Ectopic pregnancy
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
Ectopic pregnancy
An ectopic pregnancy is the implantation of an embryo outside the uterus.
Tubal, ovarian, cervical, abdominal, histerotropic, c section scar
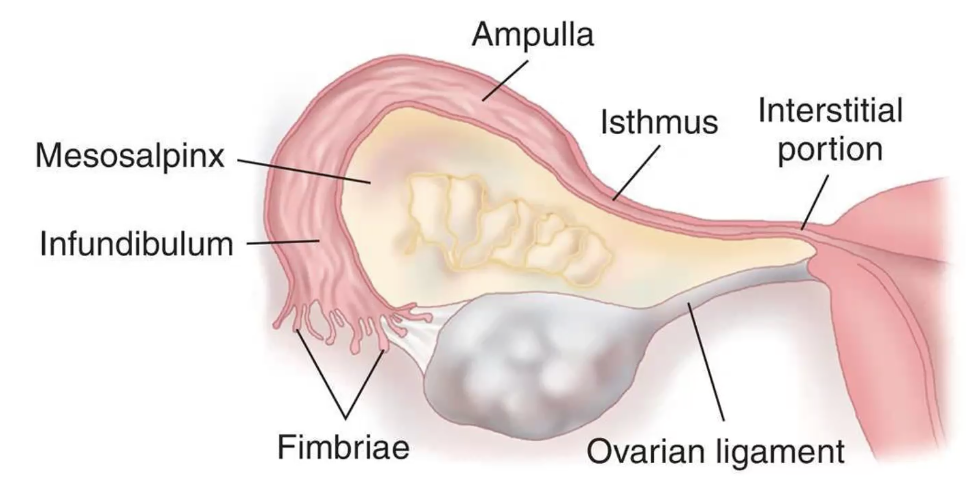
Porciones de la trompa
Sitio más común de embarazo ectópico
Trompa (90%)
Ectopic pregnancy can lead to …
Tubal rupture
Massive intra-abdominal hemorrhage > death
Tubal damage (reproductive outcome)
It is the leading pregnancy-related cause of death in the first trimester.
With reliable serum pregnancy tests and vaginal ultrasound, early detection and treatment can be posible.
Etiology
• Abnormality of fallopian tubes
• Loss of fimbrial, lumen and ciliated mucosa integrity
• Pelvic inflammatory disease
• Tubal surgery
• Infertility and assisted reproductive techniques
• Cigarette smoking
• Pregnancy with an Intrauterine Device IUD in place (DIU de cobre)
• Congenital defects of the tubes
¿Cuál es el sitio más común del embarazo ectópico?
Ampullar
95% of ectopic pregnancies occur in the:
Fallopian tubes
5% of ectopic pregnancies occur in the:
• Ovaries (3%)
• Peritoneal cavity (1%)
• Cervical
• C section scar
In the Fallopian tubes:
Ampulla (74%).
Isthmus (12%).
Fimbrial end of the tube (12%).
Interstitium (2%).
Signs and symptoms
Vaginal bleeding
Abdominal pain
Unilateral pelvic
Associated with shoulder pain
Dizziness
Fainting
Palpitations from hypotension due to intra-abdominal hemorrhage
Lower uterine hCG level that may not be detected in the urine test
Physical examination when there is tubal rupture:
Hypotension
Tachycardia
Abdominal distension due to hemoperitoneum
Signs of acute abdomen present with:
Guarding
Rebound tenderness
Cervical motion tenderness
Physical examination in the absence of rupture:
• Physical exam can be normal
• Cannot diagnose rupture of ectopic pregnancy
• Diagnostic tests needed
• Presence of anexial mass
Diagnostic tests
Transvaginal ultrasound
• Rules out the presence of an intrauterine pregnancy
Human chorionic gonadotropin: discriminatory zone (2,000 mlU/mL)
Dilation and curettage
Serial hCG testing
Laparoscopy
Serum progesterone levels
Vaginal ultrasound
• 15-35% are not seen on ultrasound
• Suspicious signs
• Empty uterus, thick endometrium
• Presence of intrauterine pseudosac
• Sign of double halo in the tube
• Visualization of gestational sac outside the uterus with yolk vesicle
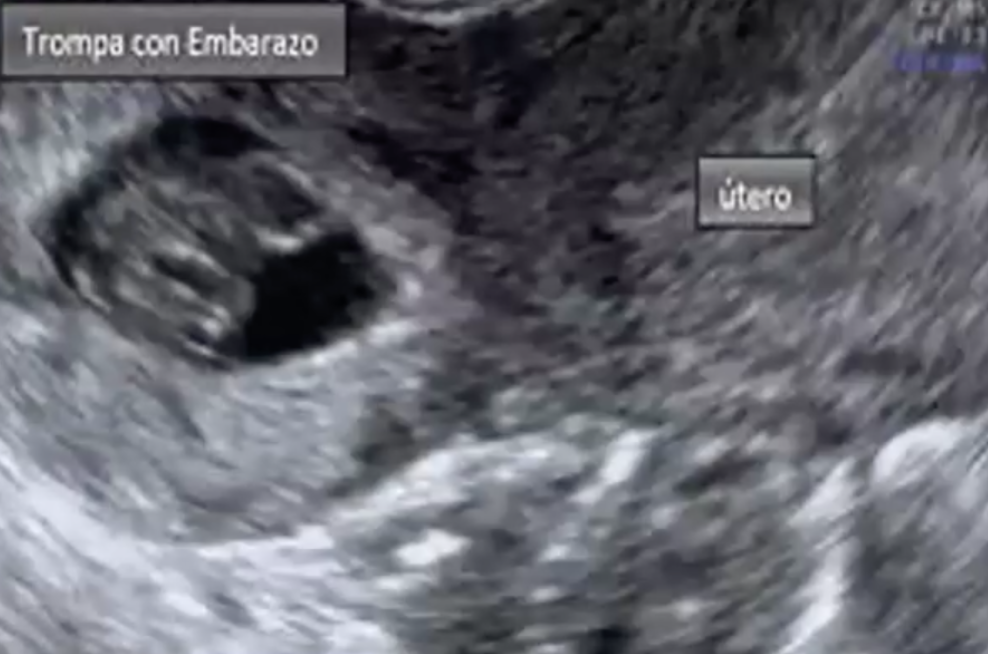
Ectopic pregnancy
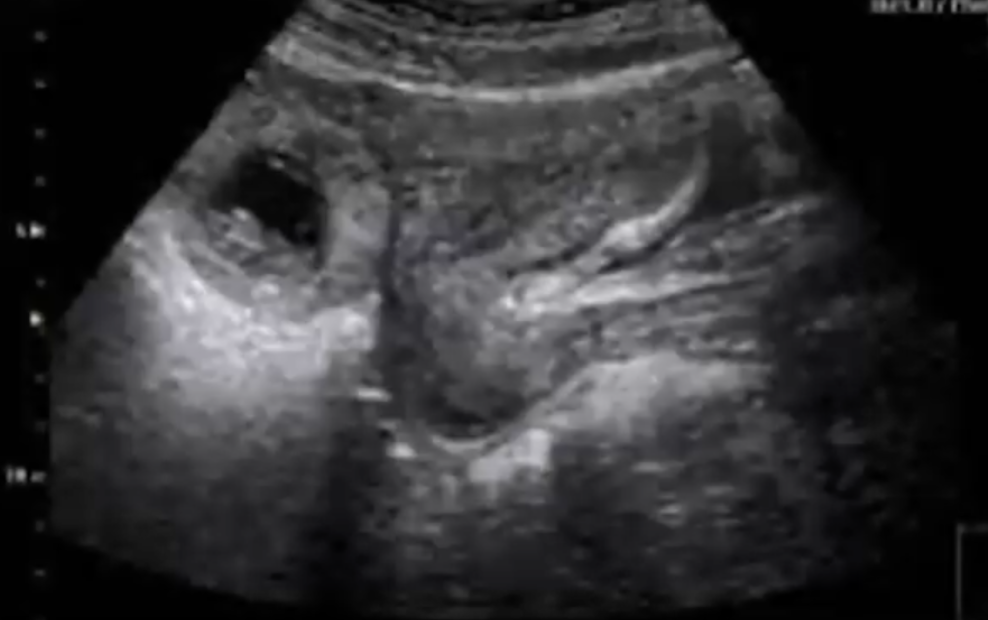
Ectopic pregnancy
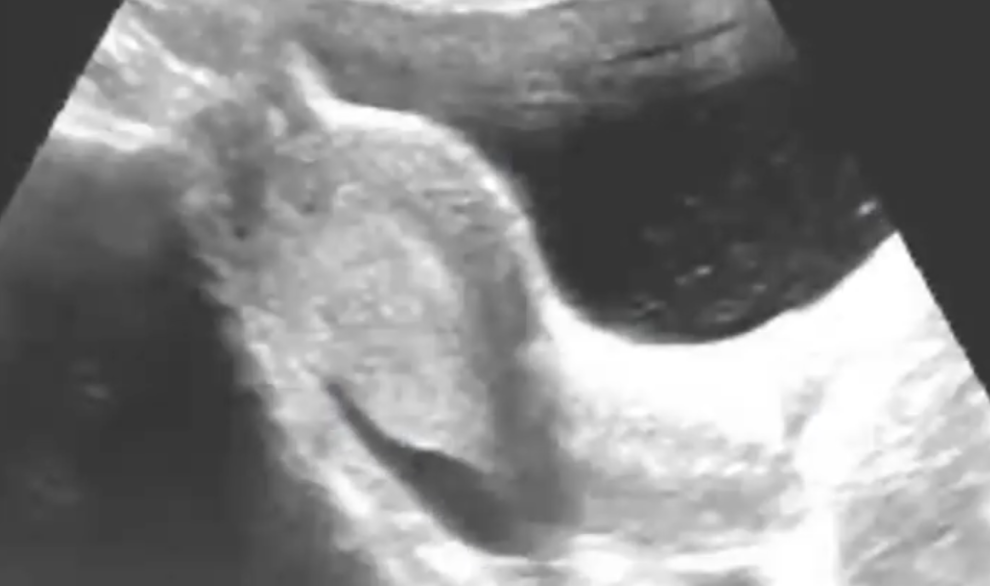
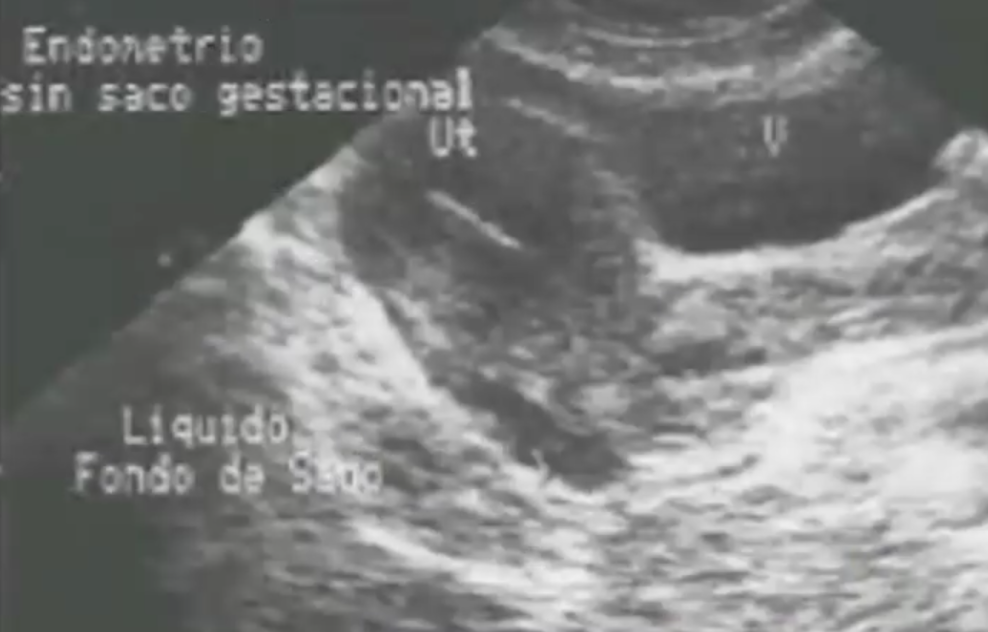
Free fluid in pelvis: inflammatory process
HCG
• Serial determination of the beta fraction
• Produced by trophoblast cells
• Doubles value every 2 days
• Minor increase is suggestive of non-viable pregnancy (miscarriage or ectopic).
When ectopic pregnancy is suspected and inconclusive with US:
perform serial determination (pedir cada 2 días)
HCG B values > 1,000 - 2,000 mU, not visible on US:
High probability of ectopic embryo
Culdocentesis
Diagnostic technique for ectopic pregnancy
Identifying the presence of unclotted blood
Methotrexate
• Folic acid antagonist
• Inhibits de novo synthesis of purines and pyrimidines
• Interferes with DNA synthesis and cell multiplication.
• Trophoblast: tissue vulnerable to methotrexate.
Methotrexate exclusion criteria
• Previous severe renal or hepatic disease.
• Abnormality in hemogram (leukocytes < 2,000, platelets < 100,000, creatinine > 1.5)
• Treatment with NSAIDs or diuretics
Methotrexate inclusion criteria
• Hemodynamically stable
• No rupture of the ectopic pregnancy
• Maximum egg diameter not greater than 4 cm.
• Bhcg less than 5,000- 10,000 mU
• Presence of heartbeat makes it less successful.
Surgical treatment options
Salpingostomy
Salpingotomy: quitar y reparar embarazo ectópico
Salpingectomy: quitar la trompa
Cornual resection: embarazo intersticial
Oophorectomy: embarazo ovárico
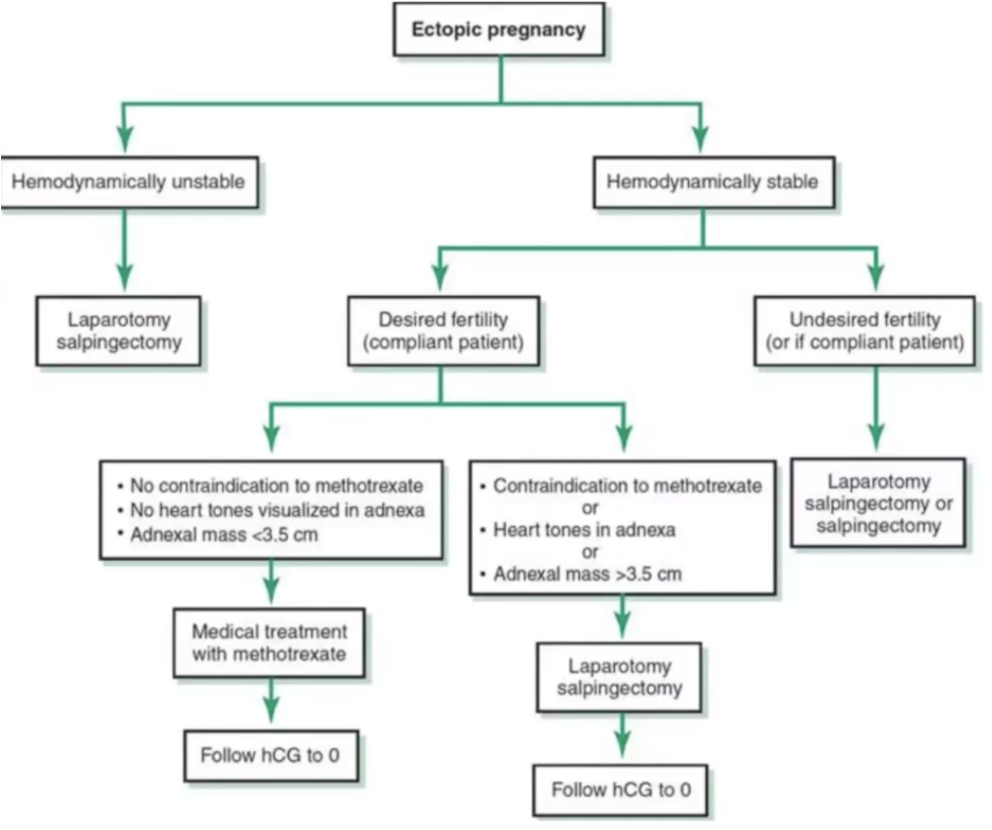
Algoritmo
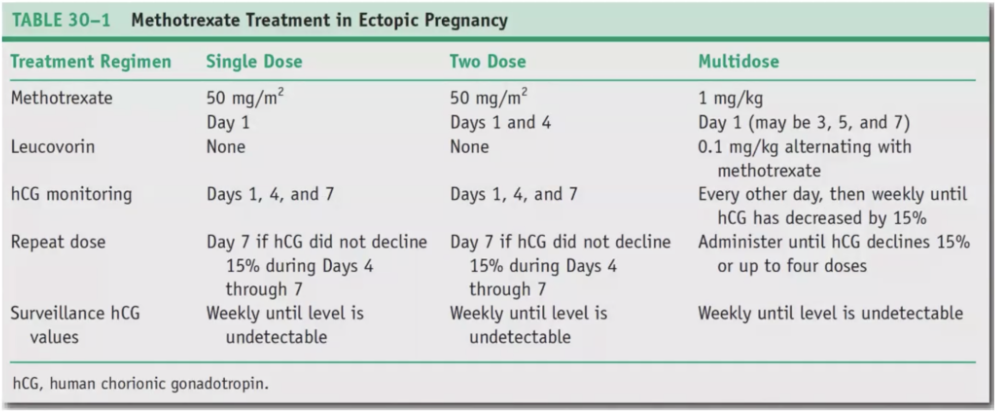
Methotrexate treatment doses
Surgical treatment
• Solves the problem definitively
• Previously considered gold standard
• Patients who do not meet the criteria for medical therapy
• Ruptured or suspected ruptured ectopic pregnancy.
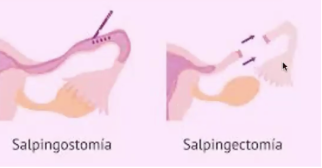
Surgical approach
Salpingectomy
Tubal rupture and hypovolemic shock data
Linear salpingostomy
Clinically stable patients
Interstitial pregnancy
• Pregnancy implants within the tubal segment that lies within the muscular uterine wall.
• Usually rupture following 8-16 weeks of amenorrhea
• Because of the proximity of these pregnancies to the uterine and ovarian arteries hemorrhage can be severe and associated with higher mortality rates.
Interstitial pregnancy management
Cornual resection
Cornuostomy
Abdominal pregnancy
• Implantation in the peritoneal cavity of tubal, ovarian or intraligamentary pregnancy.
• Secondary to rupture of the salpingeum or miscarriage.
Abdominal pregnancy diagnosis
• Abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting
• Hemorrhage
• Fetal movements, reduced or absent.
• Increase in maternal serum protein fetus.
• US: Frequent but nonspecific oligohydramnios. Fetal head adjacent to maternal bladder.
Abdominal pregnancy approach if diagnosed after 24 weeks:
Expectant until the fetus is viable.
Abdominal pregnancy approach if diagnosed before 24 weeks:
Pregnancy interruption at the diagnosis time
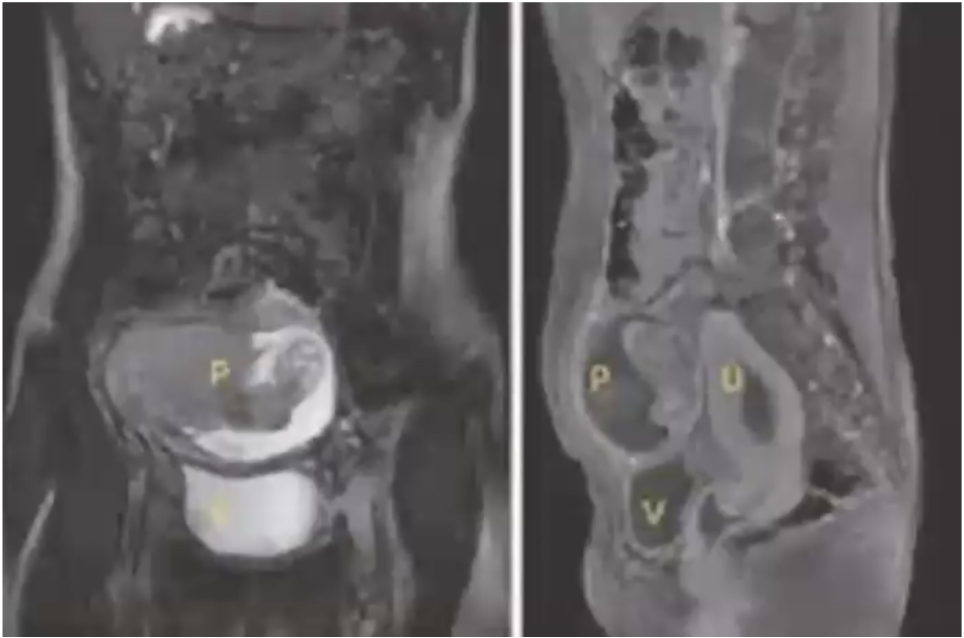
Abdominal pregnancy
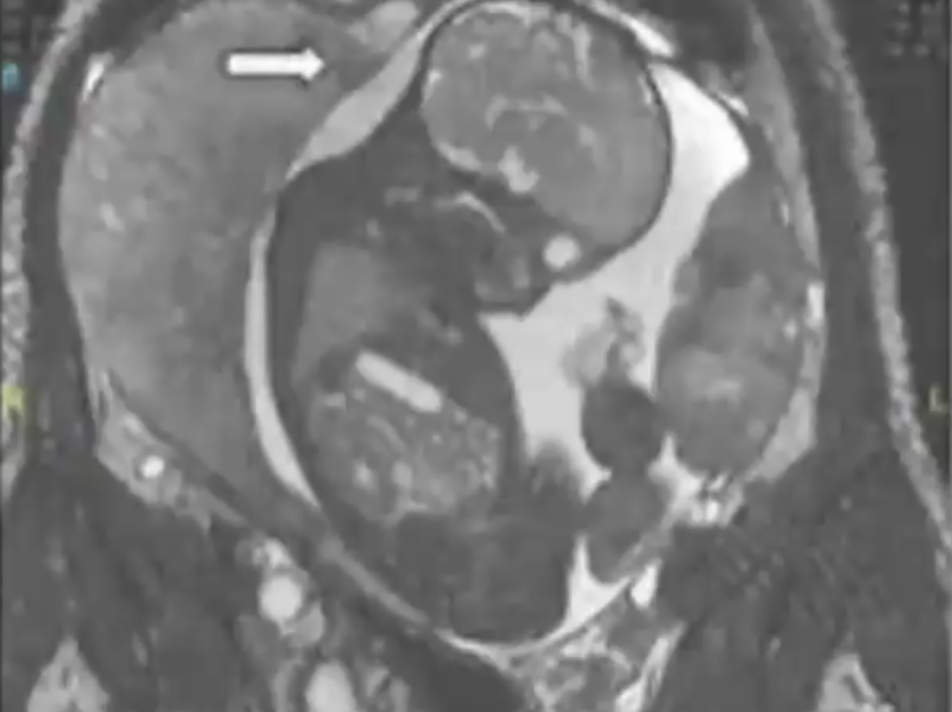
Abdominal pregnancy