AQA A Level Geography - Carbon Cycle
1/117
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
118 Terms
Major compounds with carbon
Carbon dioxide
Methane
Hydrocarbons
Calcium carbonate
Carbon biomolecules
What is sere?
A stage in the succession of plant and animal communities in an ecosystem. Seres are named after the character of their starting locations; lithosere (starting on bare rock), hydrosere (starting in fresh water), psammosere (starting in sand) and halosere (starting in saline conditions)
Whats stemflow?
Precipitation that is intercepted by vegetation and reaches the ground by flowing down stems, stalks and trunks
Fluxes
A movement of carbon between the stores
Long-term/slow carbon cycle
The movement of carbon between atmospheric, oceanic, and lithospheric stores
Short-term/fast carbon cycle
The movement of carbon from living things to the atmosphere and oceans
Time taken for the long carbon cycle
Carbon takes between 100 million and 200 million years to flow through it
Time taken for the short carbon cycle
Moves up to 1000x carbon than the long carbon cycle in a shorter time period
Percent of carbon in the biosphere
0.0012%
Forms of carbon in the biosphere
Living plants and animals including marine/aquatic life
Residence time of carbon in the biosphere
18 years
Percent of carbon in the lithosphere
99.983%
Forms of carbon in the lithosphere
Sedimentary rocks containing carbon (e.g limestone)
Hydrocarbons (fossil fuels)
Marine sediments from marine skeletons
Residence time of carbon in the lithosphere
240-300 million years
Pedosphere
The soil mantle of the earth
Percent of carbon in the pedosphere
0.0031%
Forms of carbon in the pedosphere
Organic matter in the soil, soil organisms, and the remains of dead plants and animals
Residence time of carbon in the pedosphere
Days to 1000s of years
Percent of carbon in the cryosphere
0.0018%
Forms of carbon in the cryosphere
Plant material in the permafrost
Residence time of carbon in the cryosphere
1000s of years
In ice cores, millions of years
Percent of carbon in the atmosphere
0.0015%
Forms of carbon in the atmosphere
Carbon Dioxide (CO2) and Methane (CH4)
Residence time of carbon in the atmosphere
6 years
Percent of carbon in the hydrosphere
0.0076%
Forms of carbon in the hydrosphere
90% dissolved bicarbonate with carbonate ions and dissolved CO2
Residence time of carbon in the hydrosphere
Surface - 25 years
Deep - 1250 years
GtC
Gigatonnes
1 GtC
1 billion tonnes
Hydrocarbons
The largest forms of carbon stored on Earth
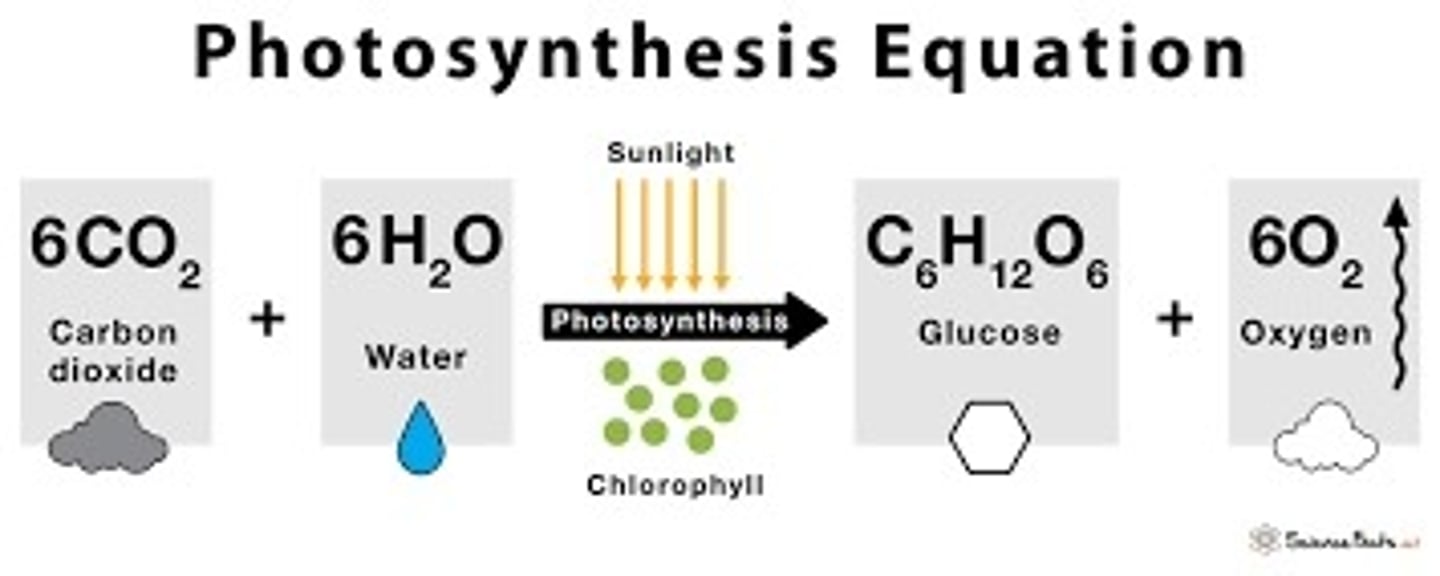
PHOTOSYNTHESIS - transfers in the local carbon cycle
Carbon sequestration when living organisms convert CO2 from the atmosphere and water into oxygen and glucose.
Occurs when chlorophyll react with CO2 creating carbohydrate glucose.
Happens at daytime.
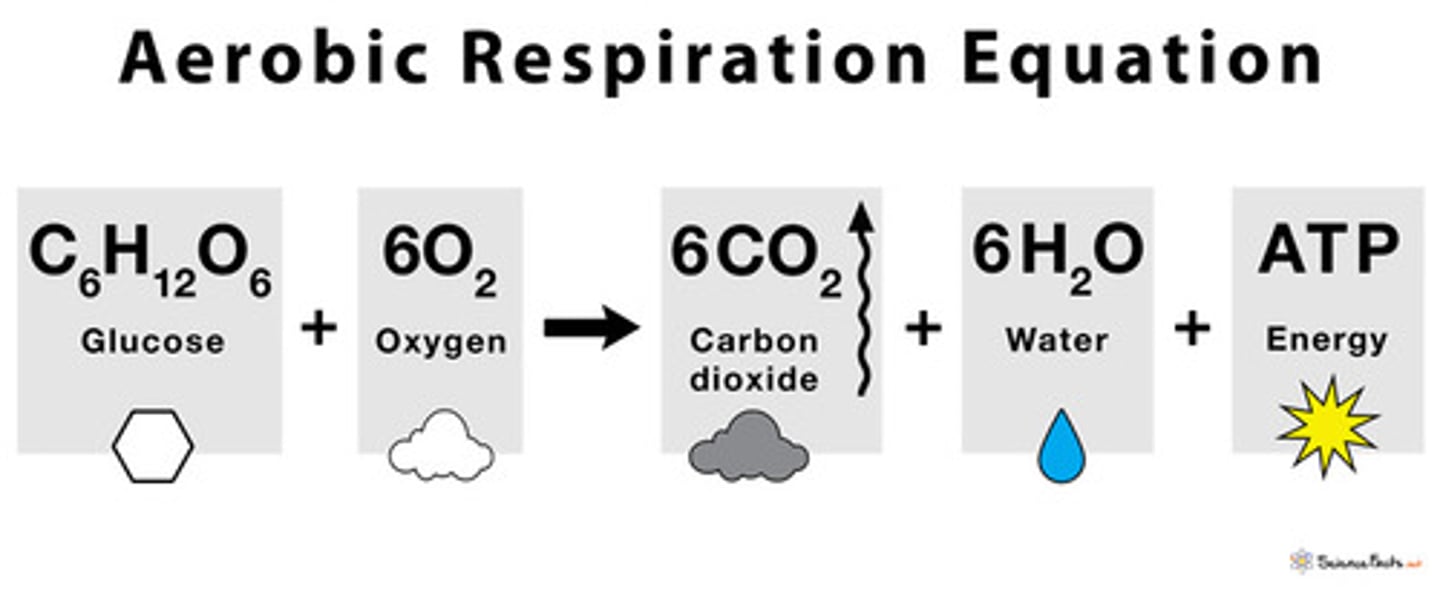
RESPIRATION - transfers in the local carbon cycle
Plants and animals convert oxygen and glucose into energy, producing water and CO2.
Happens during the night
Net carbon dioxide absorbers
Plants - they absorb more CO2 than they emit
DECOMPOSITION - transfers in the local carbon cycle
Living organisms die and are broken down by decomposers (detritivores and bacteria). They respire and return CO2 to the atmosphere. Organic matter is also returned to the soil adding carbon to the pedosphere.
Happens more when conditions are right - warm, damp, humid
DIFFUSION - transfers in the local carbon cycle
The oceans absorb CO2 from the atmosphere, increasing ocean acidity. This can harm aquatic life - coral bleaching.
THERMOHALINE CIRCULATION - continental transfer in the carbon cycle
Thermohaline circulation is the global movement of ocean water driven by temperature differences, that ac to store and transport carbon:
Warm water from the tropics is carried to colder polar regions due to oceanic surface currents
The water cools, and as a result is able to absorb more CO2 from the atmosphere (as gas solubility increases as temperature decreases)
As it is colder it is therefore denser and so sinks
When it return to the surface it warms, and so releases some CO2 to the atmosphere
This makes the ocean act as a carbon pump, giving the ocean a lot more CO2 than it would have if the surface water was not being constantly replenished
WEATHERING/EROSION - transfers in the local carbon cycle
CO2 in air mixes with rainwater creating carbonic acid, which erodes rocks by carbonation weathering.
BURIAL AND COMPACTION - transfers in the local carbon cycle
Shelled marine organisms die and their shell fragments fall and become compacted, forming limestone. Organic matter and decaying marine organisms also compact over time and this forms fossil fuel deposits.
NATURAL CARBON SEQUESTRATION - transfers in the local carbon cycle
Plants sequesters carbon during photosynthesis and stores carbon in its mass.
ARTIFICIAL CARBON SEQUESTRATION - transfers in the local carbon cycle
Carbon Engineering (name of company): Company that sequesters carbon directly from the atmosphere, and converts it into fuel, with is first commercial factor currently under construction in Texas. Initially, it aims to capture 500,000 tonnes annually, with plans to scale up to the full 1 million tonnes capacity.
Carbon Capture and Storage (CCS)
CO2 is captured and transported via pipelines to depleted gas fields and saline aquifers
Advantages of CCS
1. Can be fitted to existing coal power stations
2. Captures 90% of CO2 produced
3. Demand for CO2, transport systems already exist
4. Potential to capture half the world's CO2 emission
Disadvantages of CCS (Carbon capture and storage)
1. Very expensive
2. Increases energy demand for power stations
3. No space in existing power stations
4. Economically viable, used to push oil out of ground, further fossil fuel usage
Sere
Stage of vegetation succession
Vegetation succession
When a plant community develops and becomes more complex over time
Lithosere
Bare rock
Halosere
Salty environment
Psammosere
Sand coastal environment
Hydrosere
Freshwater environment
Carbon source
A store which emits more carbon than it stores
e.g damaged tropical rainforest
Carbon sink
A store which takes in more carbon than it emits
e.g healthy tropical rainforest
Global distribution of carbon
Unevenly distributed
Plant storage focused in tropics/northern hemisphere
Example of a changing carbon store
Trees
Carbon stocks in Brazil and Indonesia
Decrease of around 5 GtC of carbon in the last 25 years
Global pattern of forests
Forests are declining in the tropical areas in the southern hemisphere
Forests are growing in the northern hemisphere
How have Carbon stocks (amount of carbon stored in its ecosystems) in Russia, USA, China changed since the 1990s?
Increases of 0.3, 2.9, 2.3 GtC respectively
Reason for forest growth in Europe and Asia
Conversions of agricultural land and plantations to new forests (eg Afforestation of 148,000 hectares of mangrove in Bangledesh to decrease tidal flooding and cyclones
Change in rate of forest loss
9.5 million hectares per year in 1990s
5.5 million hectares per year in 2010-15
Brazil and carbon storage
Brazil has the most carbon stored on land, and also the most extensive deforested area.
China and forests
Has the largest amount of afforested area
Net Primary Productivity (NPP)
The amount of carbon absorbed by forests
NPP of the Amazon?
Positive all year round - around 13.75 GtC/year, national geographic stating this to be 25% of all terrestrial NPP (as opposed to aquatic NPP)
NPP of deciduous forests
Negative in winter but on average positive all year
WILDFIRES - natural impacts and changes in carbon cycle
Transfers carbon from biosphere to atmosphere by releasing through burning. Extreme wildfires can turn carbon sinks into carbon sources.
Example of wildfire releasing carbon cycle
Black Summer: 900 million tonnes of carbon dioxide into the atmosphere, which is approximately the same as annual emissions from commercial air travel worldwide.
2019 Tundra Wildfires
A large area of tundra in Siberia, Alaska, Canada and Greenland experienced wildfires and it contributed to a significant amount of greenhouse gases into the atmosphere.
VOLCANIC ACTIVITY - natural impacts and changes in carbon cycle
Carbon stored within the earth releases during volcanic eruptions as CO2 gas. Not much CO2 is contributed to the overall cycle.
Example of volcanic activity releasing carbon
1815 Mount Tambora eruption
1815 Mt Tambora, Indonesia
Produced sulphur dioxide gas, blocked radiation from the sun, lowered global temps by 0.4-0.7°C the next year.
This reduced photosynthesis, affecting the carbon cycle.
NATURAL CLIMATE CHANGE - natural impacts and changes in carbon cycle
Higher temperatures are associated with higher concentrations of CO2.
An increase in CO2 enhances global warming.
A change in temperature affects the levels of CO2 in atmosphere as melted permafrost releases methane.
COLD CONDITIONS - natural impacts and changes in carbon cycle
Affect weathering - cold water holds more CO2, but colder temperatures mean more freeze thaw, so more chemicals weathering.
Respiration and photosynthesis are reduced.
Decomposition is reduced.
Less sediment transported - more water stored in cryosphere.
Frozen soil stops transfer of carbon.
WARM CONDITIONS - natural impacts and changes in carbon cycle
Increase rate of deposition, increased rate of carbon transfer to soil.
Melting of permafrost, releasing carbon and methane.
This further enhances greenhouse effect.
Causes of the enhanced greenhouse gas effect
Deforestation, farming practices, urbanisation, fertilisers
DEFORESTATION (land use change) - human impacts and changes in carbon cycle
Generates 20% of global CO2 emissions
Burning of wood for heating or 'slash and burn' immediately releases CO2 into the atmosphere.
Converting woodland to grassland reduced ability to absorb CO2.
Where is deforestation concentrated?
Around tropical areas - this is due to building, mining, ranching, and commercial agriculture (soya, palm oil)
FARMING PRACTICES (land use change) - human impacts and changes in carbon cycle
Burning fossil fuels to run machinery.
Ploughing disturbs soil and releases carbon (no till farming)
Slash and burn (26% of Amazon deforested by 2022, 15% of GHG emissions linked to deforestation)
Livestock produces methane (up to 20% of GHG emissions)
Nitrous oxide in farming practices
It is produced by soil microbes that develop in rice fields
The impact is equivalent to 1200 coal power plants.
However, 50% of the world's population relies on rice as a primary food source.
However China have tired to begin shifiting to wheat, increase its production by 40Mt (million metric tonnes) from 1990-2022
Ploughing
Turning over the soil with a plough to prepare for planting

URBANISATION (land use change) - human impacts and changes to carbon cycle
Removal of trees for space for housing and concrete roads
Emissions from transport, industry, and land development
Percent of urban area on Earth
2%
Percent of anthropogenic CO2 emissions from urban areas
cities are responsible for more than 70% of global greenhouse gas emissions, with the top 25 cities accounting for 52% of the total urban emissions
Percent of anthropogenic CO2 emissions from cement industry
7.5%
Relevance of cement industry in the carbon cycle
Cement and concrete are key building materials
The chemical conversion of limestone to lime creates CO2
The amount of CO2 released depends on types of material used in production (e.g firing of limestone, burning of fossil fuels)
EXTRACTING HYDROCARBONS (fuel extraction/burning) - human impacts and changes to carbon cycle
Carbon is locked up within the lithosphere over a long time.
Extraction of hydrocarbons produce energy and heat - the rate of extraction has increased, moving lithospheric stores to the atmosphere.
Extraction processes are destroying the environment and biodiversity, reducing vegetation, reducing photosynthesis.
Formation of hydrocarbons
1. Carbon diffuses from the atmosphere, allowing phytoplankton and animal life to use the ions for shells/skeletons
2. The phytoplankton and animals die and sink to the ocean floor
3. Over a very long time, they are compressed into oil, coal, and gas.
Hydrocarbon extraction rate (rate at which hydrocarbons, eg oil, gas, coal) are removed from the earth in 1970
6 billion tonnes
Hydrocarbon extraction rate now
15 billion tonnes
Hydrocarbon
Compounds composed of only carbon and hydrogen (oil and natural gas)
BURNING HYDROCARBONS (fuel extraction/burning) - human impacts and changes to carbon cycle
CO2, methane and water vapour are released, they act as greenhouse gases and trap heat within the Earth's atmosphere. This is an increase in greenhouse gases.
1960-2022 rise in global concentrations of CO2
320 ppm to just over 418 ppm (parts per million)
Percent of CO2 emissions coming from burning fossil fuels and industry
87-89% IPCC
Countries dominating CO2 emissions
China and the USA (33% and 13% respectively, 46% collectively
Carbon Budget
Amount of carbon stored and transferred within the carbon cycle on a global or local scale - it includes carbon emissions by various processes against natural/human sequestration
Calculating the carbon budget
Carbon footprint calculator
Carbon footprint calculator
Total amount of greenhouse gases produced to support human activities, measured in Gtc/yr
Atmospheric impacts of the carbon cycle
- CO2 in atmosphere warms earth
- Increased emissions enhance greenhouse effect
- Wildfires and deliberate burning release carbon quickly into the atmosphere
- Deforestation disturbs carbon cycle
Land impacts of the carbon cycle
- Soil made from organic matter and cycled through carbon system
- Carbon in grass provides food for animals
- Carbon provides energy in fossil fuel/wood form
- Carbon is a valuable resource in diamonds, graphite, charcoal
Ocean impacts of the carbon cycle
- Forms carbonic acid and hydrogen irons that dissolve the Calcium carbonate used to build marine shells and skeletons
-eutrophication (over-enrichment of water with nutrients), leads to extensive growth of algae and aquatic plants which block of sunlight for photosynthesis, which destroys biodiverity
Enhanced greenhouse gas effect
Global warming is currently being caused because of abnormally high levels of greenhouse gases being anthropogenically produced.
Radiative forcing
The difference between incoming solar radiation absorbed by the Earth and the energy radiated back out into space.