Mitosis + Asexual Reproduction
5.0(2)
Card Sorting
1/33
Last updated 4:18 PM on 3/14/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
34 Terms
1
New cards
mitosis
* a type of cell division in which two identical daughter cells are formed
* every cell in the body is formed by mitosis except for sperm and egg cells
* every cell in the body is formed by mitosis except for sperm and egg cells
2
New cards
unicellular organisms use mitosis to:
reproduce
3
New cards
multicellular organisms use mitosis to:
grow and develop, replace worn out cells
4
New cards
chromosomes
* structures that contain DNA
* humans have 46 chromosomes in each body cell
* humans have 46 chromosomes in each body cell
5
New cards
chromosomes ___ prior to cell divison
replicate (duplicate)
6
New cards
chromosomes replicate to form sister ___
chromatid
7
New cards
most of the time the cell is not actively dividing, it is in:
interphase
8
New cards
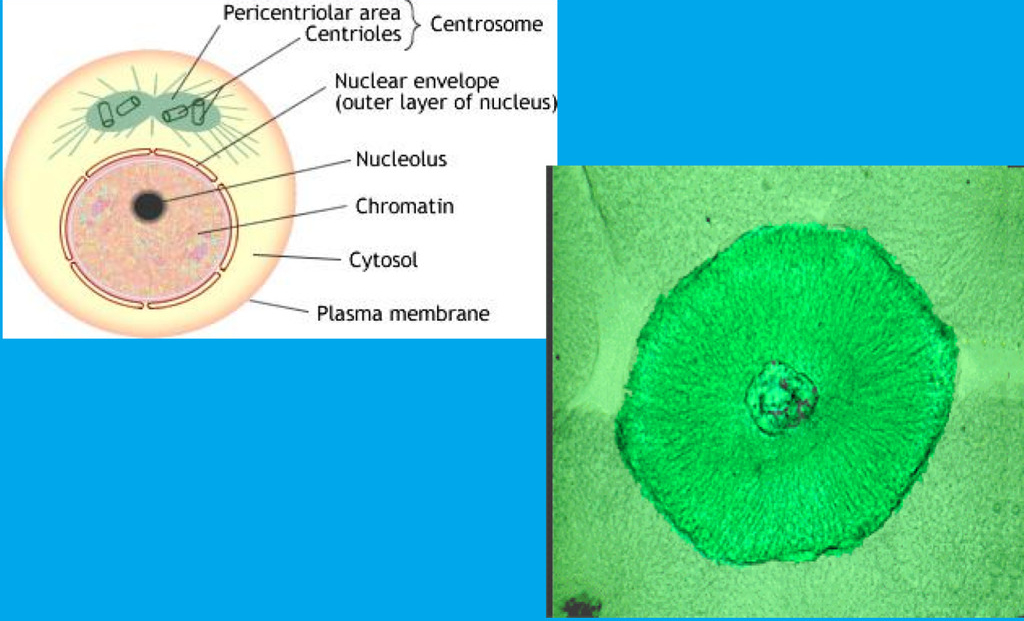
interphase
a) chromosomes are in the form of chromat__**in**__(DNA is loosely wrapped around the protein - __**in**__visible
b) nickname - “resting phase” (inaccurate because the cell is carrying out normal activities
c) chromosomes replicate
b) nickname - “resting phase” (inaccurate because the cell is carrying out normal activities
c) chromosomes replicate
9
New cards
**Asexual Reproduction**
* A single organism makes an identical copy of itself
* Reproduction by **MITOSIS**
* only one parent
* offspring is genetically identical to parent organism
* Reproduction by **MITOSIS**
* only one parent
* offspring is genetically identical to parent organism
10
New cards
examples of Asexual Reproduction
* binary fission
* budding
* sporulation
* regeneration
* vegetative propagation
* budding
* sporulation
* regeneration
* vegetative propagation
11
New cards
Advantages of Asexual Reproduciton
* rapid and results in the production of large numbers of offspring
* helps organism reproduce in large numbers when environmental conditions are good
* helps organism reproduce in large numbers when environmental conditions are good
12
New cards
Disatvantages of Asexual Reproduction
* All offspring are genetically identical
* If environment changes, none of the organisms have a different trait that might allow them to survive
* They cannot evolve!
* If environment changes, none of the organisms have a different trait that might allow them to survive
* They cannot evolve!
13
New cards
**Binary Fission**
parent organism divides into 2 **equal** parts (ex. bacteria, protists)
14
New cards
**Budding**
parent organism divides into two **UNEQUAL** parts (ex. hydra)
15
New cards
**Sporulation**
* Spores are single, specialized cells produced by mitosis
* Spore germination requires an environment that is warm, has nutrients and moisture
* Spore germination requires an environment that is warm, has nutrients and moisture
16
New cards
Regeneration
* The ability of an organism to regrow lost body parts
* Regeneration decreases as an animal becomes more complex
* (ex. starfish)
* Regeneration decreases as an animal becomes more complex
* (ex. starfish)
17
New cards
Vegetative Propagation
* A type of regeneration that occurs in plants
* Complete new plants develop from a part of the parent plant (root, stem, leaf)
* Complete new plants develop from a part of the parent plant (root, stem, leaf)
18
New cards
Examples of vegatative propagation
NATURAL - bulbs, tubers, rhizomes,
MAN-MADE - cuttings, grafing
MAN-MADE - cuttings, grafing
19
New cards
**Advantages of Vegetative Propagation**
* Produces plants with identical desired characteristics
(Seeds come from two different parents and offspring plant shows different traits)
* Faster
* Higher yields of fruits
(Seeds come from two different parents and offspring plant shows different traits)
* Faster
* Higher yields of fruits
20
New cards
Why not become one big cell?
* surface area of the membrane (roadways) could not transport all the food, oxygen, and wastes necessary for the volume of the cell
* the dna library would not be able to serve all the cell’s needs
* the dna library would not be able to serve all the cell’s needs
21
New cards
surface area + volume ratio
cell’s require a large surface area to volume ratio
22
New cards
2 components of cell division
1) nuclear division (mitosis)
2) cytoplasmic division (cytokinesis)
2) cytoplasmic division (cytokinesis)
23
New cards
nuclear division (mitosis)
genetic material must be divided so that each cell has a new complete set of chromosomes
24
New cards
cytoplasmic division (cytokenisis)
the contents of the cytoplasm must be divided so that each new cell has a complete set of organelles
25
New cards
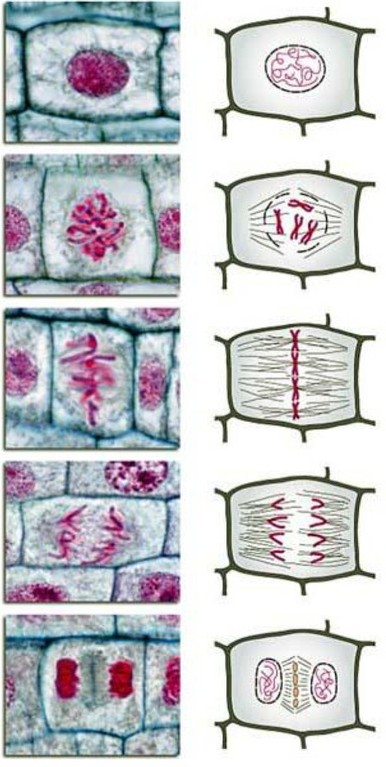
phases of mitosis
1. prophase
2. metaphase
3. anaphase
4. telophase
26
New cards
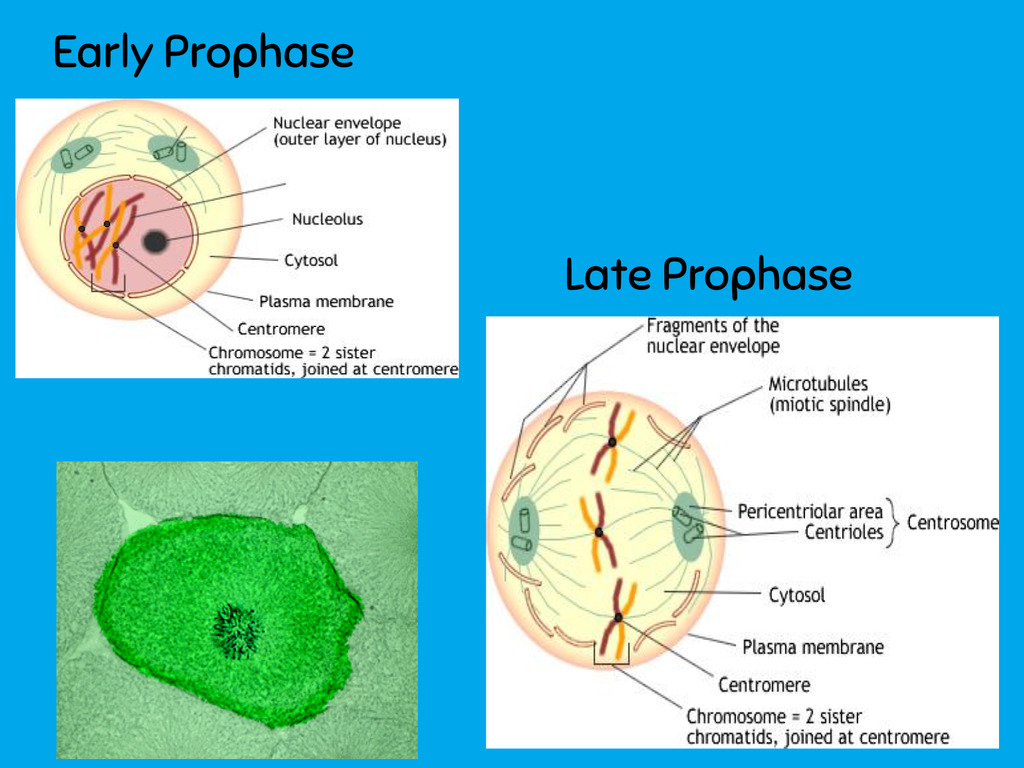
__**p**__rophase
Beginning of mitosis __**p**__repares cell for division
a) nuclear membrane disintegrates; nucleolus dissapears
b) chromosomes coil and contract (thicken) and become visible (chromati__**d**__s) \*\*link the D in chromatids to the D in __**d**__ividing
c) replicated chromosomes are held together by a protein called a __**centromere**__
d) centriole moves to the opposite poles of the cell
e) spindle apparatus forms
a) nuclear membrane disintegrates; nucleolus dissapears
b) chromosomes coil and contract (thicken) and become visible (chromati__**d**__s) \*\*link the D in chromatids to the D in __**d**__ividing
c) replicated chromosomes are held together by a protein called a __**centromere**__
d) centriole moves to the opposite poles of the cell
e) spindle apparatus forms
27
New cards
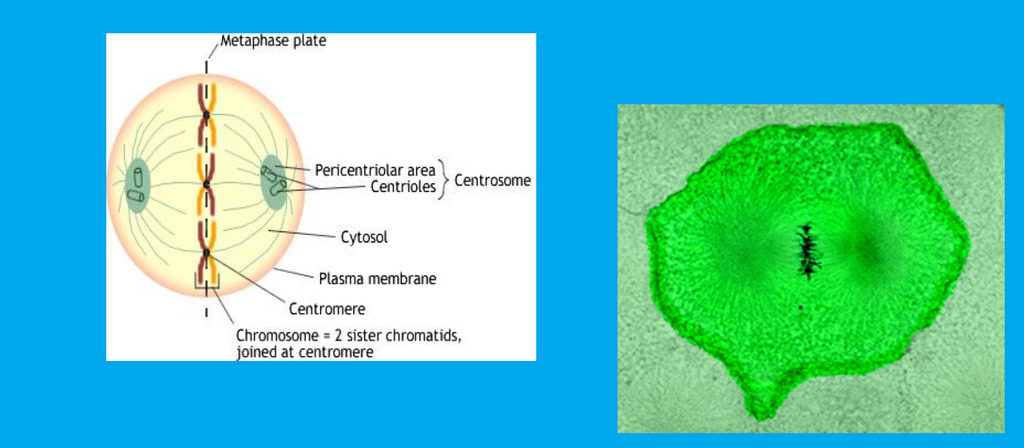
__**m**__etaphase
a) replicated chromosomes line up in the __**m**__iddle of the cell
28
New cards
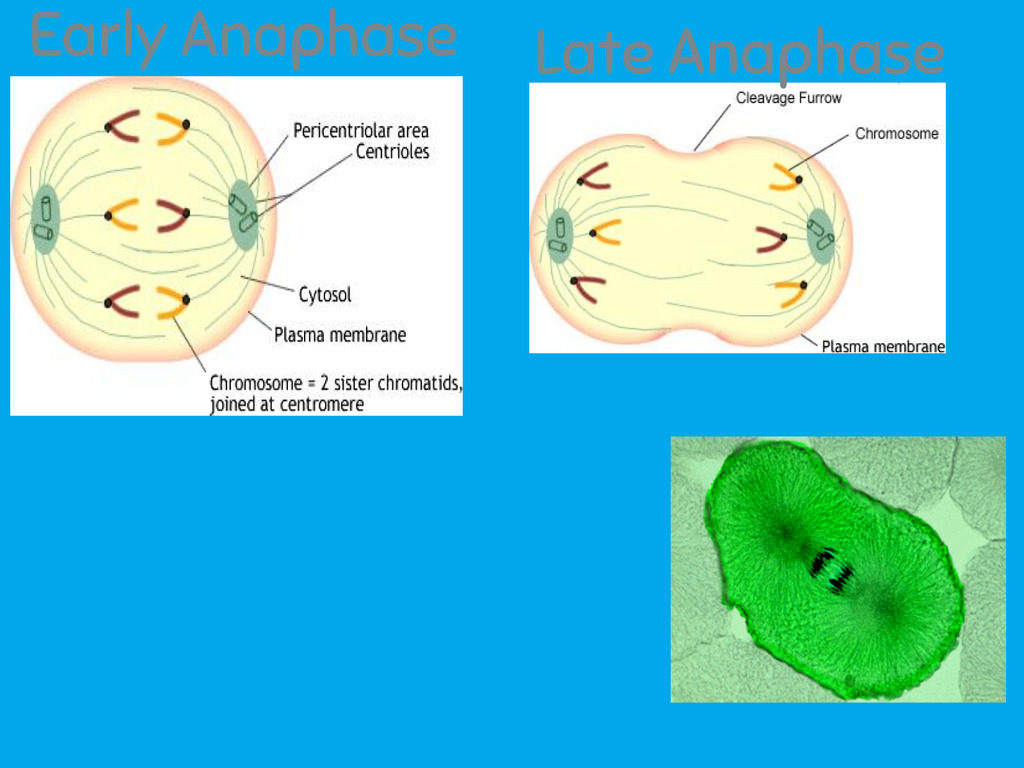
__**a**__naphase
a) chromatids move apart to opposite poles of the cell with the help of spindle fibers
29
New cards
__**t**__elophase
a) chromosomes uncoil, become threadlike (chromatin)
b) spindle disentigrates
c) nuclear membrane, nucleolus reforms
d) __**t**__wo new cells are formed
b) spindle disentigrates
c) nuclear membrane, nucleolus reforms
d) __**t**__wo new cells are formed
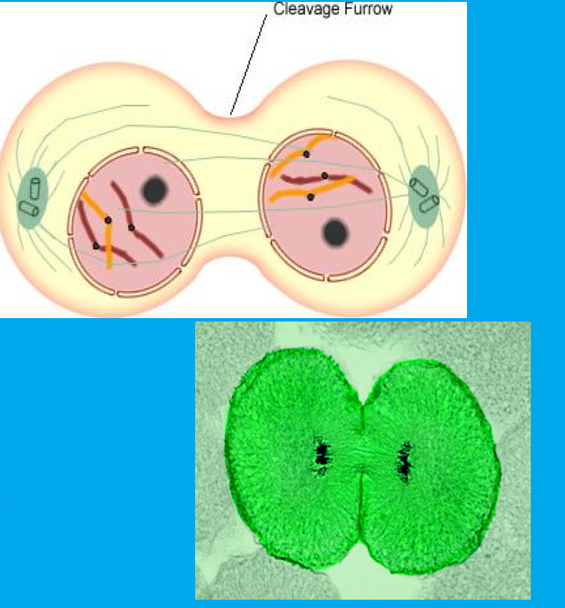
30
New cards
cytokinesis
* occurs the same time as a telophase
* division of cytoplasm
* division of cytoplasm
31
New cards
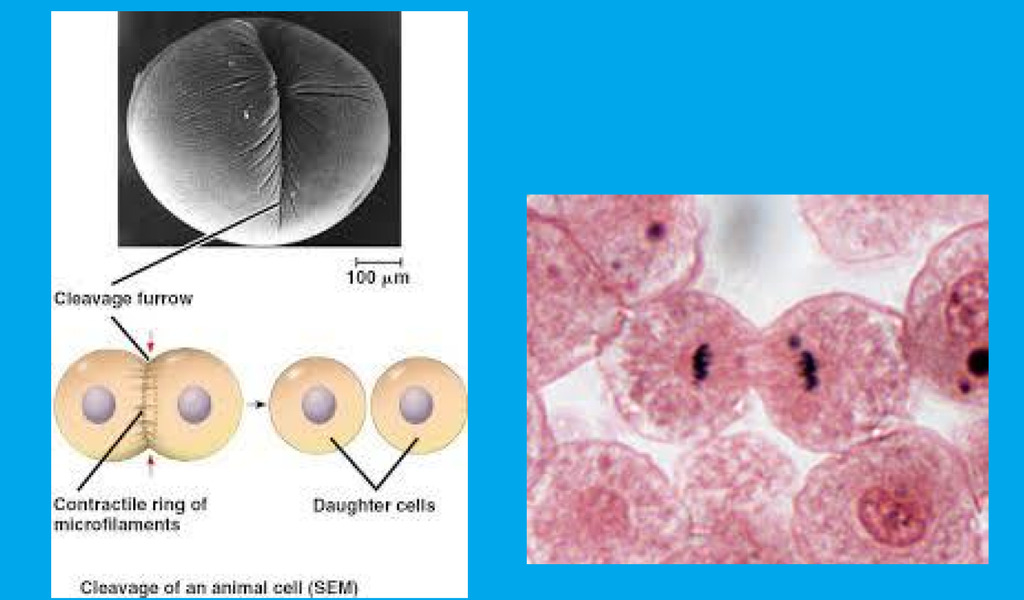
(cytokinesis) in animal cells:
membrane pinches inward
32
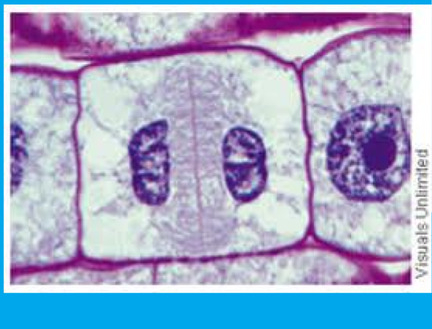
New cards
(cytokinesis) in plant cells:
a cell plate forms
* new membranes and cell walls are formed in the center of the cell to seperate two new cells
* new membranes and cell walls are formed in the center of the cell to seperate two new cells
33
New cards
mitosis in plant cells:
* plant cells have **no** centrioles
* spindle fibers connect to cell wall
* spindle fibers connect to cell wall
34
New cards
cancer
* uncontrolled cell division
* cancer cells are frequently “immortal”: normal cells divide about 50 times and then die, cancer cells can go on dividing indefinetly if supplied with nutrients
* can produce abnormal cells with an abnormal amount of chromosomes
* use excess nutrients and oxygen so normal cells are deprived
* can spread to other tissues
* cancer cells are frequently “immortal”: normal cells divide about 50 times and then die, cancer cells can go on dividing indefinetly if supplied with nutrients
* can produce abnormal cells with an abnormal amount of chromosomes
* use excess nutrients and oxygen so normal cells are deprived
* can spread to other tissues
Explore top notes
Princeton Review AP Calculus BC, Chapter 6: Contextual Applications of Differentiation
Updated 1032d ago0.0(0)
Princeton Review AP Calculus BC, Chapter 6: Contextual Applications of Differentiation
Updated 1032d ago0.0(0)
Explore top flashcards
1984: The Theory and Practice of Oligarchical Collectivism (Goldstein's book)
26Updated 840d ago0.0(0)
1984: The Theory and Practice of Oligarchical Collectivism (Goldstein's book)
26Updated 840d ago0.0(0)