Pathogenic Bacteriology - UNF
1/84
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
85 Terms
The primary target of penicillin is an enzyme known as: ____________
The primary target of penicillin is an enzyme known as: Transpeptidase
Transpeptidase forms ___ ___ disaccharide cross-links.
Transpeptidase forms NAG NAM disaccharide cross-links.
Penicillin is effective against gram negative/gram positive bacteria.
Penicillin is effective against gram negative/gram positive bacteria.
When transpeptidase is damaged it break cross links in the petidoglycan which allow cellular pressure to ___ the cell.
When transpeptidase is damaged it break cross links in the petidoglycan which allow cellular pressure to lyse the cell.
One of the main reasons bacteria upkeep a peptidogylcan layer is to maintain ______ _______ and semi-premability.
One of the main reasons bacteria upkeep a peptidogylcan layer is to maintain cellular pressure and semi-premability.
Teichoic is attached ________ to the peptidogylcan and contributes to its overall negative charge.
Teichoic is attached covalently to the peptidogylcan and contributes to its overall negative charge.
True or false
LPS contains three primary components:
A uniform lipid part at the bottom which acts as an anchor
Long sets of sugars closest to the lipids which are called core polysaccharides
O-antigen side chain sugars (Loooong). These can vary between species and strains.
True or false
LPS contains three primary components:
A uniform lipid part at the bottom which acts as an anchor
Long sets of sugars closest to the lipids which are called core polysaccharides
O-antigen side chain sugars (Loooong). These can vary between species and strains.
True or false
Different parts of the immune system recognize different parts of the LPS. The adaptive immune system can regonize the lipids in LPS and trigger an immune response.
True or false
Different parts of the immune system recognize different parts of the LPS. The adaptive innate immune system can regonize the lipids in LPS and trigger an immune response.
True or false
The O-antigen side chain is very long to hide from the immune system.
True or false
The O-antigen side chain is very long to hide from the immune system.
True or false
Due to the size of the O-antigen side chain, they are very long to support nutrient transfer
True or false
Due to the size of the O-antigen side chain, they are very long to support nutrient transfer
True or false
The capsule has four main components.
An outer protein rich coat
Cortex of thick peptidoglycan
Germ cell wall needed for sporulation
Core of DNA, RNA, and enzymes (DRY)
True or false
The capsule endospore has four main components.
An outer protein rich coat
Cortex of thick peptidoglycan
Germ cell wall needed for sporulation
Core of DNA, RNA, and enzymes (DRY)
True or False
Mycobacterium are susceptible to discovery by the immune system and certain drugs due to their waxy coat.
True or False
Mycobacterium are susceptible to discovery by the immune system and certain drugs due to their waxy coat.
They are harder to detect and are more resistant to drugs and immune clearance.
The capsule is a thick secreted layer of primarily _______ that cloaks the entirety of the bacteria. This makes them slimy and allows them to resist phagocytosis.
The capsule is a thick secreted layer of primarily proteins that cloaks the entirety of the bacteria. This makes them slimy and allows them to resist phagocytosis.
Bacteria are more susceptible to phenotypically exhibiting DNA mutations because they are ______ ( n).
Bacteria are more susceptible to DNA mutations because they are haploid (1n).
True or false
Plasmids are not as susceptible to phenotypically exhibiting DNA mutations.
True or false
Plasmids are not as susceptible to phenotypically exhibiting DNA mutations.
This is because they are not limited to one copy of a plasmid and often have several copies of the same gene. This gene can be present on multiple plamids or even in its genome on the chromosome.
True or False
Bacteria group genes of similar function together making them able to co-regulate expression, producing all necessary proteins simultaneously from a single promoter.
True or False
Bacteria group genes of similar function together making them able to co-regulate expression, producing all necessary proteins simultaneously from a single promoter.
The electron transport chain occur on the inner/outer lipid membrane of gram negative bacteria.
The electron transport chain occur on the inner/outer lipid membrane of gram negative bacteria.
The interior of the human body is devoid of oxygen and is inherently _______.
The interior of the human body is devoid of oxygen and is inherently anaerobic.
Bacteria in environments devoid of oxygen can undergo the following forms of respiration:
respiration and
Bacteria in environments devoid of oxygen can undergo the following forms of respiration:
Anaerobic respiration and Fermentation
True or false
Fimbrea are long hair like extensions that support the ability of bacteria to adhere on to surfaces.
True or false
Fimbrea are external structures that support the ability of bacteria to adhere on to surfaces.
The glycocalyx is a modified _____ which makes bacteria sticky and able to adhere to the host cells.
The glycocalyx is a modified capsule which makes bacteria sticky and able to adhere to the host cells.
The following are strategies/structures to aid bacteria to adhere to a host:
G x
F a
A s
B s
The following are strategies/structures to aid bacteria to adhere to a host:
Glycocalyx
Fimbrea
Adhesins
Biofilms
Antibodies are secreted by the ______ immune system of the body.
Antibodies are secreted by the adaptive immune system of the body.
B and T cells are referred to a __________. These are members of the adaptive immune system.
B and T cells are referred to a lymphocytes. These are members of the adaptive immune system.
Phagocytes are members of the _____ immune system.
Phagocytes are members of the innate immune system.
True or false
Neutrophils are also referred to as PMNs. polymorphonuclear leukocytes..
True or false
Neutrophils are also referred to as PMNs. polymorphonuclear leukocytes..
True or false
Phagocytes contain granules, secreted extracellular vesicles containing antimicrobial molecules which are released upon antigenic contact with an unrecognized cell.
True or false
Phagocytes contain granules, secreted extracellular vesicles containing antimicrobial molecules which are released upon antigenic contact with an unrecognized cell.
Explanation
Phagocytes contain granules that fuse with phagosomes after a microbe is engulfed. These granules release antimicrobial molecules such as lysozyme, defensins, and proteases into the phagosome, where they degrade and kill the ingested pathogen.
Monocytes circulate in the blood supply in response to infectious conditions until they contact surface receptors on vascular epithelial cells signalling an inbound infection. The signalling cascade that up-regulates the formation of these receptors also opens gaps in the vascular epithelial cells that allow monocytes to enter the infected area through. This process is called ____________.
Monocytes circulate in the blood supply in response to infectious conditions until they contact surface receptors on vascular epithelial cells signalling an inbound infection. The signalling cascade that up-regulates the formation of these receptors also opens gaps in the vascular epithelial cells that allow monocytes to enter the infected area through. This process is called extravasation.
When bacteria are phagocytosed, they are enclosed in a membrane-bound vesicle called a __________, which creates a protective separation between the microbe and the phagocyte’s cytoplasm. This structure then fuses with intracellular granules and lysosomes to form a _____________, where antimicrobial molecules such as lysozyme, proteases, defensins, reactive oxygen species, and reactive nitrogen intermediates are released to kill and degrade the bacteria
When bacteria are phagocytosed, they are enclosed in a membrane-bound vesicle called a phagosome, which creates a protective separation between the microbe and the phagocyte’s cytoplasm. This structure then fuses with intracellular granules and lysosomes to form a phagolysosome, where antimicrobial molecules such as lysozyme, proteases, defensins, reactive oxygen species, and reactive nitrogen intermediates are released to kill and degrade the bacteria
Why are oxygen radicals dangerous and used to kill bacteria?
How do phagocytes take advantage of this property?
How do we measure phagocytic activity?
Why are oxygen radicals dangerous and used to kill bacteria?
They are extremely electronegative and attract electrons which can then bind to surrounding molecular components in an unregulated manner which can possibly trigger downstream damage.
How do phagocytes take advantage of this property?
Phagocytic cells utilize a property known as “oxidative burst” which weaponizes these oxygen radicals to kill bacteria trapped in the phagolysosome.
How do we measure phagocytic activity?
When oxidative burst occurs the environment indirectly becomes more acidic throughout the process. It can often be far more economical to correlatively measure pH than superoxide concentration.
True or false
Antimicrobial molecules such as lysozyme, lipases, proteases, defensins, reactive oxygen species, and reactive nitrogen intermediates are released to kill and degrade the bacteria when in the phagolysosome.
True or false
Antimicrobial molecules such as lysozyme, lipases, proteases, defensins, reactive oxygen species, and reactive nitrogen intermediates are released to kill and degrade the bacteria when in the phagolysosome.
The process of counting the number of phagocytic cells in a blood sample is known as a _________ ____.
The process of counting the number of phagocytic cells in a blood sample is known as a differential count.
What is a PAMP?
What is a PAMP?
A PAMP is a Pathogen Associated Molecule Poop. These are molecules unique to prokaryotic organisms such as:
The O antigen of Lipid A found in the LPS of gram-negative bacteria.
Lipoteichoic acid in the peptidoglycan of gram-positive bacteria.
Flagellin a conserved protein in the flagella of bacteria.
Unmethylated CpG DNA
What are examples of the most well understood PAMPs and what receptors recognize them?
Peptidoglycan is recognized by TLR2
LPS is recognized by TLR4
Flagellin is recognized by TLR5
Methylation patterns are recognized by TLR9
TLR is an example of a _____ recognition receptor.
TLR is an example of a pattern recognition receptor.
True or False
Both TLRs and NOD (NLRs) receptors can be found extra and intercellularly.
True or False
Both TLRs and NOD (NLRs) receptors can be found extra and intercellularly.
TLRs: Found on the cell surface and on endosomal membranes.
NOD-like receptors (NLRs): Found only in the cytoplasm, where they sense intracellular PAMPs/DAMPs.
What is a DAMP?
What is a DAMP?
A DAMP is a Damage Associated Pattern, a signature of host cellular damage. Detection of these molecules can be indicative of a cellular damage.
What is the complement system?
What is the complement system?
A combination of over 30 different proteins produced in the liver that are secreted into the blood designed to bind to the surface of foreign organic structures such as bacterial surfaces.
They can bind to antigens on the surface of bacteria and form pores to lyse bacterial membranes, make it easier for phagocytes to latch on to bacterial to begin phagocytosis. Their attachment also marks the object as foreign.
The process of a complement binding to a bacterial surface such as mycobacterium to make it easier to bind to is called ___________.
The process of a complement binding to a bacterial surface such as mycobacterium to make it easier to bind to is called opsonization.
Mycobacterium in specific resist phagocytosis and opsonization by the complement system in lieu of being cloaked in dissacharide chains that mask their antigens. However, complements are capable of attaching antigens to these structures through a process which makes it easier for phagocytes to begin phagocytosis.
True or false
Cytokines are capable of activating macrophages, drawing them to the site of an infection,
True or false
Cytokines are capable of activating macrophages, drawing them to the site of an infection,
The site of a bacterial infection undergoing inflammation exhibits several classical hallmarks:
Increased temperature
Red
Painful
Why do these factors occur?
The site of a bacterial infection undergoing inflammation exhibits several classical hallmarks:
Increased temperature
Red
Painful
Why do these factors occur?
This occurs primarily due to the increased presence of phagocytic cells to the site of infection, dilated blood vessels, increased fluid flow, blood cells in the tissue. Oxidative burst releases ROS species which affect nearby host tissues as phagocytic cells are “messy eaters”
What cell type are TLRs found on?
What cell type are TLRs found on?
Innate immune cells:
Macrophages
Dendritic cells
Neutrophils
Monocytes
Mast cells
Natural killer (NK) cells (some TLRs)
Adaptive immune cells:
B cells (certain TLRs help activate them)
Some subsets of T cells (less prominent)
Non-immune cells:
Epithelial cells (skin, respiratory, GI, urogenital tracts)
Endothelial cells
Fibroblasts
This is the primary reason why mass spread of PAMPs across the body in the blood stream is so dangerous. As these will trigger a systemic immune response and bodily inflammation. Ultimately resulting in organ failure and death. This is called septic shock.
Antigens can have multiple antibodies that recognize different _______ on the antigen if large enough. This increases the likelihood that it is recognized,
Antigens can have multiple antibodies that recognize different epitopes on the antigen if large enough. This increases the likelihood that it is recognized,
True or false
An antibody has two pockets that are capable of binding an antigen at different epitopes.
Example: Y
True or false
An antibody has two pockets that are capable of binding an antigen at different epitopes.
Example: Y
Both sites bind to the same epitope
In reference to the host immune system, what is an IgG?
An IgG is the most abundant class of circulatory antibodies which are capable of blocking viruses and toxins from interacting with cells of the host.
In reference to the host immune system, what is an IgG?
An IgG is the most abundant class of circulatory antibodies which are capable of blocking viruses and toxins from interacting with cells of the host.
Name and define the six ways that antibodies protect the host.
Ne________
Im__________ and pre____n of ad______
Ag_______n
Op________
Co_________
An_____-de_______ cell-m______ cyto_____y
Name and define the three ways that antibodies protect the host.
Neutralization
IgG - block the attachment to host cells
Prevent toxin from interacting with cells
Immobilization and prevention of adherence
Antibody bonding to cellular structures to interfere with bacterial function.
Agglutination
Antigens and antibodies can attach to two identical epitopes simultaneously, this allows them to attach to two bacteria at once clumping them together.
Makes it easier to phagocytose foreign bodies.
Opsonization
Coating a bacterium in antibodies
Enhances lysis and phagocytosis
Complements
Antibody bonding triggers the classical complement pathway
Antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity
Primarily for parasites, coating them in antibodies to signal NK cells to kill the parasite.
When initially exposed to an antigen what are the characteristics of the primary response?
When initially exposed to an antigen what are the characteristics of the primary response?
It takes 10-12 days before an antibody is detected in the blood. When it is, B cells will proliferate and differentiate into plasma cells.
Initially these IgM (first ever antibodies) are inefficient and can has lower bonding affinity. Some B-cells can undergo class switching which will improve binding affinity in this first hump.
On second exposure to the antigen new high affinity antibodies are produced (IgG).
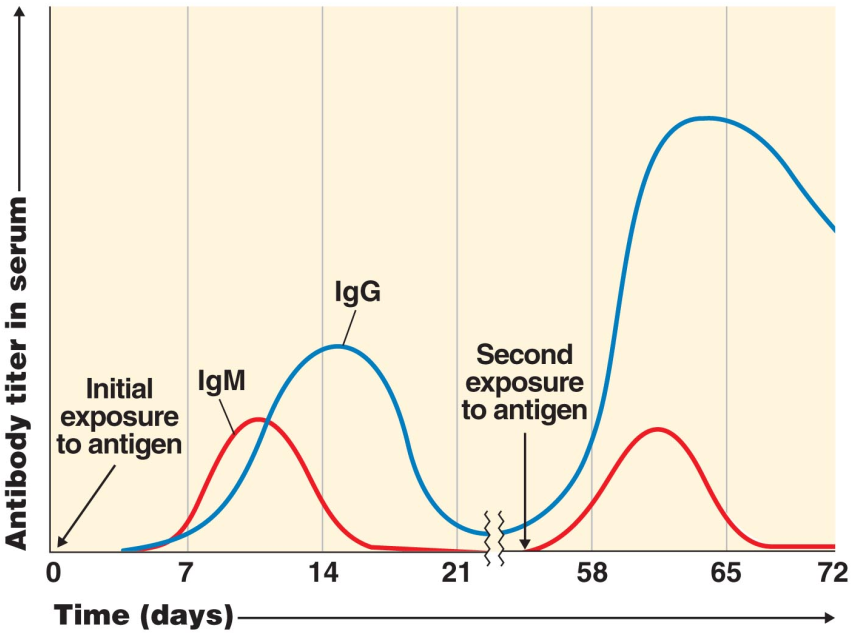
How does the formation of the memory cell contribute to the high-affinity secondary response titer?
How does the formation of the memory cell contribute to the high-affinity secondary response titer?
Memory cells are the main contributors to this powerful high-affinity secondary response curve. They rapidly proliferate and produce large amount of IgG that have been optimized for the immune response.
What do memory cells differentiate into and what to these cells do?
What do memory cells differentiate into and what to these cells do?
Memory B cells differentiate into plasma cells which are capable of rapid antibody production.
How do vaccines exploit the phenomenon of immunologic memory?
Define microbial antagonism.
Define microbial antagonism.
Competition between microbes. Normally host microbiota protect you be occupying niches that pathogens might occupy, producing acids, producing bacteriocins (toxic proteins of peptides that inhibit competitor microbial growth).
Define Koch’s bacterial postulates.
_
_
_
_
Define Koch’s bacterial postulates.
The pathogen must be present in all cases of the disease.
The pathogen must be isolated from the diseased host and grown in pure culture.
The pathogen from pure culture must cause the disease when inoculated into a healthy, susceptible organism.
The pathogen must be re-isolated from the inoculated animals and be shown to be the original organism.
Why must a pathogen be re-isolated from the inoculated animals and be shown to be the original organism in #4 for Koch’s postulates?
Why must a pathogen be re-isolated from the inoculated animals and be shown to be the original organism in #4 for Koch’s postulates?
This confirms that the microbe is a related contaminant and that is the same organism implicated in the disease present in the population as opposed to a subject of horizontal gene transfer.
When do Koch’s postulates not apply?
When do Koch’s postulates not apply?
Some microbes cannot be isolated in pure culture
Some organisms lack an animal model
What makes pathogenic bacterial strains different?
What makes pathogenic bacterial strains different?
Virulence factor
What is the clearest case of virulence factor.
What is the clearest case of virulence factor.
Toxins, the most notable.
How many bacteria must you need to come in contact with to establish a colony? This measurement is called an ____.
How many bacteria must you need to come in contact with to establish a colony? This measurement is called an ID50.
We don’t use the 100% mark as this makes it difficult to measure differences in population sensitivity. IE we can easier detect a shift of 200-300 but not 5000-6000.
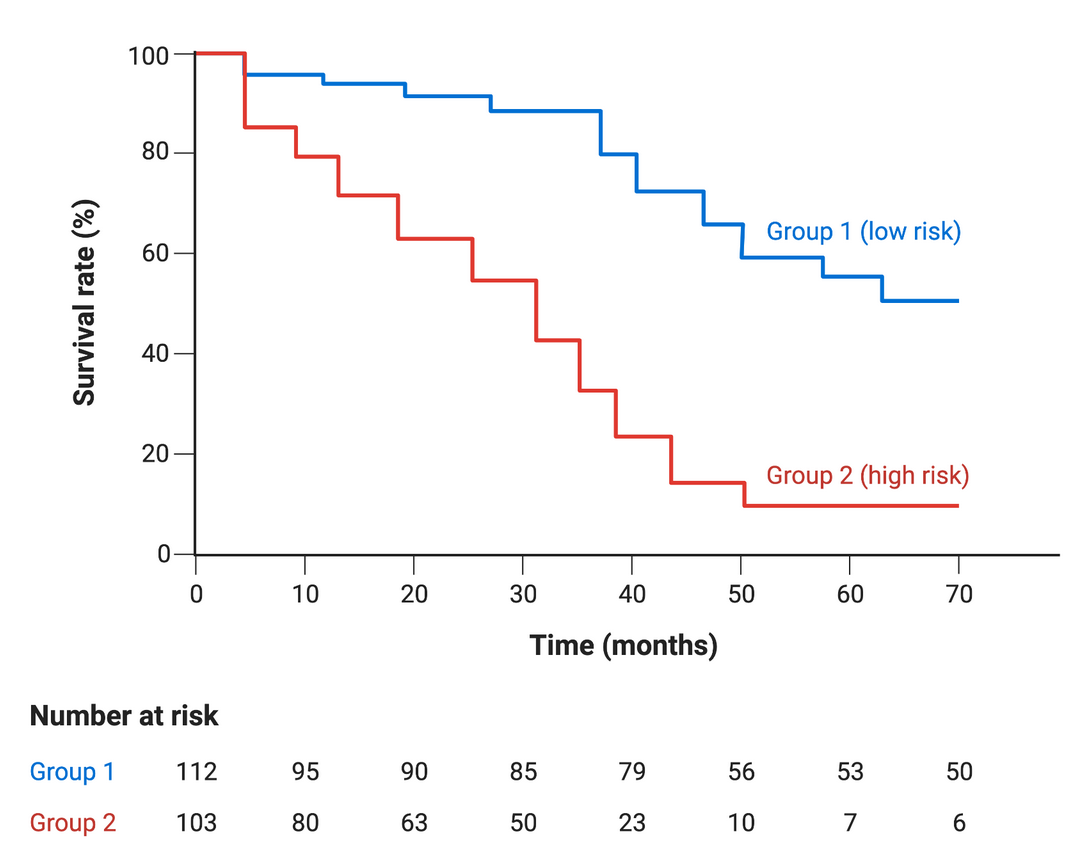
What graph is this?
What graph is this?
Kaplan Meyer survival curve
True or false
25-250 Is the sweet spot for counting CFU traditionally.
True or false
25-250 Is the sweet spot for counting CFU traditionally.
One way we can determine the presence of a virulence factor is to see knock it out an observe the effect on the bacteria with a control strain. Then we can transform it with a plasma with varying accuracy.
This is referred to as a knock out in assay.
One way we can determine the presence of a virulence factor is to see knock it out an observe the effect on the bacteria with a control strain. Then we can transform it with a plasma with varying accuracy.
This is referred to as a knock out in assay.
Define a reporter assay.
Define a reporter assay.
A reporter assay is an experimental system where a reporter gene is fused to a regulatory sequence of interest so that its activity can be easily measured.
What is the first step of an infection?
What is the first step of an infection?
Adhesion
Provide an example of a reporter assay.
Provide an example of a reporter assay.
Luciferase
What assays allows us to measure adhesion and internalization in bacteriology?
Adhesion
Internalization
What assays allows us to measure adhesion and internalization in bacteriology?
Adhesion
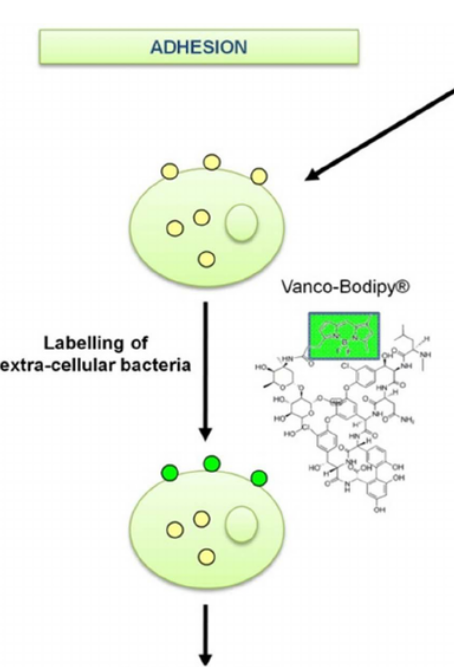
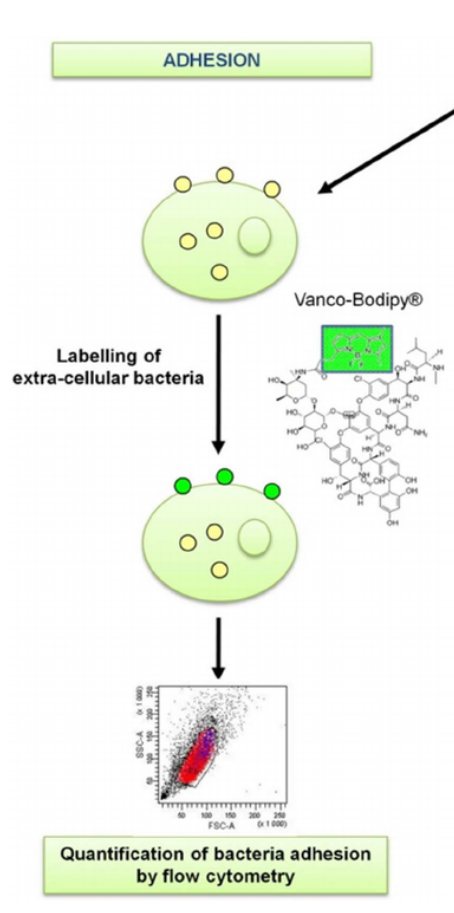
Vancomycin
Antibiotic that binds to peptidoglycan but doesn’t traverse into cells allowing the labeling of extracellular membrane bound bacteria.
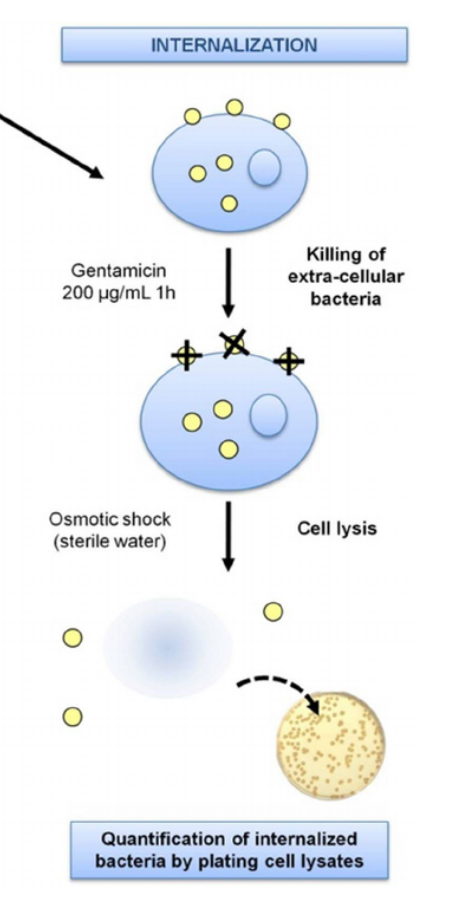
Internalization
Gentamicin
Kills bacteria outside cells but doesn’t traverse the membrane. After a wash, cells can be lysed and content plated to count the CFU of intracellular bacteria.
True or false
Vancomicin can be used in a Vanco-Bodipy assay to measure the number of extracellular bacteria by plating cell lysates.
True or false
Vancomicin can be used in a Vanco-Bodipy assay to measure the number of extracellular bacteria by plating cell lysates.
Typically flow cytometry is utilized to quantify the number of bacterial adhesion following a cell wash.
True or false
Internalization can be measured using a gentamicn assay to measure the number of CFU in cell lysates following wash.
True or false
Internalization can be measured using a gentamicn assay to measure the number of CFU in cell lysates following wash.
MOI stands for ________ of _______.
MOI stands for multiplicity of infection.
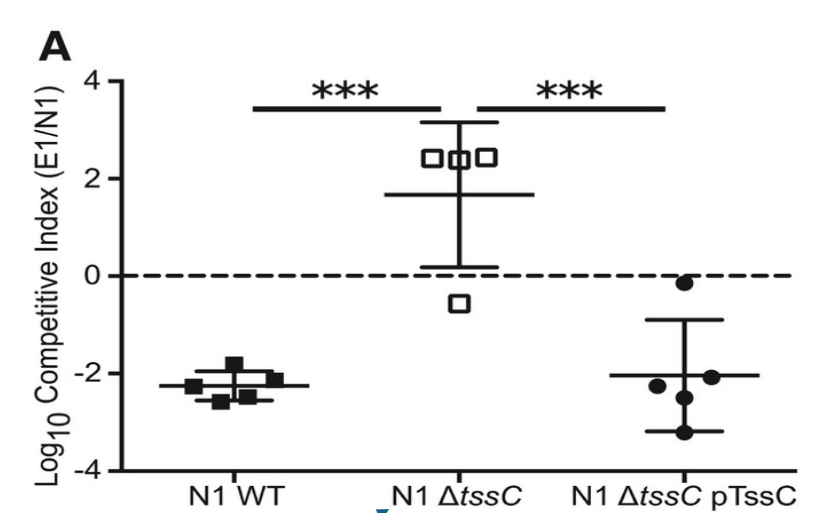
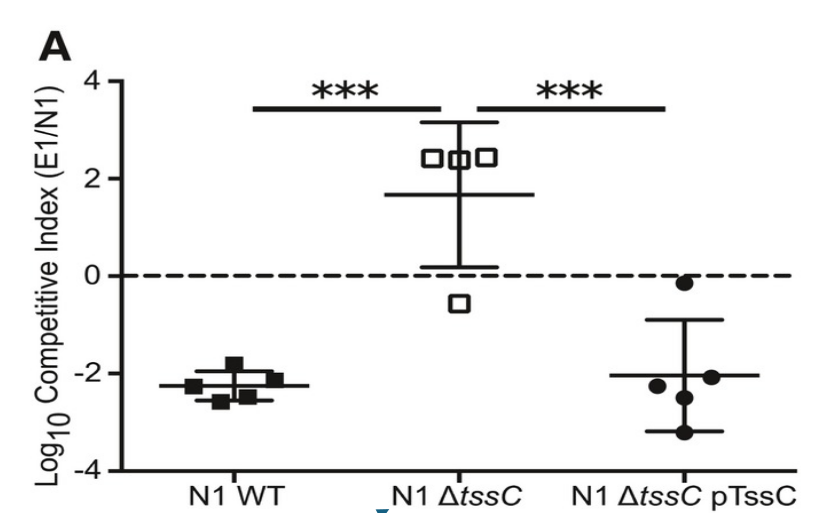
This image is an example of a _______ _______ competition/rescue assay.
This image is an example of a knockout knockin competition/rescue assay.
It is used to measure the competitive index assay and mutants of virulence factors.