Post Op Care and Surgical Complications PT2
1/62
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
63 Terms
AKI
due to shock, sepsis, hypovolemia, bleeding, toxins, CV failure, or urinary retention
common form of post op kidney dysfunction
ATN
MCC of ATN leading to post-op kidney dysfunction
poor perfusion
AKI diagnostics
BUN/Cr
AKI treatment
-if poor perfusion or hypovolemic: fluids
-if retention: remove obstruction
Seroma
collection of serous fluid that delays healing and increases infection
Seroma treatment
compression dressing or needle aspiration
Hematoma
collection of blood and clot due to inadequate hemostasis
Hematoma RFs
-history of coagulopathy
-anticoagulation therapy
hematoma treatment
-if small: leave alone
-if large: evacuate, ligation, reclose
_______ hematomas can cause airway compromise
neck
Patient Surg Site Infection RFs
-age
-nutritional status
-DM
-smoking
-obesity
-coexistent infection
-altered immune system
Operative Surg Site Infection RFs
-antiseptic prep
-antimicrobial prophylaxis
-duration of surgery
-venting of OR
-use of foreign material
-surgical site
-surgical technique
Surg Site Infection Treatment
-if mild: abxs
-if moderate: open wound irrigation or debridement
-if severe: go back to OR for exploration, washout, and drainage
-remove involved implanted material
Dehiscence
-partial or total disruption of any layer of the wound
-MC on POD 5-8
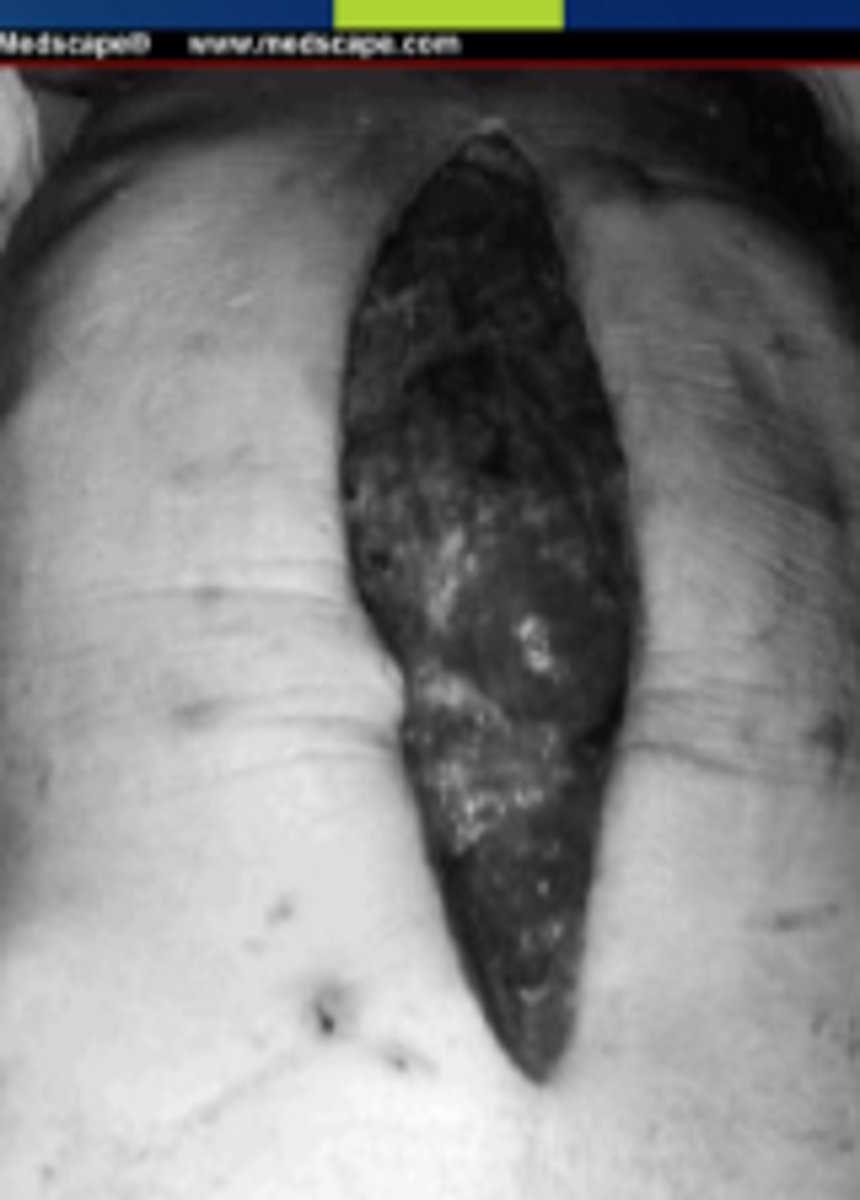
Evisceration
total dehiscence and extrusion of the viscera
Dehiscence Increased RFs
->60 yo
-DM
-uremia
-sepsis
-steroid use
-immunosuppression
-poor nutritional status
-obesity
-smoking
Dehiscence Local RFs
-inadequate wound closure
-increased intra-abdominal pressure
-deficient wound healing
earliest sign of dehiscence
serosanguineous drainage
VTE/DVT/PE RFs
-Virchows triad
-prolonged immobilization
-cancer
-surgery
-dissections of pelvis
VTE/DVT/PE Prevention
-anticoagulation
-compression stockings
-pneumatic compression devices
-early ambulation
VTE/DVT/PE Diagnostics
-CBC, CMP, ABG, coag studies
-venous doppler
-CTA for PE
-EKG
VTE/DVT/PE treatment
anticoagulation (heparin/LMWH, NOACs, warfarin)
**prophylaxis can be used for mod-high risk VTE 2 hrs prior then post op
those who develop VTE from surgery alone should be on anticoagulation therapy for ________ following the incident
3 months
Ileus/Pseudo-Obstruction
-MC after major GI surgeries due to anesthesia and manipulation
-meds, electrolyte abnormalities, inflammatory conditions, pain, and type of surgery influence risk
peristalsis after non-abdominal surgery returns within _______
24 hours
peristalsis after laparotomy returns within __________
48 hours
illeus/pseudo-obstruction diagnostics
CBC, CMP, KUB
Ileus/ Pseudo-Obstruction Treatment
-NPO
-electrolyte correction
-NG tube decompression if obstruction
Constipation post op most commonly occurs due to ____ ___
opioid use
CVA
most commonly thromboembolic occuring within 72 hours post-op
CVA RFs
-type of surgery
-hx of: CVA, afib, valve disease, HTN, CAD, COPD, etc
-advanced age
-cancer
-smoking
-intraoperative HoTN
-discontinuation of anticoag therapy
CVA S/S
-facial droop
-mental status changes
-extremity weakness
-slurred speech
CVA Diagnostics
-non contrast head CT
-CBC, BMP
-EKG, Echo
Paraplegia
-caused by spinal cord ischemia
-surgery/ manipulation of descending thoracic aorta poses most risk
surgeries involving the deep pelvis (ex. proctectomy, hysterectomy) resulting in hypoperfusion or injury of certain nerves pose the most risk for ______
sexual dysfunction
MI RFs
-history of CHF
-preop cardiac ischemia
-advanced age
-surgeries for atherosclerotic disease
-HoTN
-hypoxemia
MI diagnostics
-cardiac enzymes
-EKG
MI Treatment
-PCI
-fibrinolysis
-CABG
most common post-op heart failure
left ventricular
Heart Failure Etiology
-fluid overload
-post-op MI
-dysarhythmias
Heart Failure Diagnostics
-BNP, ABG
-EKG, Echo, CXR
-pulmonary wedge pressure
Heart Failure Treatment
-diuretics
-nitroprusside
-ACE
-beta blocker
Dysrhythmias
-appear during surgery or within the first 3 post-op days
-MC: A fib and flutter
MC cause of dysrhythmias intra-op
general anesthesia
MC causes of dysrhythmias post-op
-electrolyte abnormalities
-hypoxemia
-stress
-MI
Dysrhythmia Diagnostics
-CBC, BMP
-EKG
Dysrhythmia Treatment
-meds
-cardioversion
-defibrillation
Central Venous Line Complications
-pneumothorax
-line infection
-air embolus
prevention of central venous line complications
US guidance and sterile technique
Pulmonary Artery Catheters
-most common type is Swan-Ganz catheter
-indications: cardiogenic shock, ventricular failure, HF, etc
-CIs: routine pulm cath in high risk pt or non-cardiac pt
Pulmonary Artery Catheter Complications
-cardiac perforation
-intracardiac knotting of the catheter
-dysrhythmias
-pulmonary hemorrhage
-air embolus
Pulmonary Artery Catheter Complication Prevention
-careful placement
-advancing under continuous pressure monitoring
-checking position of tip before inflation
_____ prevent accumulation of fluid
drains
Drain Complications
-infection
-perforation of viscera or vessels
-fistula formation
-bleeding
Retained Foreign Bodies
-almost always requires re-operation
-exs: sponges and instruments
Retained FB Prevention
formal sponge and instrument counts before surgery and before closing
superficial parotidectomy poses threat of direct injury to ________
facial nerve
carotid endarterectomy poses threat of direct injury to __________
hypoglossal nerve
thyroidectomy poses threat of direct injury to ___________
recurrent laryngeal nerve
prostatectomy poses threat of direct injury to ___________
pelvic splanchnic nerves
inguinal herniorrhaphy poses threat of direct injury to __________
ilioinguinal nerve
mastectomy poses threat of direct injury to ________ and __________
long thoracic and thoracodorsal nerves