Anatomy Unit 3
1/89
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Neurons
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
90 Terms
Central Nervous System (CNS)
Brain and Spinal Cord
Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
Cranial, Spinal Nerves & Gangllia
Sensory Nervous System
(Afferent) Carries intro & detects change in environment
Motor
(Efferent) Responds to info and initiates nerve impulse to react to change
Motor Somatic
Voluntary Contraction of skeleton
Motor Autonomic
Involuntary smooth & cardiac muscle
Sensory Somatic
Touch,pain, change in temp
Sensory Visceral
Involuntary mvmnt of blood vessels and organs
Dendrite
Recieves nerve impulses and carries it to the rest of the body
Axon
Transmits nerve impulses away from the cell body
Axon hillock
transmits impulses
What type of neuron is a motornueron
multipolar
What type of neuron is sensory neuron
Unipolar
What type of neuron transmits sensory receptors to the CNS
sensory
What type of neuron transmits impulses to the muscles
motor
Nerve
Bundles of nerve fibers in PNS (white matter)
Tract
Bundles of nerve fibers within CNS (white matter)
White matter
Inner brain, sends signals quicker
Grey matter
outter brain, unmyelinated
Ganglia
Cell bodies in group
Action potential
Electrical signals that travel down axon
Dura mater
keeps brain in place
Dural sinus
drains blood
Arachnoid mater
loose fibrous tissue
Cerebral cortex
superficial gray matter
Frontal lobe
voluntary motor, personality, decisions, planning
Parietal lobe
sensory functions, processing, touch, balance
Occipital
Hearing and smell
Temporal
Visual info, stores memories
Isula
Emotional response
Primary motor cortex
Planning and exectuing voluntary movments
Premotor area
complex and repetitive movments
Primary somatosensory
Interprets touch, pina, pressure, temperature
Somatosensory
helps to determine shape,texture, pressue, feeling of object
Primary olfactory
sense of smell
Primary gustatoy area
sensation of taste
Prefrontal cortex
intellect, cognition
Motor speech
controls muscles for speech production
Wernikcke’s area
speech comprehension and association
Thalamus
Relays signals
Hypothalamus
Regulates body temp, emotional behavior
Cerebelllum
motor control os subconscious movement
Nerve
bundles of axons from nuerons
olefactory
sense of smell
optic
vision, sense of sight
Oculomotor Nerve
eyeball movement & eyelid muscles
Trochlear nerve
moves rectus eye muscles
Trigeminal nerve
Sensation of face & chewing muscles
Abducens
Controls lateral rectus eye muscles
Facial
Taste, face, tear and saliva glands
Vestibulocochlear
Auditory and Balance
Glossopharyngeal
Taste,swalling and saliva
Vagus
Sensation of organs
Hypoglossal nerve
tongue muscles, swallowing and talking
Clauda Equina
Nerve roots, extends to coccyx
Conus Medullaris
Where spinal cord tapers to an end
Filum Terminale
Thin stand of pia mater
Horn
Cell bodies & dendrites in spinal cord
Column
Bundles of myelinated fibers in spinal cord
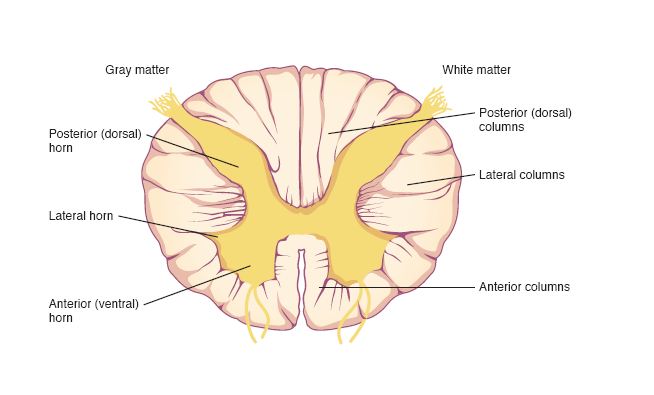
Posterior white column
sends info to brain
Anterior and lateral white columns
Transmits info to / away the brain
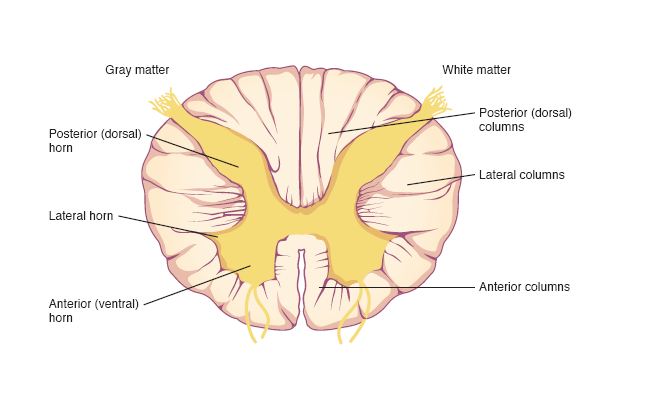
Posterior gray horn
Sends info to/away brain
Posterior gray horn
sends infro to brain
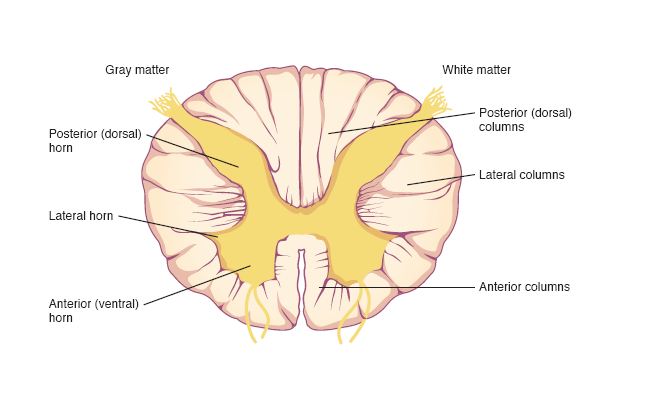
Lateral gray horn
innervates cardiac muscle
anterior gray horn
innervates skeletal muscle
Autonomic
Involuntary muscle function
Sympathetic Nervous System
Fight or Flight- prepares body for physical action
Parasympathetic
Rest and digest- controls involuntary bodily function, slows HR, lowers, BP and stimulates digestion
Long ganglionic
brainstem to ganglia
Short ganglionic
ganglia to tissue
Preganglionic cells
Cell in CNS to ganglia
Postganglionic cells
Cell in ganglia and body
Visceral
voluntray- controlled by somatic NS, acts on skeletal muscle
Somatic
involuntrary- controlled by autnomic NS, acts on smooth muscle and cardias
Viseral reflexes
Regulates internal organs to maintain a stable enviornment/homeostasis
Mechanoreceptors
Responds to touch and hearing
Thermoreceptors
Detects changes in temperature
Photoreceptors
Responds to light
Chemoreceptors
Percieves presence of taste and smell
Nocireceptors
Senses harmful stimuli like tissue injury
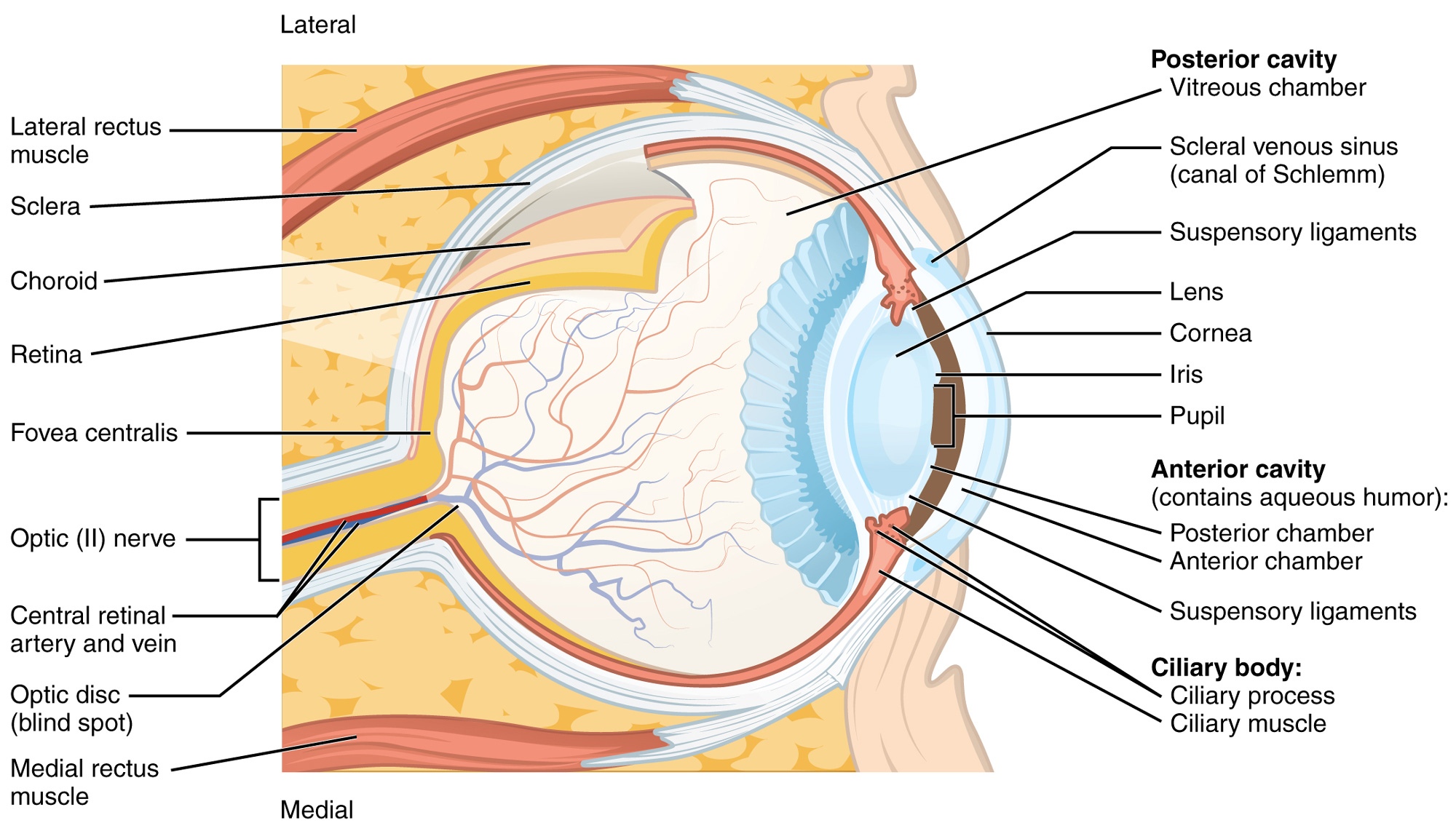
Sclera
covers posterior eye, protects eyes
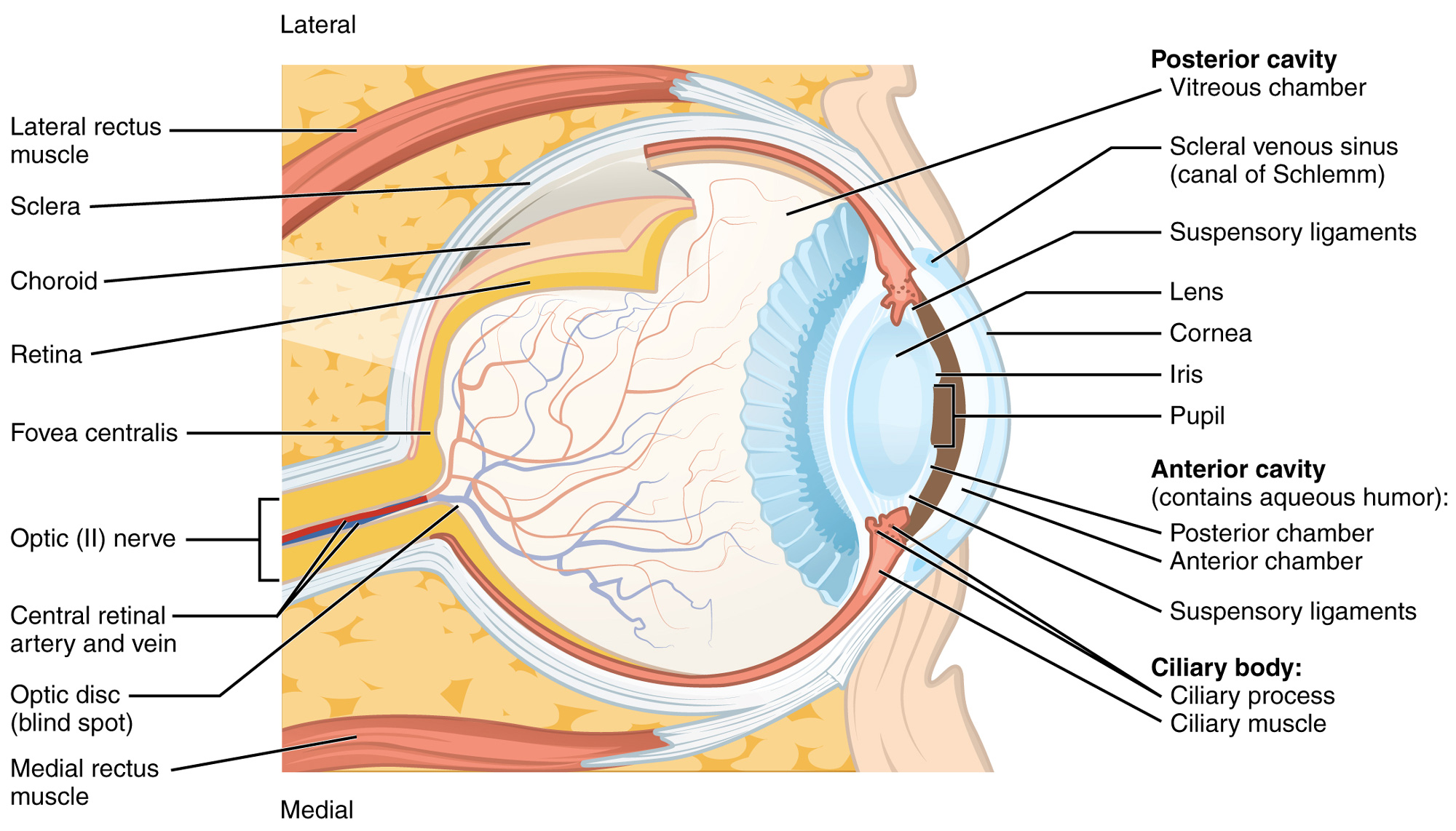
Cornea
allows passage of ligt
Choroid
Posterior dark brown mem, supplies blood
Iris
colored part that regulates amount of light being enetered with muscles
lens
allows precise focusing of light,
Aqueous humor
removes waste products
Vitreous humor
transmits light, holds lens and shape of eye
Rods
responds to dim light; peripheral vision
Cones
bright light, colored vision
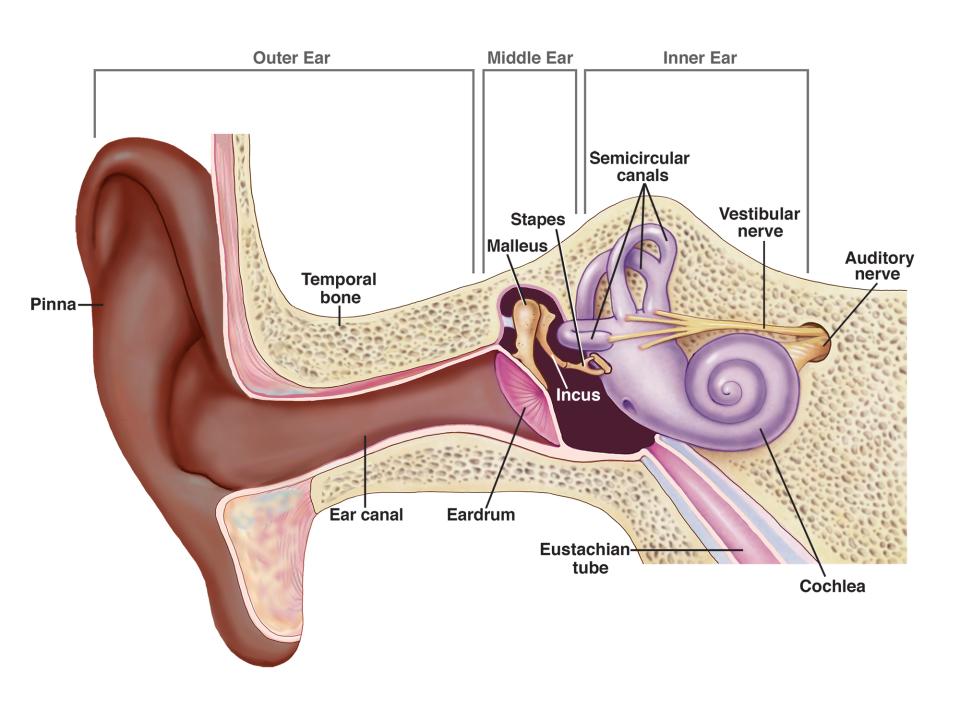
Vestibule
balance and spatial orientation