Anatomy and Physiology Introduction
1/59
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
60 Terms
Anatomy
study of the structure of an organism and relationship to its parts
Anatomy
Anatomists learn about the body by dissection
Cellular
Smallest “living” units of structure and function
Organ
(group of several different kinds of tissues arranged in a way that allows them to act as a unit to perform a special function)
Tissue
organizations of many cells that act together to perform common function
body system
organization of varying numbers and kinds of organs that can work together to perform complex functions for the body
11 organ systems
how many organ systems are there
a bag of fluid separated from the external environment
the human body is like
homeostasis
A dynamic, and relatively stable state in the internal environment
Digestive System
Takes in and digests food
Provides nutrients molecules that replace used nutrients
The Respiratory System
Adds oxygen to the blood
Removes carbon dioxide
The liver and pancreas
Stores excess glucose as glycogen
later , glycogen is broken down to replace the glucose used. The hormone insulin regulates glycogen storage
The Kidneys
Under hormonal control, they excrete wastes and salts that can affect the pH of the blood
Feedback loop:
body’s general control system
Negative Feedback
opposes change in controlled condition (Example: controlling room temperature)
Positive feedback
amplifies occurring change (example: childbirth)
positive feedback
Output enhances or amplifies a change so that the controlled variable continues to move in the direction of the initial change
positive feedback
less common between the two (negative/positive) feedback
Anatomical Positions
The way the body moves, its posture, or the relationship of on area to another
supine and prone
are terms used to describe the position of the body when it is not in anatomical position
BILATERAL
Body has __________ SYMMETRY
Proximal
toward or nearest the trunk, or nearest the point of origin
Distal
away from a farthest from the trunk, or farther from a structure’s point of origin
Superficial
nearer the body surface
Deep
farther away from the body surface
posterior
toward the back.
anterior
forward
Sagittal Plane :
lengthwise plane that divides the body into right and left sections
Midsagittal
sagittal plane that divides the body into two equal halves
Frontal (coronal) plane
lengthwise plane that divides a structure into anterior and posterior portions
Transverse plane:
horizontal plane that divides a structure into upper and lower parts
Oblique
other than at a right angle
Longitudinal
cut along the length of an organ
Transverse
cut at a right angle to the length of the organ
Oblique
cut at any but a right angle
longitudinal

transverse
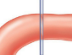
oblique
Cranial cavity
space inside the skull that contains the brain
Spinal cavity
the space inside the spinal column
Thoracic and abdominopelvic cavities
Ventral Cavities
hypochondriac
upper right and left regions
lumbar region
middle right and left region
iliac region
lower right and left region
epigastric region
middle up
umbilical region
middle middle
hypogastric region
lower middle
Axial Region:
head, neck, and torso or trunk
Appendicular Region:
upper and lower extremities
RIGHT UPPER QUADRANT:
: contains the liver, gallbladder, duodenum, pancreas,
right kidney and large intestine (ascending colon and transverse colon)
LEFT UPPER QUADRANT:
contains the liver, spleen, stomach, upper small intestine
(jejunum), pancreas, left kidney, and large intestine (descending and transverse
colon)
RIGHT LOWER QUADRANT
contains the appendix, most of the small intestine, large
intestine (cecum and ascending colon), right ovary (females only), right ureter,
urinary bladder, and uterus (females only)
LEFT LOWER QUADRANT:
contains the large intestine (descending and sigmoid colon), left ovary (females only), left ureter, urinary bladder, and uterus (females only)
left upper quadrant
jejunum/ small intestine
left lower quadrant
sigmoid colon
right lower quadrant
cecum
right upper quadrant
duodenum / small intestine
thoracic
thymus gland cavity
thoracic
lymph node cavity
abdominal cavity
small intestine cavity