Unit 11 Genetics quiz science
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
14 Terms
Introns
Parts of a gene that are cut out of the mRNA before it's used to make a protein.
Extrons
Parts of a gene that are kept in the mRNA and contain the instructions for making a protein.
A codon is a three-nucleotide sequence on RNA?DNA that codes for an amino acid, while an anticodon is a complementary three-nucleotide sequence on tRNA
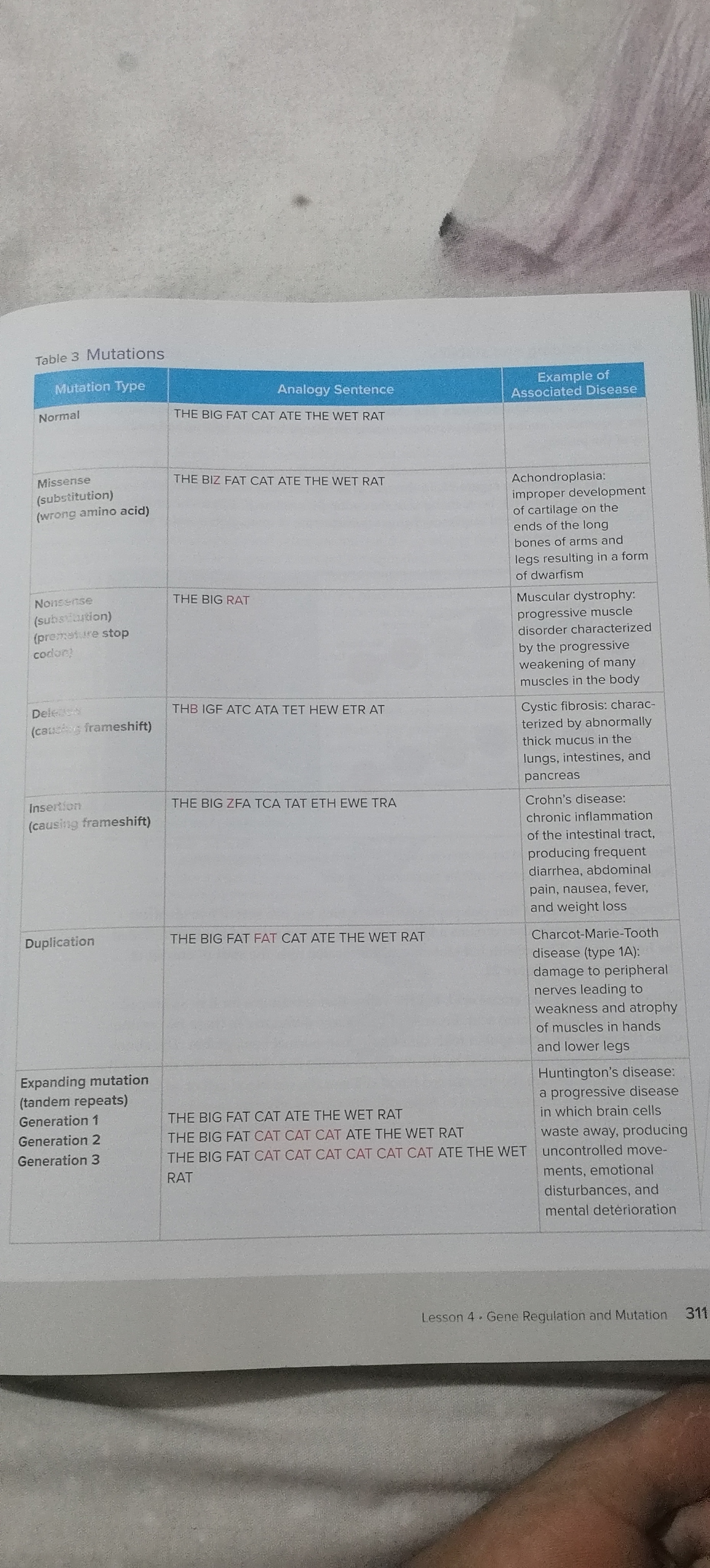
Contast RNA and DNA
RNA differs from DNA in that it is usually single-stranded, contains ribose sugar instead of deoxyribose, and uses uracil in place of thymine.
Describe protein synthesis
Simplified;
Transcription: DNA code is copied to mRNA in the nucleus.
Translation: mRNA code is read to make proteins in the ribosome.
Detailified😂😂:
Transcription occurs in the nucleus. DNA's information is copied into messenger RNA (mRNA). RNA polymerase binds to DNA, unwinds it, and synthesizes mRNA using complementary base pairing (A with U, G with C). This mRNA molecule then carries the genetic code from the nucleus to the cytoplasm.
Translation takes place in the cytoplasm at ribosomes. Here, mRNA binds to a ribosome. Transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules, each carrying a specific amino acid, recognize mRNA codons (three-nucleotide sequences) and bring the corresponding amino acids. These amino acids are joined by peptide bonds, forming a polypeptide chain. This chain folds into a functional protein. The process continues until a stop codon is reached, and the protein is released.
Explain what an operon is and how it functions
In genetics, an operon is a functioning unit of DNA containing a cluster of genes under the control of a single promoter. It's a clever way for bacteria to control the production of proteins involved in a specific process, like digesting a certain sugar.
An operon includes:
Promoter: Where RNA polymerase binds to start transcription.
Operator: A "switch" where a regulatory protein can bind.
Genes: The DNA sequences that code for the proteins.
When the regulatory protein (a repressor) binds to the operator, it blocks RNA polymerase, and transcription is turned OFF. When the repressor is absent or inactived (i.e when lactose stops the repressor from working by attaching to it and changing its shape, ), RNA polymerase can bind to the promoter, and the genes are transcribed, turning the operon ON. This allows bacteria to respond quickly to changes in their environment.