Work and Energy
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
relation b/w work and energy
work done by a force on an object (process of energy transfer) = energy the force gives/takes away from the object (amount of energy transferred)
how work and kinetic energy are related (using a kinematic equation)?
vf2 = vi2 + 2ad
v2 = 2ad
v2 = 2dF/m
v2 = 2W/m
1/2mv2 = W
how net work and kinetic energy are related (using kinematic equation)?
vf2 = vi2 + 2ad
(vf2 - vi2)/2 = ad
Wnet = Fnetd
Wnet = mad
Wnet = m(vf2 - vi2)/2
Wnet = 1/2mvf2 - 1/2mvi2
what is the force from Hooke’s law?
the restorative force, the force from the spring that counteracts the applied force
how is work from a spring determined?
from the area under Hooke’s law curve (F = kx) for applied force
W = Fd
W = 1/2kx2
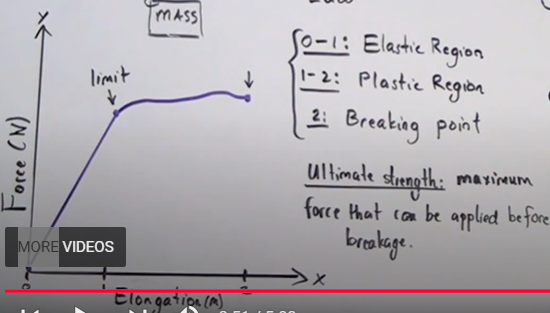
does Hooke’s law apply to the elasticity of solid objects?
only up to the elastic region, once force is released the object moves back to original place, past it (plastic region) Hooke’s law does not uphold (will not reset to original shape)
+ vs - work
force gives energy vs force takes away energy
why nonconservative forces don’t have a PE conterpart?
can’t get that energy back out, usually lost to ie. thermal energy which gets randomly distributed along the surroundings/object
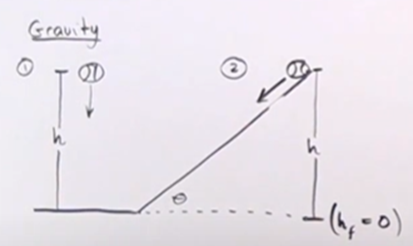
Do both balls have the same amount of work done on them?
yes, the work for 1) is just mgh. for 2) the force is based on mgsin(theta) while distance is based on h/sin(theta), W = Fd so W = mgh
how is a lever and fulcrum mechanically advantageous in trying to lift up an object?
the Fd required to lift up the object is proportionate to the Fd applied to the other side of the fulcrum (W in = W out; FiDi = FoDo), their vertical distances are proportionate based on O/I ratio where input F has to put in more distance to move the object with same output F for lesser distance
T or F, kinetic energy is related to velocity
False, kinetic energy is related to speed, not velocity. an object has the same KE regardless of direction
first law of thermodynamics
accounts for the conservation of mechanical energy, energy is never created nor destroyed, it is merely transferred from one form to another
relation b/w pressure, volume and work (for gas in piston)
when gas expands, work was done by the gas (+), volume of system increases. when gas is compressed,work was done on the gas (-), decreasing volume of system. work was done to change the volume
isochloric process
on P-V graph, volume stays constant while pressure changes, no work is done
isobaric process
on P-V graph, pressure remains constant while volume changes, work can be calculated (W=PV)
why is the net work done relating to the change in an object’s KE important to understand?
allows one to calculate work without knowing the magnitude of the forces acting on an object or the displacement
how pressing the brake pads put the work-energy theorum into practice
the brake pads exert frictional forces doing work against the wheels, causing them ro decelerate, bringing the car to a halt
what is mechanical advantage?
a measure of the increase in force accomplished by using a tool
force exerted on an object by a simple machine/force actually applied on simple machine
how inclines provide mechanical advantage?
they make it easier to lift objects because they distribute the required work over a larger distance, decreasing required force
how pulley’s provide mechanical advantage?
the number of rope attached to the load will evenly distributed the weight through tension forces, but you have to pull the rope equal to the number of rope times the object displacement (each rope has to lose the obejcts displacement)
another way to define efficiency
Wout/Win
(load)(load distance)/(effort)(effort distance)
Carla receives a pogo stick for her 6th birthday. She weighs 40kg and the pogo stick weighs 10kg; it has a spring constant of 2000 N/m. Approximately, she has to compress the spring 0.7m if she wants to jump to a height of 1 meter. What is the transfer of energy?
Carla and the pogo stick need to experience gravitational potential energy of (50)(10)(1) that came from the springs potential energy, also 500J

a) 65m
b) 70m
c) 60m
d) 55m
b) 70m


a) 4.5 N
b) 86N
c) 5.6 N
d) 68 N

c) 5.6 N
A 15 kg barrel is thrown into the air by a 2 m tall man. The barrel passes the mans head with a velocity of 10 m/s, just 0.5 seconds after leaving the ground. What energy is involved to determine total average power?
the work done has been transferred to kinetic energy and potential energy; finding those energies will determine average power
Jeremy is an auto mechanic, and he wants to switch out the shock absorbers on his truck. His truck weighs 2500kg and at rest, the space between the body and tires is 10cm. When he puts in the new shocks, which were originally the same length as the old ones, his truck now sits 20cm above the tires. explain why the ratio is
k2/k1 = x/(x-0.1)
imagine the springs actual length to be 50 cm. The first shock absorber makes it so the spring gets compressed 40 cm, leaving only 10 cm. the new shock absorber makes it so the spring gets compressed 30 cm, leaving only 20 cm. If x is 0.4 m, then the conversion for the new shock would be x-0.1 to get 0.3 m. The force depends on the weight of the truck, which stays constant.