Phase 1
1/130
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
131 Terms
function of spinothalamic tract
sharp pain, temperature, crude touch
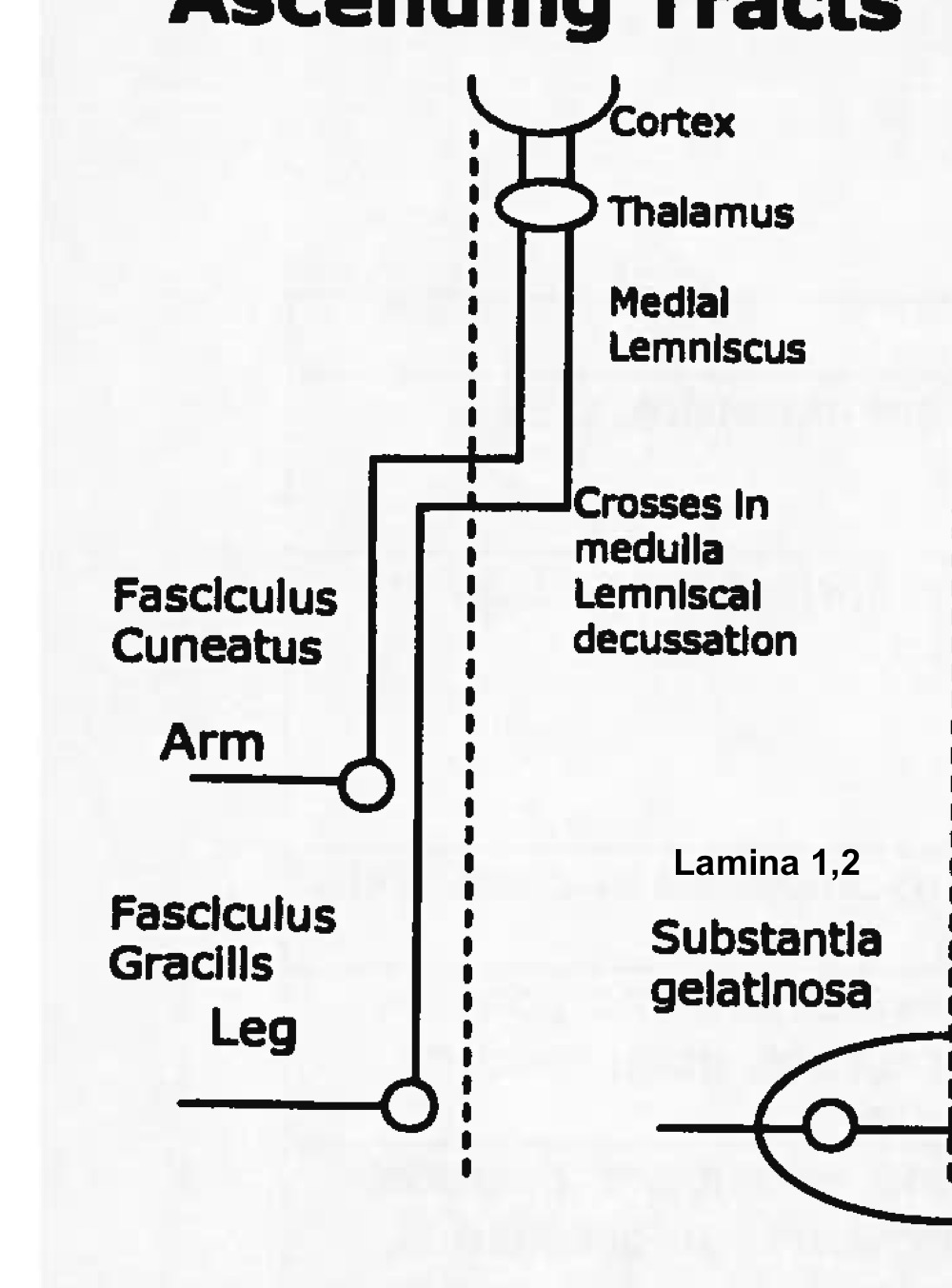
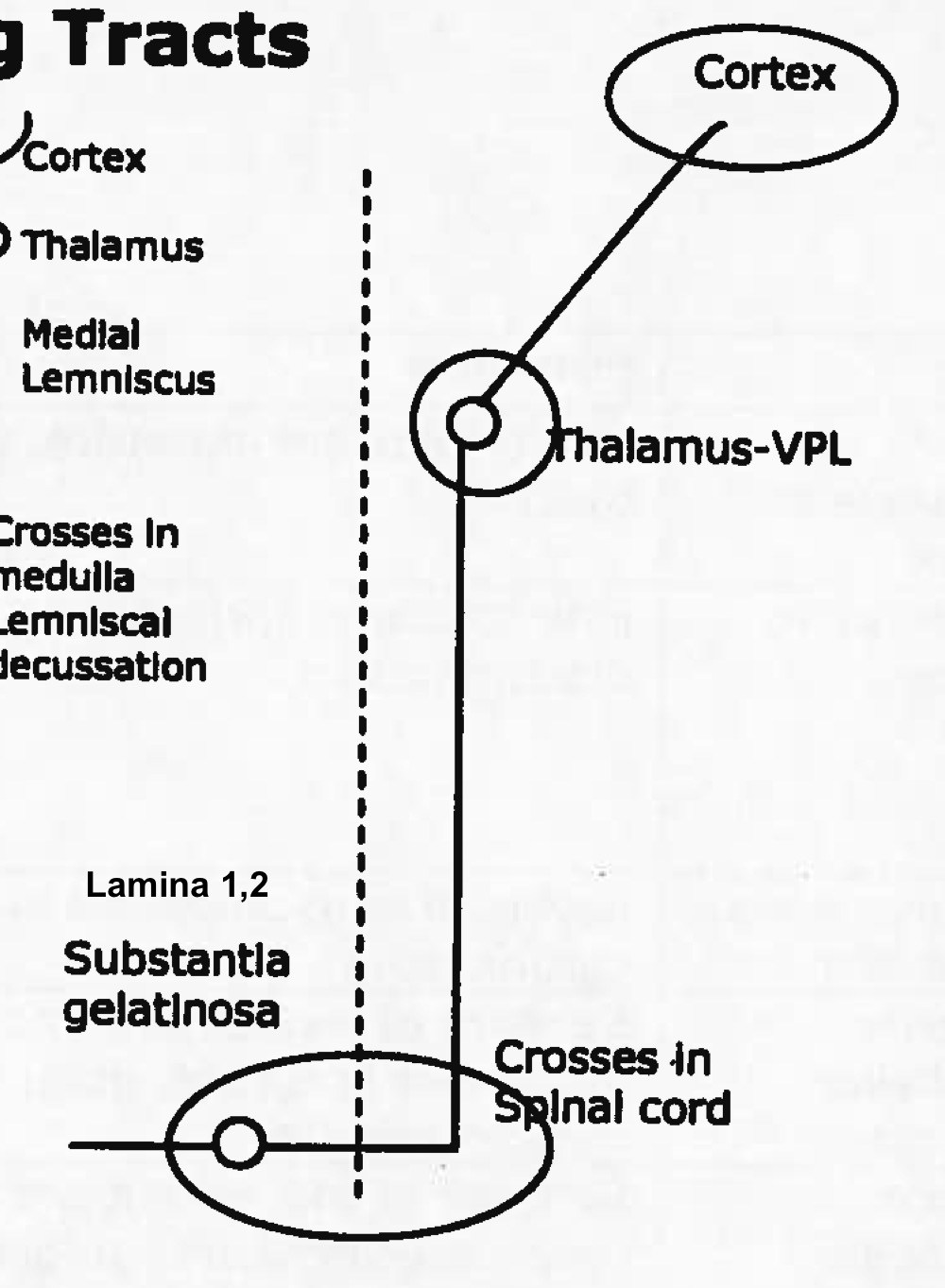
function of dorsal columns tract
fine touch, proprioception, 2 point discrimination
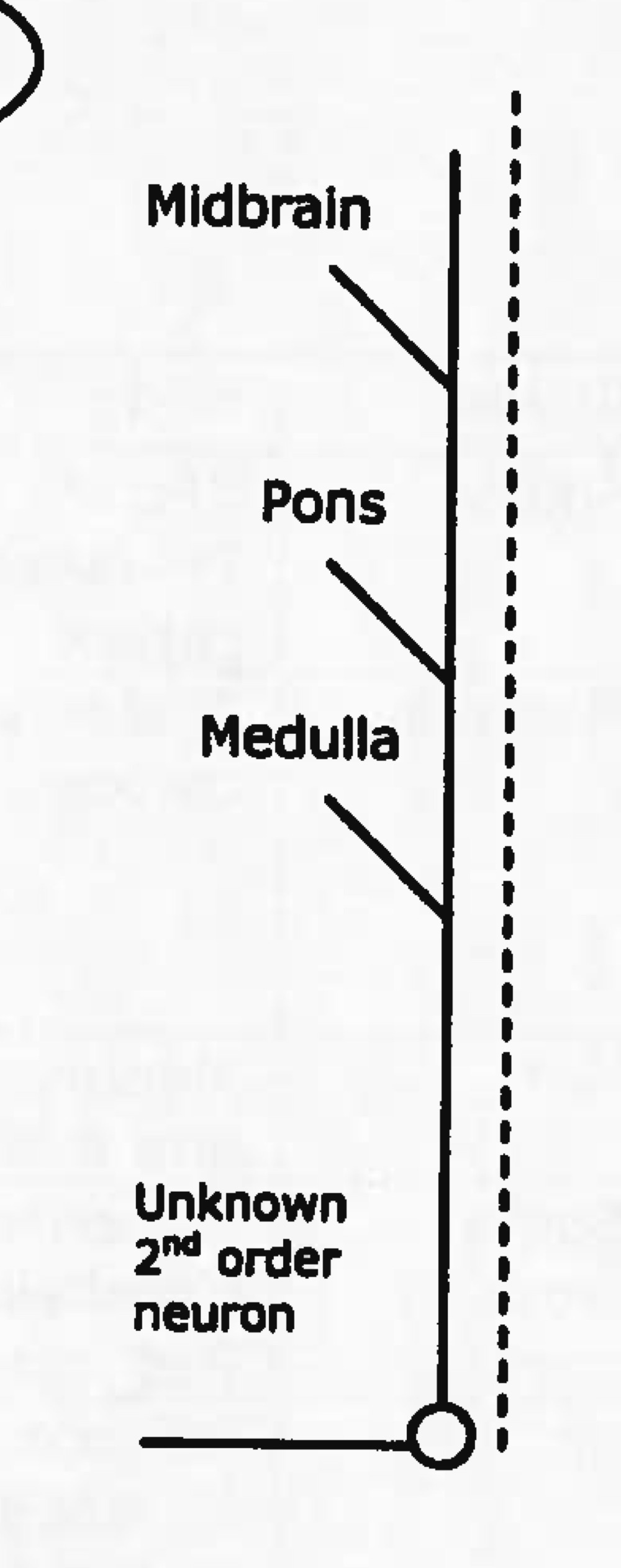
function of spinoreticular tract
levels of consciousness of deep and chronic pain
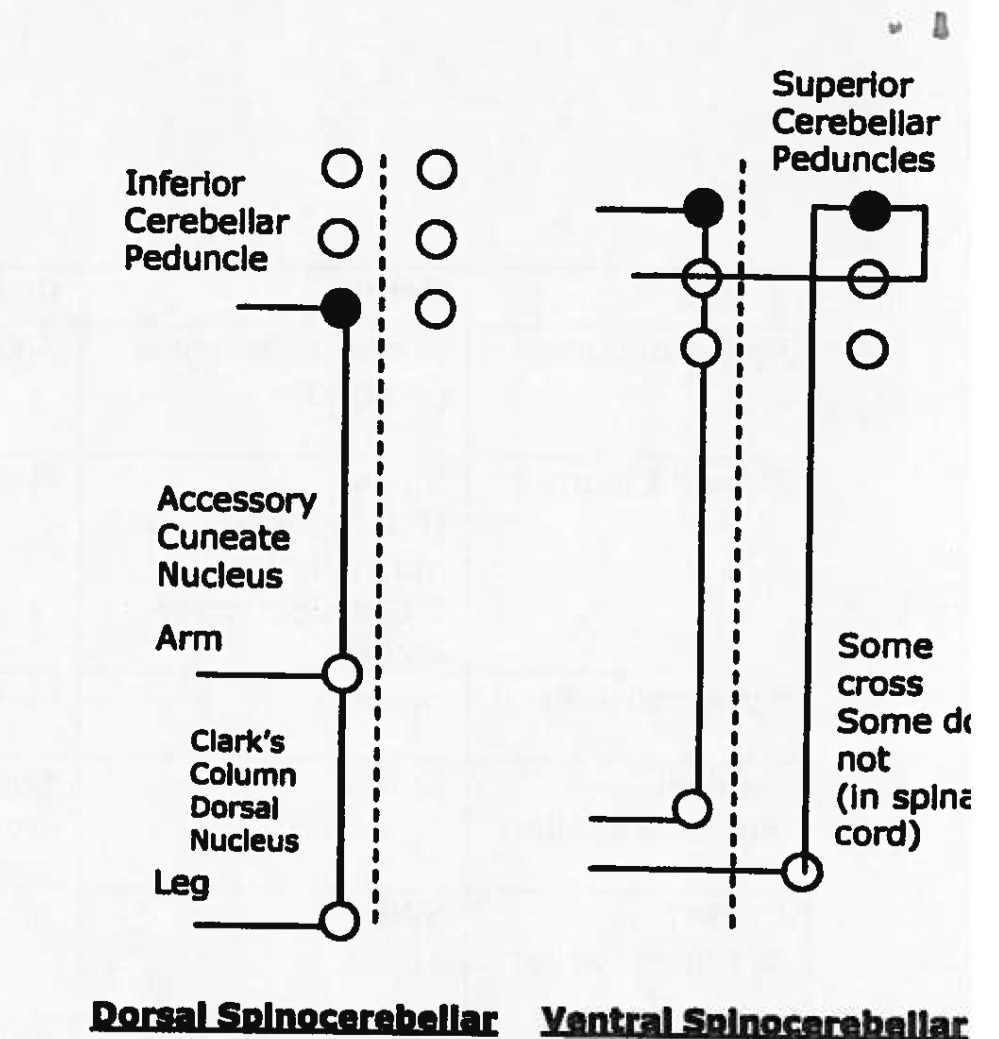
function of ventral and dorsal spinocerebellar tract
sensory of movement and position, touch, and pressure, golgi tendons, muscle spindles
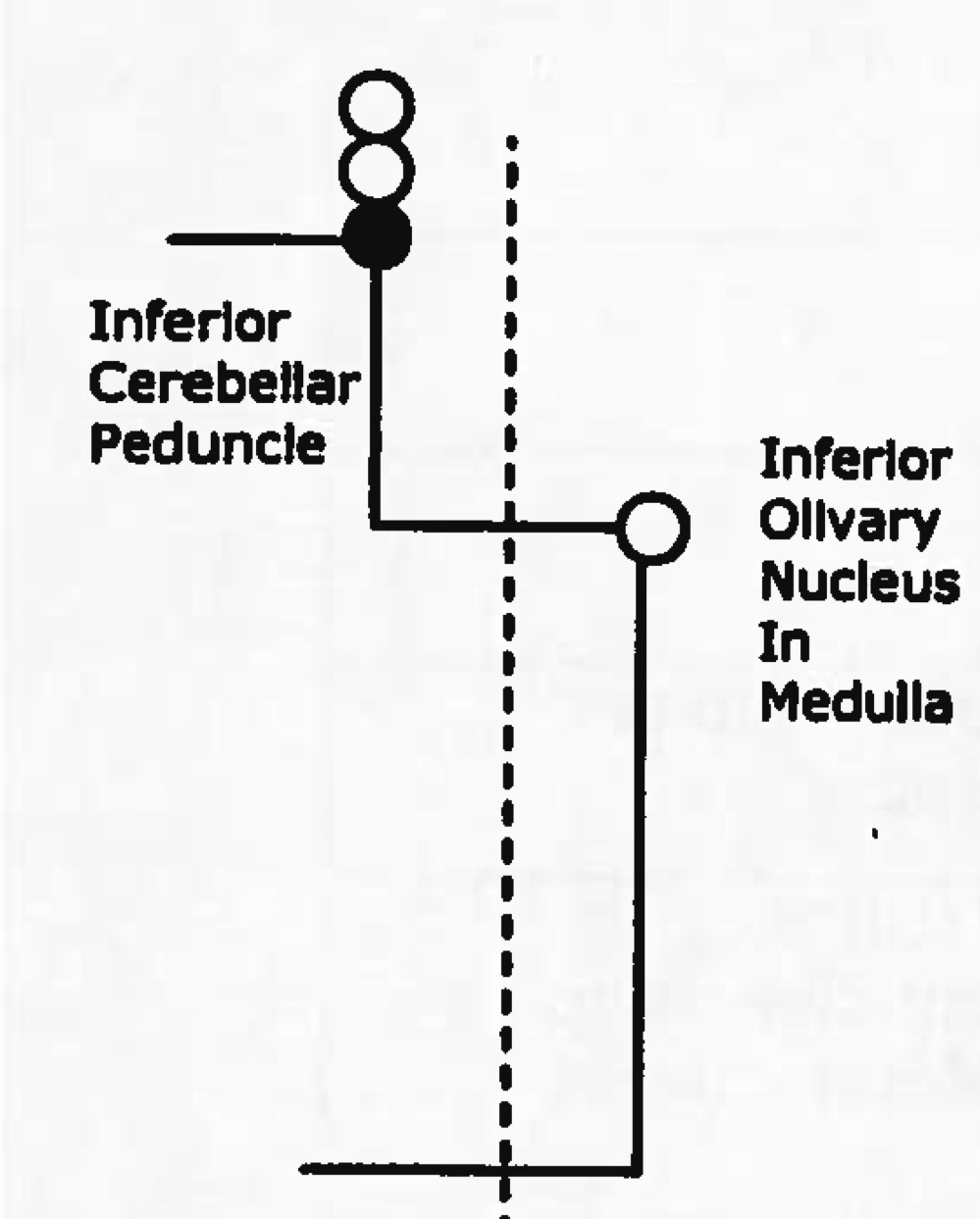
function of spino-olivary tract
conveys info to cerebellum from proprioceptive organs
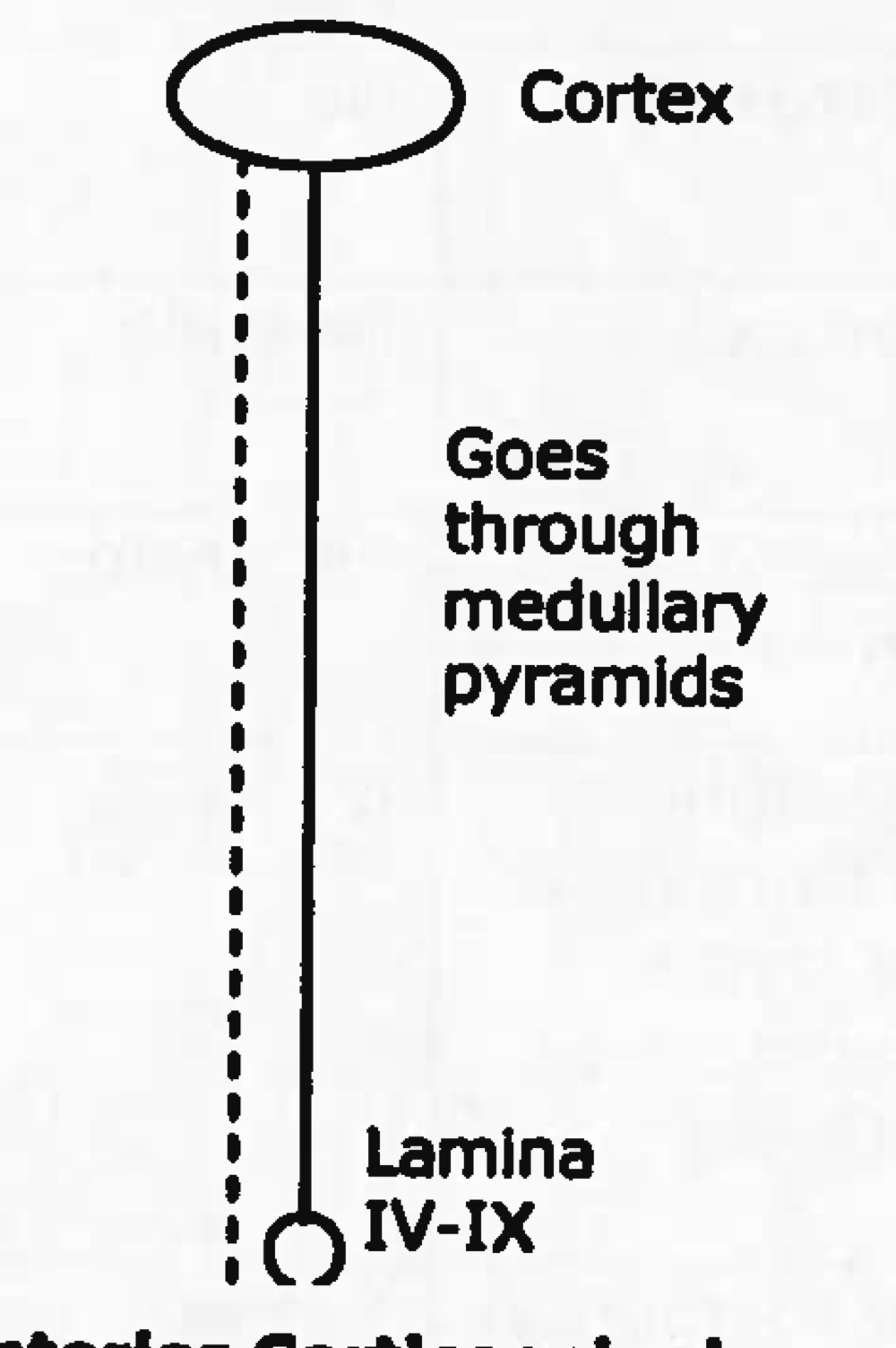
function of anterior corticospinal tract
gross postural
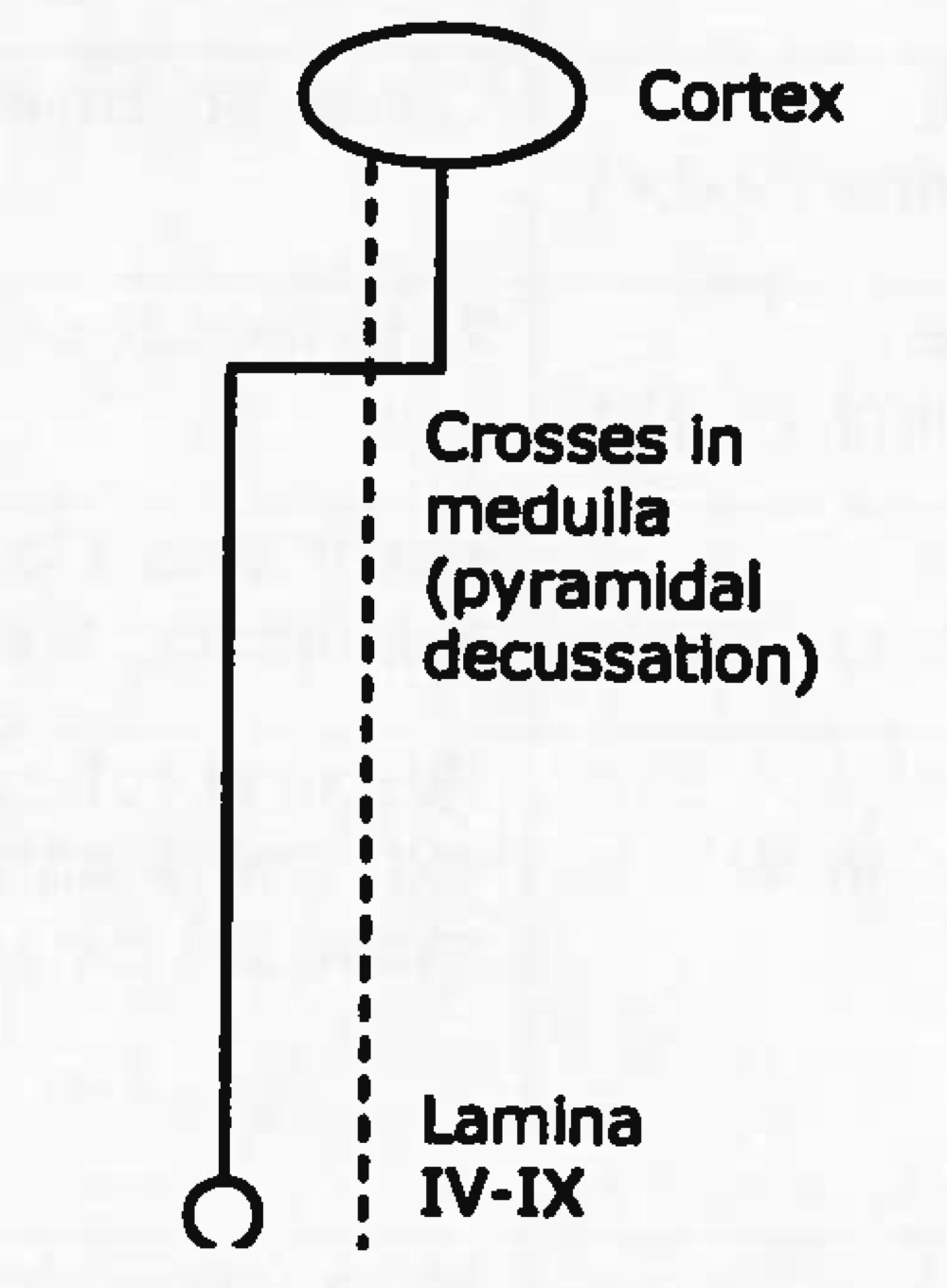
function of lateral corticospinal tract
fine motor control
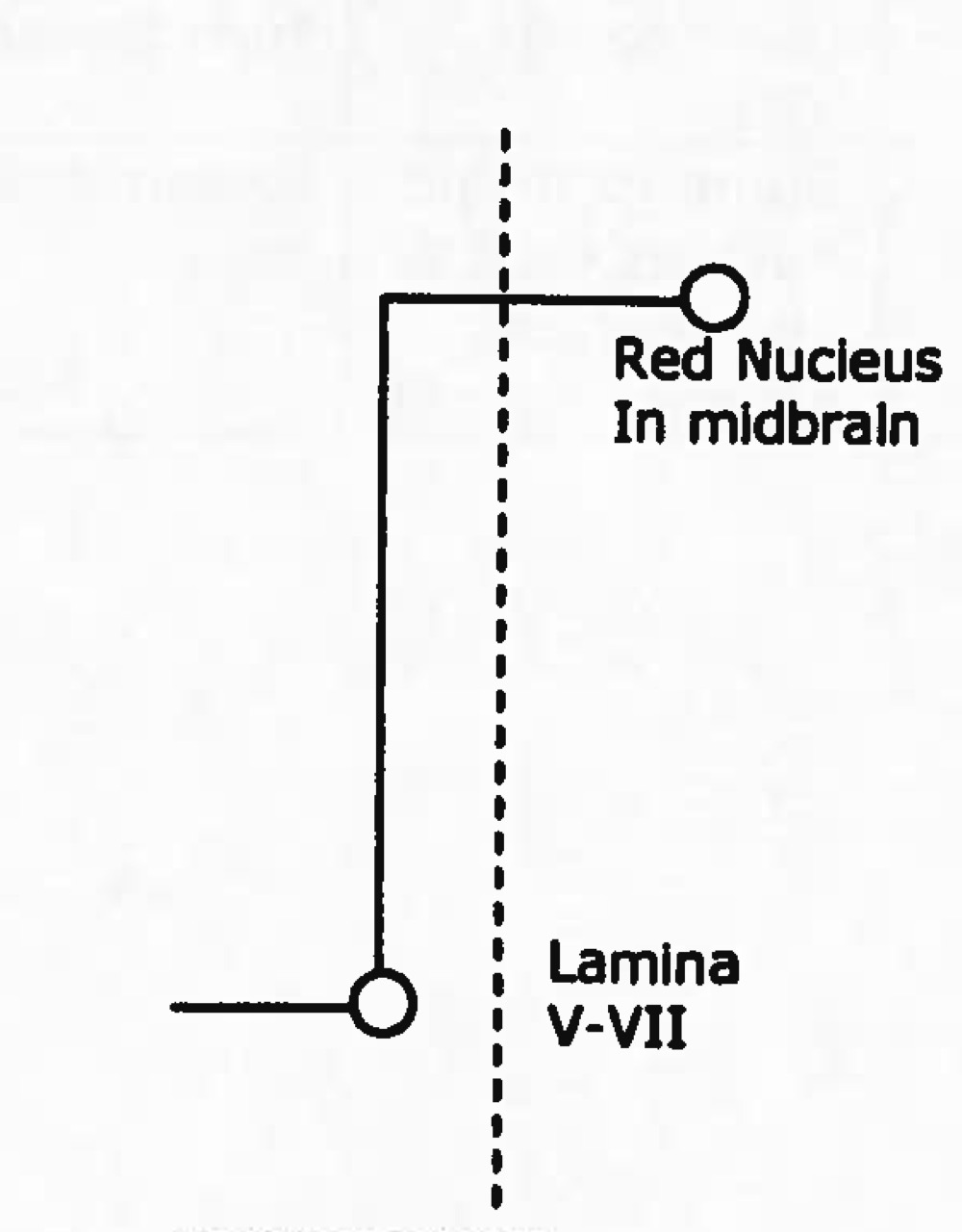
rubrospinal tract function
facillitates flexors and inhibits extensors, motor control
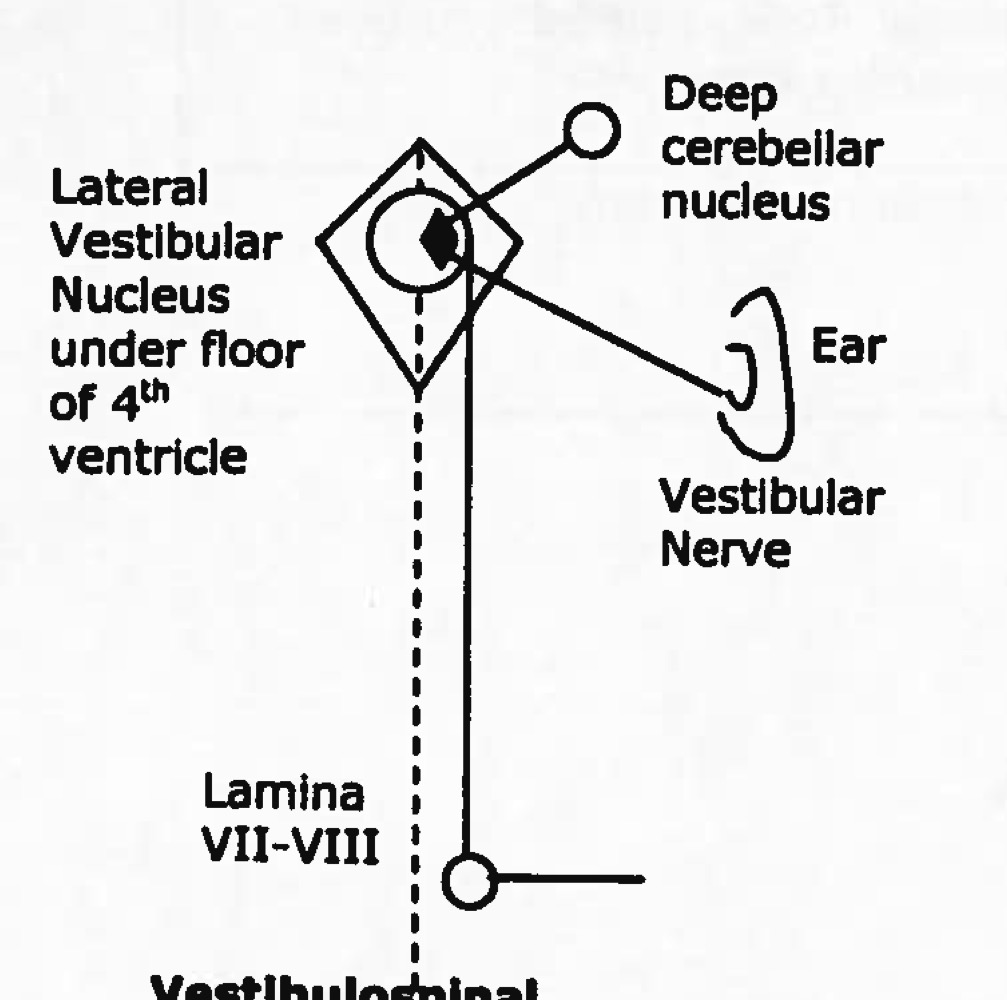
function of vestibulospinal tract
postural reflexes, facilitates extensors and inhibits flexors to maintain balance, motor control
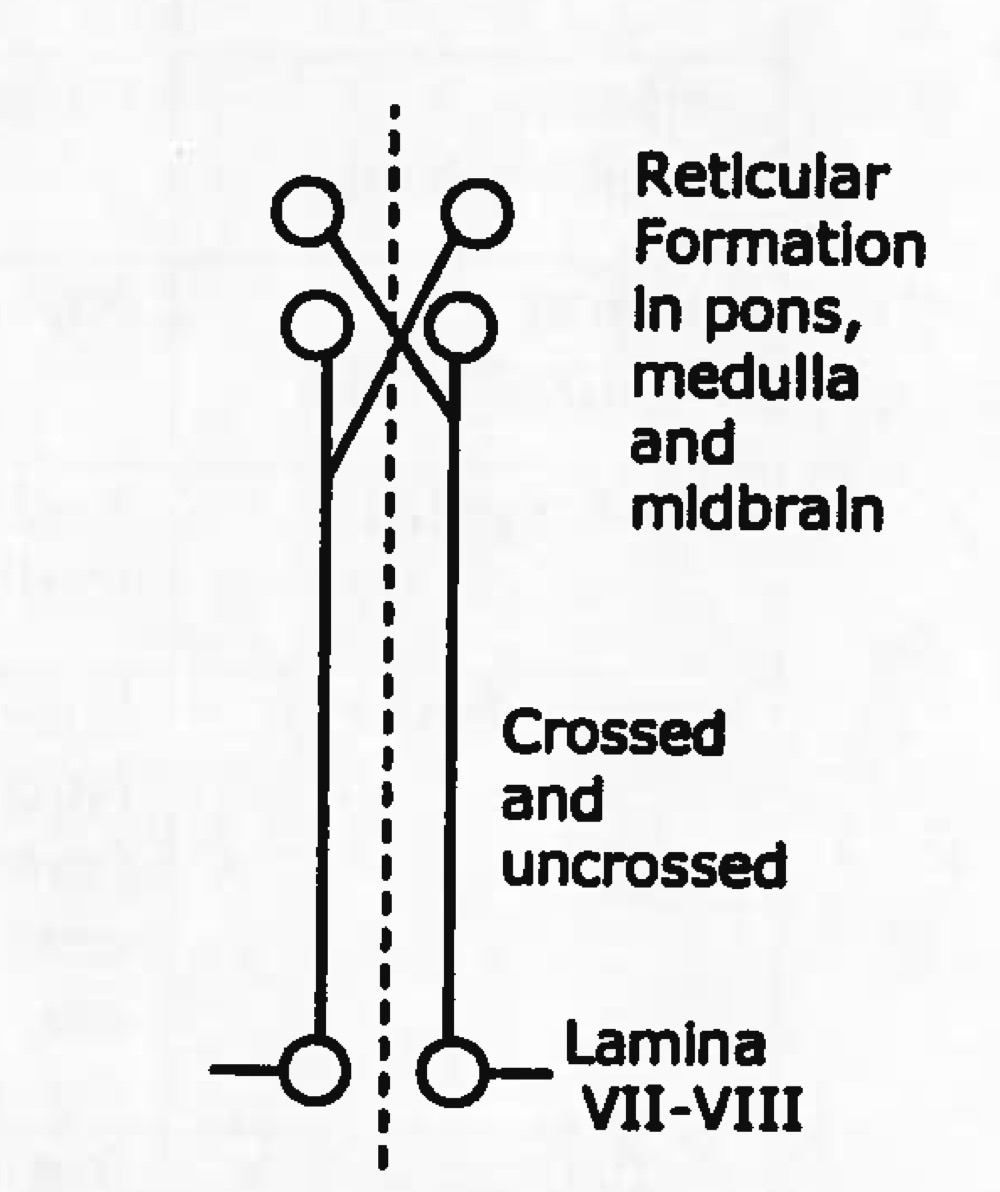
function of reticulospinal tract
modulate spinal reflexes
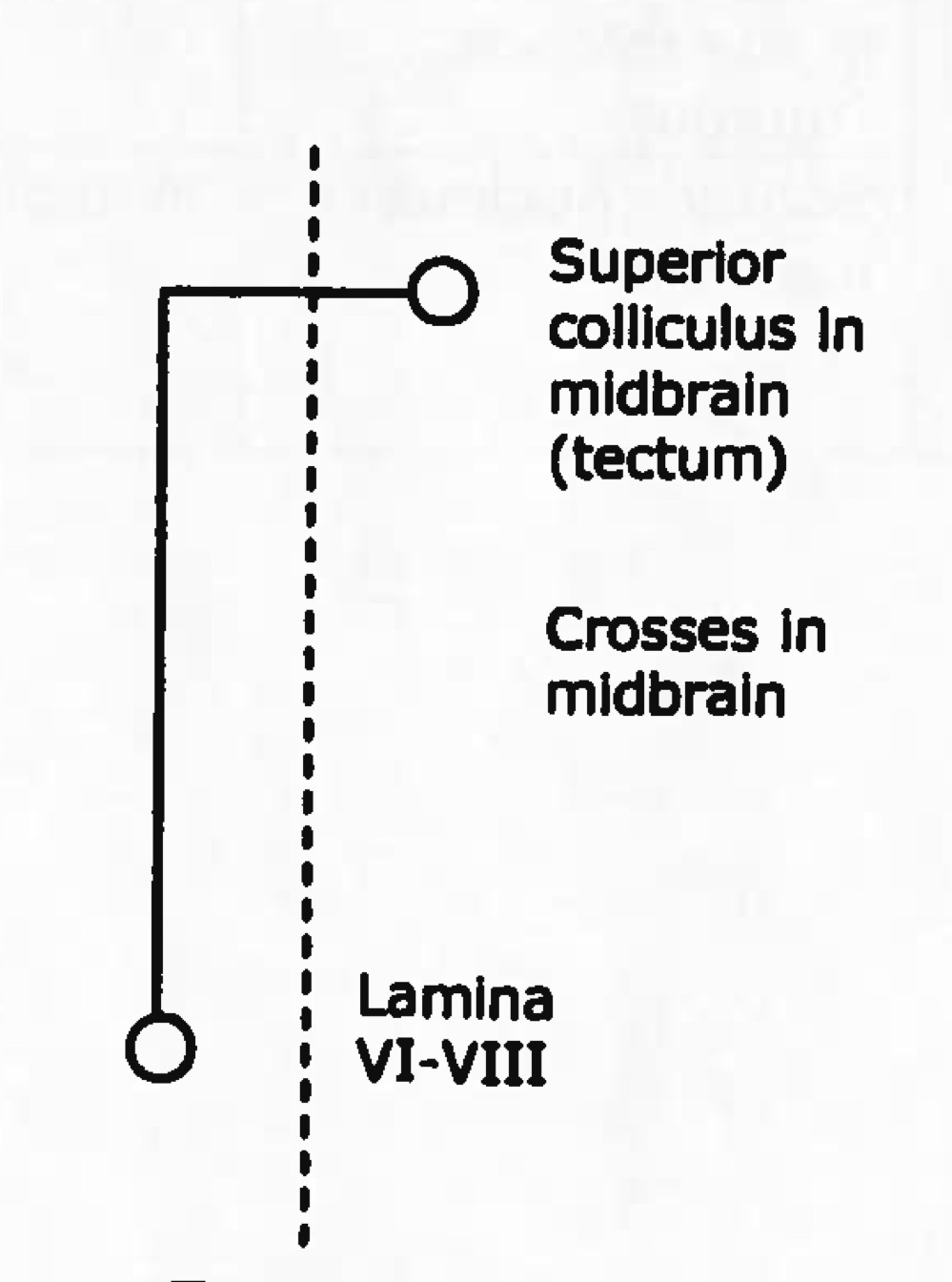
function of tectospinal tract
spinovisual reflex, heads and eyes turning toward stimulus
function of solitariospinal tract
respiration modulation
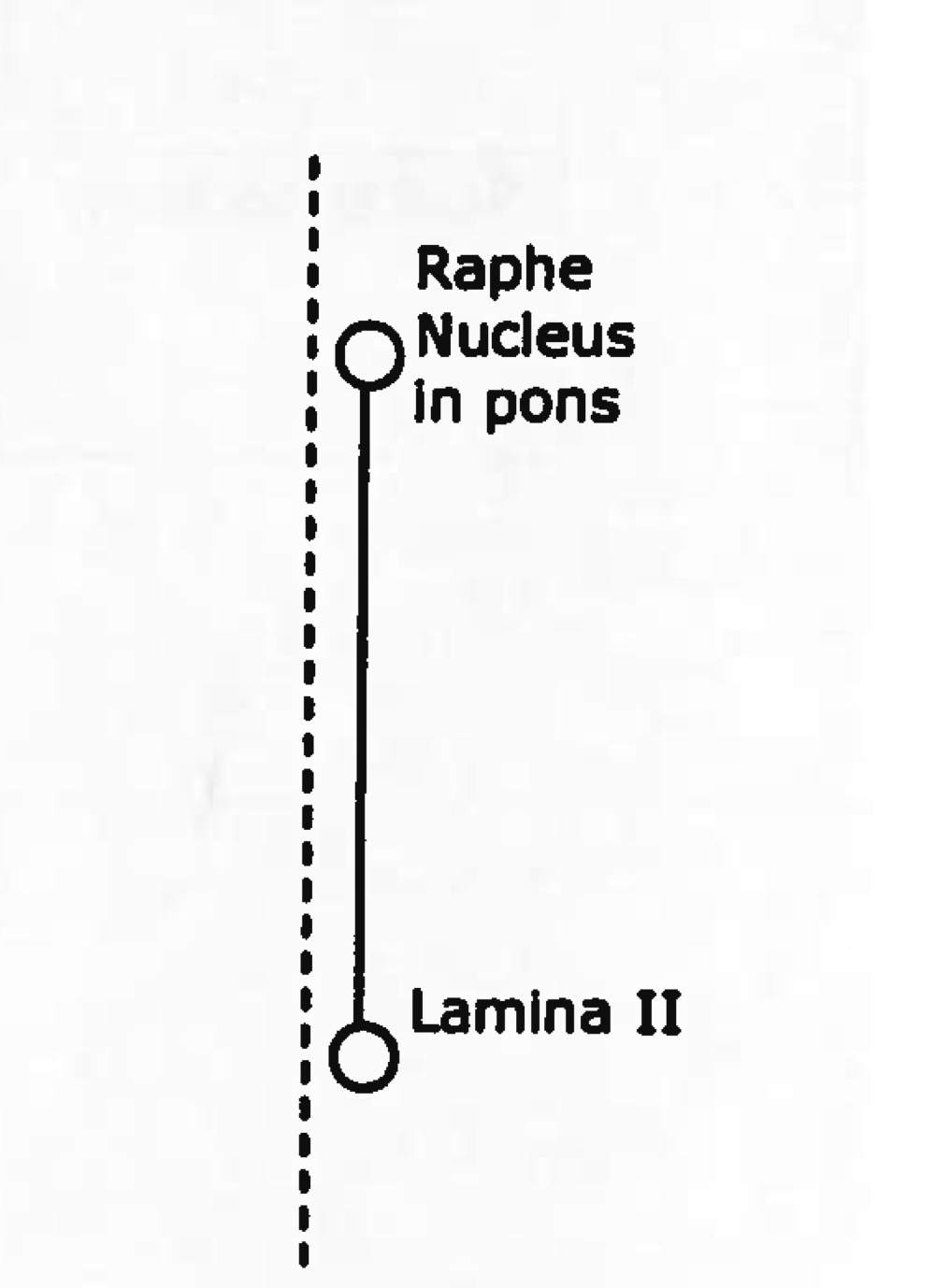
Function of raphespinal
Modified transmission of sensation and pain
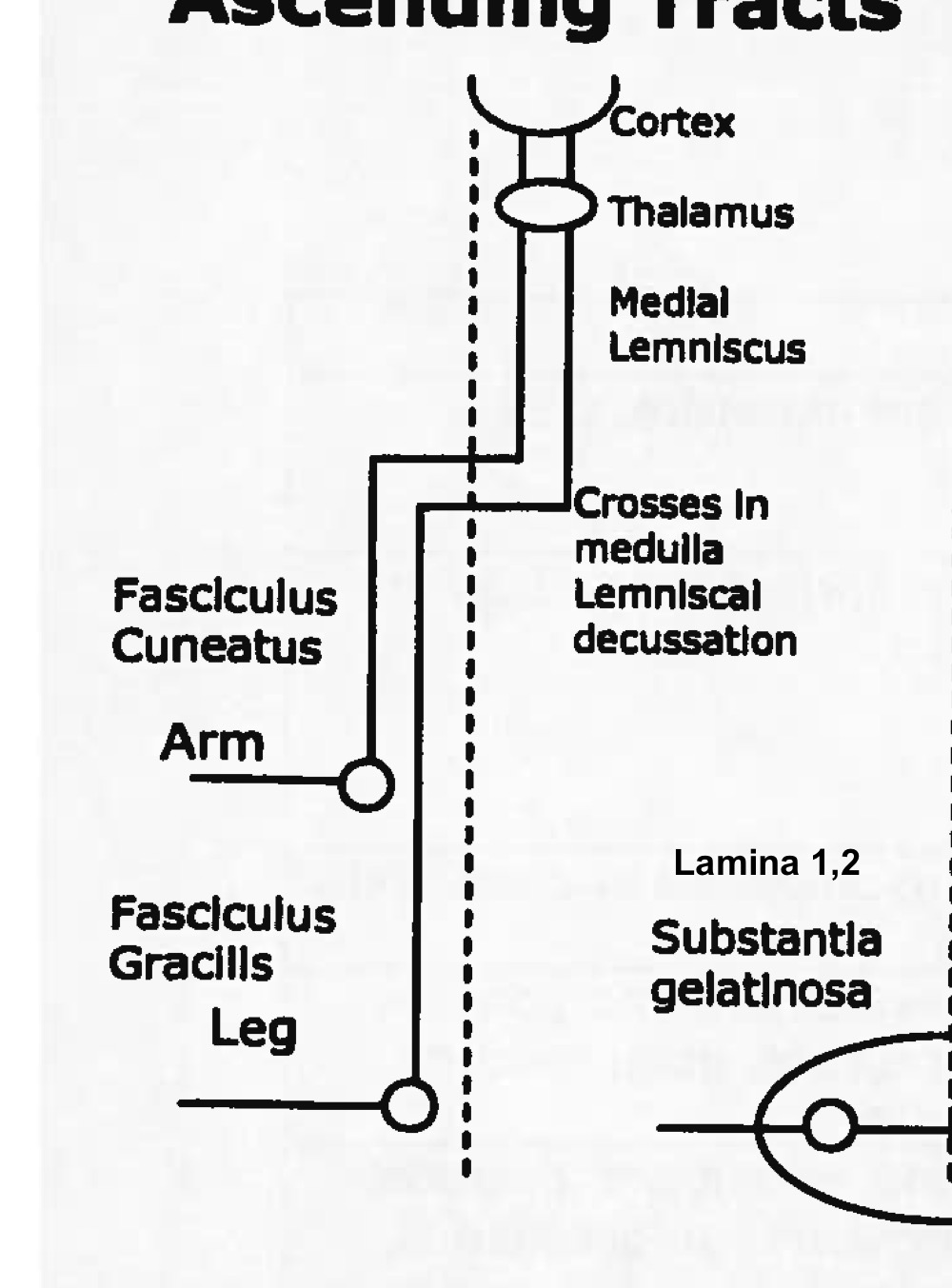
Name tract
Ascending or descending?
dorsal column tract
ascending (sensory)
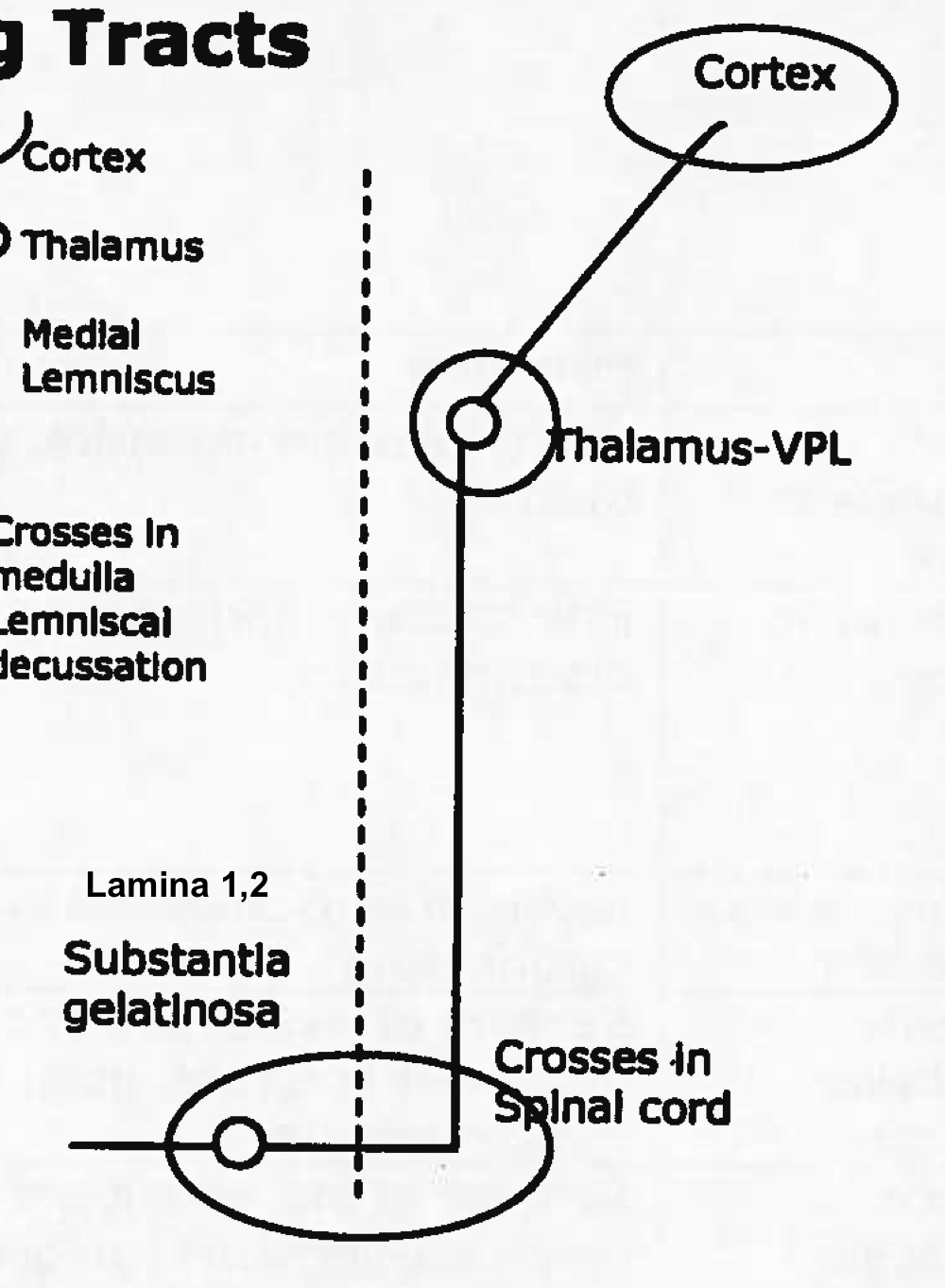
Name tract
Ascending or descending?
spinothalamic tract
ascending (sensory)
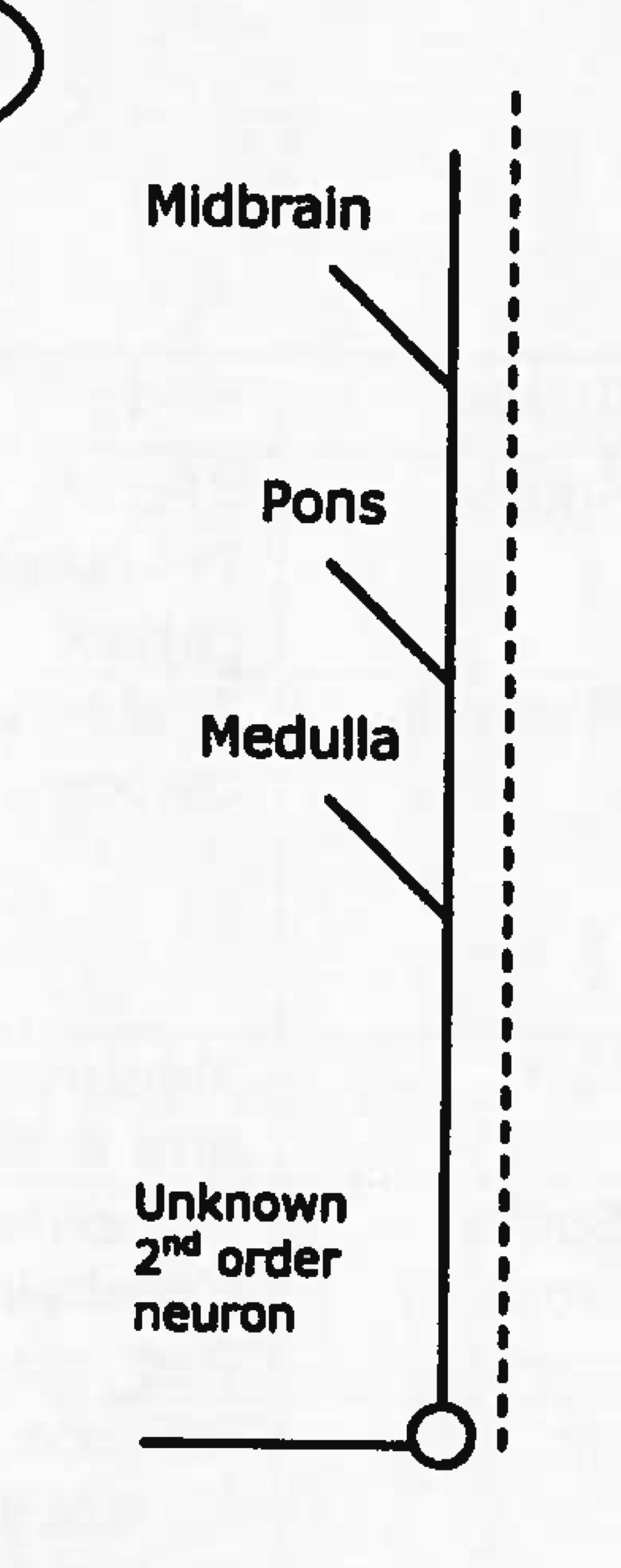
Name tract
Ascending or descending?
spinoreticular tract
ascending (sensory)
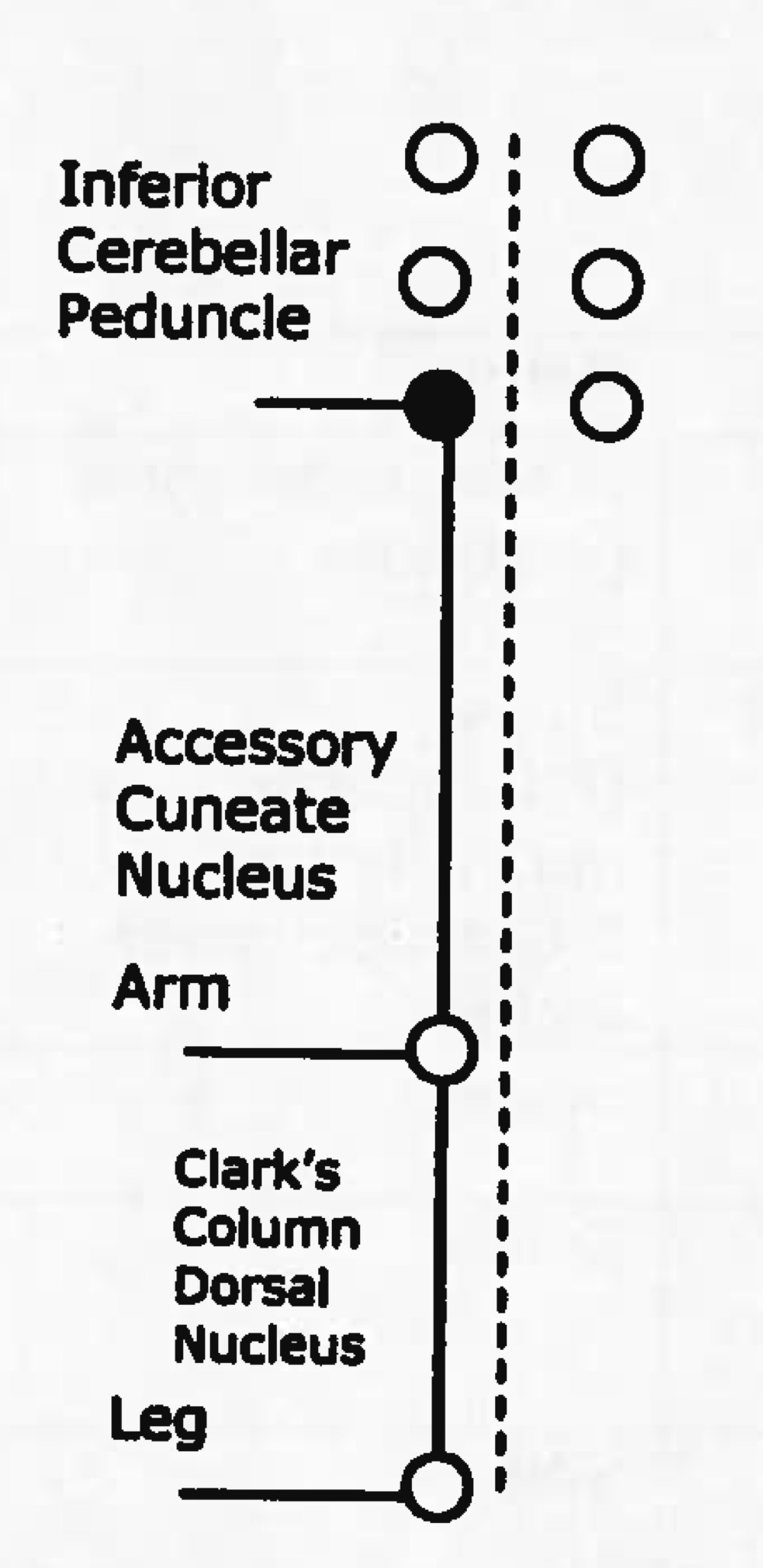
Name tract
Ascending or descending?
dorsal spinocerebellar tract
ascending (sensory)
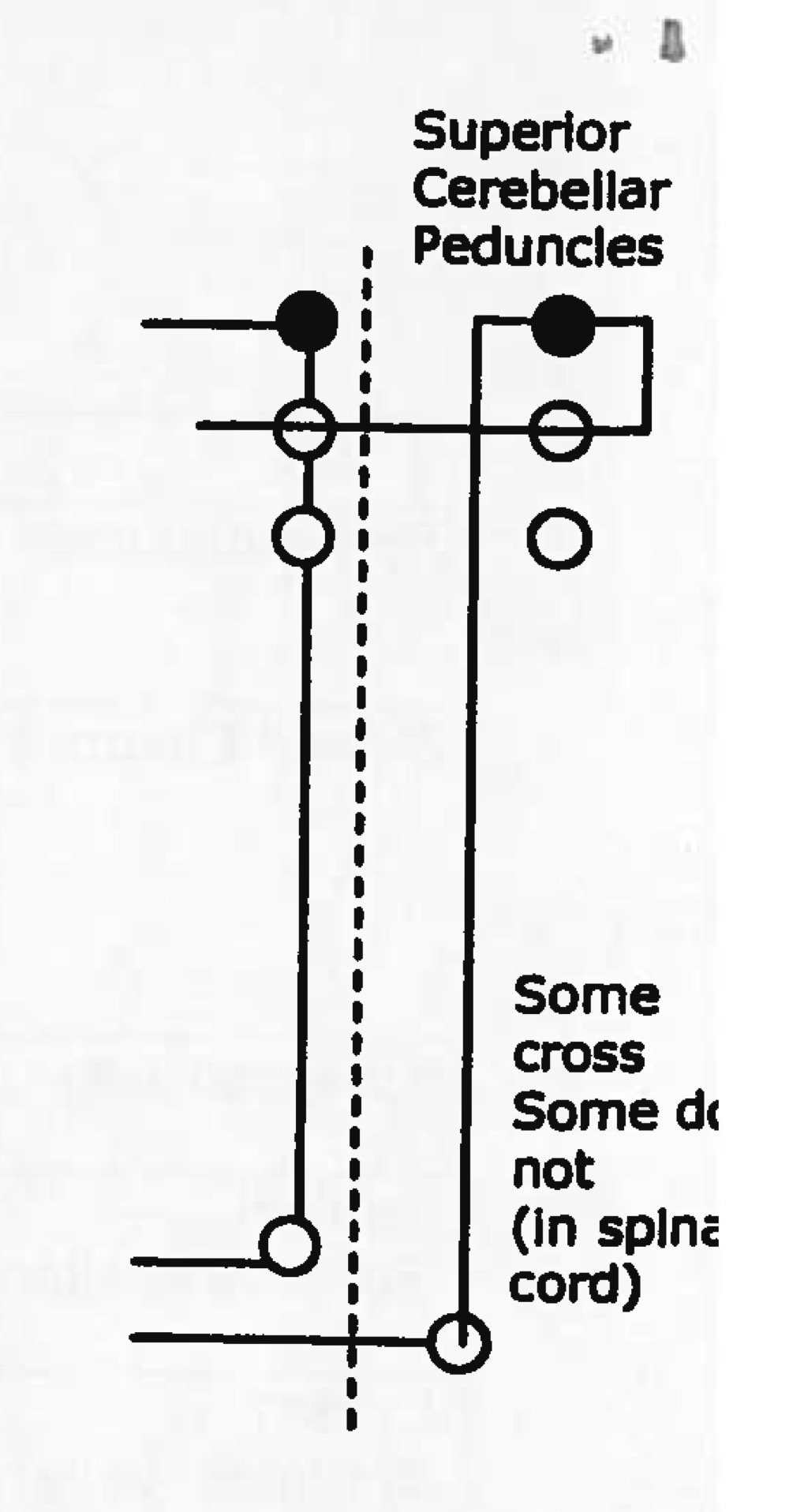
Name tract
Ascending or descending?
ventral spinocerebellar tract
ascending (sensory)
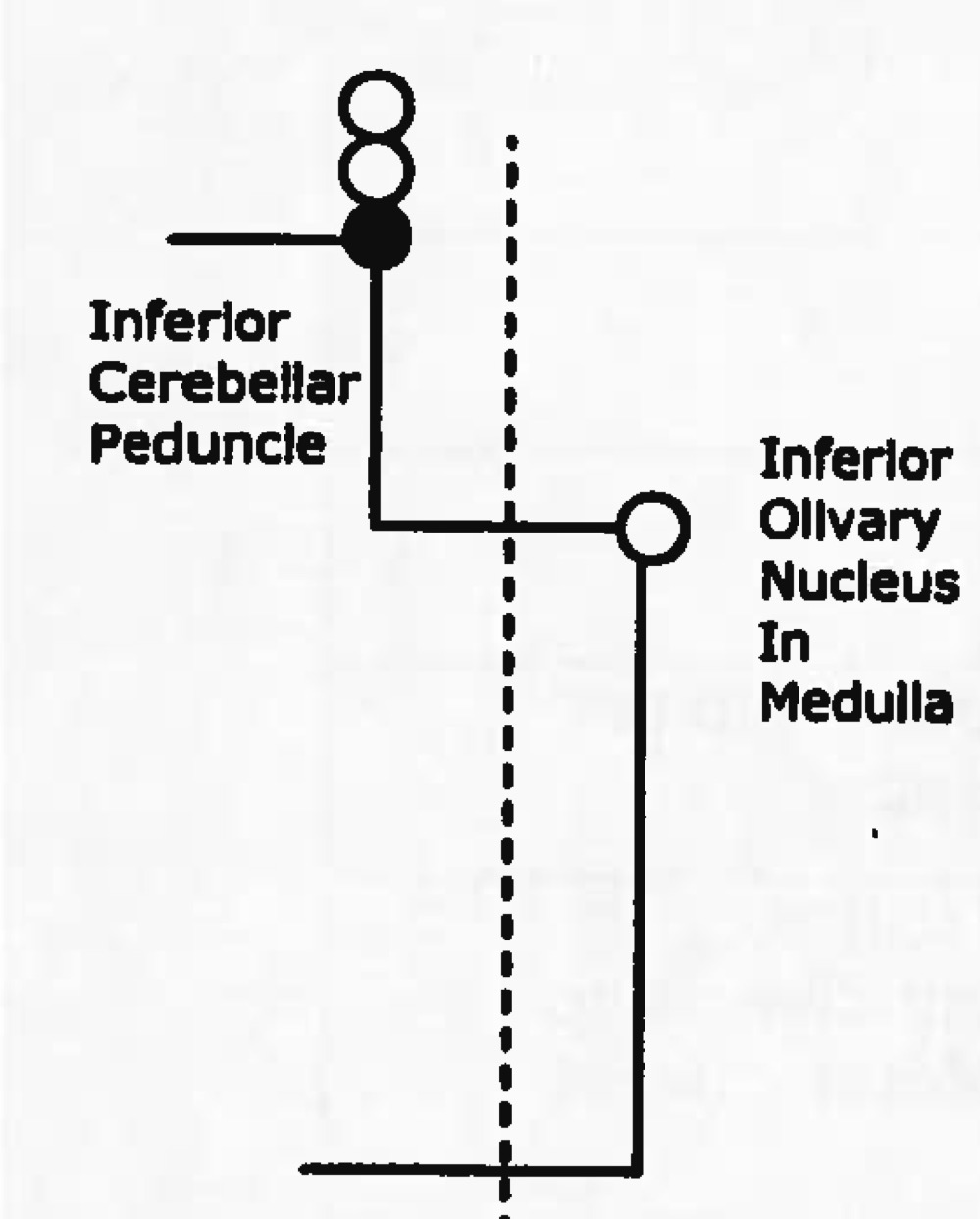
Name tract
Ascending or descending?
spino-olivary tract
ascending (sensory)
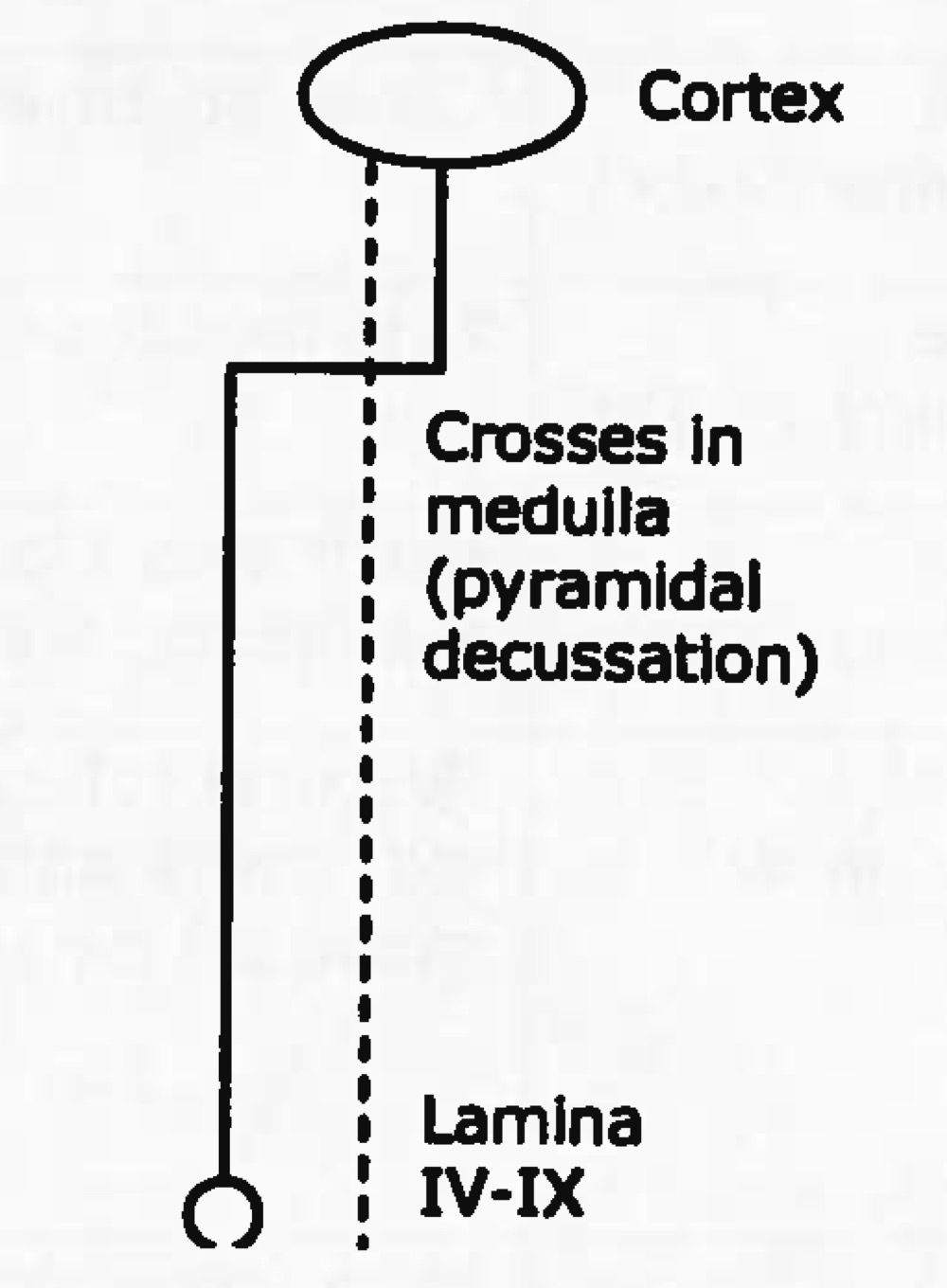
Name tract
Ascending or descending?
lateral corticospinal tract
descending (motor)
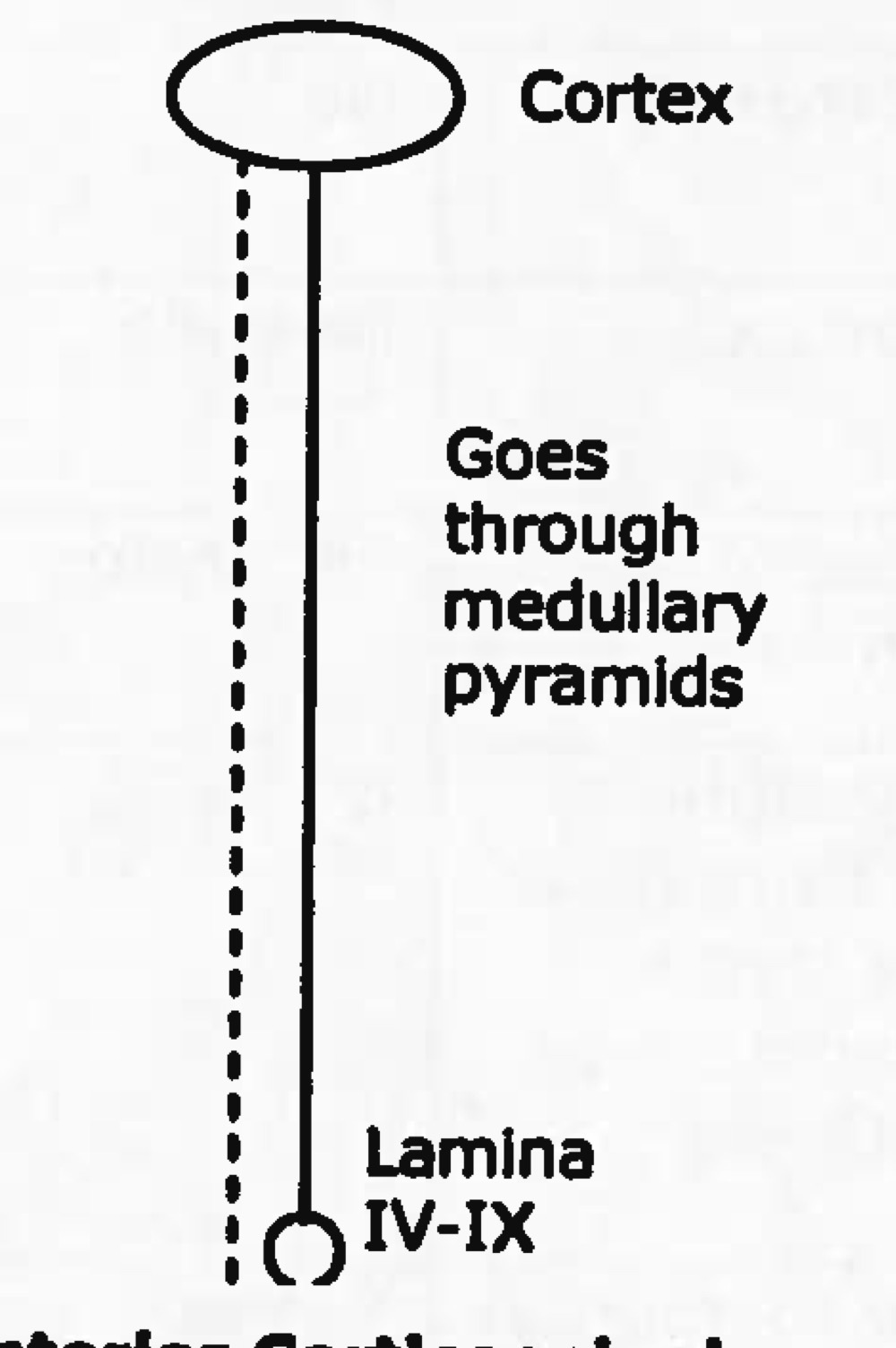
Name tract
Ascending or descending?
anterior corticospinal tract
descending (motor)
Name tract
Ascending or descending?
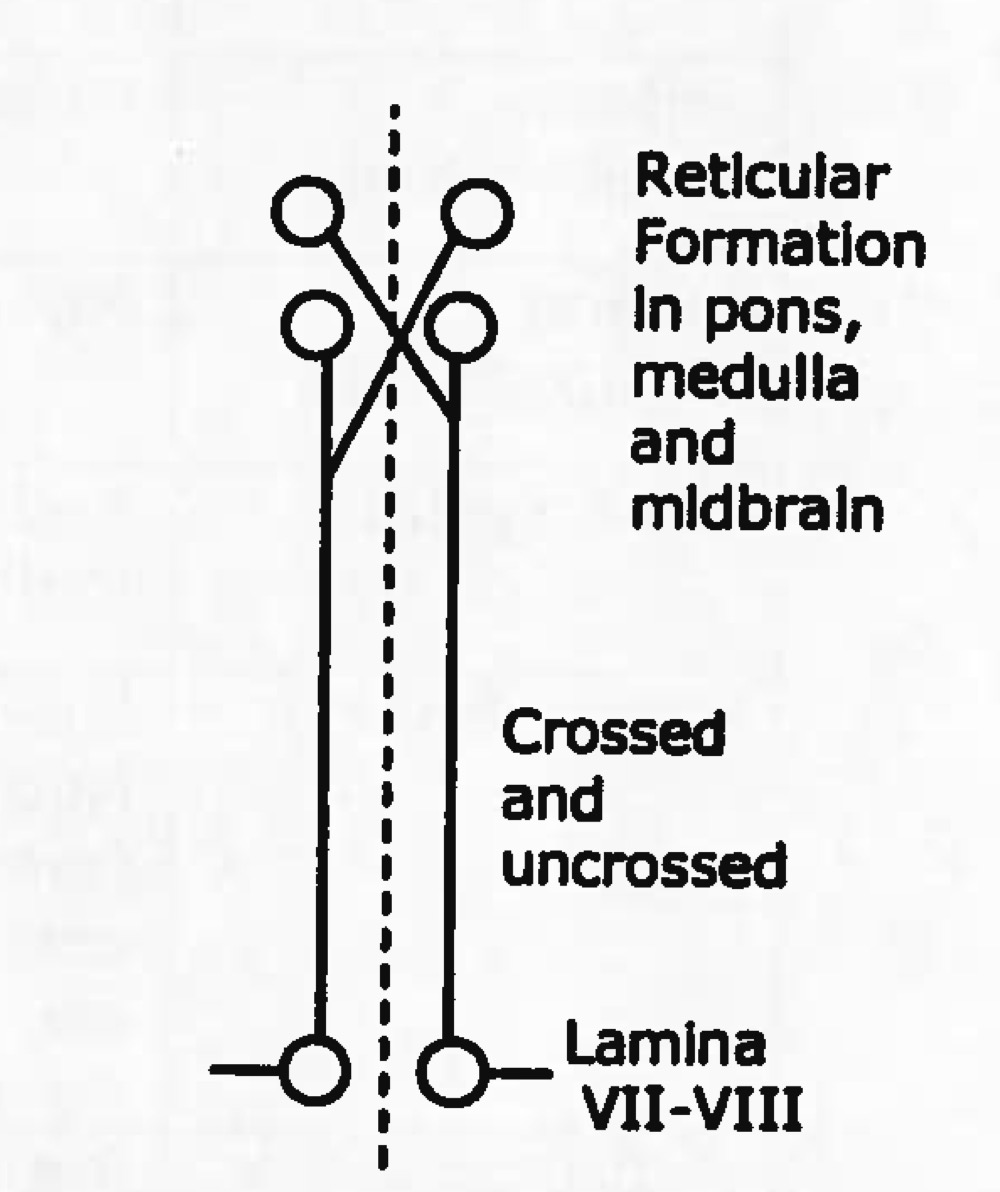
reticulospinal tract
descending (motor)
Name tract
Ascending or descending?
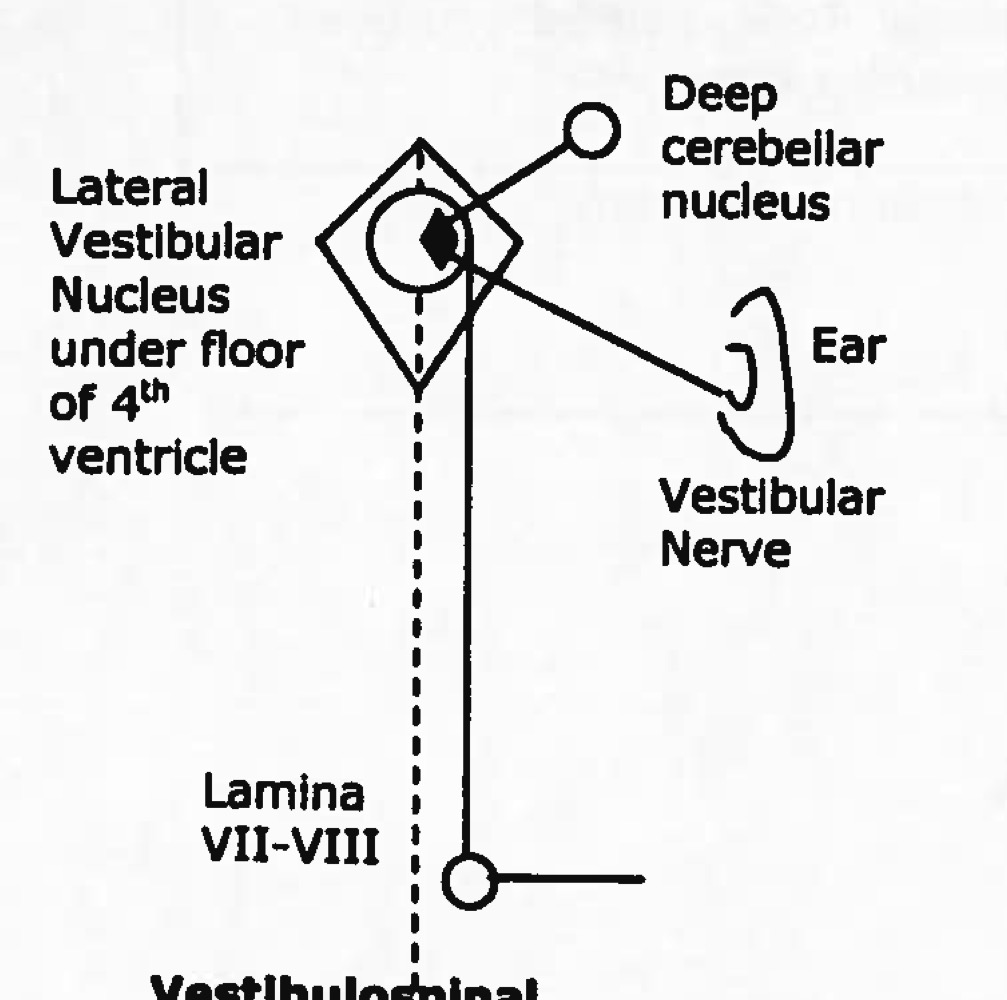
vestibulospinal tract
descending (motor)
Name tract
Ascending or descending?
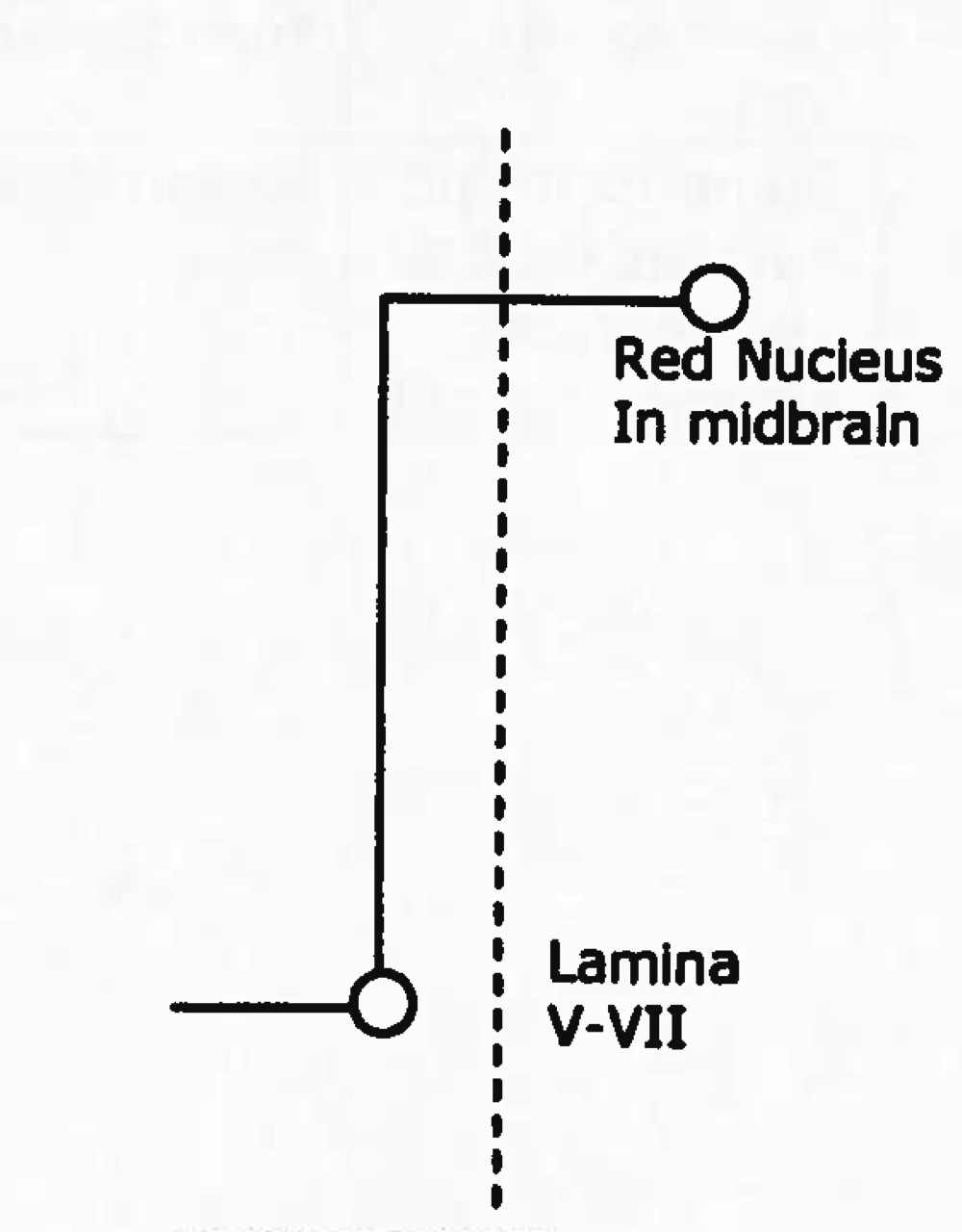
rubrospinal tract
descending (motor)
Name tract
Ascending or descending?
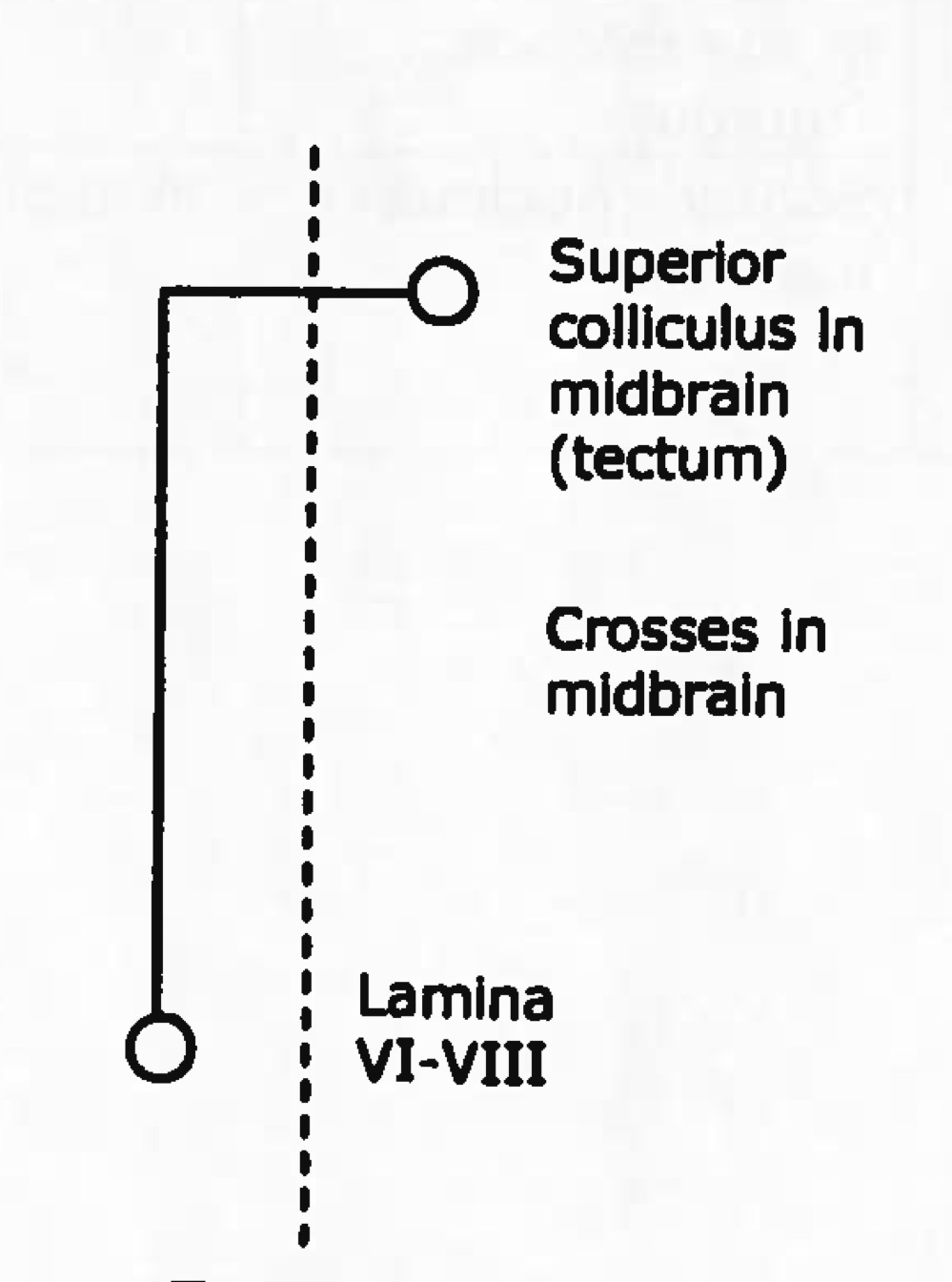
tectospinal tract
descending (motor)
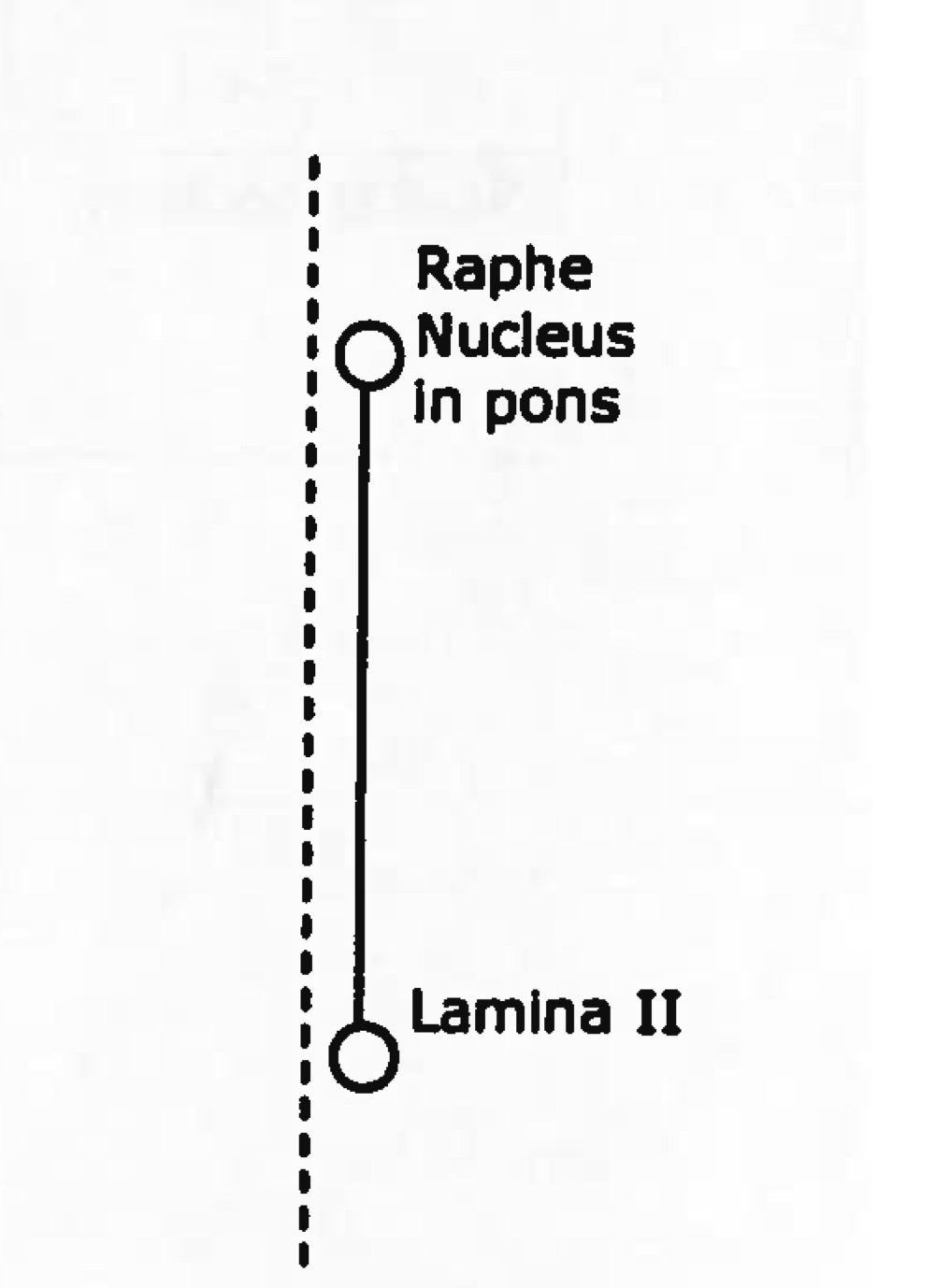
Name tract
Ascending or descending?
raphespinal tract
descending (motor)
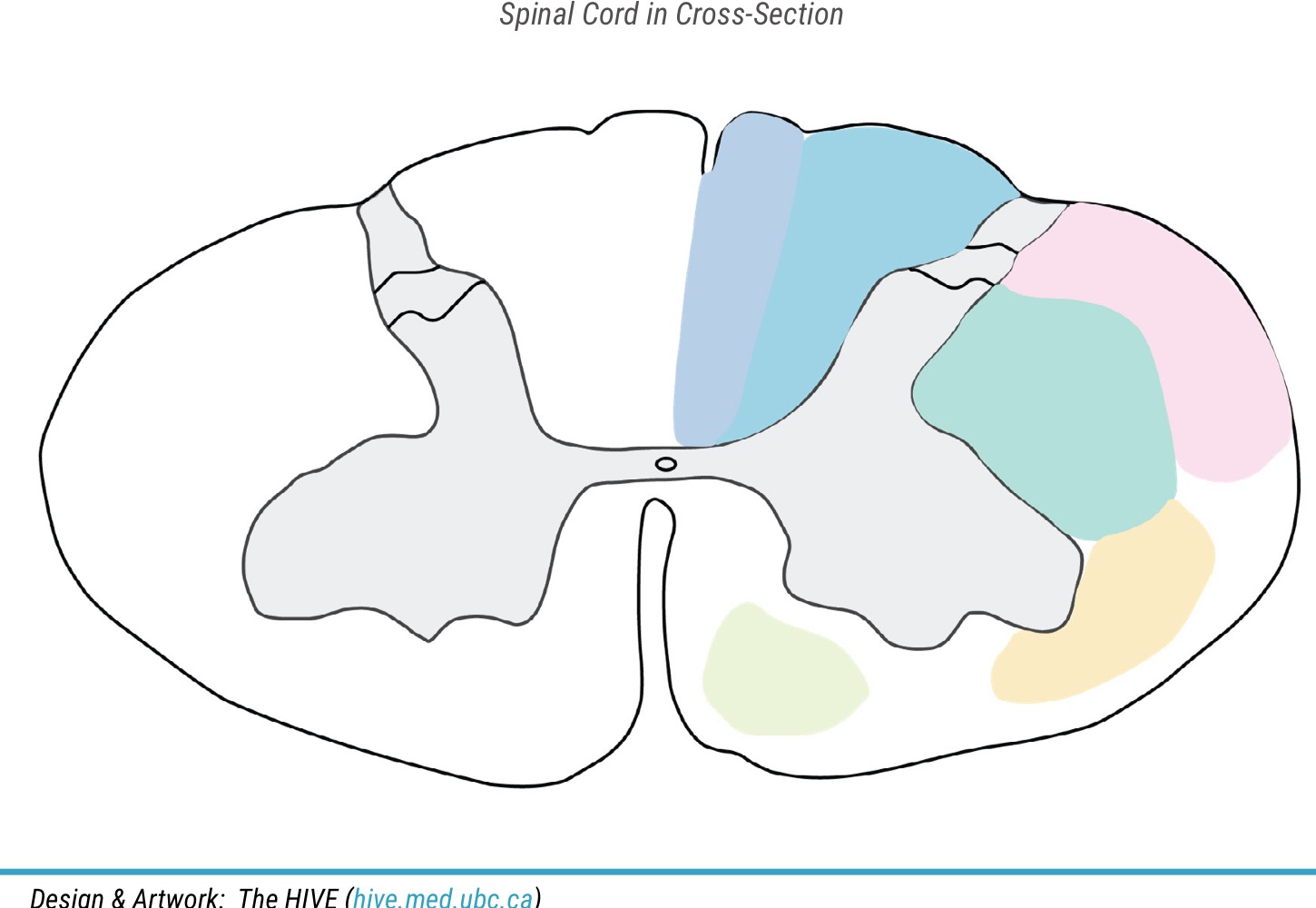
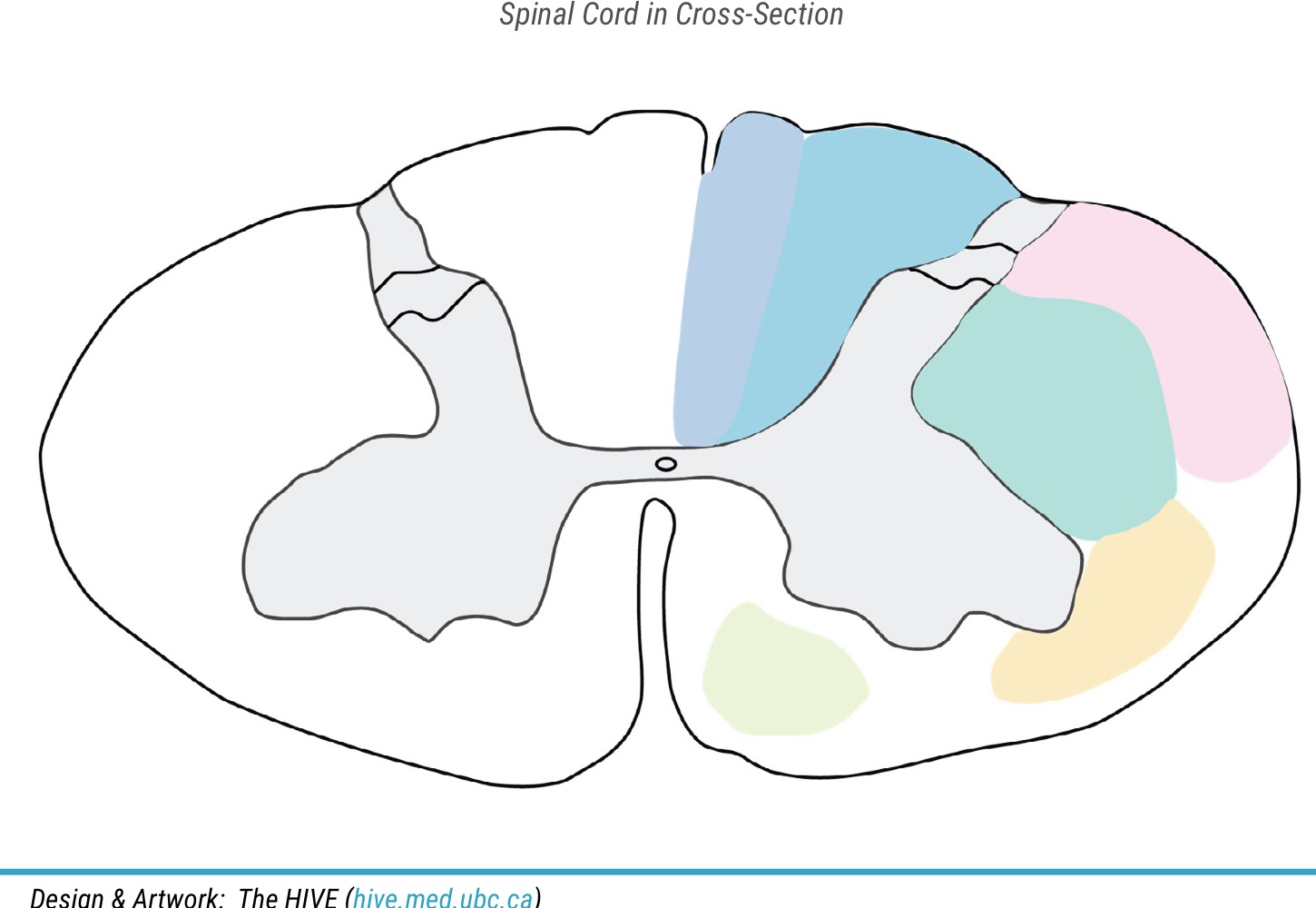
Name light blue area
fasciculus cuneatus
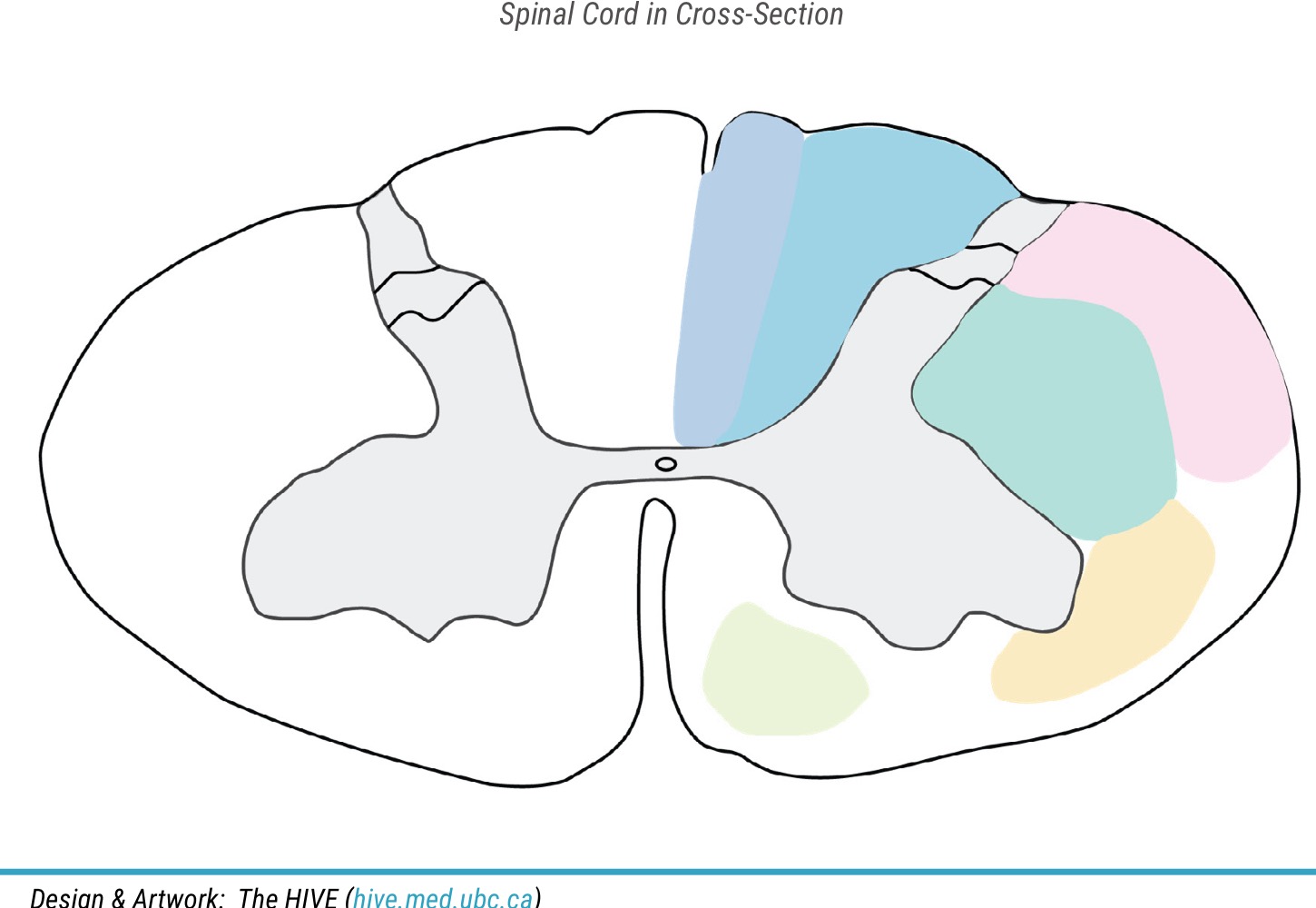
Name purple area
fasciculus gracilis
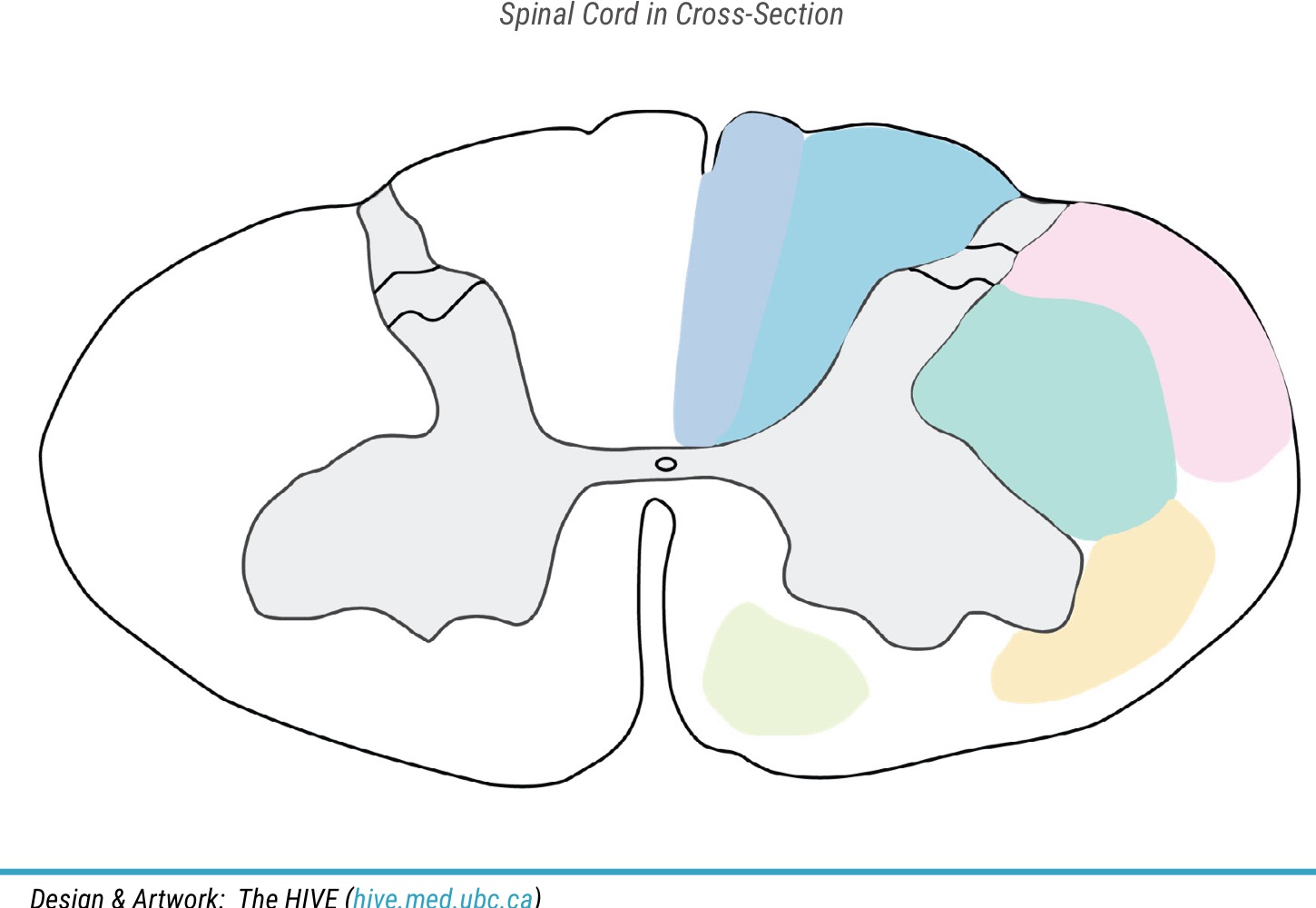
name dark green color
lateral corticospinal tract
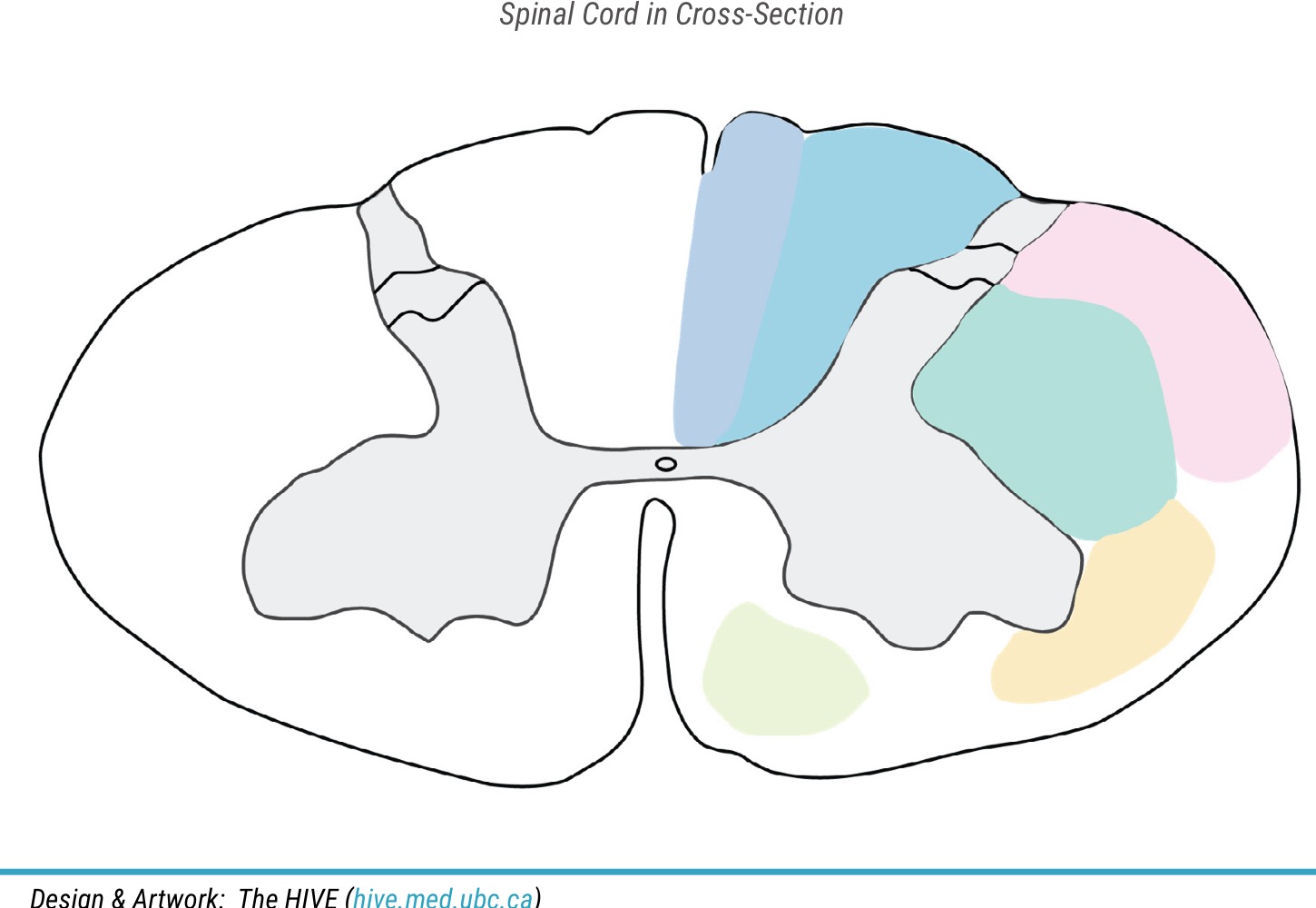
name light green color
anterior corticospinal tract
name yellow color
spinothalamic tract
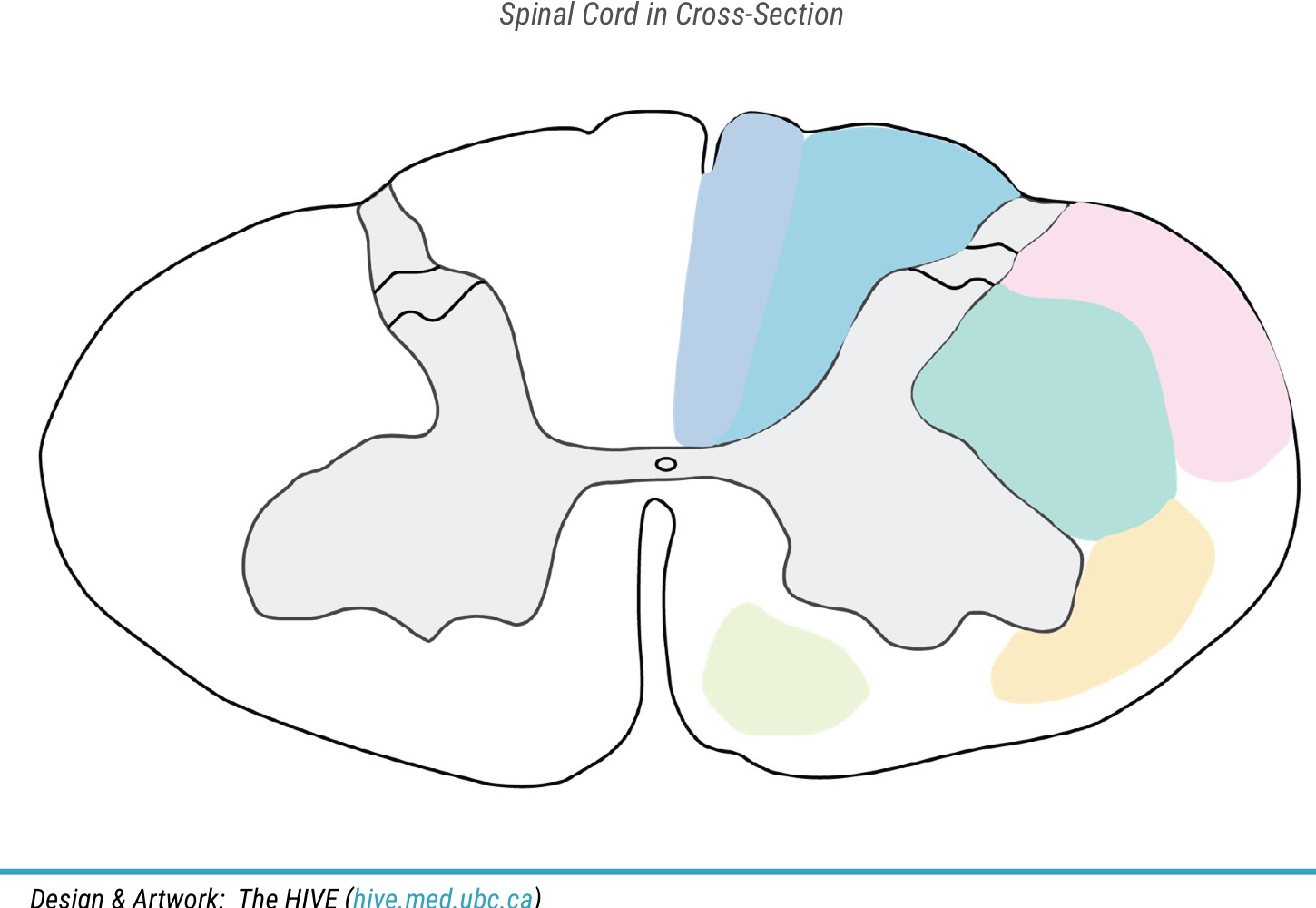
name pink color
spinocerebellar tract
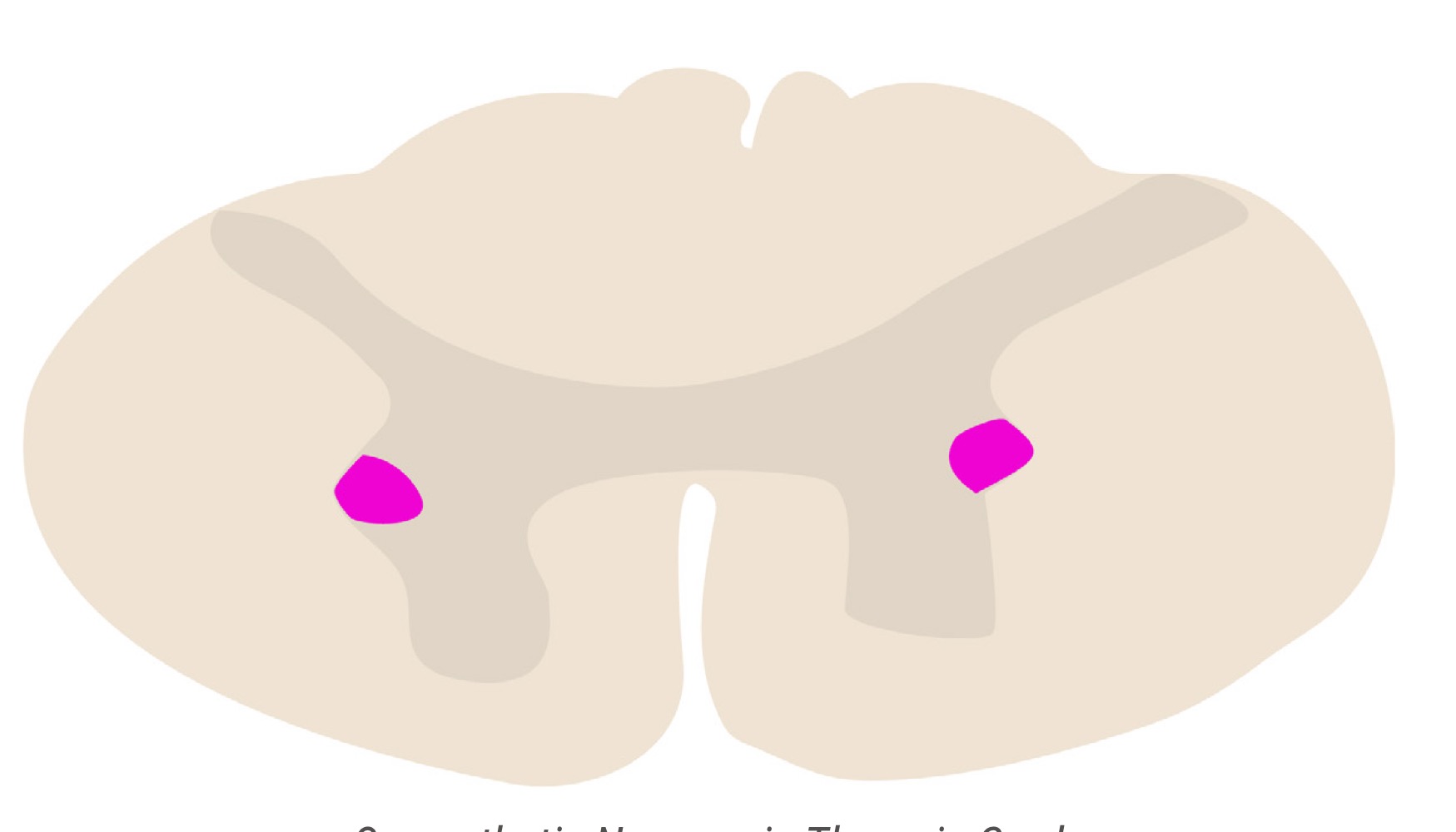
name highlighted area
sympathetic neurons in lateral horns of thoracic region
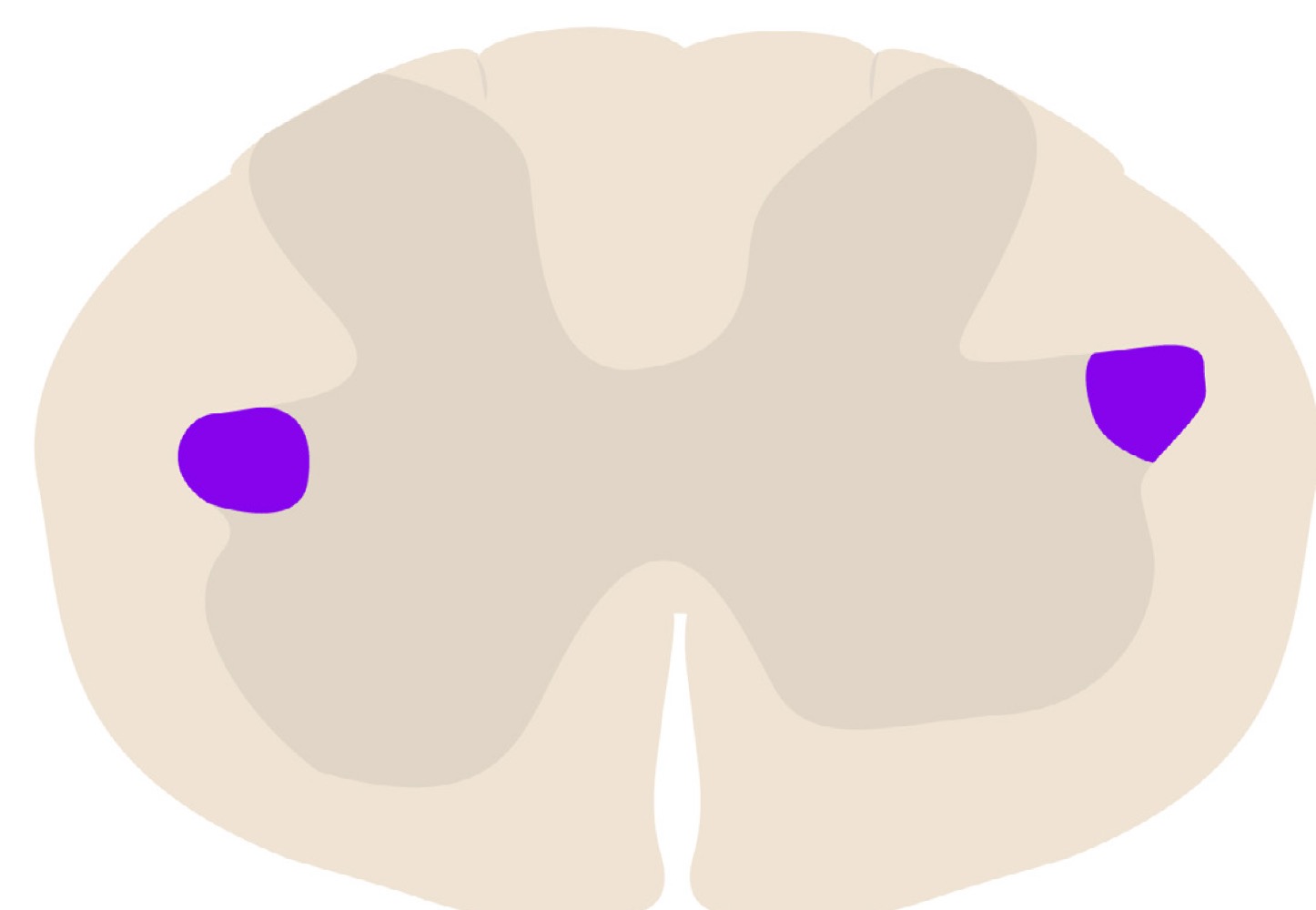
name highlighted area
parasympathetic neurons in brainstem and sacral cord
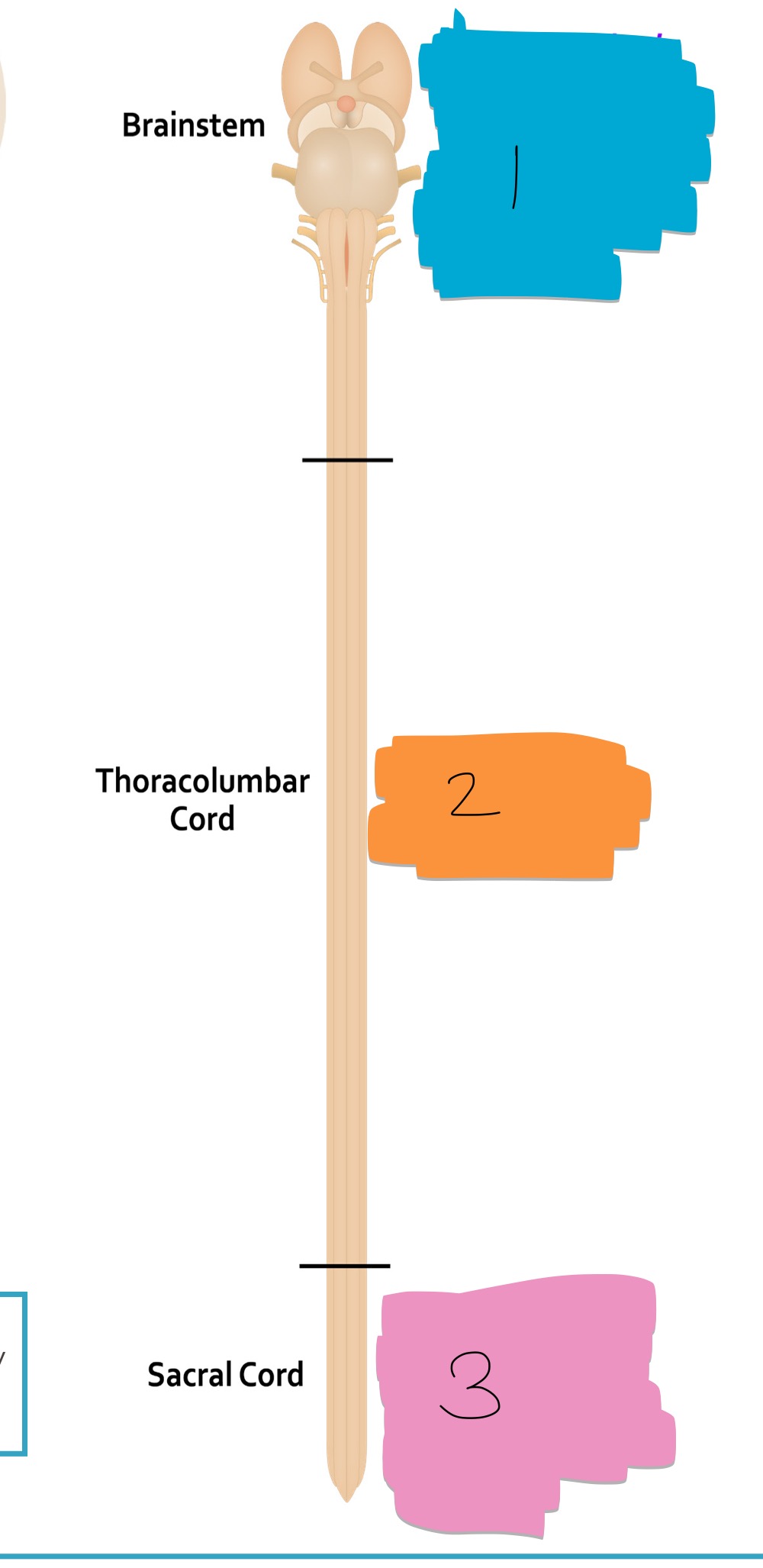
what number(s) denote an area of parasympathetic innervation
1, 3
what number(s) denote an area of sympathetic innervation
2
biceps tendon reflex nerve root
C5
brachioradialis reflex nerve root
C6
triceps reflex nerve root
C7
patellar reflex nerve root
L4
hamstring reflex nerve root
L5
achilles reflex nerve root
S1
C5 myotome
deltoid - shoulder abduction
C6 myotome
ext carp radialis and ulnaris - wrist extension
biceps - elbow flexion
C7 myotome
triceps - elbow extension
flex carpi radialis and ulnaris - wrist flexion
extensor muscles - wrist extension
C8 myotome
flexor digitorum - finger flexion
T1 myotome
finger abductors and adductors
L1 myotome
hip flexion
L2 myotome
hip flexion
L3 myotome
hip flexion
L4 myotome
quad- knee ext
anterior tibialis - ankle dorsiflexion and inversion
L5 myotome
hamstrings - knee flex
extensor hallucis and digitorum longus - ankle dorsiflexion and big toe extension
S1 myotome
gastrocnemius - plantar flexion
peroneus longus and brevis - eversion and plantar flexion
C5 dermatome
lateral upper arm
C6 dermatome
lateral forearm/thumb
C7 dermatome
middle finger
C8 dermatome
medial forearm
T1 dermatome
medial upper arm
L1 dermatome
inguinal region
L2 dermatome
distal 2/3 anterior thigh
L3 dermatome
distal 3rd of anterior thigh
L4 dermatome
medial leg and foot
L5 dermatome
lateral leg and dorsum of foot
S1 dermatome
lateral foot/heel
what is a fasciculi
connection between groups of neurons in the CNS
what is a funiculi
descending or ascending groups of fibers in the spinal cord
what is decussation
vertical pathways crossing over to other side in CNS
what is a commissure
horizontal connection between white matter
what is a lemniscus
tract in the brain
what exceptions in the body are not controlled by the opposite brain
cerebellum controls ipsilaterally
SCM to cortex (due to contralateral rotation occurring)
what is a part of the lower brain level
medulla
pons
mesencephalon
hypothalamus
thalamus
cerebellum
basal ganglia
what is the function of the lower brain level
control of subconscious body activities (arterial pressure, respiration, equilibrium, feeding reflexes, emotional patterns
what is the function of the higher brain or cortical level
store memories
thought processes
what is modulation
inhibition of transmission of impulse
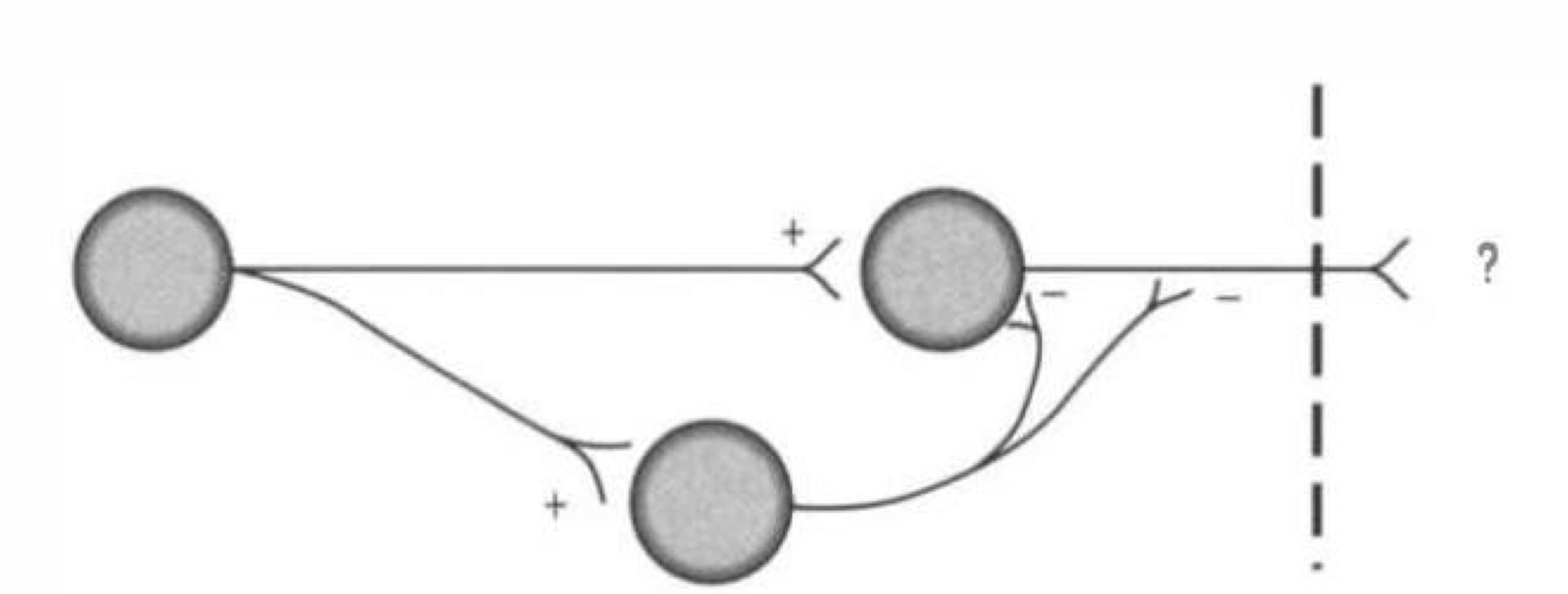
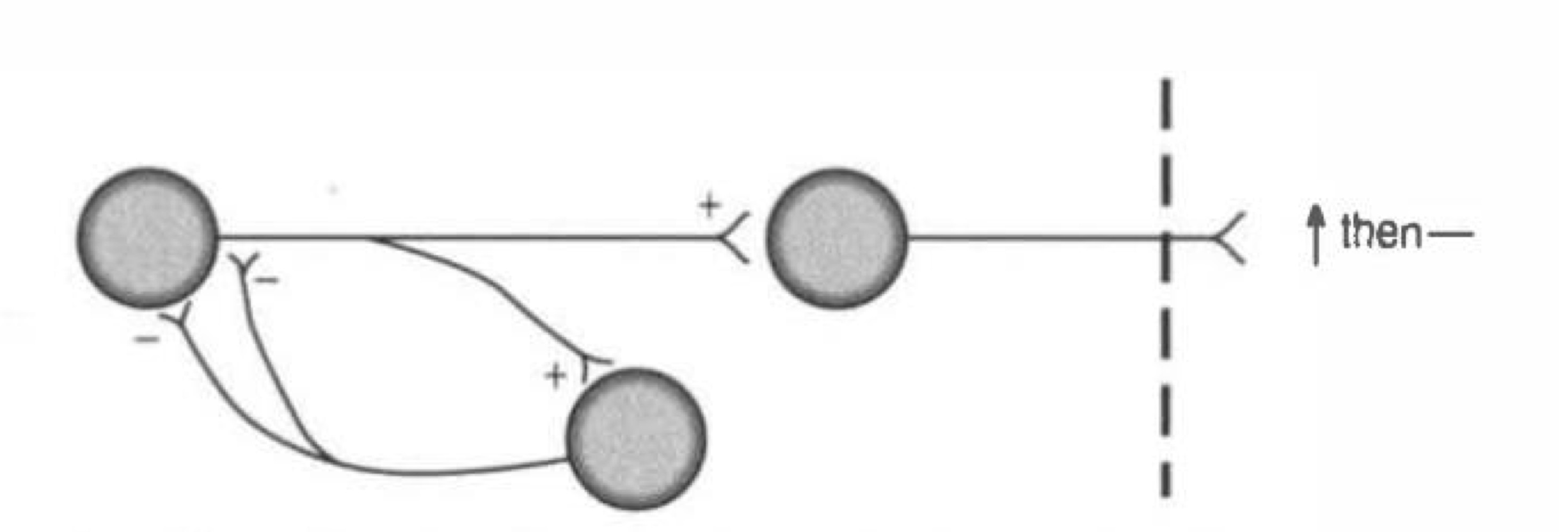
what type of connection is this
feedforward inhibition
what type of connection is this
feedback inhibition
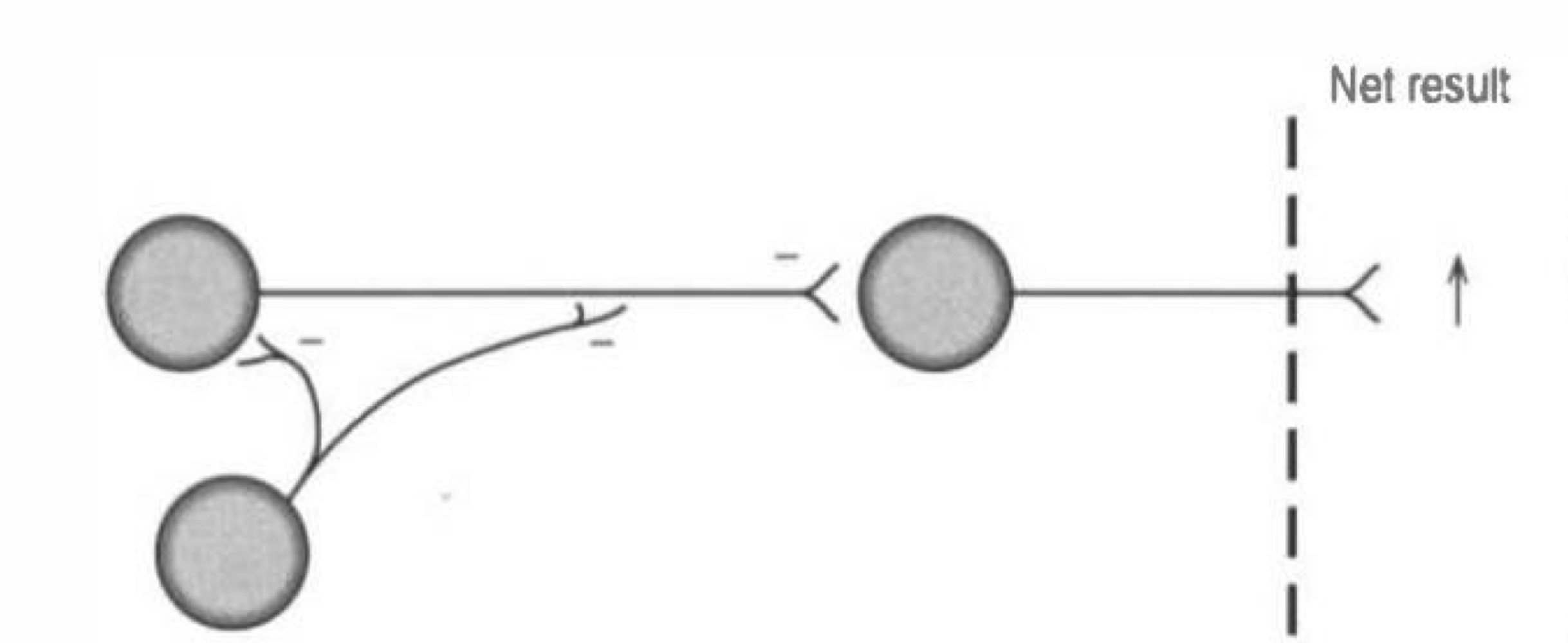
what type of connection is this
disinhibition
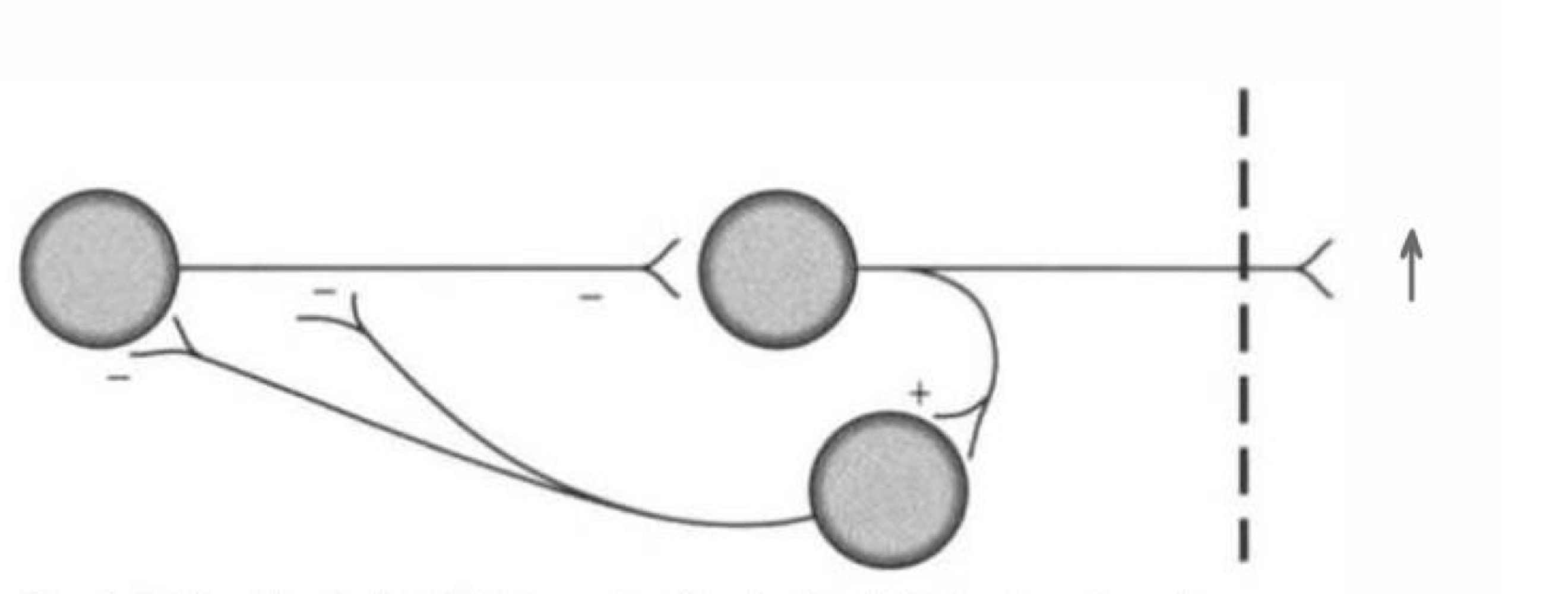
what type of connection is this
feedback disinhibition
what is feedforward inhibition
activation of target neuron and inhibitory neuron by same neuron upstream
inhibitory neuron inhibits target neuron
target neuron does NOT fire
what is feedback inhibition
orginal stimulating neuron stimulates a downstream inhibitory neuron
inhibitory neuron inhibits original stimulating neuron
target neuron fires but then stops
what is disinhibition
inhibitory neuron is inhibited by another neuron
decreased inhibition occurs on target neuron, allowing it to fire
what is feedback disinhibition
secondary inhibitory neuron is stimulated by target neuron firing
inhibits that primary inhibitory neuron of target neuron
target neuron is able to continue firing
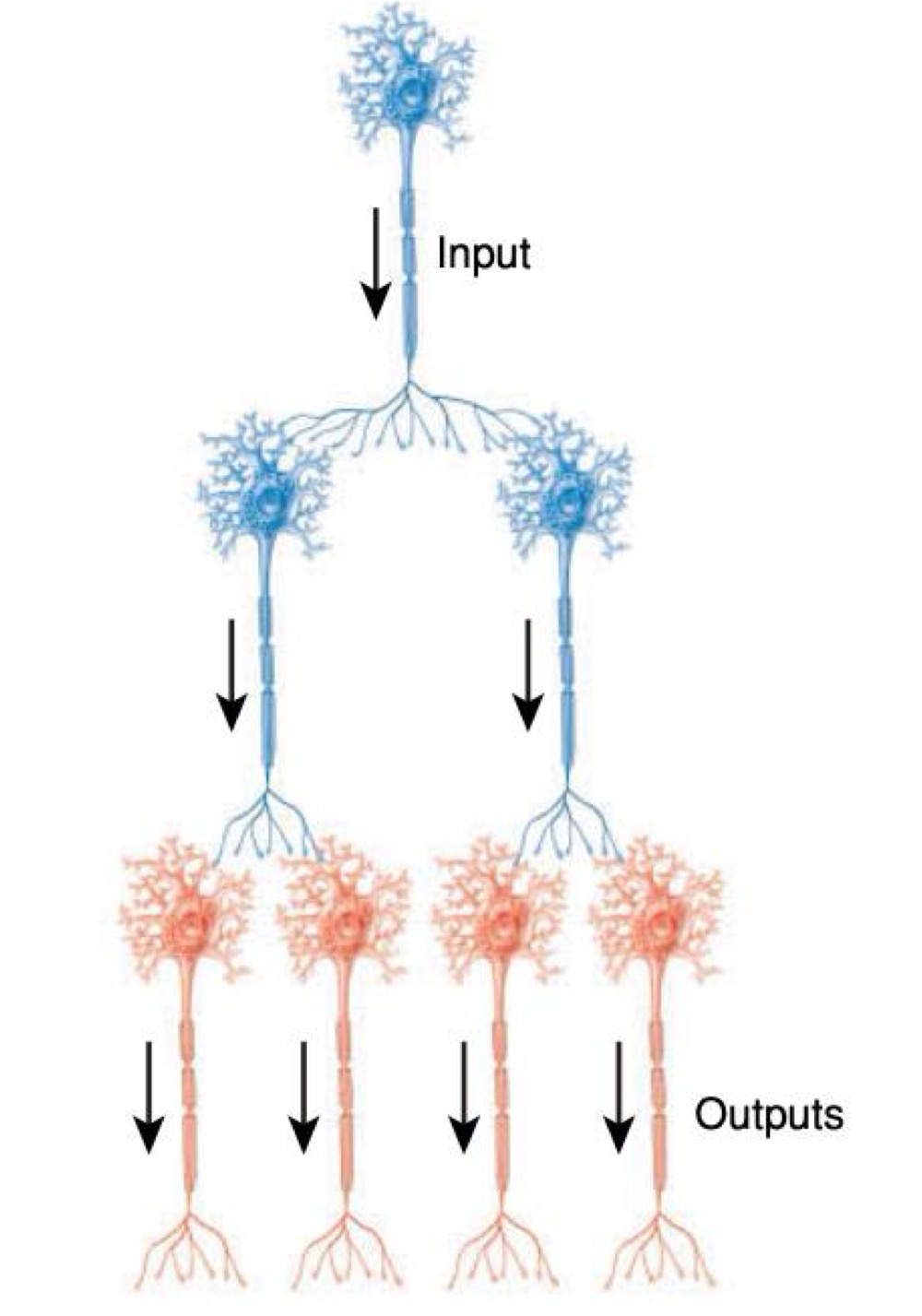
what kind of neural circuit is this
diverging circuit
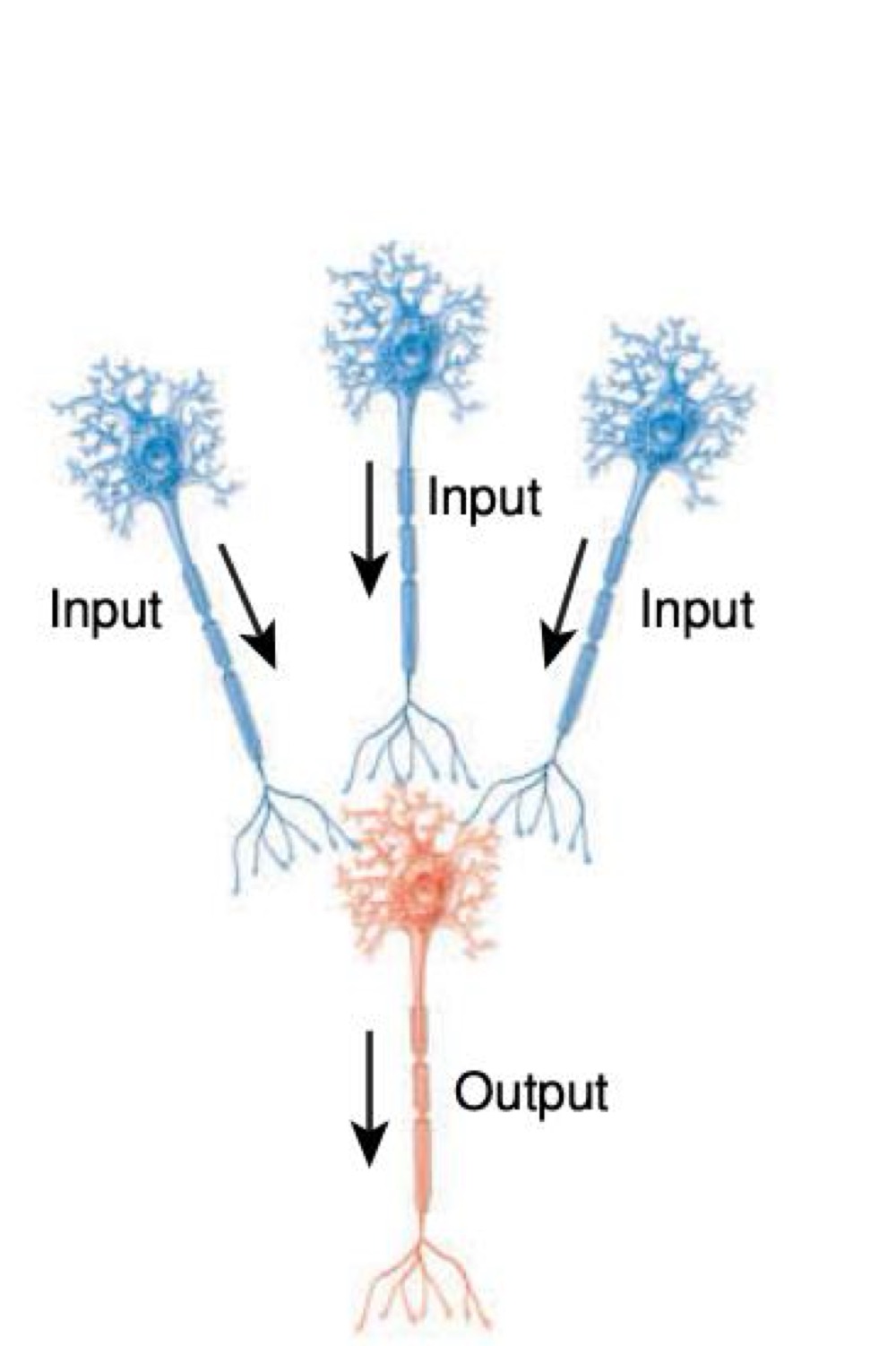
what kind of neural circuit is this
converging circuit
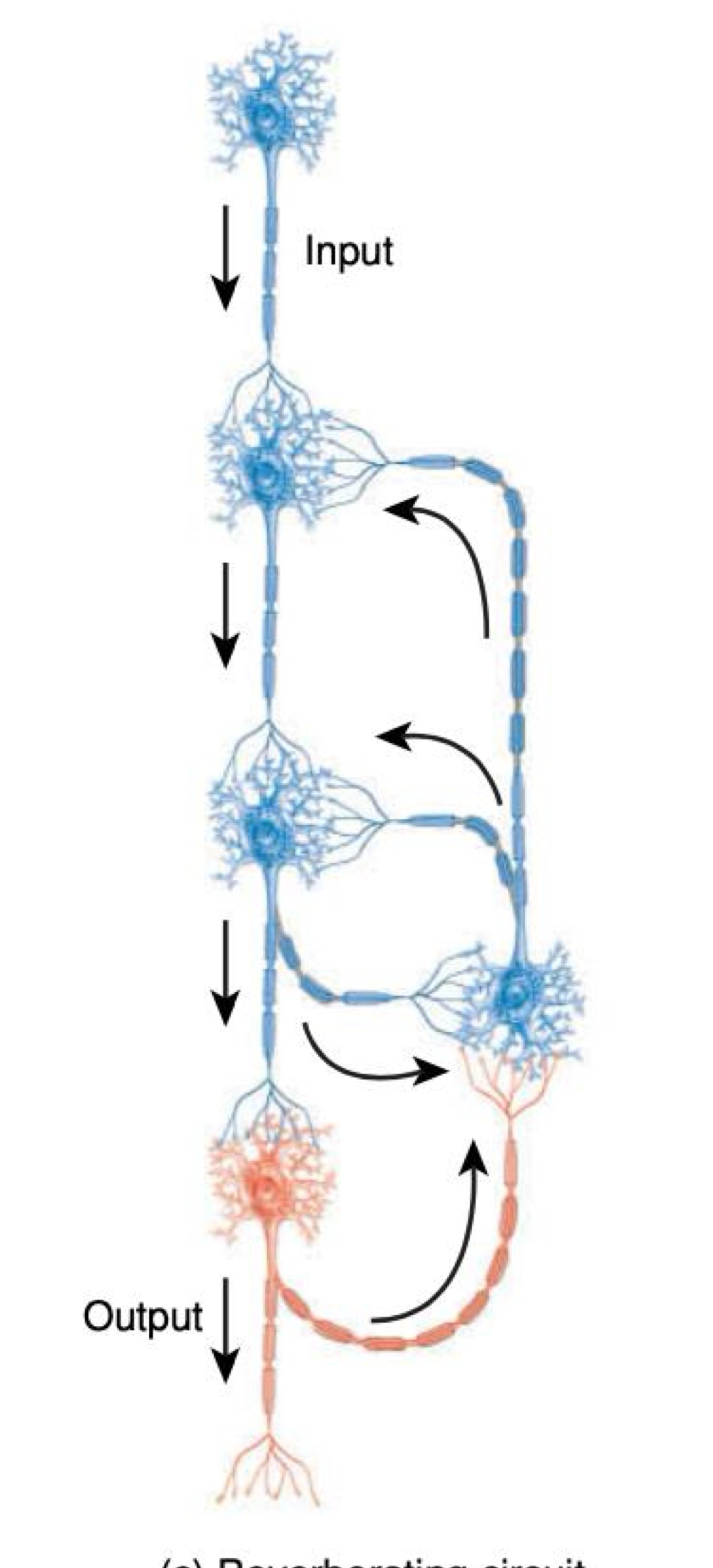
what kind of neural circuit is this
reverberating circuit
what sensory receptor senses vibration and deep pressure
pacinian
what sensory receptor senses stretch and joint position
ruffini
what sensory receptor senses fine touch or discriminatory touch
meissner
what sensory receptor senses light pressure
merkel disk
what sensory receptor senses light touch and direction
hair follicle receptor
what sensory receptor senses pain
free nerve ending
what sensory receptor senses temperature
free nerve ending
what sensory receptor senses stretch
muscle spindle
what sensory receptor senses tension
golgi tendon organ
what pain nerve fiber is this quickest
A alpha/ Ia
waht pain nerve fiber is this slowest
C/IV
what are examples of rapidly adapting sensory fibers
pacinian
meissner
hair follicle
free nerve endings
what are examples of slow adapting sensory fibers
merkel
ruffini
muscle spindle
golgi tendon
what is wallerian degeneration
anything past the point of injury gets affected
describe differences between slow and fast axonal transport
slow conveys axoplasm in one direction only
fast conveys axoplasm in two directions