dna replication and mitosis
5.0(2)
Card Sorting
1/22
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
1
New cards
dna replication
* how dna copies exactly to prepare for cell division
* semi-conservative - one new strand, one original to make two new helices
* semi-conservative - one new strand, one original to make two new helices
2
New cards
enzymes involved
* helicase
* dna polymerase
* ligase
* dna polymerase
* ligase
3
New cards
helicase
* breaks the hydrogen bonds in the double helix, separating the two strands
4
New cards
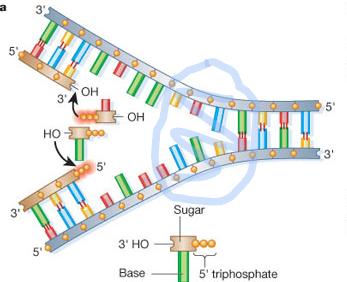
replication fork
* the place where the helicase is separating the two strands
5
New cards
rna primer
* enzyme called primase attaches to each strand
* primase puts an rna primer as a foundation upon which the polymerase can build
* later, the primer is removed and filled in with dna
* primase puts an rna primer as a foundation upon which the polymerase can build
* later, the primer is removed and filled in with dna
6
New cards
dna polymerase
* wraps around the strand at the primer
* attaches new nucleotides to the exposed ones according to the rule of base pairings
* only attaches single nucleotides w/ hydrogen bonds - no backbone yet
* attaches new nucleotides to the exposed ones according to the rule of base pairings
* only attaches single nucleotides w/ hydrogen bonds - no backbone yet
7
New cards
base pairing
* a with t, g with c
* two hydrogen bonds between a and t
* three between g and c
* two hydrogen bonds between a and t
* three between g and c
8
New cards
ligase
* forms backbone and joins new nucleotides together
* uses atp to link oh (hydroxyl group) on the 3’ to the phosphate group on the 5’ end of another
* uses atp to link oh (hydroxyl group) on the 3’ to the phosphate group on the 5’ end of another
9
New cards
okazaki fragment
* pieces of new dna that haven’t been connected by ligase yet
* found on the lagging strand
* found on the lagging strand
10
New cards
polymerase direction
* only moves from 5’ to 3’
* this creates one leading and one lagging strand bc of antiparallel structure
* this creates one leading and one lagging strand bc of antiparallel structure
11
New cards
cell cycle
* the process of a cell growing, replicating dna, going through mitosis, and finally cell division
* stages: g1, synthesis, g2, mitosis, cytokinesis
* stages: g1, synthesis, g2, mitosis, cytokinesis
12
New cards
interphase
* made up of of g1, s, and g2
* cell grows and replicated dna
* cell grows and replicated dna
13
New cards
g1 phase
* growth 1 or gap 1
* cell grows larger
* everything is duplicated except dna
* g1 → s checkpoint: cell size, nutrients, dna damage - becomes irrevokably committed to cell division
* cell grows larger
* everything is duplicated except dna
* g1 → s checkpoint: cell size, nutrients, dna damage - becomes irrevokably committed to cell division
14
New cards
s phase
* synthesis
* dna is copied
* two strings of chromatin called sister chromatids - attached duplicates you can’t see because it’s still spaghetti-like
* centrosomes are duplicated
* dna is copied
* two strings of chromatin called sister chromatids - attached duplicates you can’t see because it’s still spaghetti-like
* centrosomes are duplicated
15
New cards
g2 phase
* grows more, makes proteins and organelles, reorganizes contents in preparation for mitosis
* g2 → m checkpoint: no errors in dna replication, dna has been totally replicated
* this is the last chance the cell has to pause for repairs - it may repair damaged dna or finish replicating dna fully. if the damage is too severe, the cell may undergo apoptosis.
* g2 → m checkpoint: no errors in dna replication, dna has been totally replicated
* this is the last chance the cell has to pause for repairs - it may repair damaged dna or finish replicating dna fully. if the damage is too severe, the cell may undergo apoptosis.
16
New cards
mitosis
* process of nucleic division in preparation for cell division
* four stages: prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase
* four stages: prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase
17
New cards
prophase
* dna is condensed into chromosomes
18
New cards
mitotic spindle
* formed during early prophase
* made in the centrosome by centrioles
* a structure made out of microtubules (strong fibers)
* grows between the centrosomes as they move apart
* made in the centrosome by centrioles
* a structure made out of microtubules (strong fibers)
* grows between the centrosomes as they move apart
19
New cards
prometaphase
* nuclear envelope breaks down, releasing chromosomes
* spindles begin attaching to chromosomes
* they bind to chromosomes at kinetochore (patch of proteins on centromere)
* spindles begin attaching to chromosomes
* they bind to chromosomes at kinetochore (patch of proteins on centromere)
20
New cards
metaphase
* chromosomes are lined up in the middle of the cell, all attached to mitotic spindle microtubules
* both kinetochores on each chromosome are attached to microtubules from each side (one tubules from the top, one tubule from the bottom so they can be pulled apart)
* m checkpoint/spindle checkpoint: making sure all chromosomes are properly attached to the spindle
* both kinetochores on each chromosome are attached to microtubules from each side (one tubules from the top, one tubule from the bottom so they can be pulled apart)
* m checkpoint/spindle checkpoint: making sure all chromosomes are properly attached to the spindle
21
New cards
anaphase
* microtubules pull sister chromatids apart to make each its own chromosome
* they are pulled to opposite poles of the cell
* they are pulled to opposite poles of the cell
22
New cards
telophase
* cell starts to return to normal
* chromosomes decondense, nuclear membrane returns, spindle disappears
* there are now two nuclei on either side of the cell
* chromosomes decondense, nuclear membrane returns, spindle disappears
* there are now two nuclei on either side of the cell
23
New cards
cytokinesis
* starts in the final phases of mitosis - may overlap with anaphase or telophase
* cell is pinched in two and finally separate properly
* cell is pinched in two and finally separate properly