Zoology Lab. Act 10 (Anatomical Positions, Directions And Movements Including Body Cavities, Planes And Regions)
1/64
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
65 Terms
Anatomy and Physiology
The study of the structure and function of the human body.
Terminology
Specific words or terms used in a particular field or discipline.
Frontal
Relating to the forehead; examples include the frontal bone, frontalis muscle, and frontal lobe of the brain.
Occipital
Relating to the back of the head; examples include the occipital bone, occipitalis muscle, and occipital lobe of the brain.
Brachial
Relating to the upper arm; used to describe nerves, vessels, and muscles in the upper arm region.
Type OK

Type OK
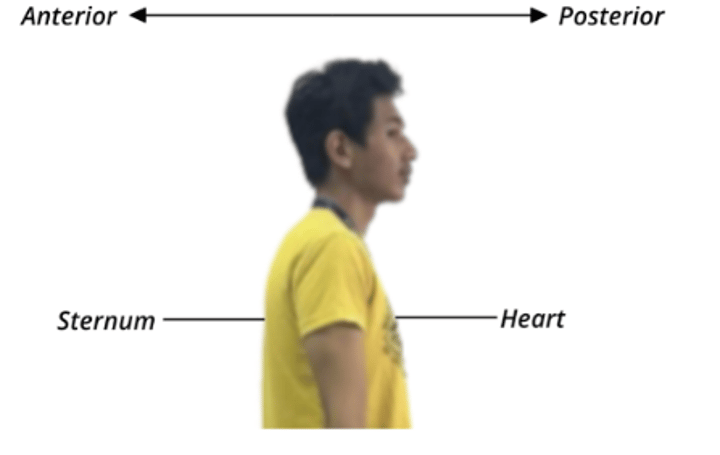
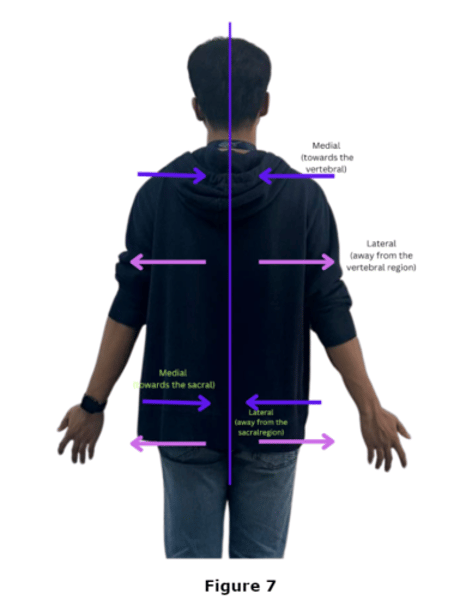
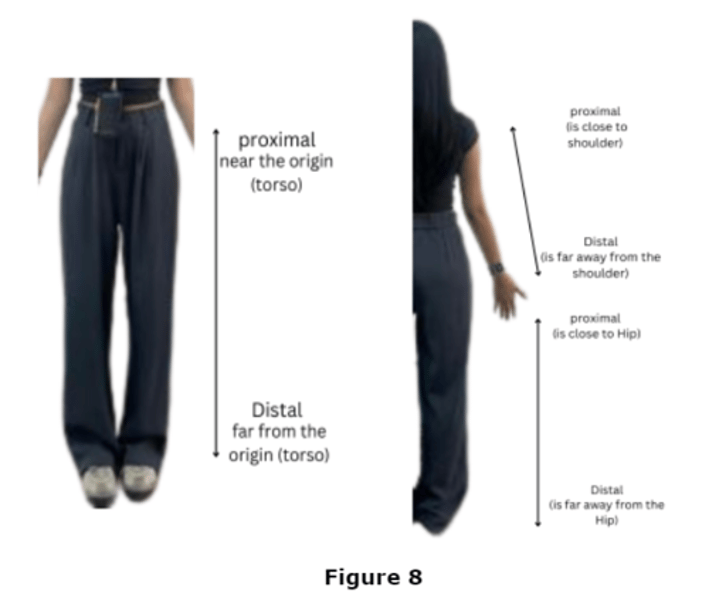
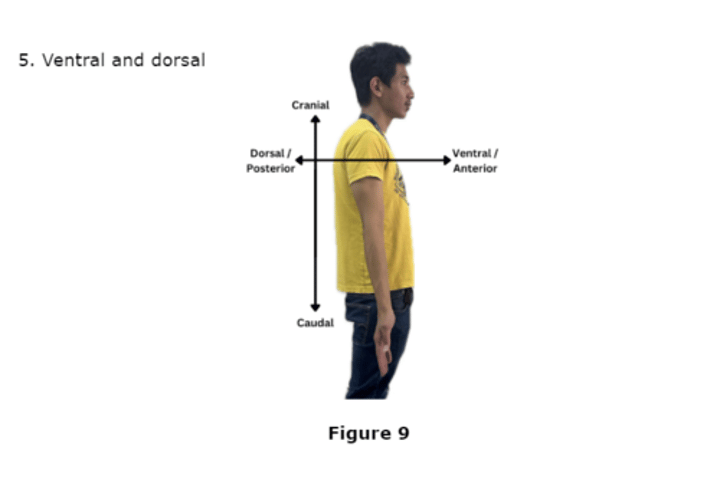
Dorsal Body Cavity
The cavity located along the posterior aspect of the body, which includes the cranial cavity housing the brain and the spinal cavity housing the spinal cord.
Cranial Cavity
The space within the skull that houses the brain.
Spinal Cavity
The space within the vertebral column that houses the spinal cord.
Ventral Body Cavity
The cavity located along the anterior aspect of the body, which includes the thoracic cavity and abdominopelvic cavity.
Thoracic Cavity
The cavity superior to the diaphragm containing the heart and lungs, protected by the rib cage.
Abdominopelvic Cavity
The cavity inferior to the diaphragm, which includes the abdominal and pelvic cavities.
Abdominal Cavity
The superior portion of the abdominopelvic cavity, housing organs such as the stomach, intestines, and liver.
Pelvic Cavity
The inferior portion of the abdominopelvic cavity, housing reproductive organs, bladder, and rectum, partially enclosed by the bony pelvis and tipping posteriorly away from the abdominal cavity.
Cranial cavity and Spinal cavity
Dorsal Body Cavity (2)
Thoracic cavity and Abdominopelvic cavity
Ventral Body Cavity (2)
Sagittal Plane
A longitudinal plane that runs down the length of the body, dividing it into right and left parts. If it divides the body into equal halves along the midline, it's called a median or midsagittal plane.
Frontal (Coronal) Plane
A longitudinal plane that divides the body (or an organ) into anterior and posterior parts.
Transverse Plane
A horizontal plane that divides the body into superior and inferior parts. These sections are also known as cross sections.
right upper, right lower, left upper, left lower quadrants
FOUR Abdomino-pelvic Quadrants and Regions
Umbilical Region
Centermost region containing the umbilicus.
Epigastric Region
Superior to the umbilical region; overlies most of the stomach.
Hypogastric (Pubic) Region
Inferior to the umbilical region; encompasses the pubic area
Iliac Regions
Lateral to the hypogastric region, overlying the superior parts of the hip bones.
Lumbar Regions
Between the ribs and the flaring portions of the hip bones, lateral to the umbilical region.
Hypochondriac Regions
Flanking the epigastric region laterally and overlying the lower ribs.
Abdominal
Anterior body trunk region inferior to the ribs.
Antecubital
"Anterior surface of the elbow."
Axillary
"Armpit"
Brachial
"Arm"
Buccal
"Cheek"
Carpal
"Wrist"
Cervical
"Neck region"
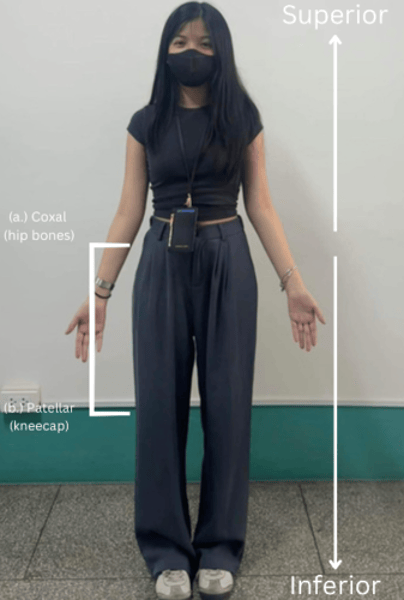
Coxal
"Hip"
Deltoid
"Roundness of the shoulder caused by the underlying deltoid muscle"
Digital
"Fingers or toes"
Femoral
"Thigh"
Fibular
"Side of the leg"
Inguinal
"Groin"
Mammary
"Breast"
Manus
"Hand"
Nasal
"Nose"
Oral
"Mouth"
Orbital
"Bony eye socket (orbit)"
Patellar
"Anterior knee (kneecap) region"
Pelvic
"Pelvis region"
Pubic
"Genital region"
Sternal
"Region of the breastbone"
Thoracic
"Chest"
Umbilical
"Navel"
Cephalic
"Cephalic"
Gluteal
"Buttocks or rump"
Lumbar
"Area of the back between the ribs and hips; the loin"
Occipital
"Posterior aspect of the head or base of the skull"
Popliteal
"Back of the knee"
Sacral
"Area between the hips"
Scapular
"Scapula or shoulder blade area"
Sural
"Calf or posterior surface of the leg"
Vertebral
"Area of the spinal column."
Tarsal
"Ankle"