BIOL4417 Epigenetic Regulation and Cancer Cells
1/66
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
67 Terms
co-factor proteins
Help transcription factors in binding
Where are most CpG islands found?
In gene promoters
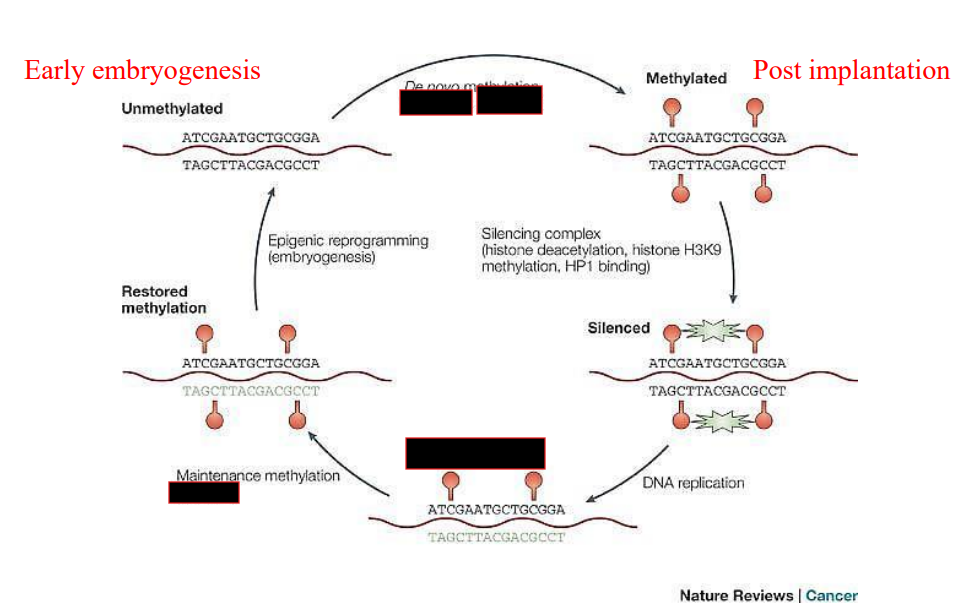
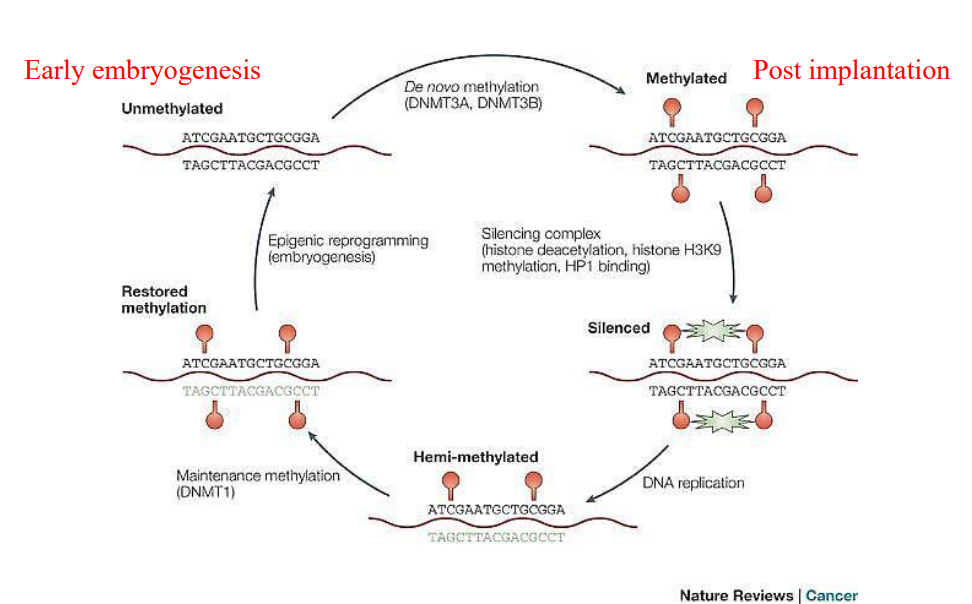
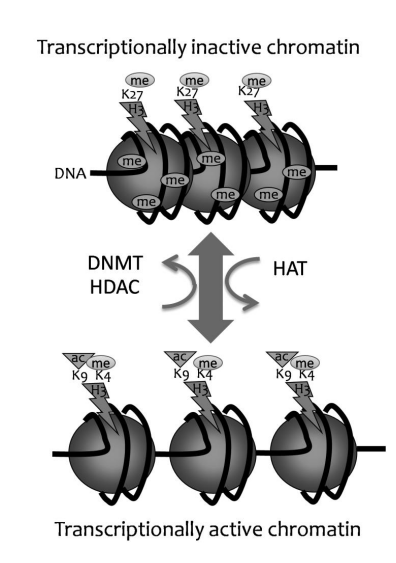
What methylates CpG islands?
Methyltransferase adds methyl groups to Cytosines, inactivating the promoter or the gene
When does de novo methylation take place?
Following implantation in the uterus
5 DNMTs
DNMT3a
DNMT3b
DNMT1
DNMT2
DNMT31
Which DNMTs are responsible for de-novo methylation
DNMT3a and DNMT3b
2 mechanisms through which DNA methylation silences genes
Methylation restricts access of transcription cofactors
Methylated nucleotides recruit MBD proteins, restricting access to other TFs or cofactors
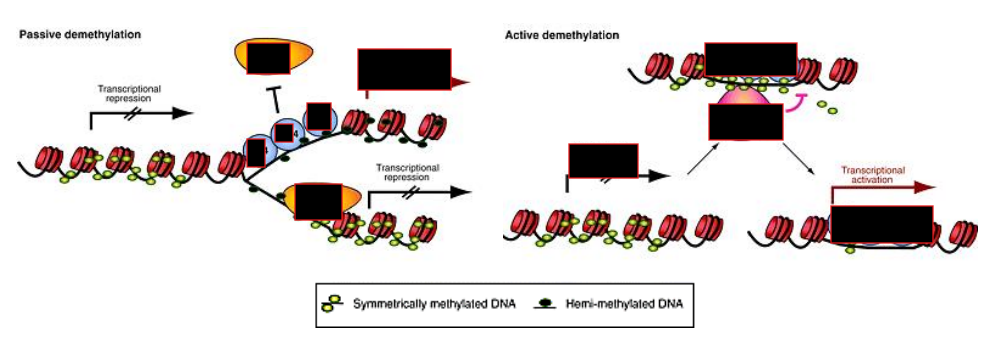
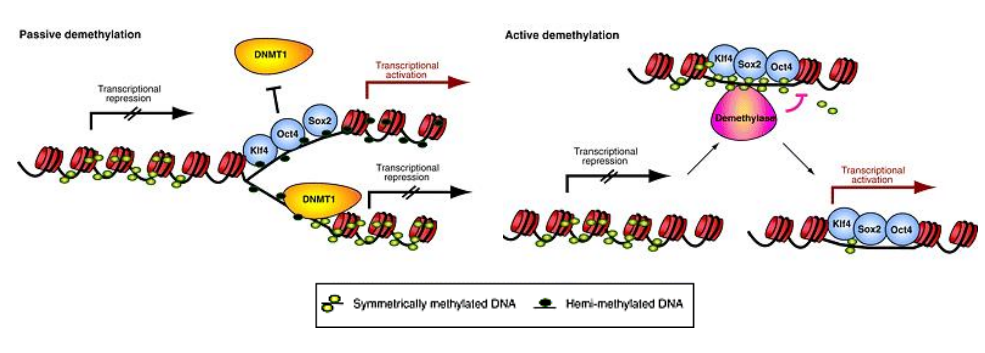
How can DNA methylation be lost?
Passively during DNA replication
Actively via enzymatic action
DNA bisulfite conversion
Treating DNA with bisulfite salt can cause methylated Cs to be converted into Uracil, allowing them to be detected and allow for tracking of methylation patterns
Which DNMT is responsible for maintenance methylation?
DNMT1, following DNA replication
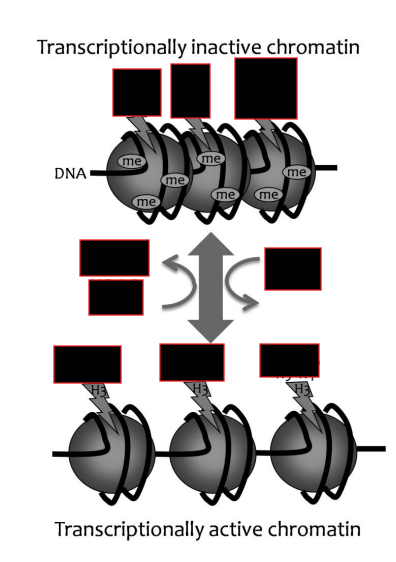
Formation of closed chromatin steps
CpG island is methylated
Methyl binding proteins bind
H3K9 gets deacetylated, then methylated
Recruits HP1, which closes the chromatin
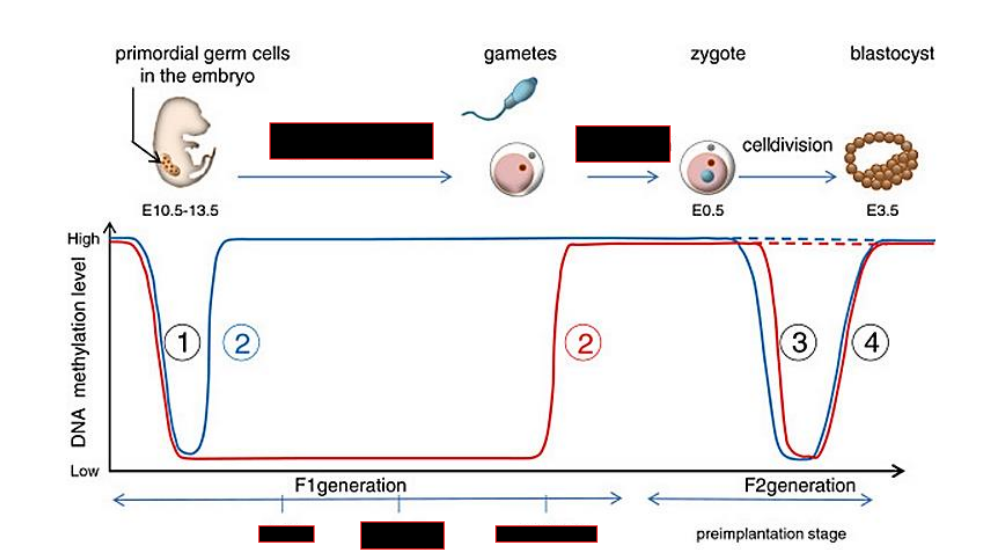
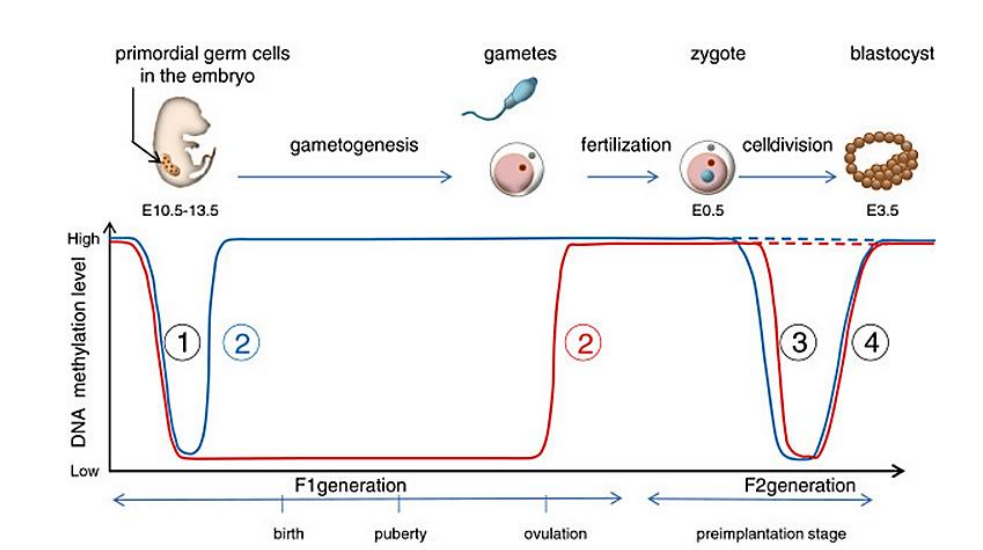
2 waves of demethylation of the genome
First occurs in primordial germ cells, which will differentiate into gametes and undergo de-novo methylation
Second occurs upon fertilization, followed by de-novo methylation upon implantation
What is special about imprinted genes?
They do not get demethylated for the 2nd time, allowing for parent specific epigenetic markers to be passed down
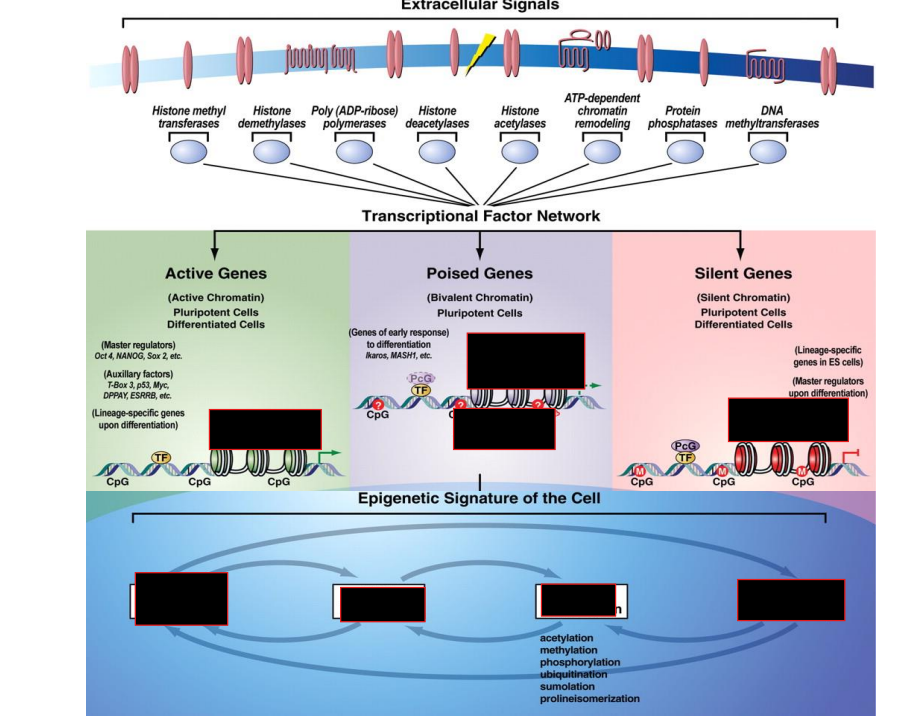
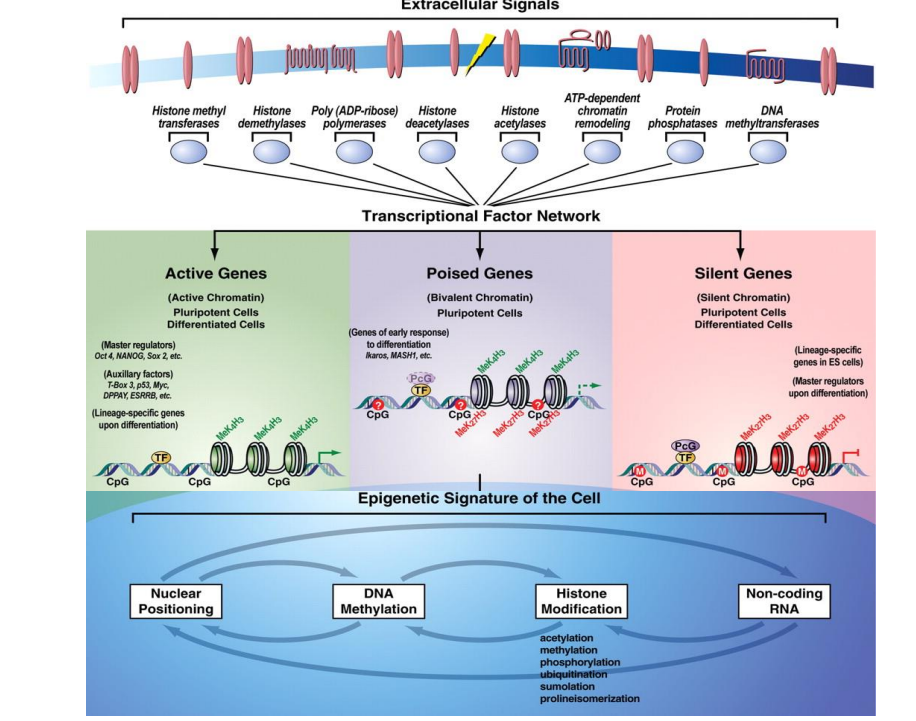
5 types of modifications which can be done to histones
Acetylation
Methylation
Ubiquitination
SUMOylating
Phosphorylation
Nucleosome structure
147bp wrapped via supethelical turns around histone octamer, itself consisting of H2A, H2B, H3, H4
Which terminal are histones modified at?
N-terminal tails
Histone structure of an actively transcribed promoter
H3K4me4
Histone structure of an active enhancer
H3K4me1
What histone modification is generally linked to activation
Acetylation
Mechanism through which acetylation allows for active transcription of genes/ making them open.
Histone tails are positively charged, and acetyls are negatively charged, thus neutralizing the charge, and ensuring positively charged histone does not interact with negatively charged DNA
How does acetyl get onto Lysine on histone tails
Histone acetyltransferases use acetyl-CoA as a donor
Epigenetic changes can either ensure hematopoietic stem cells differentiate into healthy or tumor lineages
Epigenetic changes can either ensure hematopoietic stem cells differentiate into healthy or tumor lineages
ES cells chromatin structure
It is bivalent.
Activating H3K4me3
Repressive H3K27me3
both of these tails exist, allowing for rapid demethylation of whichever tail is fated for demethylation
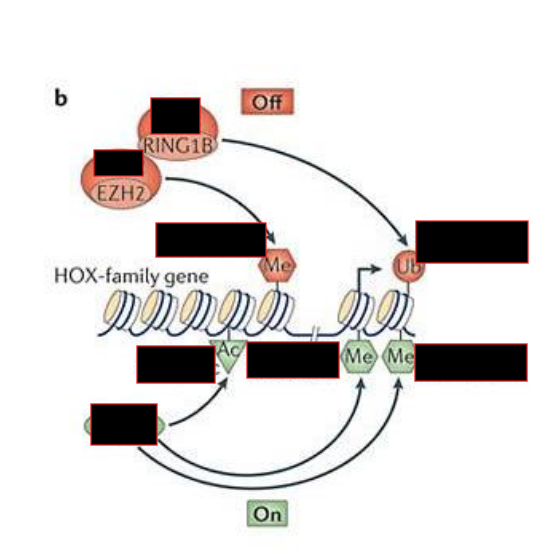
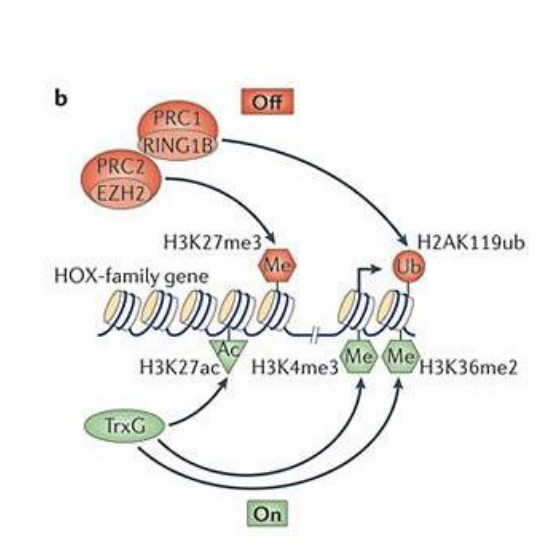
Which 2 enzymes are needed for poising of genes in ES cells? How do they work?
Trithorax trimethylated H3K4 recruits chromatic remodeling complexes and histone acetylases, preparing gene for activating
Polycomb complex negatively regulates activation of genes by trimethylating H3K27, promoting closed chromatin structure
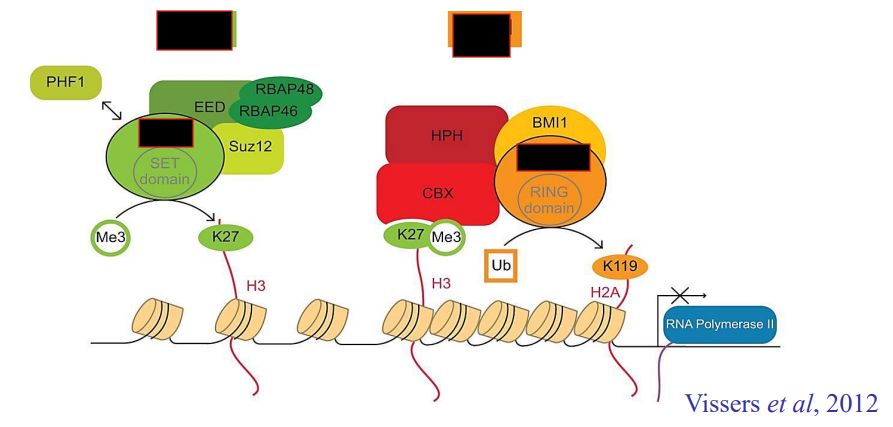
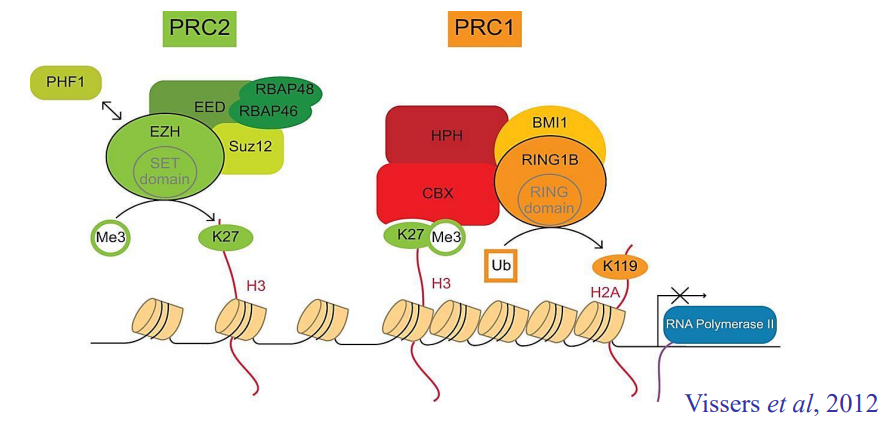
How does PRC repression work?
PRC2 recognizes and trimethylated H3K27
This mark is recognized by PRC1, which brings other histones closer, repressing chromatin
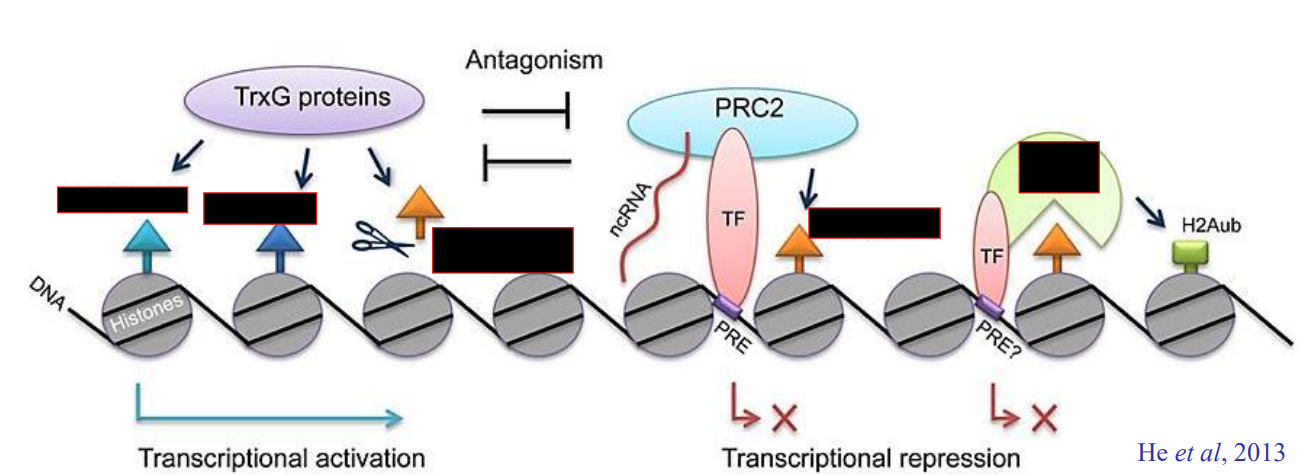
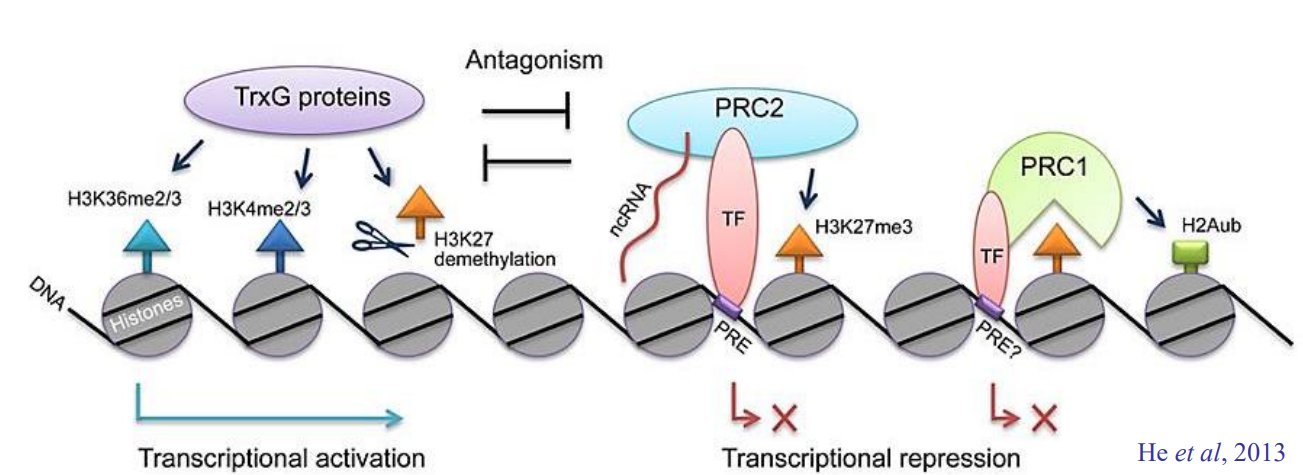
Trithorax G actions on chromatin
Demethylate H3K27me3
Methylate H3K4
Methylate H3K36
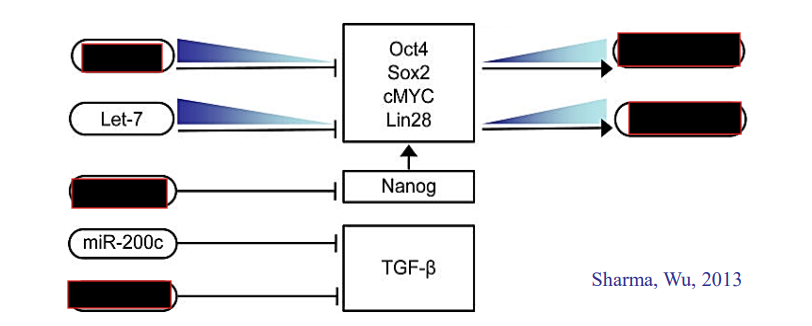
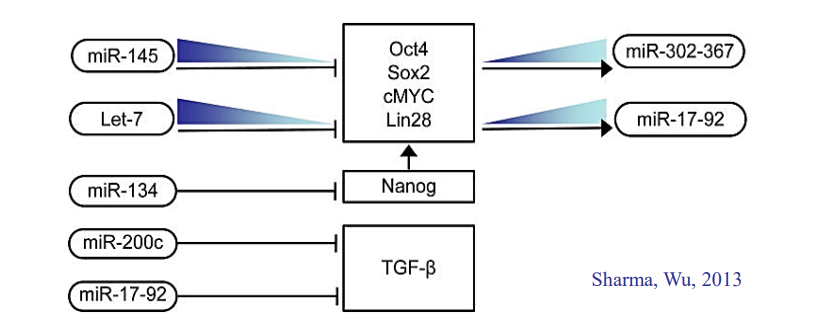
What does miR-145 do? Where is it expressed?
Blocks translation of Klf4, Oct3/4, Sox2
Expressed in differentiated cells
What does miR17/92 do?
Regulates TGF-beta signaling on cellular differentiation
How are iPS cells created
Induce specialized cells to produce Oct3/4, Sox2, Klf4, c-Myc
Order in which pluripotency genes are added to specialized cells, and why it matters.
c-Myc induces immortality and opens chromatin
Klf4 represses apoptosis and senescence
Oct3/4 changes cell fate from tumor cells to stem cells
Sox2 established pluripotency
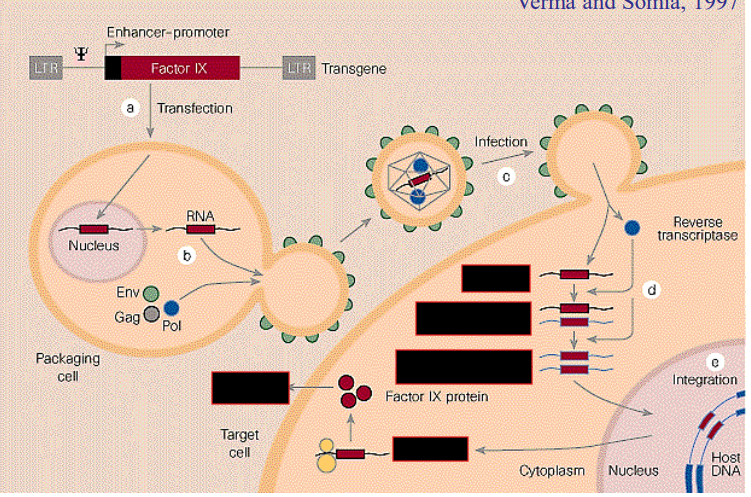
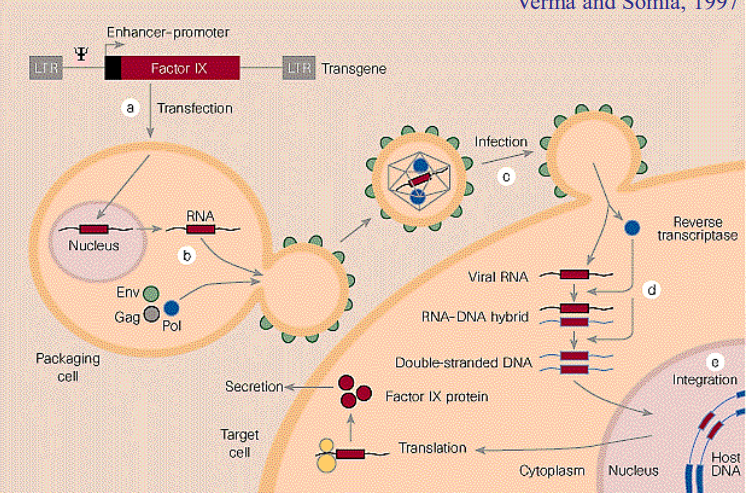
How does retroviral pluripotency gene transduction work
Use a retrovirus to insert the necessary genes into the cell, which will then be transcribed. As time passes, viral promoter is repressed, but by then the cell should be differentiated back into a stem cell
Problem with using retroviruses to insert new genes
They can cause cancers
Polycistronic lentiviral vectors
Contain all necessary genes in a single lentivirus, ensuring lesser chance of cancer development
2 iPS cell problems
Low efficiency
Variation in gene expression profiling between ESCs and iPSCs
How was pluripotent mouse derived
Form a chimera mouse, and that descendants of one original iPSCs will become primordial germ cells and then a new generation of mice
What is more efficient at being transformed into iPSCs than fibroblasts? Why?
Keratinocytes, because they express higher levels of Klf4 and c-Myc, as well as being in epithelial state
What needs to happen to somatic cells before they are introduced to pluripotency factors
They must undergo MET
Higher expression of E-cadherin and Epcam
Downregulation of Snail and N-cadherin
Which of the 4 factors is an oncogene
c-Myc
How to ensure that inserted pluripotency genes do not cause cancer
Do not use retroviruses or lentiviruses, you can use episomes
Makes sure that the genes are transient, and are not fully integrated
Small molecules which can trigger transcription of necessary factors
Epigenetic memory
Inability of iPSCs to completely demethylate their genome, causing dissimilarities between them and ESCs
3 cellular origins of cancer stem cells
Mutation in a stem cell
Mutation in a somatic cell, resulting in transformation into a cancer stem cell
Fusion of somatic and stem cell
Risk factors for formation of cancer cell
Mutagen
Environmental stress
Viral infection
Chronic inflammation
Cancer stem cell hypothesis
Suggests that there is a subset of cancer stem cells which are responsible for tumor growth. Just like in regular stem cells, they can undergo symmetric or asymmetric division
Implications of CSCs (2 of them)
Strategy for tumor killing would have to focus on eliminating all cancer stem cells, and majority of differentiated cells
This complicates the search for a definitive cure, as new therapies are needed, and CSCs seem to be more resistant to radiation treatment compared to other cancer cells
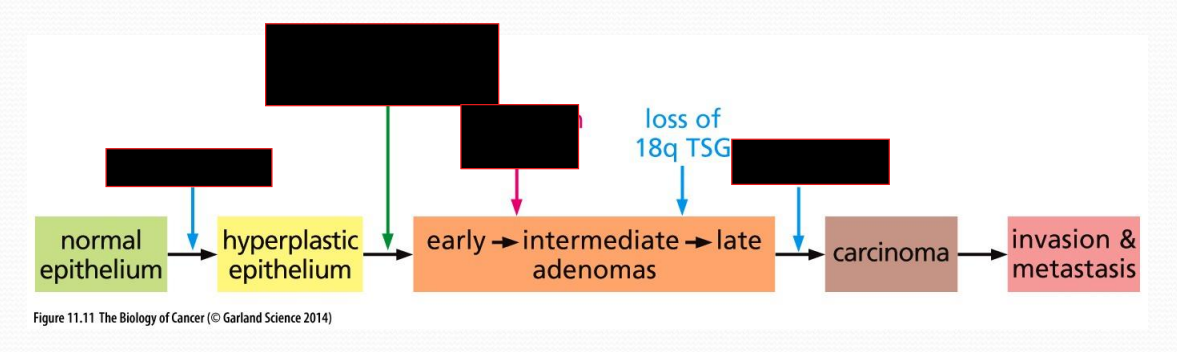
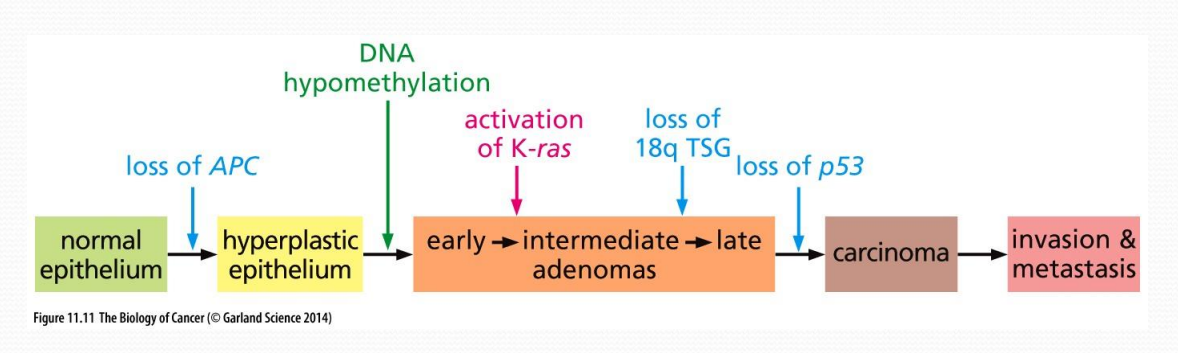
Progression of colon cancer, from healthy to carcinoma
Loss of APC leading to hyper plasticity
DNA hypomethylation, leading to loss of cancer suppressants, such as p53
Adenoma turns into carcinoma by loss of p53
Multi-hit model of cancer
Since cells have multiple safeguards against cancer development, a combination of LOF and GOF mutations are needed to cause cancer
3 layers or the colon crypt
Differentiated upper layer
Middle area with proliferating and differentiating cells
Bottom layer with stem cells which replenish the stem cells
How does colon cancer start? What gene is affected?
APC gene is turned off on both alleles, and thus the cells on top can no longer undergo apoptosis
How does APC gene work?
It codes for APC protein which is antagonistic to Wnt signaling pathway. It does so by binding Beta-catenin. It’s inactivation leads to beta-catenin entering nucleus
Leukemia stem cells
They represent a small subset of total leukemic population, less than 1%, but they produce all the leukemia cells. If you transfer them into mice, mice will get AML
Leukemia stem cell markers
Thy1-
CD34+
CD38-
3 ways to target cancer stem cells
Target CSC specific receptors
Target CSC molecules, like nanog
Take advantage of differential signaling required for CSC
Label retaining experiment
Pulse the cells with a marker, like BrdU
Fast proliferating cells will dilute the marker faster than slow proliferating cells
Clonogenic assay
Tests the ability of a cell to form colonies.
The colonies are grown on Agar, Matrigel, HEMA-fibroblasts, methylcellulose
Side population assay
Identify stem cells using flow cytometry
Hoechst DNA dye is passively absorbed by all cells
Stem cells and progenitor cells have a pump which allows them to remove the dye, done via ATP-binding cassette (ABC)
These cells low i Hoechst dye are called side-population, and are the cancer causing cells
What drugs inhibit ABC protein pump
Verapamil