Mineralogy
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
7 crystal systems
cool teens only remember holy matrimony talk
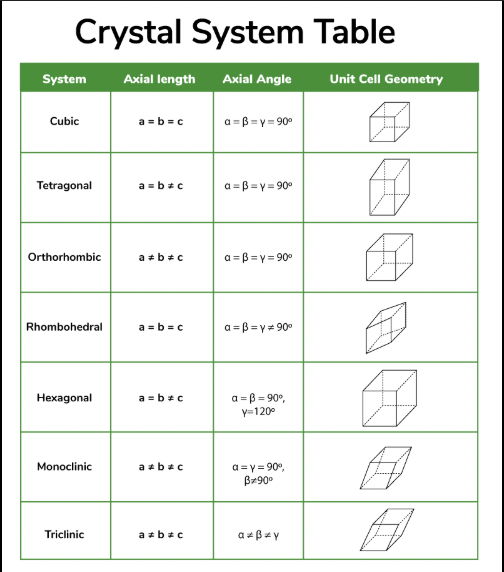
cubic
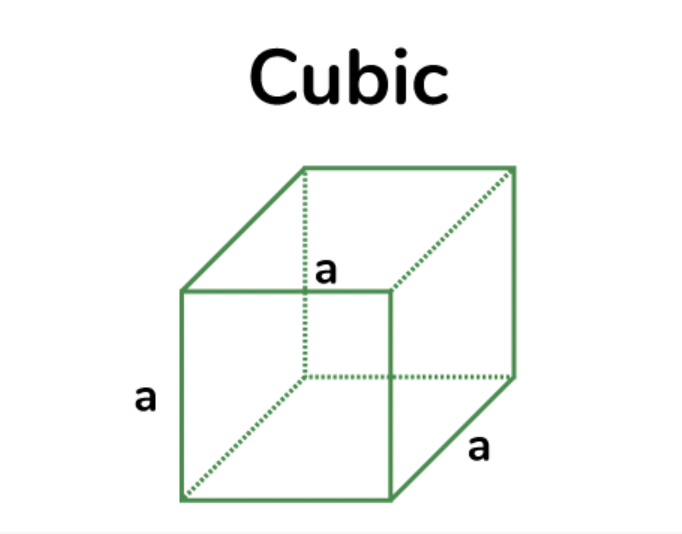
tetragonal
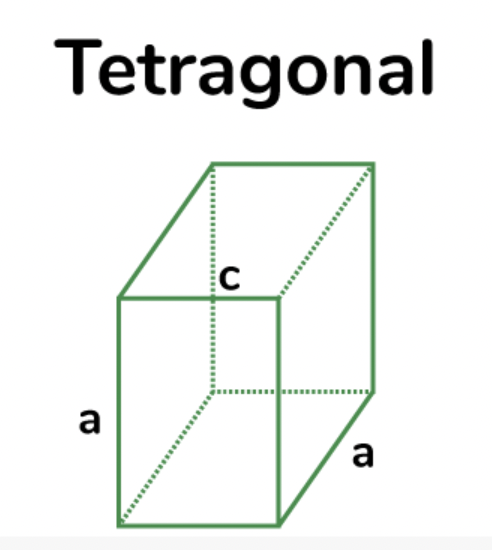
orthorhombic
OPX
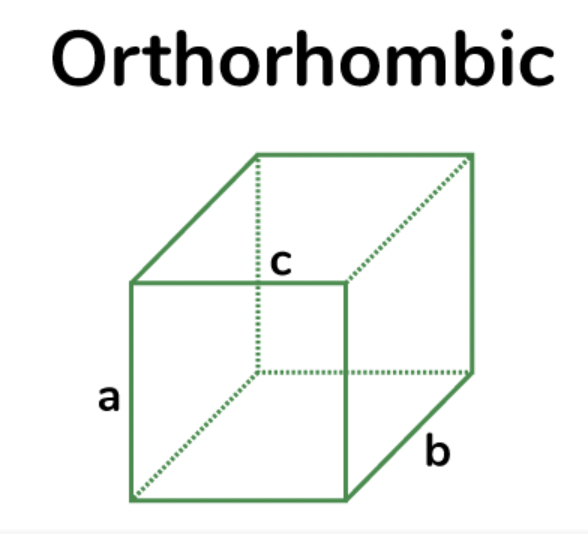
monoclinic
clinoamphiboles, CPX, orthoclase
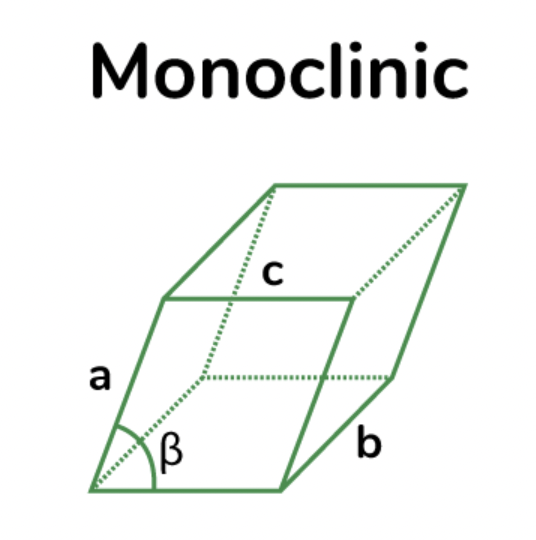
triclinic
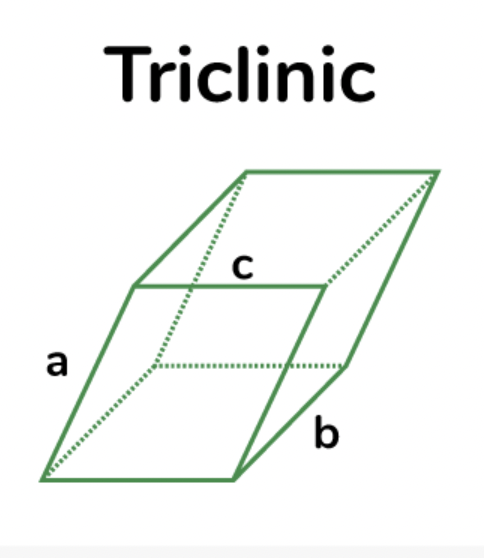
rhombohedral
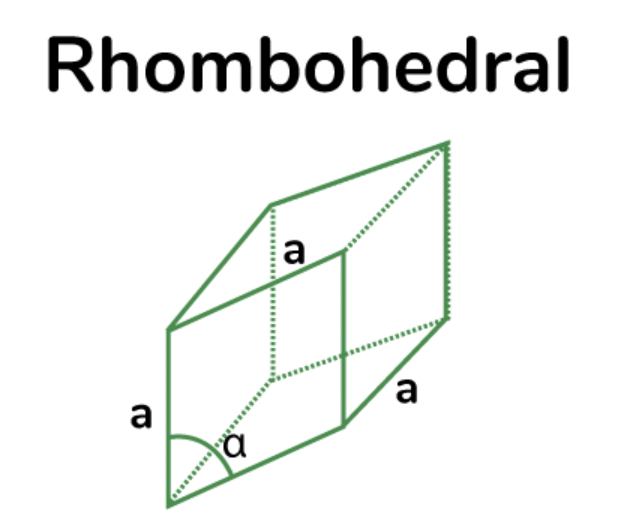
hexagonal
Qtz
divergent plate boundary
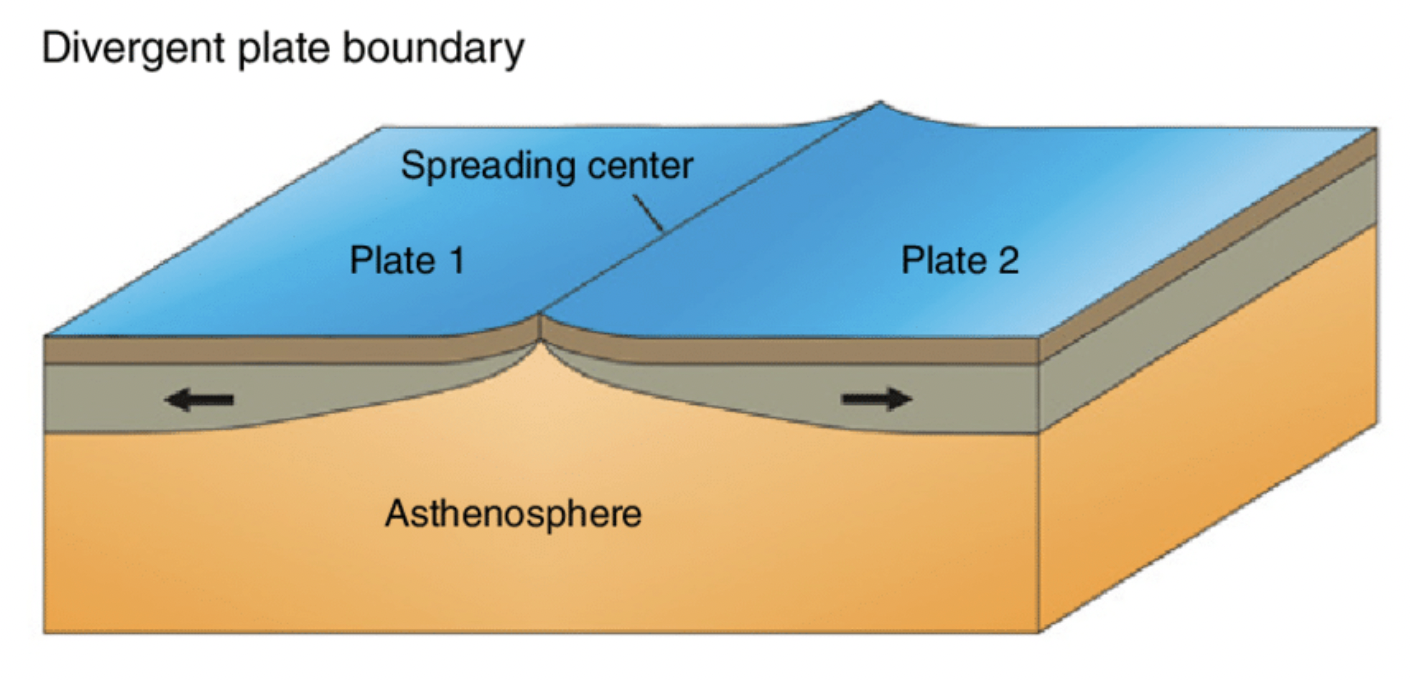
convergent plate boundary
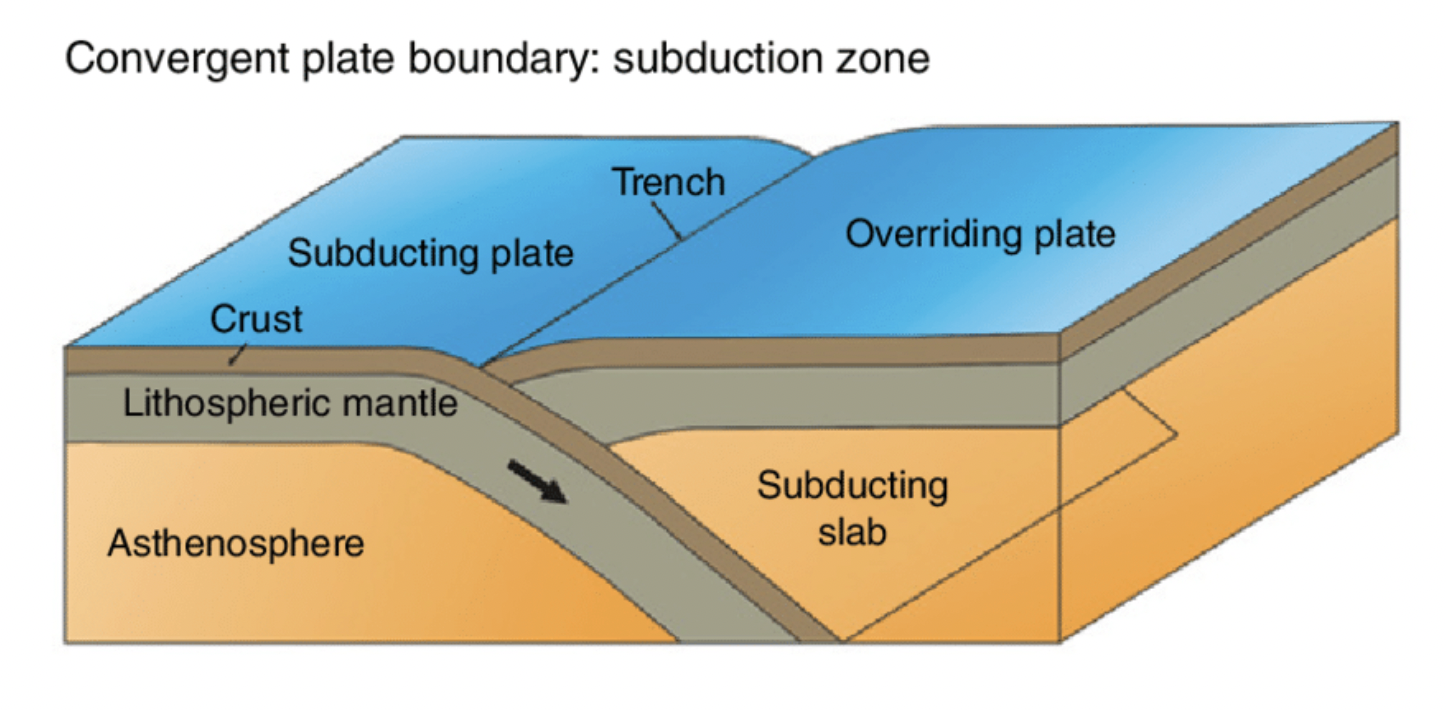
transform plate boundary
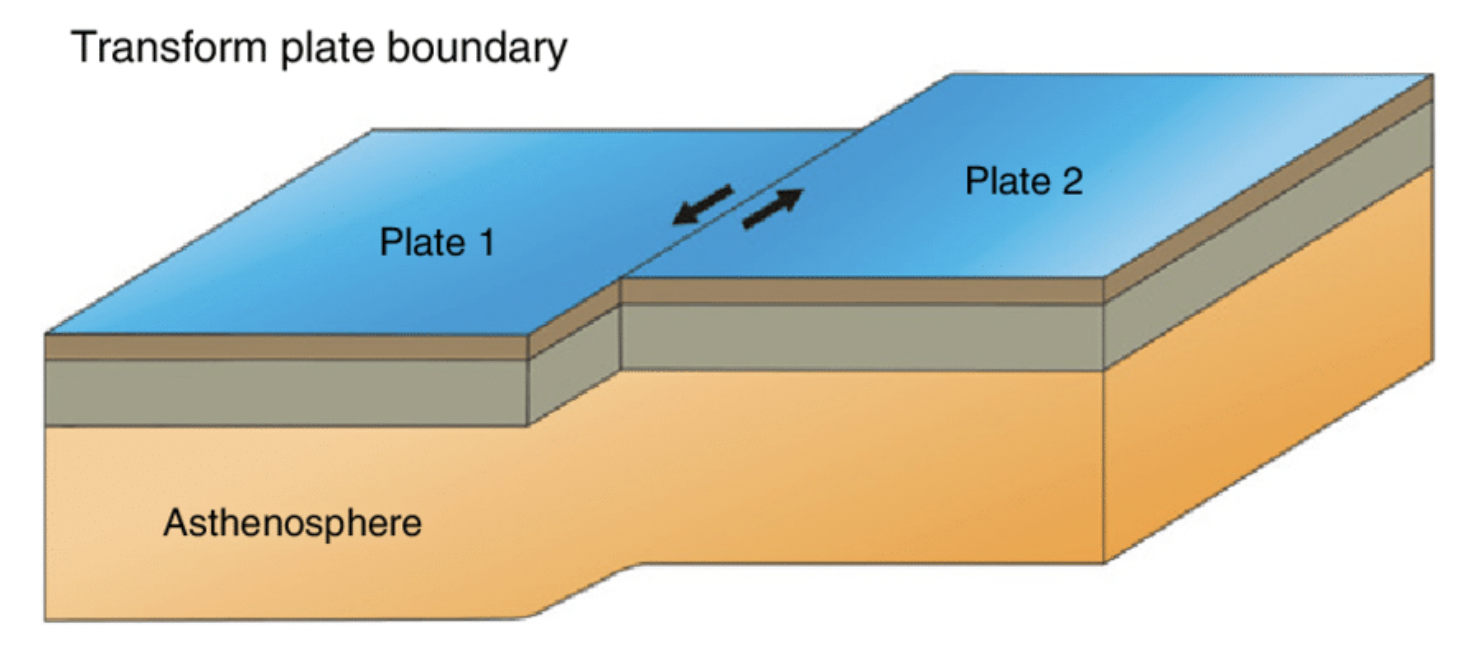
layers of the earth
oceanic crust 7-10km
continental crust 25 - 40km
mantle 2,900km
outer core 2,200km
inner core 2,414km
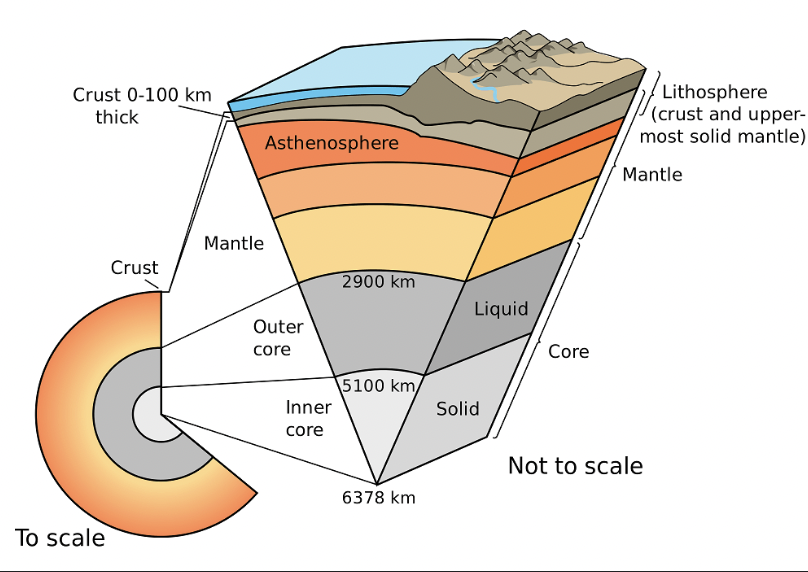
composition of oceanic lithosphere
basaltic rocks - Fe, Mg
mineral
A mineral is a naturally occurring inorganic element or compound having an orderly internal structure and characteristic chemical composition
rock
any naturally occurring solid mass or aggregate of minerals
different between a mineral and crystal
Minerals have a naturally formed, organized atomic structure with a specific chemical composition. Crystals for the most part will share these features, however the atoms are arranged in a repeating pattern that results in a crystal lattice, often presenting itself with crystal faces
polymorph
A polymorph is a mineral with the same chemical composition but a different internal structure
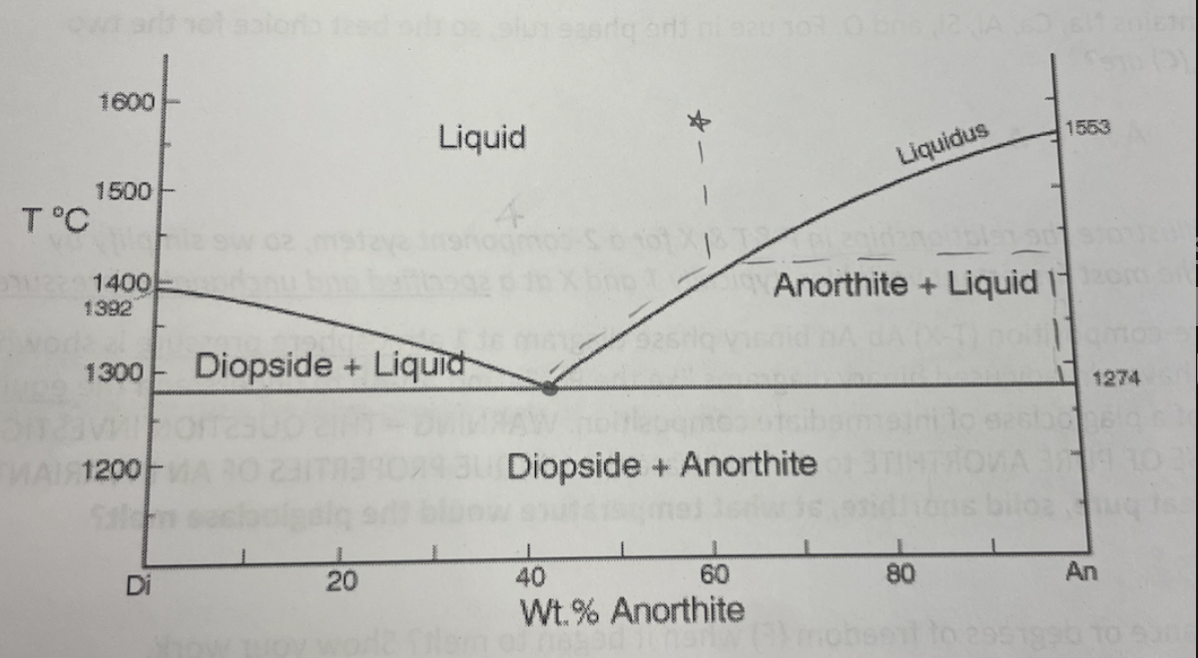
binary eutectic with solid solution
solid solution is range between Di and An (end members)
two different chemical compositions are possible (dependant on T and P)
EX: with exsolution lamellae, the more An end member will form first and then Di end member at a lower T and P
silicate mineral groups
orthosilicates
pyrosilicates
ring silicates
single chain silicates (pyroxenes)
double chain silicates (amphiboles)
sheet silicates
framework/tectosilicate/3D
old papa rings saying don’t say fuck
orthosilicates
simplest silicates which contain discrete SiO44- tetrahedral units
Olivine
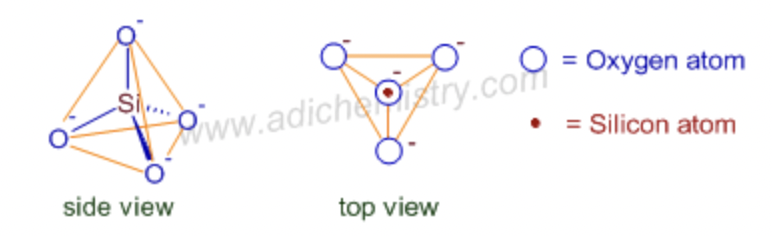
pyrosilicate
joining two tetrahedral SiO44- which share one oxygen atom between them
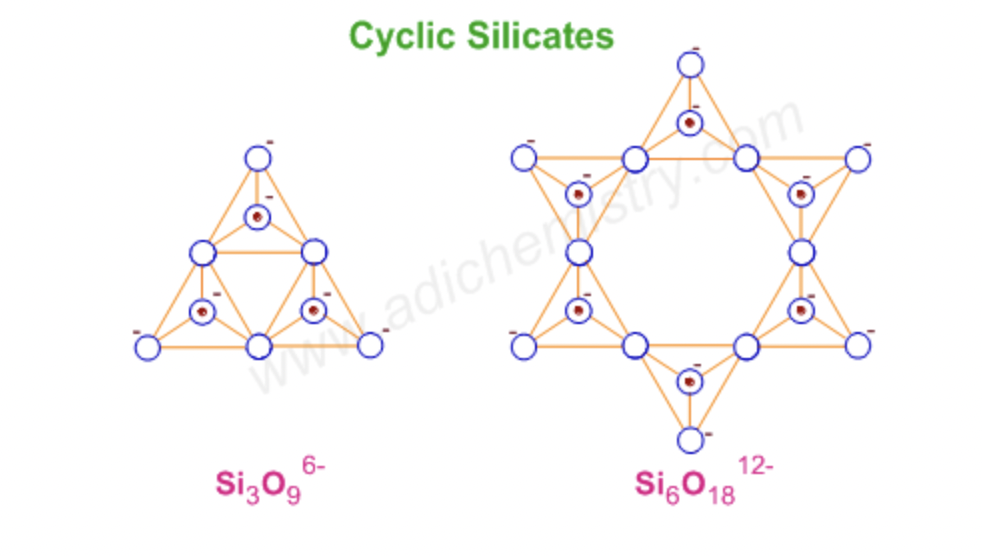
ring silicates
linking three or more tetrahedral SiO44- units
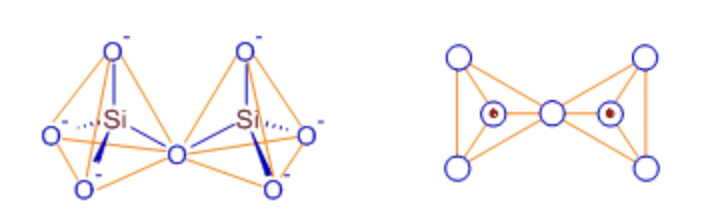
single chain silicates
linked, alternating SiO44- tetrahedra units
Pyroxenes
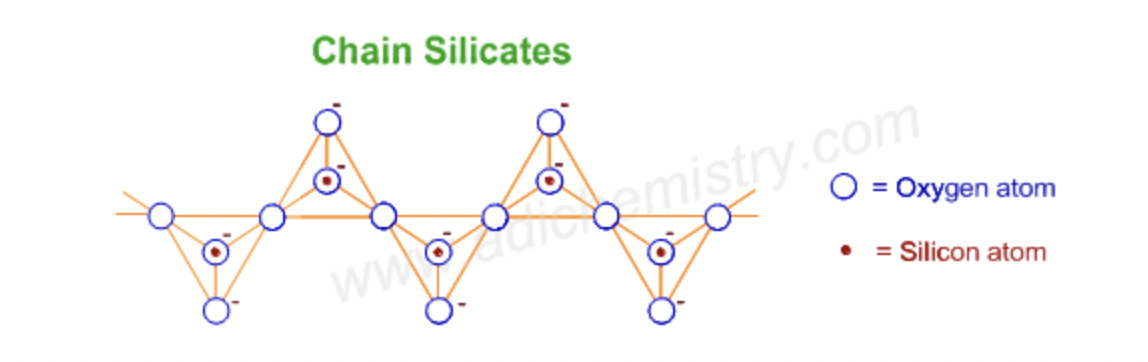
double chain silicates
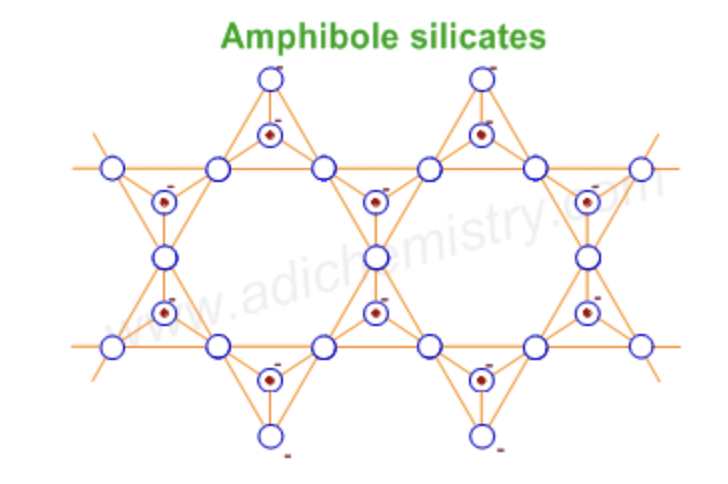
chain of ring silicates
Amphiboles
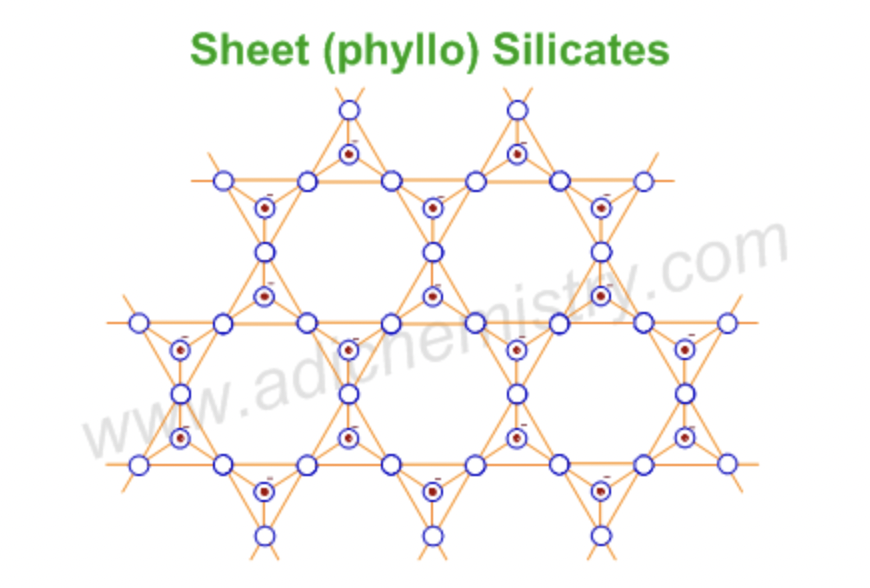
sheet silicates
each SiO4 tetrahedron shares three oxygen atoms, forming sheets
Micas, Clays
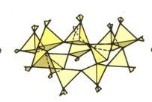
Framework/tectosilicate (3D)
shares all oxygens
Quartz, Feldspars
how are minerals classified
defined/grouped by their common anion/anionic groups
silicates
sulfides
oxides
halides
carbonates
elemental/native metals
sulfates
so, chess?
silicates
anion: SiO4
sulfides
anion: S2
metal cation bonded to a sulfide anion
oxides
anion: O
metal cations bonded to oxygen anion
halides
salt anion (F- or Cl-)
carbonates
anion: CO3
Ca or Mg bond to carbonate anion
sulfates
anion: SO4
metal cation bonds to sulfate anion
why do alkali feldspars show exsolution lamellae
Exsolution lamellae are fine crystals that were dissolved entirely in their host mineral structures at high temperature (e.g., clino- and orthopyroxenes) and/or pressure (e.g., majorite-pyroxenes), but are produced when their host minerals lose the solubility as a result of cooling to low temperatures
why do clays have higher cation coefficients?
Because clay particles are so small, pure clay has at least 1000 times more external surface area than coarse sand. Because clays have a large surface area and negative charges, they can attract and hold positively charged ions
As a result, the cations remain within the soil root zone and are not easily lost through leaching.
composition of continental lithosphere
granitic - Al, Si
composition of mantle
O, Si, Mg
composition of outer core
liquid - Fe, Ni and smaller amounts of Si, O
composition of inner core
solid - Fe, Ni
elemental/native metal
pure mass of a single metal (e.g. copper)