific, and usually obligatory for the parasite.
Endosymbiosis
Many insect species are infected by intracellular bacteria (endosymbionts)
ex) Wolbachia infects ~50% of insect species.
🔹 Used to fight malaria & mosquito-borne viruses by competing with parasites.
🔹 Shortens mosquito lifespan, reducing disease transmission.
Synergism
they can exist independent of each other
Parsitism
Barry Marshall
Barry Marshall swallowed H. pylori to prove it causes stomach ulcers.
🔹 His experiment confirmed the bacterial cause, overturning prior beliefs.
🔹 Led to effective antibiotic treatments for ulcers
H. pylori infections of young children
protects them from the development of allergies and asthma so in this case its not parasitic, but instead synergism.
Commensalism
in the bottom case we see synergism
Endosymbiosis
One of the closest relatives nowadays to mitochondria is called riketsia. It speaks a chemical language that mitochondria understands.