Chapter 22 - Descent with modification
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
Evolution
Change in the genetic makeup of a population over generations (descent with modification).
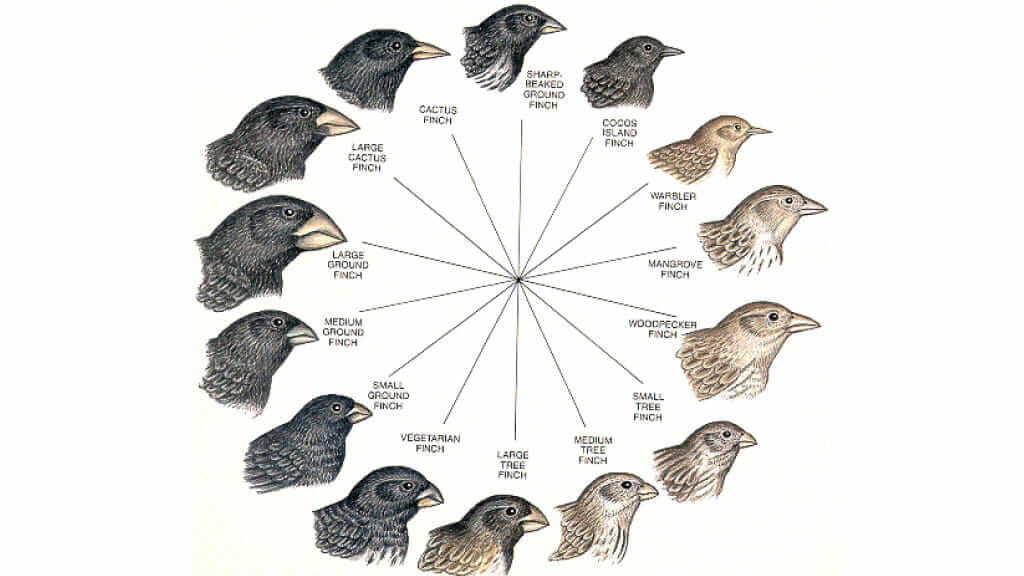
Descent with Modification
All species share common ancestry but diverge over time (darwin’s finches evolved different beak shapes from a common ancestor)
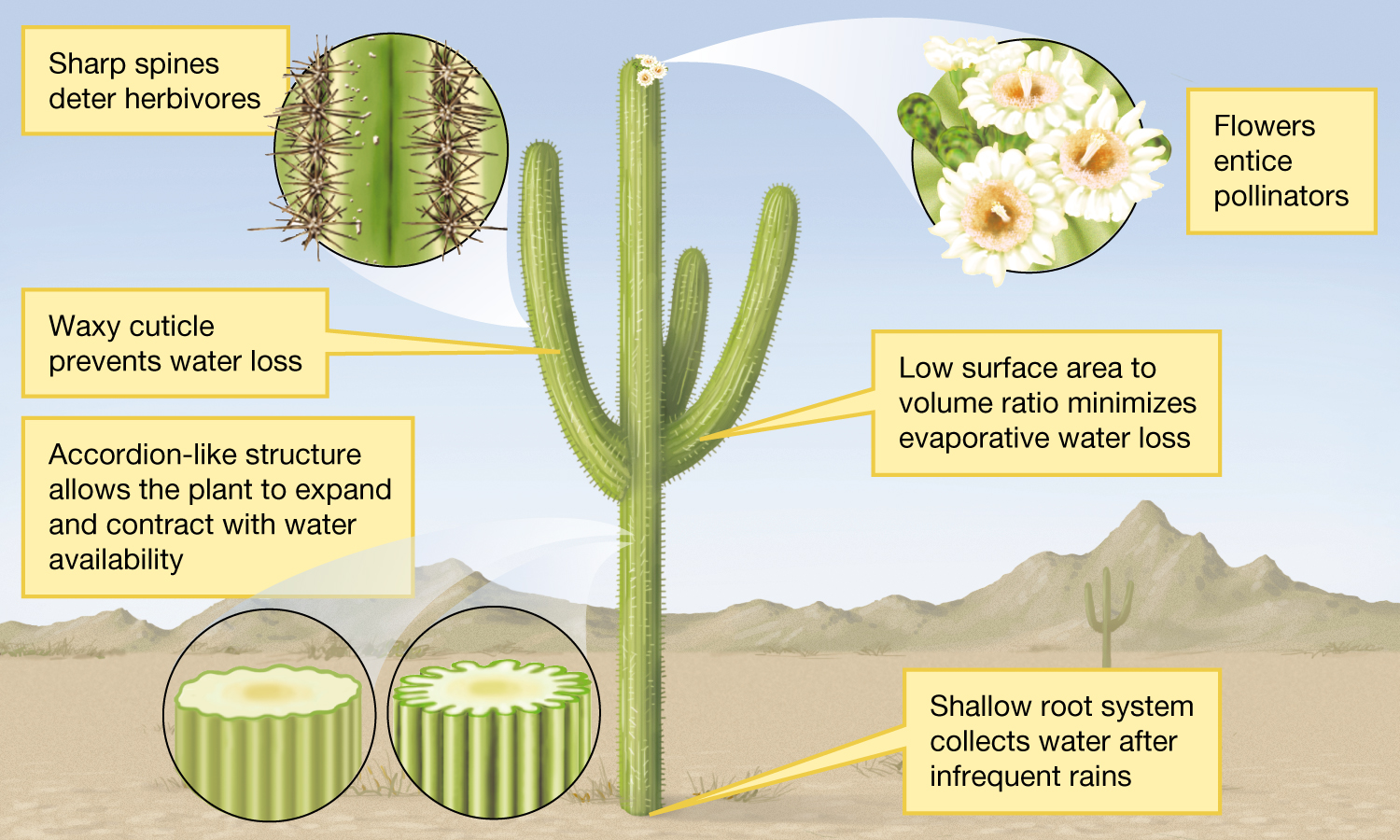
Adaptation
A heritable trait that increases survival or reproduction in a specific environment (cactus spines reduce water loss and protect from herbivores)
Fitness (reproductive success)
The ability to survive and reproduce, passing on genes (faster cheetahs are more likely to catch prey, survive, and raise more offspring)
Darwin’s Observation #1
Members of a population vary in inherited traits (ladybugs differ in spot number and shell color)
Darwin’s Observation #2
Species produce more offspring than the environment can support, so many fail to survive (sea turtles lay 100+ eggs, but few survive)
Darwin’s Inference #1
Individuals with favorable traits leave more offspring (camouflage, powerful jaw)
Darwin’s Inference #2
Favorable traits accumulate in populations over generations (antibiotic resistant bacteria dominate populations)
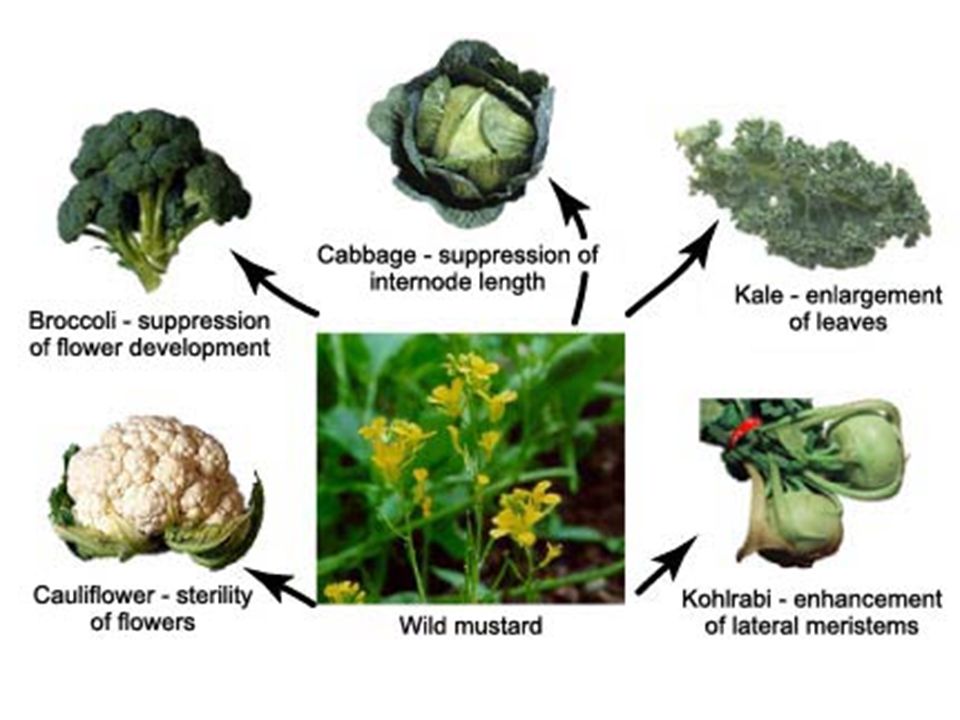
Artificial Selection
Humans intentionally breed individuals with desirable traits (broccoli, cabbage, and kale all bred from wild mustard)
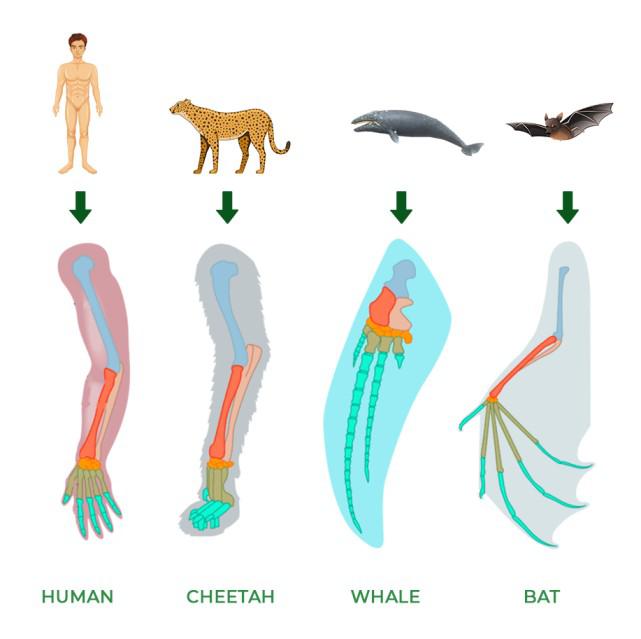
Homology
Similarity from a common ancestor (human arm, cheetah leg, whale flipper, bat wing)
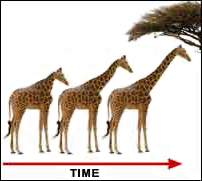
Natural Selection
Individuals with favorable traits survive/reproduce more (giraffes evolving longer necks to reach food)
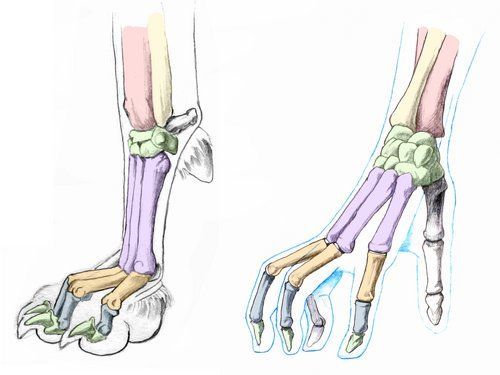
Homologous Structures
Same origin, different functions (cat paw vs human hand)
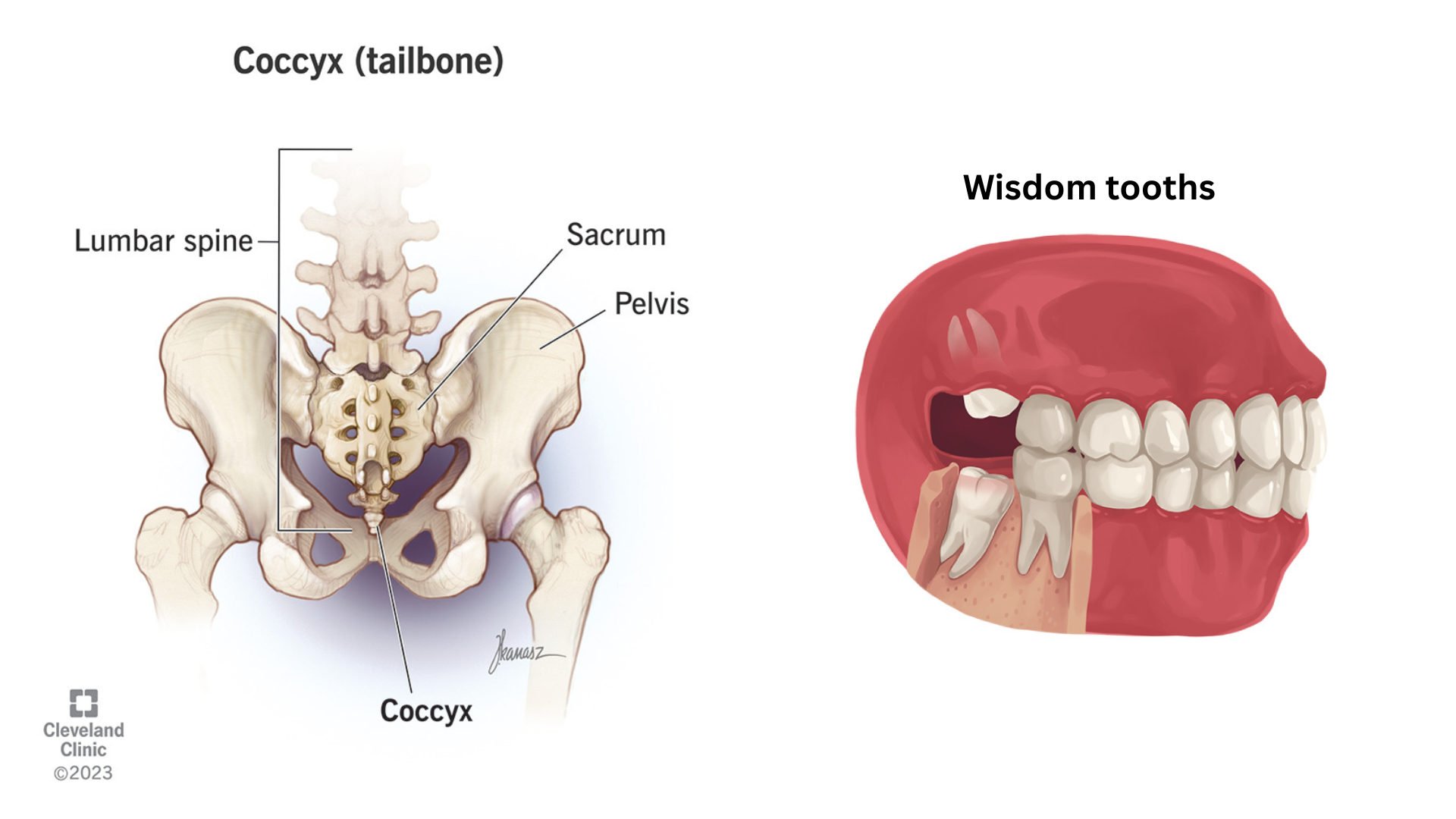
Vestigial Structures
Structures that have no use for function currently, but were at one time in the past (human tailbone, wisdom teeth, whale pelvis)
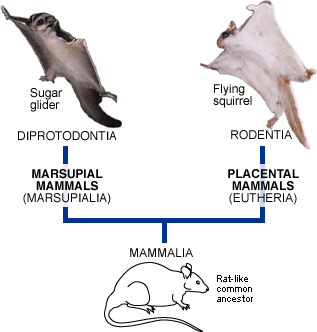
Convergent Evolution
Independent evolution of similar traits in different lineages (sugar glider; marsupial, and flying squirrel; placental mammal)
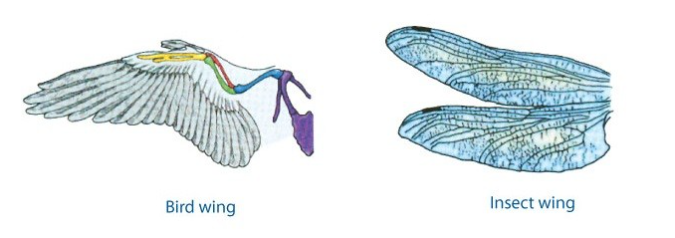
Analogy
Similar traits from convergence, no common ancestry (bird wing vs insect wing)
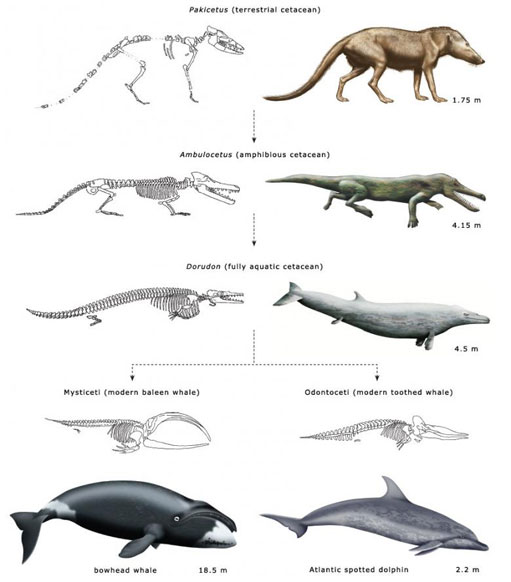
Fossil Record
Providing evidence of past life and how organisms have evolved over geologic time (whales going from land predators to aquatic mammals)
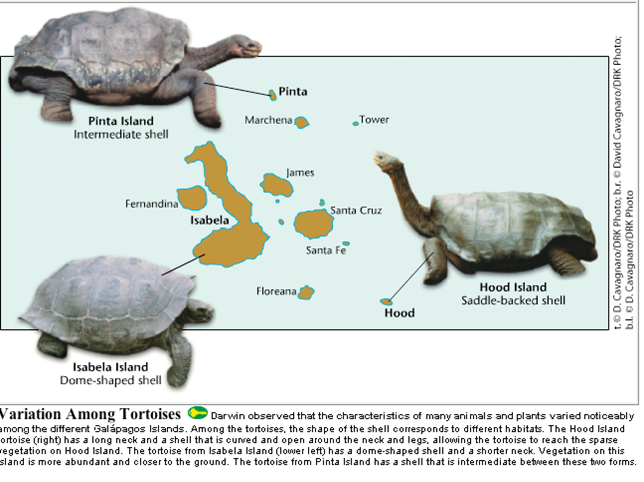
Biogeography
The study of how and why plants and animals are distributed across different places on Earth, both now and in the past (tortoises shell shape and neck length on different islands)
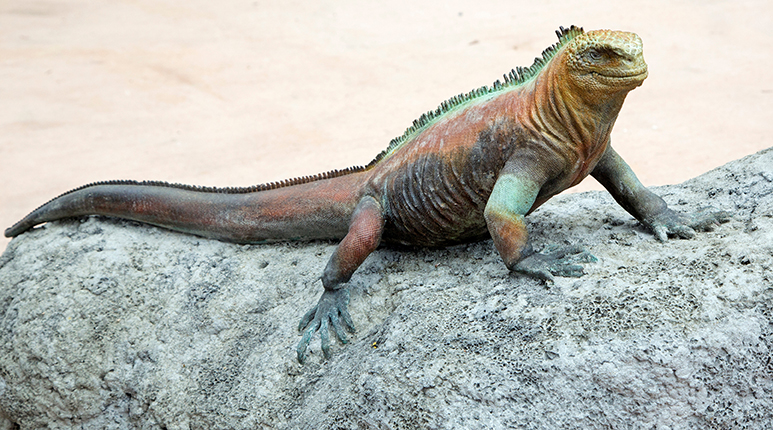

Endemic Species
Species found only in one place and nowhere else (galapagos marine iguanas)
Scientific Theory
Broad, testable explanation supported by evidence (evolution by natural selection explains unity, diversity, and adaptations)
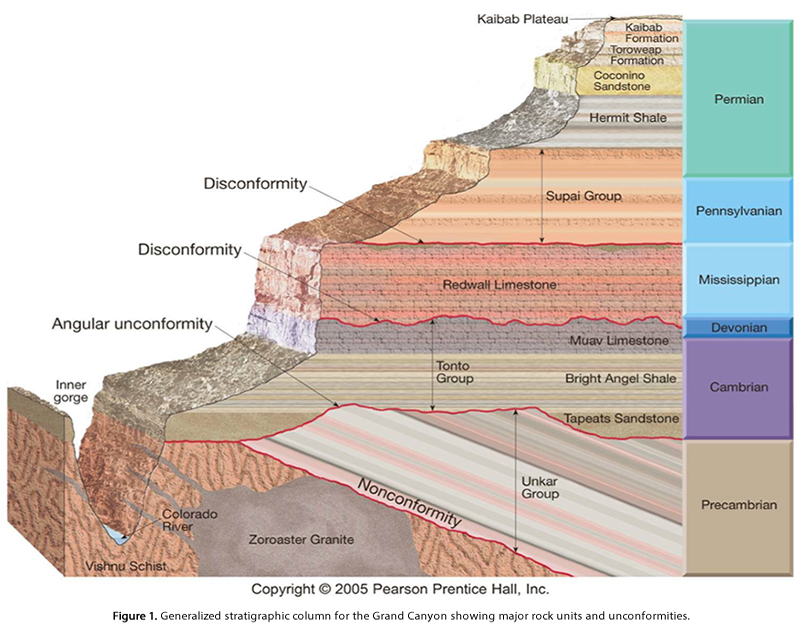
What did Hutton and Lyell contribute to Darwin’s thinking
Earth changes slowly over long periods, allowing time for evolution (grand canyon formed by gradual erosion, not sudden events)

Catastrophism
Earth’s features shaped by sudden disasters (earthquakes, floods, volcanoes)
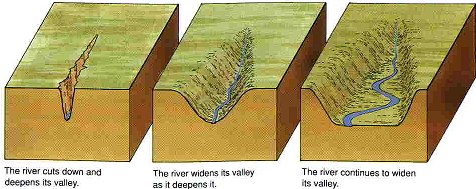
Gradualism
Big changes happen slowly over long time by small processes (valleys formed by river erosions happens over millions of years)
Uniformitarianism
The same natural processes shaping Earth today also shaped it in the past (volcanoes erupt now as they did in the past)