2.1.1 Cell strucutre
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
49 Terms
What are the different elements of a eukaryotic cell (12)
Cell wall
Cell membrane
Nucleus
Mitochondria
Chloroplast
Ribosomes
Rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER)
Smooth endoplasmic reticulum (SER)
Golgi apparatus (Golgi complex)
Vesicles
Vacuole
Lysosome
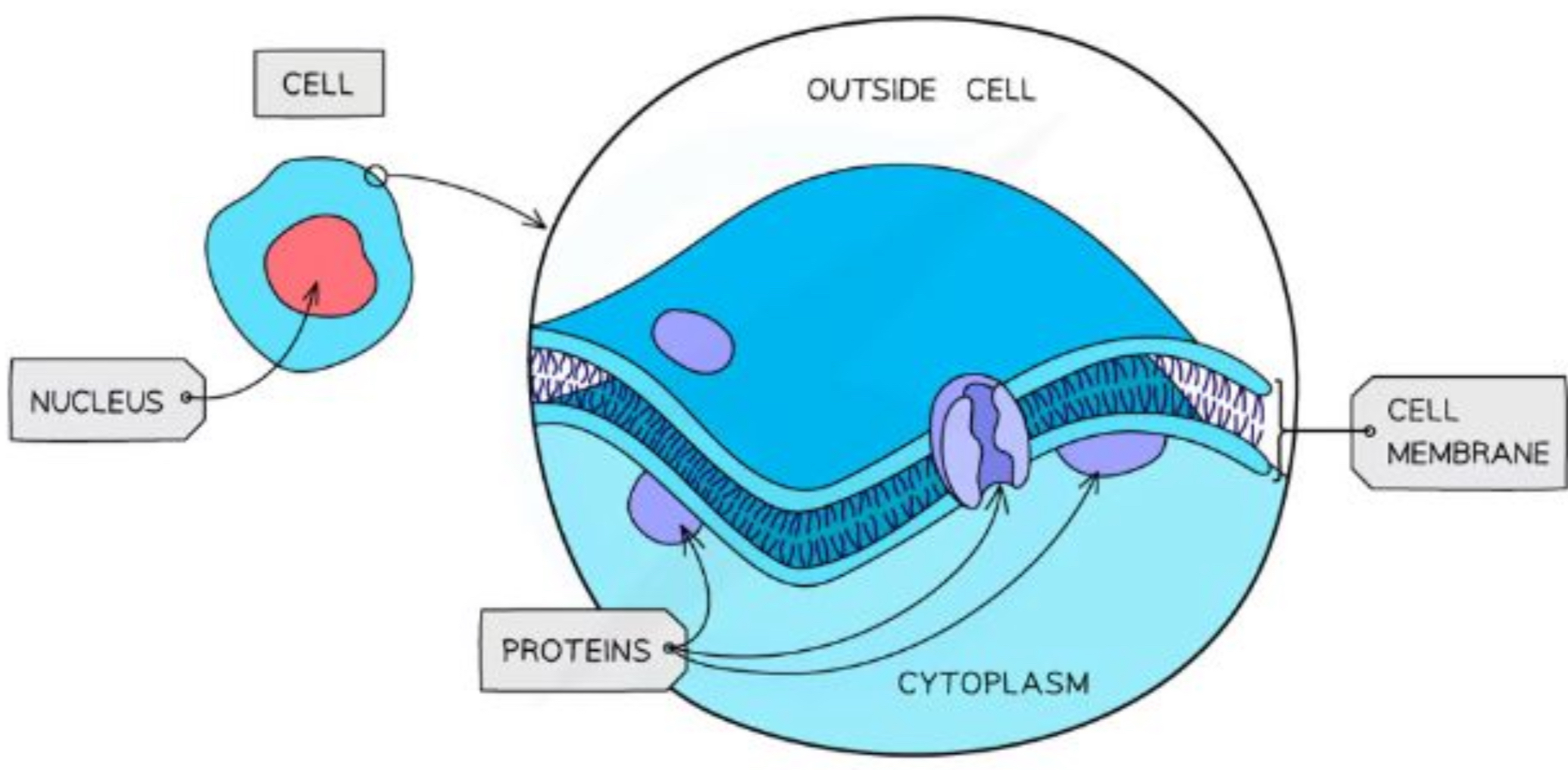
What is the structure and purpose of the cell membrane
Controls the exchange of materials between the internal cell environment and the external cell environment
Partially permeable
Fluid - constantly in motion
Due to the 2 layers of fat constantly attracting and repelling each other
Primarily made up of phospholipids
What is the structure and purpose of the cell wall
Provides structural support to the cell
Made up of polysaccharides (type of carbohydrate)
Cellulose in plants
Peptidoglycan in most bacterial cells
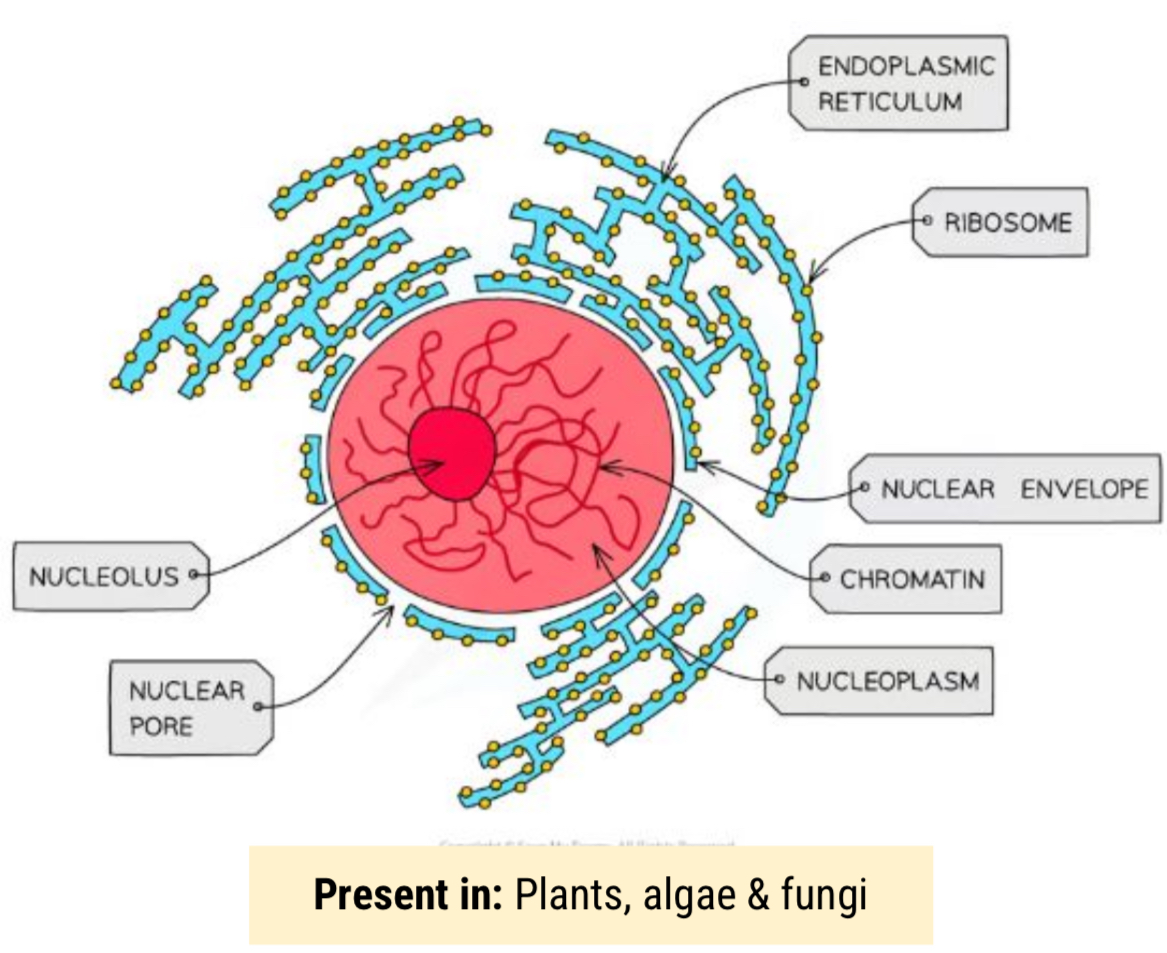
What is the structure and purpose of the nucleus
Contains chromatin (linear DNA bound to histone proteins)
Separated from the cytoplasm by a double membrane which is full of pores
allows MRNA & ribosomes to leave the nucleus and enzymes
Contains Nucleolus - site of ribosome production, some cells have multiple nucleoli
What are histone proteins
Condenses DNA into chromosomes
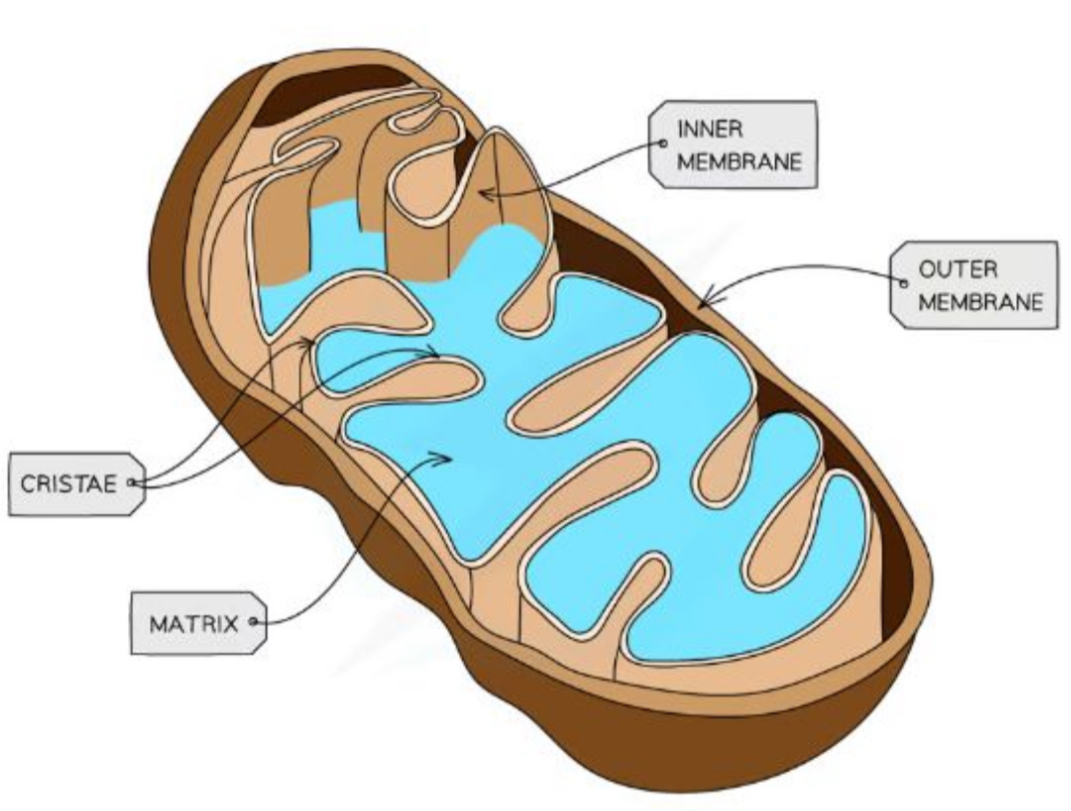
What is the structure and purpose of mitochondria
Site of aerobic respiration
Surrounded by a double membrane
Inner membrane folds in on itself to form a cristae - this increases it surface area
The cristae forms the matrix, where many enzymes that are needed for respiration can be found
Smaller, circular mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) and ribosomes are also found here
They need their own to supply themselves to deal with their ‘high work load’
Can vary in shape and size
What is the structure and purpose of the chloroplast
Site of photosynthesis
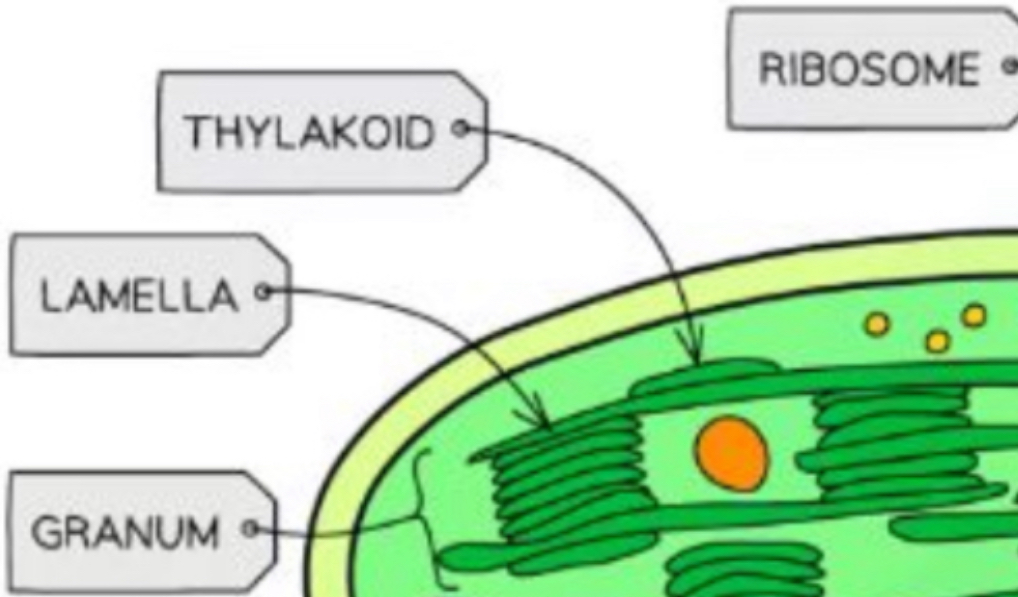
Light dependent phase: Takes place in thylakoids - which stack to form granum
The light independent phase (Calvin cycle): Takes place in the stomata
Surrounded by a double membrane
Also contain small, circular DNA and ribosomes
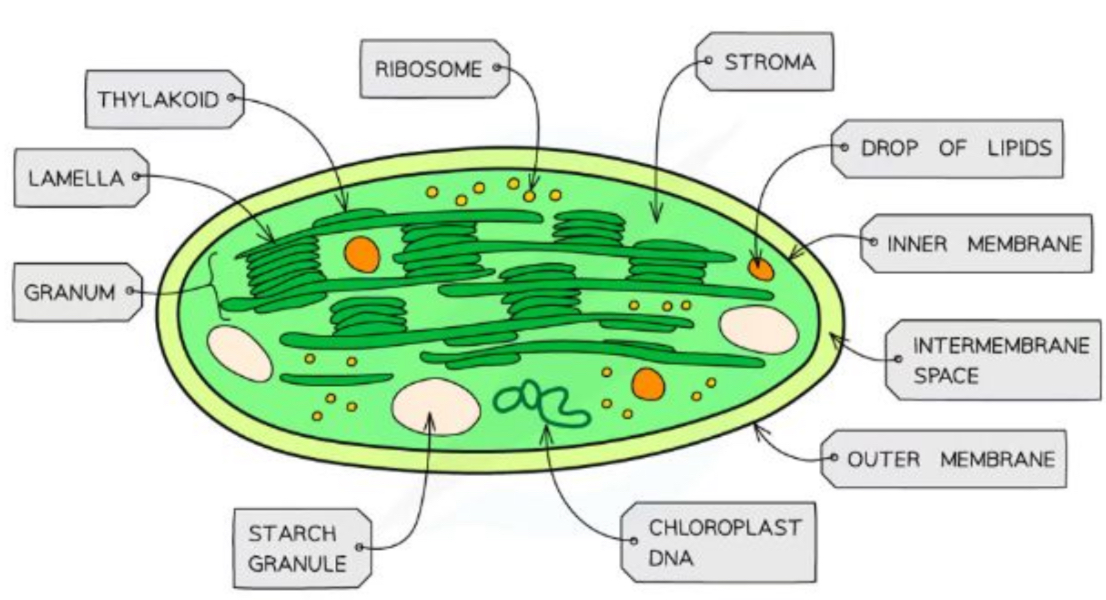
How are lamella built
Thylakoids (containing chlorophyll) stack to form a granum (grana) - to increase its surface area
Grana stack to form a lamella (lamella)
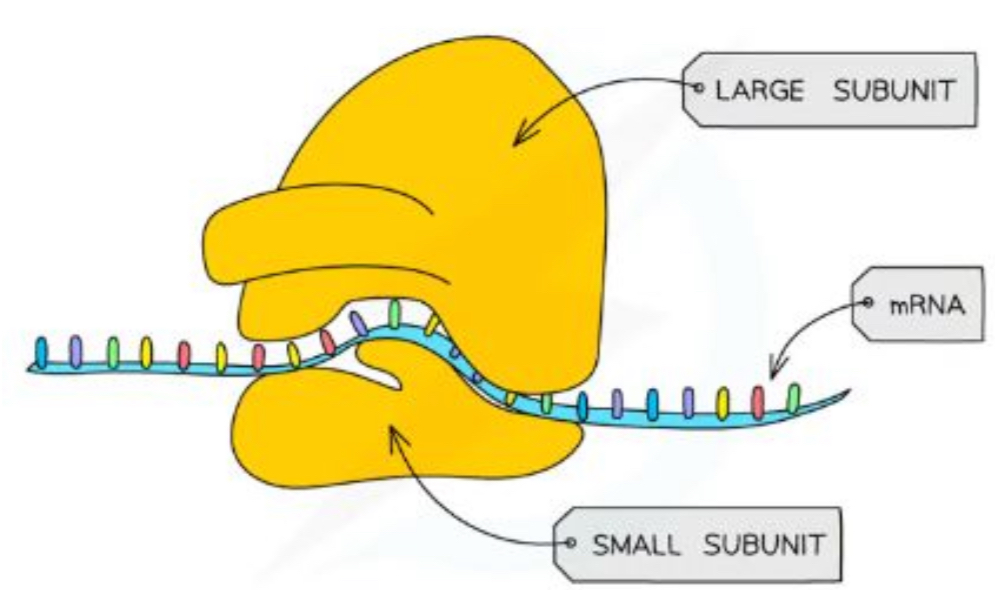
What is the structure and purpose of ribosomes
Found freely in the cytoplasm of all cells or as part of the rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER)
Site of translation - protein synthesis
Each ribosome is a complex of ribosomal RNA (rRNA) and proteins
Eukaryotes have larger ribosomes due to being larger + making larger proteins
Eukaryotic cells contain 80s ribosomes
Prokaryotes, mitochondria and chloroplasts contain 70s ribosomes
(‘S’ stands for a unit of measurement)
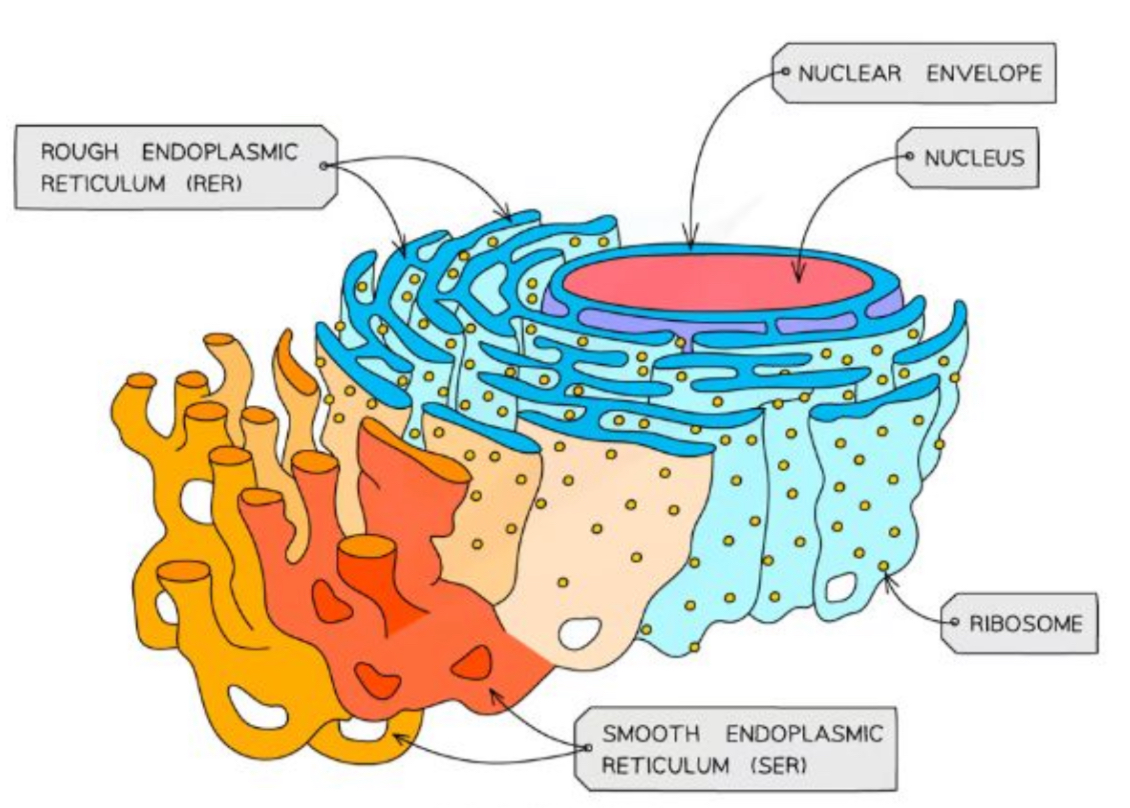
What is the structure and purpose of the Rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER)
Where protein is ‘edited’
Surface covered in ribosomes
Formed from continuous folds of membrane that is attracted to the nuclear envelope
Process proteins made by the ribosomes
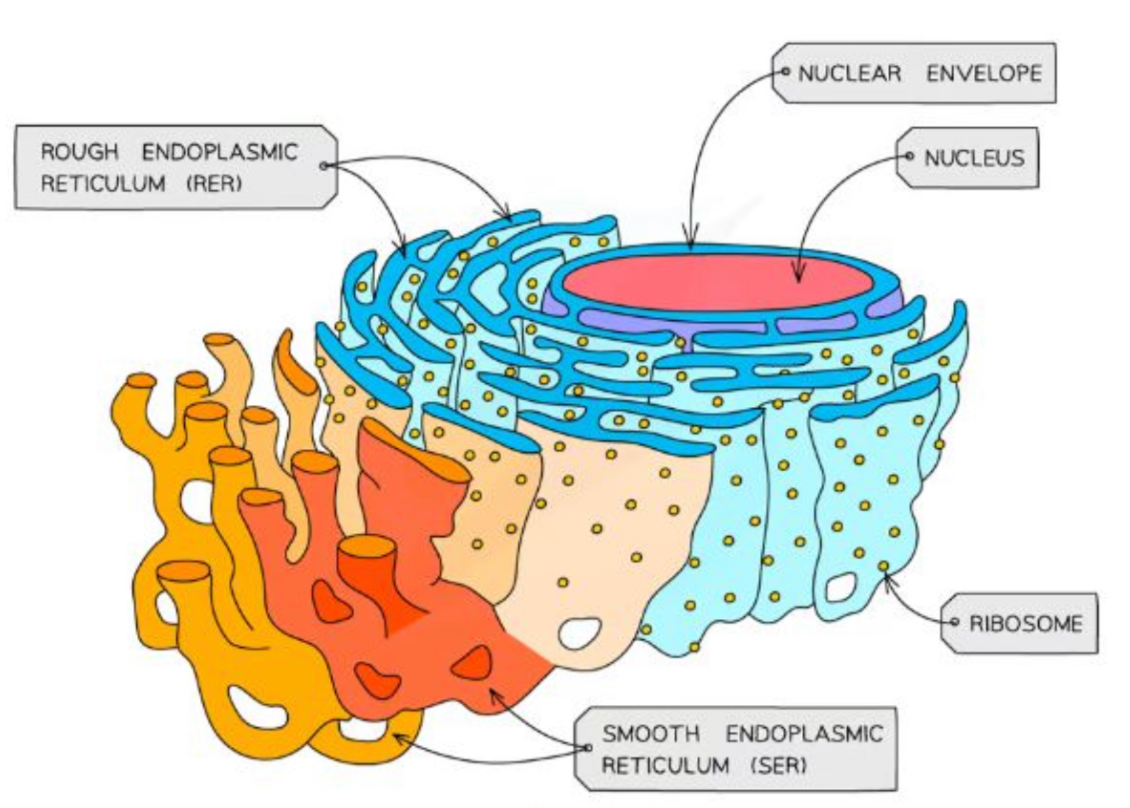
What is the structure and purpose of the Smooth endoplasmic reticulum (SER)
Does not have ribosomes on the surface
Involved in the production, processing and storage of lipids, carbohydrates and steroids
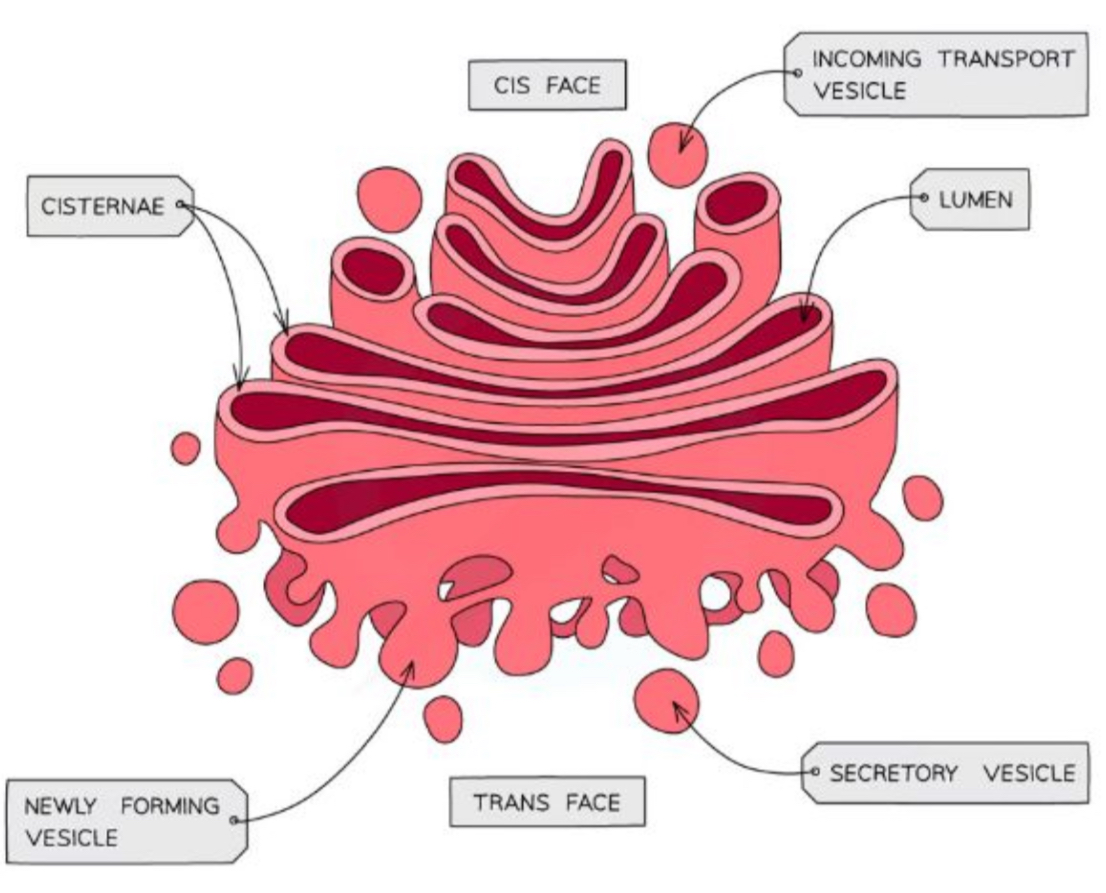
What is the structure and purpose of the Golgi apparatus (Golgi complex)
Flattened sacs of membranes
Responsible for modifying proteins and lipids
Pack them into Golgi vesicles
Vesicles transport proteins and lipids to their destination
Proteins that go through the Golgi apparatus are usually exported, put into lysosomes or delivered to membrane-bound organelles
Proteins enter through a vesicle on the cis face (side) and exists through a vesicle on the trans face
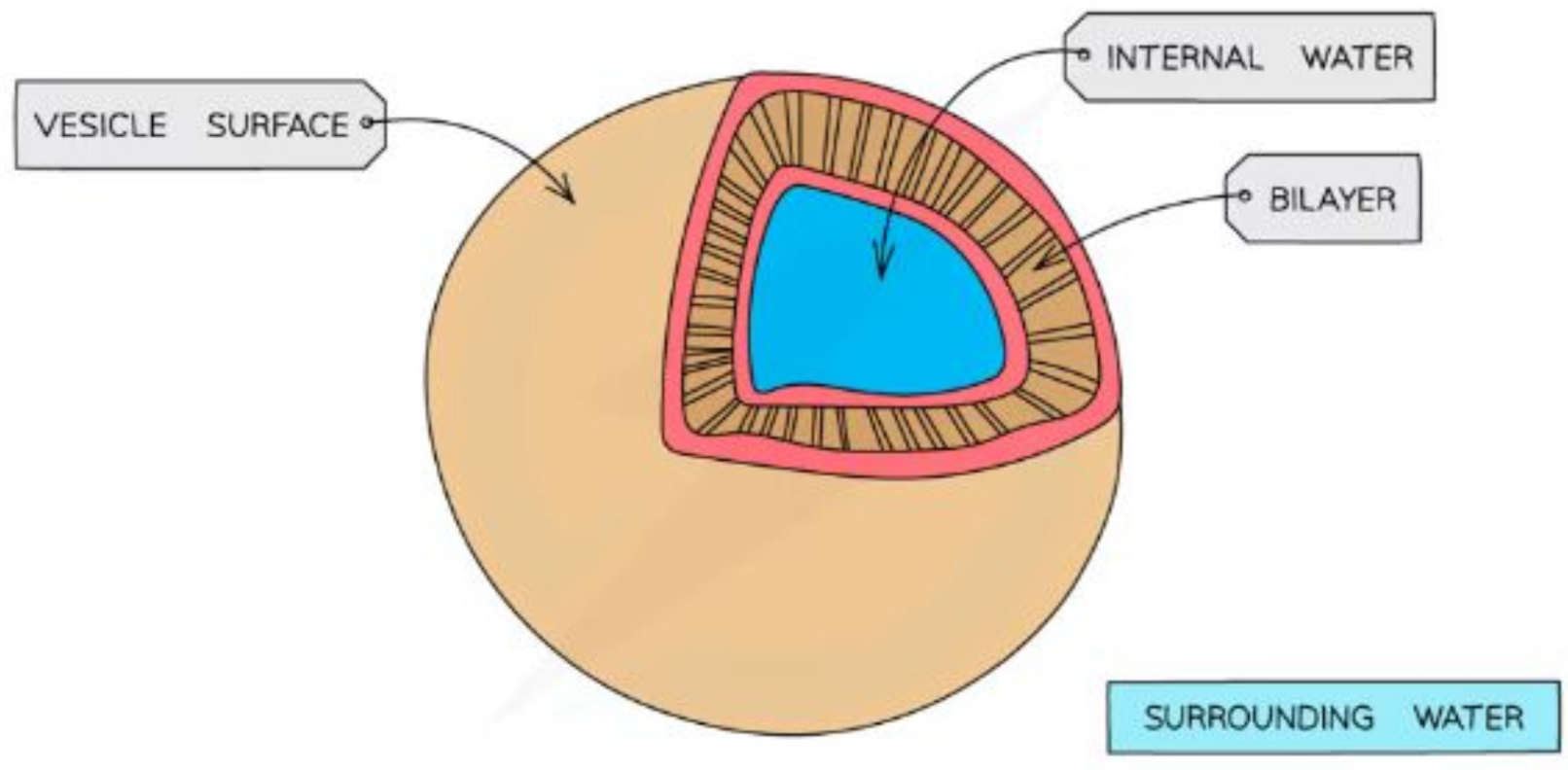
What is the purpose of vesicles
Membrane - bound sacs for transports & storage
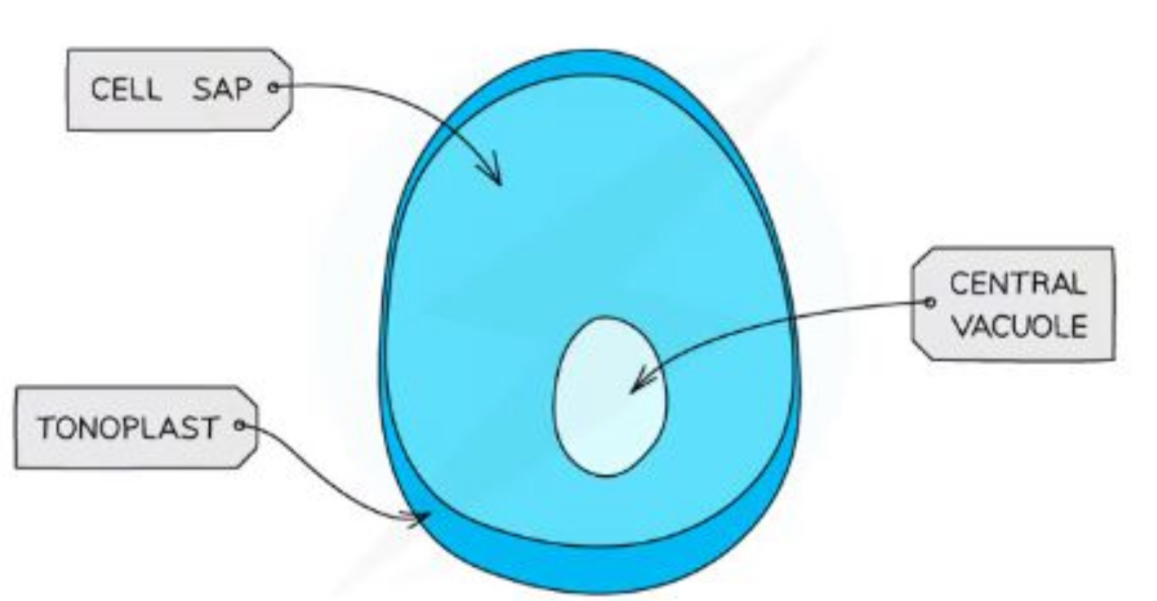
What is the structure and purpose of large permanent vacuoles
Sacs in plant cells surrounded by the tonoplast - a selectively permeable membrane
Helps maintain tugor pressure
Stores water, salts, minerals, pigments & proteins within a cell
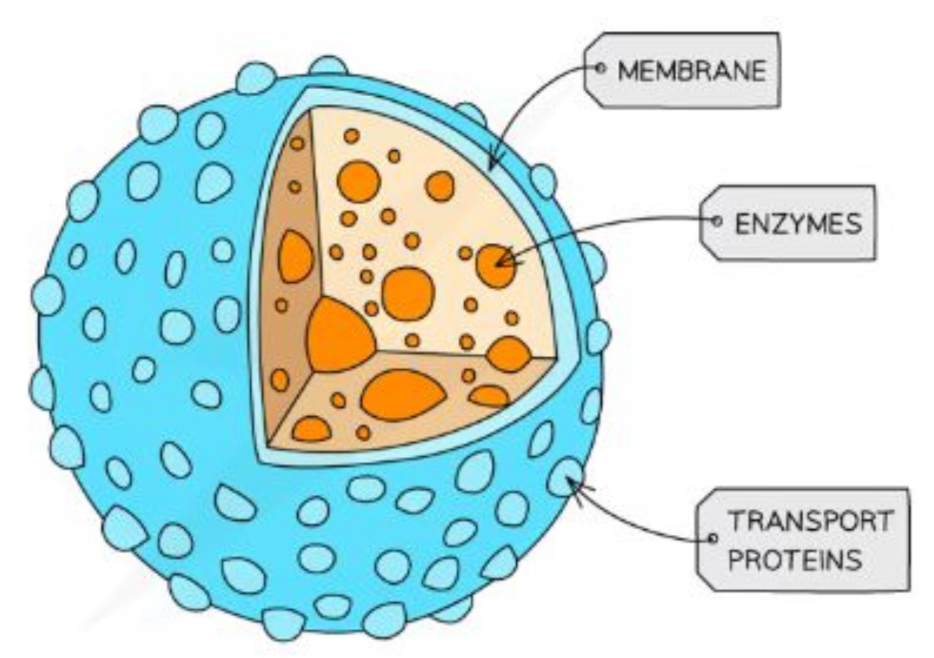
What is the structure and purpose of a lysosome
Specialist forms of vesicles which contain hydrolytic enzymes (enzymes that break down biological molecules)
The enzymes break down waste materials such as worn-out organelles
Cells of the immune system & cells involved in apoptosis (when the cell is instructed to kill itself) use lysosomes a lot
What is the purpose of a microvilli
Cell membrane projections that increase the surface area for absorption
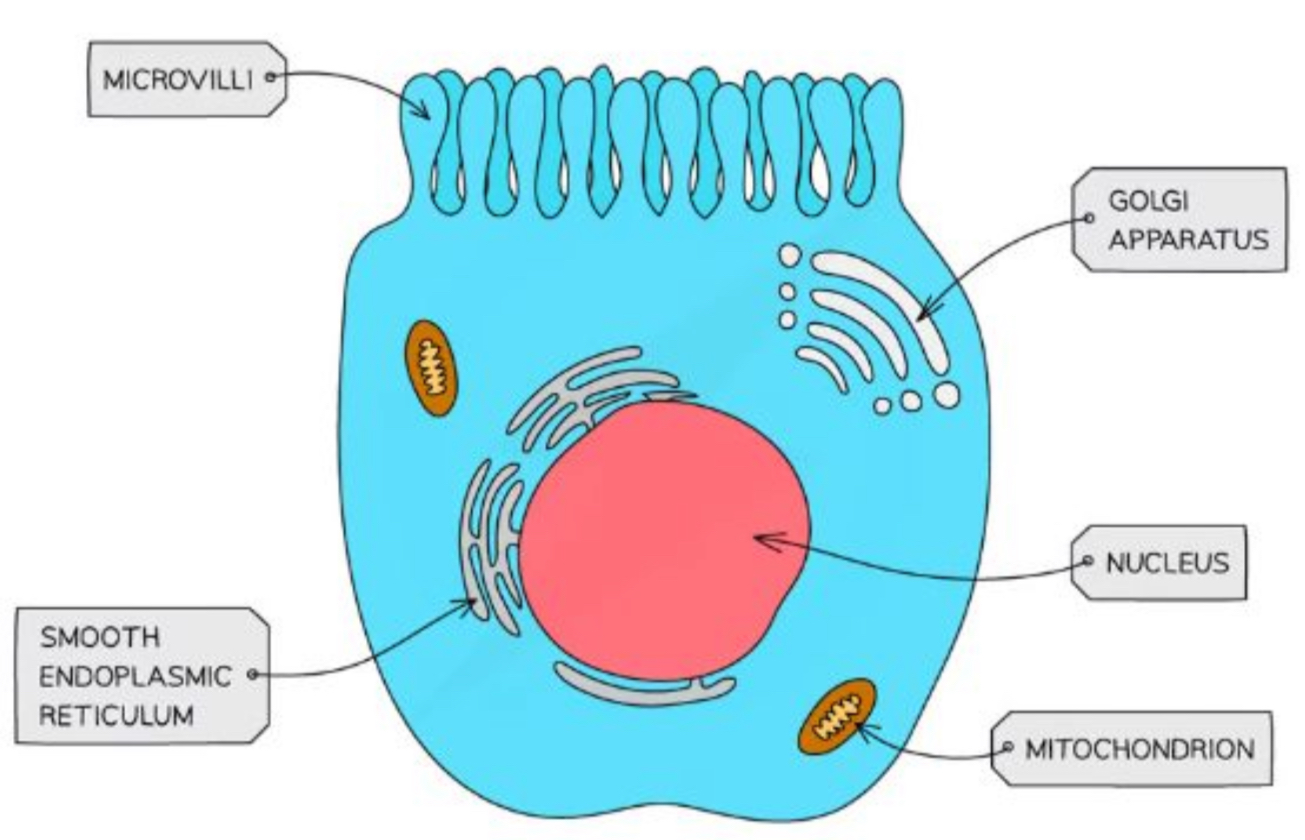
What is the structure and purpose of the cilia
Hair like projections made form micro tubules
Allows the movement of substances over the cell surface
What is the structure of flagella
Similar to cilia in structure but made of larger micro-tubules
What are the different elements of prokaryotic cells (10)
Flagellum - sometimes present
Capsule - sometimes present
In folding of cell surface membrane - sometimes present
Plasmid - sometimes present
Pili - sometimes present
Cell wall
Cell membrane
Cytoplasm
Circular DNA
Ribosomes
What are the structures unique to prokaryotic cells
Plasmids
Capsule
Flagellum
What is the structure and purpose of plasmids
Small loops of DNA that are separate from the main circular DNA molecule
Contains DNA that can be passed between prokaryotes
What is the structure and purpose of capsules
Helps protect bacteria from drying out and from attack from by cells from the hosts immune system
What is the structure and purpose of the flagellum
Long, hair like structure that rotates, enabling movement
Some have more then 1
What is the purpose of the infolding of the cell membrane
May allow for photosynthesis
May carry out nitrogen fixation
What is the purpose of the pili
For attachement to other cells or surfaces
Involved in sexual reproduction
Prokaryotes vs Eukaryotes
Prokaryotes are 100-1000 x smaller
Cytoplasm lacks membrane-bound organelles
Smaller ribosomes (70s)
No nucleus, no histone proteins - free floating DNA
Cell wall made up of peptidoglycan & murein
What is magnification
How many times bigger the image produced by the microscope is, compared to the real object under the microscope
What is resolution
The ability to distinguish between objects that are close together
What are the two main types of microscopes
Optical (or light)
Electron
Transmission electron microscopes (TEMs)
Scanning electron microscopes (SEMs)
How is total magnification calculated
Eyepiece lens magnification x objective lens magnification
Optical light microscopes fact file
Maximum resolution: ~ 0.2 micrometers
Maximum magnification: x1500
Structures you can visualise: eukaryotic cells, nuclei, (sometimes) mitochondria and chloroplast
Advantages:
Inexpensive
small and portable
simple slide preparation (doesn’t usually distort sample)
specimens can be living or dead
Produced a coloured image
Disadvantages:
Lower magnification then electron microscopes
Lower resolving power then electron microscopes (200nm)
How do transmission electron microscopes work
Use electromagnets to focus a beam of electrons which is then transmitted through the specimen
Denser parts of specimen absorb more electrons so appear darker
In black and white as they don’t absorb light
What are the advantages of transmission electron microscopes
High resolution images
Allows the internal structures within cells & organelles to be seen
What are the disadvantages of transmission electron microscopes
Only to be used with very thin specimens/thin sections
Can’t be used to observe live specimens
Specimens take time to prepare which increases the chance of artefacts being produced
Artefacts - something not part of the organism e.g dust, air particles
Do not produce a colourful image
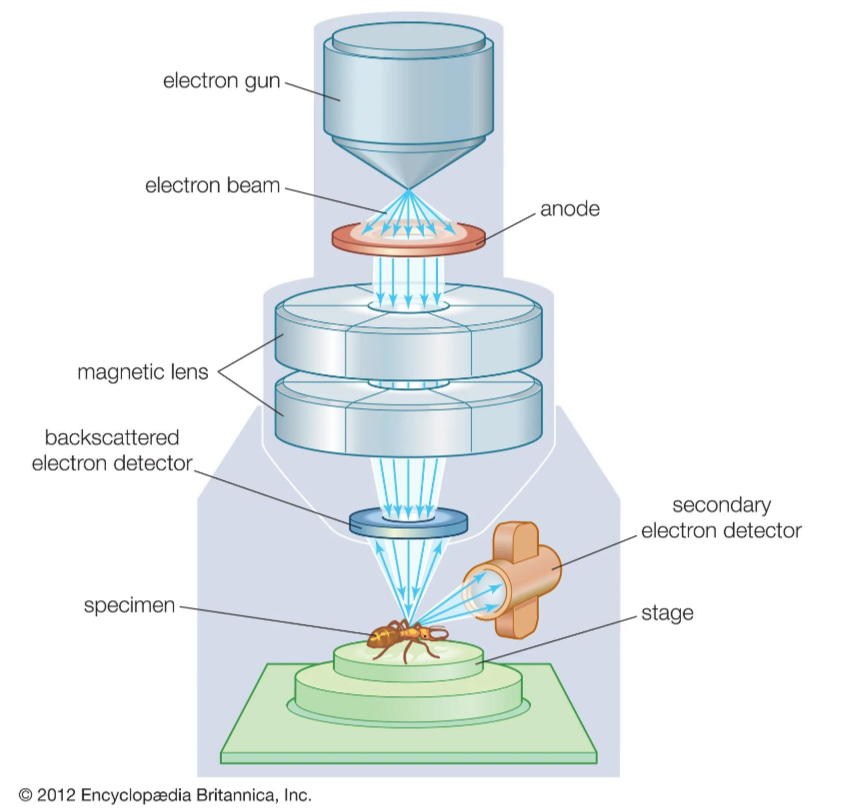
How do scanning emission microscopes work
They scan a beam of electrons across the specimen
Beam bounces off the surface of the specimen
Electrons are detected
Forms an image
Produce 3D images that show the surface of specimens
What are the advantages of scanning emission microscopes
Can be used on thick or 3D structures
Allows the external 3D structure to be observed
What are the disadvantages of scanning emission microscopes
Give a lower resolution images then TEMs
Can’t be used to observe live specimens
Do not produce a coloured image
Election microscopes fact file
Maximum resolution: 0.2 nm
Maximum magnification: ~ x 1,500,00
Structures you can visualise: small organelles - ribosomes, endoplasmic reticulum, lysosomes
What are the light microscope sample preparation methods
Dry mount
Wet mount
Squash slides
Smear slides
How does a dry mount work
Solid specimens
Viewed whole or sectioned
Specimen placed in the centre of the slide
Coverslip placed on top
How does a wet mount work
Specimens are suspended in a liquid (oil or water) and a cover slip is placed on top from an angle
Can be used for aquatic samples or other living organisms
How do squash slides work
Used for soft samples e.g. root tips - to look at cell division
A wet mount is prepared
The cover slip is gently pressed down upon
How do smear slides work
Sample is smeared by the edge of a slide to create a thin even coating/ layer
The coverslip is then placed on top
Used with blood
How is staining used with light microscopes
To prepare a sample for staining:
Placed on slide
Allowed to air dry
Heat fixed by passing through a flame
Specimen will adhere to slide and will then take up stains
Why is staining used with light microscopes
Stains are used to increase contrast as different components within a cell take up stains to different degrees
Increase in contrast allows components to become visible so they can be identified
How are samples prepared in electron microscopes
Samples must be prepared in a specific way due to the vacuums inside the microscope
Specimens must be fixated using chemicals or freezing, staining with heavy metals and dehydration with solvents
What is differential staining
Helps distinguish between different organisms or between organelles in a tissue sample
What is Gram staining
Uses crystal violet and iodine to help divide bacteria into gram positive (charge) and gram negative groups (charge)
What is acid fast staining
Differential staining used to identify acid fast organisms (micro organisms with highly impermeable cell walls)